Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The College of Maasin: Module 3: Operation On Functions
The College of Maasin: Module 3: Operation On Functions
Uploaded by
rose ynqueOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The College of Maasin: Module 3: Operation On Functions
The College of Maasin: Module 3: Operation On Functions
Uploaded by
rose ynqueCopyright:
Available Formats
THE COLLEGE OF MAASIN
“Nisi Dominus Frustra”
Maasin City
General Mathematics for Grade 11
S.Y 2020-2021
Instructor for STEM 11-1, HUMSS 11 1-3
Ms. Charlyn O. Granada, SHS Faculty
Instructor for STEM 11 2-3, ABM 11, TVL 11
Mrs. Rosemarie Ynque-Gerbolingo, SHS Faculty
Module 3: OPERATION ON FUNCTIONS
Instruction: Read and familiarize the concepts in Mathematics. If you have any questions and clarifications,
you may contact me through Facebook: www.facebook.com/charlyngranada or via mobile: +639754647436
or www.facebook.com/roseynque-gerbolingo (09266500409)
Learning Objectives:
At the end of the module, the learner is able to:
Perform operations on functions.
I. INTRODUCTION:
In this module, the different operations on functions were discussed. Examples
were provided for you to be able to learn the five (5) operations: addition,
subtraction, multiplication, and division of functions. Activities were provided to
enhance your learning. Your task is to answer a guided real-world example that
involves operations on functions.
II. ACTIVITIES:
Activity 1. Motivation: Answer the following:
Luara went to a bookstore to shop for supplies. The price list is shown below.
Notebooks: P23 Pens: P12 Folders: P8
How much will she spend if she buys 8 notebooks, 4 pens, and 3 folders?
Let N (x) ne the function that determines the amount paid for notebooks.
What is the independent variable, x?
What is the dependent variable, N (x)?
Let P (x) be the function that determines the amount paid for pens.
What are the independent and dependent variables?
Let F (x) be the function that determines the amount paid for folders.
What are the independent and dependent variables?
THIS IS NOT FOR REPRODUCTION
Write an expression, in terms of the N, P, and F, which represents the total amount to be
paid for all of Laura’s purchases.
Let f and g be two functions. We can define the following:
Sum of Functions:
The sum of f and g, denoted by (f + g), given by (f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x)
Difference of Functions:
The difference of f and g, denoted by (f - g), given by (f - g)(x) = f(x) - g(x)
Product of Functions:
The product of f and g, denoted by (fg)(x), is defined by (fg)(x) = f(x) · g(x)
Quotient of Functions:
𝑓 𝑓 𝑓(𝑥)
The quotient of f and g, denoted by ( )(x), is defined by ( )(x) = , where g(x) ≠ 0
𝑔 𝑔 𝑔(𝑥)
Example 1. Given the functions:
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 + 5 𝑔(𝑥) = 2𝑥 − 1 ℎ(𝑥) = 2𝑥2 + 9𝑥 – 5
Determine the following:
a. (𝑓 + 𝑔)(𝑥) e. (𝑓 + 𝑔)(3)
b. (𝑓 − 𝑔)(𝑥) f. (𝑓 − 𝑔)(3)
c. (𝑓 • 𝑔)(𝑥) g. (𝑓 • 𝑔)(3)
ℎ ℎ
d. ( )(x) h. ( )(3)
𝑔 𝑔
Solution:
𝑎. (𝑓 + 𝑔)(𝑥) = 𝑓(𝑥) + 𝑔(𝑥) definition of addition of functions
= (𝑥 + 5) + (2𝑥 − 1) replace f(x) and g(x) by the given values
= 3𝑥 + 4 combine like terms
b. (𝑓 − 𝑔)(𝑥) = 𝑓(𝑥) − 𝑔(𝑥) definition of subtraction of functions
= (𝑥 + 5) − (2𝑥 − 1) replace f(x) and g(x) by the given values
= 𝑥 + 5 − 2𝑥 + 1 distribute the negative sign
= −𝑥 + 6 combine like terms
2 | General Mathematics THIS IS NOT FOR REPRODUCTION
c. (𝑓 • 𝑔)(𝑥) = 𝑓(𝑥) • 𝑔(𝑥) definition of multiplication of functions
= (𝑥 + 5) • (2𝑥 − 1) replace f(x) and g(x) by the given values
= 2𝑥2 + 9𝑥 – 5 multiply the binomials
ℎ ℎ(𝑥)
d. ( )(x) = definition of division of functions
𝑔 𝑔(𝑥)
2𝑥2+9𝑥−5
= replace h(x) and g(x) by the given values
2𝑥−1
(𝑥+5)(2𝑥−1)
= factor the numerator
2𝑥−1
(x+5) (2x−1)
= cancel out common factors
(2x−1)
=𝑥 +5
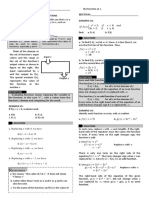
e. (𝑓 + 𝑔)(3) = 𝑓(3) + 𝑔(3)
Solve for 𝑓(3) and 𝑔(3) separately:
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 + 5 𝑔(𝑥) = 2𝑥 − 1
𝑓(3) = 3 + 5 𝑔(3) = 2(3) − 1
=8 =5
∴ 𝑓(3) + 𝑔(3) = 8 + 5 = 13
Alternative solution:
We know that (𝑓 + 𝑔)(3) means evaluating the function (𝑓 + 𝑔) at 3.
(𝑓 + 𝑔)(𝑥) = 3𝑥 + 4 resulted function from item a
(𝑓 + 𝑔)(3) = 3(3) + 4 replace x by 3
=9 +4 multiply
= 13 add
For item 𝑓 𝑡𝑜 ℎ we will use the values of 𝑓(3) = 8 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑔(3) = 5
f. (𝑓 − 𝑔)(3) = 𝑓(3) − 𝑔(3) definition of subtraction of functions
=8 –5 replace f(3) and g(3) by the given values
=3 subtract
Alternative solution:
(𝑓 − 𝑔)(𝑥) = −𝑥 + 6 resulted function from item b
3 | General Mathematics THIS IS NOT FOR REPRODUCTION
(𝑓 − 𝑔)(3) = −3 + 6 replace x by 3
=3 simplify
g. (𝑓 • 𝑔)(3) = 𝑓(3) • 𝑔(3) definition of multiplication of functions
=8 •5 replace f(3) and g(3) by the given values
= 40 multiply
Alternative solution:
(𝑓 • 𝑔)(𝑥) = 2𝑥2 + 9𝑥 − 5 resulted function from item c
(𝑓 • 𝑔)(3) = 2(3)2 + 9(3) – 5 replace x by 3
= 2(9) + 27 − 5 square and multiply
= 18 + 27 – 5 multiply
= 40 simplify
ℎ ℎ(3)
h. ( )(3) =
𝑔 𝑔(3)
Solve for ℎ(3) and 𝑔(3) separately:
ℎ(𝑥) = 2𝑥2 + 9𝑥 − 5 𝑔(𝑥) = 2𝑥 − 1
ℎ(3) = 2(3)2 + 9(3) − 5 𝑔(3) = 2(3) − 1
= 18 + 27 − 5 =5
= 40
ℎ ℎ(3) 40
∴ ( )(3) = = =8
𝑔 𝑔(3) 5
Alternative solution:
ℎ
( )(x) = x + 5 resulted function from item d
𝑔
ℎ
( )(x) = 3 + 5 replace x by 3
𝑔
=8 simplify
III. EXERCISES:
Exercise 1. Drill and Exercise:
Given f(x)= 8x-5 and g(x)= 2(𝑥 − 1)2 + 4, find the following
1. (f + g)(x)
2. (f - g)(1)
3. (fg)(1)
4 | General Mathematics THIS IS NOT FOR REPRODUCTION
Exercise 2.
MATCHING FUNCTIONS
Direction: Match column A with column B by writing the letter of the
correct answer on the blank before each number
Given:
𝑎(𝑥) = 𝑥 + 2
𝑏(𝑥) = 5𝑥 – 3
𝑥+5
c(𝑥) =
𝑥−7
d(𝑥) = √𝑥 + 5
3
e(𝑥) =
𝑥−7
IV. ASSESSMENT:
Directions: Encircle the letter of the correct answer.
1. Find ℎ(3) + 𝑑(2) 𝑖𝑓 ℎ(𝑥) = 𝑥 − 1 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑑(𝑥) = 7𝑥 + 3
a. 2 b. 5 c. 14 d. 19
2. 𝑡(𝑥) = −𝑥2 + 7𝑥 + 1 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑟(𝑥) = 5𝑥2 − 2 𝑥 + 8, 𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑑 (𝑡 − 𝑟)(2).
a. 18 b. -18 c. -13 d. 13
3. 𝑓(𝑥) = 4𝑥 + 2 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑔(𝑥) = 3𝑥 − 1, 𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑑 (𝑓 − 𝑔)(4).
a. 0 b. -9 c. 7 d. -8
4. 𝐼𝑓 𝑔(𝑥) = 𝑥 − 4 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 + 5 𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑑 𝑓(𝑥) • 𝑔(𝑥)
a. 𝑥2 + 𝑥 + 20 c. 𝑥 2 – 𝑥 − 20
b. 𝑥 2 – 𝑥 + 20 d. 𝑥 2 + 𝑥 – 20
5 | General Mathematics THIS IS NOT FOR REPRODUCTION
𝑛+6 𝑛+6 ℎ
5. Given ℎ(𝑛) = 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑝(𝑛) = . 𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑑 (𝑛).
𝑛−4 𝑛2 +4𝑛−32 𝑝
1 1
a. b. n – 8 c. d. n+8
𝑛+8 𝑛−8
𝑓
For numbers 6-8, use the given functions f and g to find f + g , f - g , f g , and .
𝑔
Show your solutions.
6. 𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 + 3 , 𝑔(𝑥) = 𝑥 − 1
7. 𝑓(𝑥) = 5 − 𝑥 2 , 𝑔(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 − 12
3𝑥+1 2𝑥−4
8. 𝑓(𝑥) = , 𝑔(𝑥) =
𝑥 2 −25 𝑥 2 −25
Reflection writing:
1. How will you relate this topic in a real life situation? Cite some real-life examples.
V. FEEDBACK: In this activity, you will be asked to complete the 3-2-1 Chart regarding the evaluation
of functions that you have learned.
3-2-1 Chart
Three things I found out:
1.
2.
3.
Two Interesting things:
1.
2.
One question I still have:
1.
VI. RESOURCES:
Melosantos, A., Sacluti, B., Math Connections in the digital age, Evaluation of functions, page
8-13.
6 | General Mathematics THIS IS NOT FOR REPRODUCTION
You might also like
- MATH 1201 Unit 4 Written Assignment Official SolutionDocument4 pagesMATH 1201 Unit 4 Written Assignment Official SolutionAmara Alpha Vandi100% (2)
- Epic Fails in Global Branding: Intercultural CommunicationDocument7 pagesEpic Fails in Global Branding: Intercultural Communicationrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Unit 1: Self-Development Lesson 1: Knowing Oneself - Strengths and LimitationsDocument6 pagesQuarter 1 - Unit 1: Self-Development Lesson 1: Knowing Oneself - Strengths and Limitationsrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Development 2011Document14 pagesChild and Adolescent Development 2011Rey Mel Resposo100% (3)
- GenMath Module 3 Week 3Document16 pagesGenMath Module 3 Week 3Immanuel CañecaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 GEN MATHDocument7 pagesModule 3 GEN MATHVenice CalimutanNo ratings yet
- Operations On Function StemDocument19 pagesOperations On Function StemAngela MagpantayNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Week 1Document7 pagesGen Math Week 1France Dave Mercado MadrigalNo ratings yet
- GMQ1M2 Week 11Document14 pagesGMQ1M2 Week 11Paula BurogNo ratings yet
- Logic Course OutlineDocument6 pagesLogic Course OutlineGimena, Elijah JohnNo ratings yet
- W#1 M#3 Evaluation of FunctionsDocument12 pagesW#1 M#3 Evaluation of FunctionsIsabel PerezNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Functions Chpter 1 Page 4Document4 pagesEvaluating Functions Chpter 1 Page 4ski3013No ratings yet
- Module 3 Operations On FunctionsDocument29 pagesModule 3 Operations On FunctionsRoger CorrosNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Algebra of FunctionsDocument9 pages10.2 Algebra of FunctionsChristian LumangayaNo ratings yet
- Ast 222 M1Document12 pagesAst 222 M1Sharmaine H. FlavianoNo ratings yet
- GEn Math Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesGEn Math Lecture NotesAna Marie Valenzuela100% (1)
- 1 Study Guide Gen MathDocument8 pages1 Study Guide Gen MathKevin Ryan CalderonNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Evaluating ExpressionsDocument20 pagesModule 2 Evaluating ExpressionsRoger CorrosNo ratings yet
- Nmath 1stqrtDocument27 pagesNmath 1stqrtTerence GuiritanNo ratings yet
- Operations ON Functions: Lesson 3Document27 pagesOperations ON Functions: Lesson 3Terence GuiritanNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Module 2 and 3Document14 pagesGeneral Mathematics Module 2 and 3Dawn Dumalang100% (1)
- Gen. Math Module 2Document5 pagesGen. Math Module 2Robert Clavo100% (1)
- GMQ1M3 Week 1Document16 pagesGMQ1M3 Week 1Lerwin GaringaNo ratings yet
- W5 IntegrationDocument37 pagesW5 IntegrationYuri ParkNo ratings yet
- NP - General Mathematics Q1W1Document8 pagesNP - General Mathematics Q1W1charles stone panuncilloNo ratings yet
- 100 Ways To Motivate OthersDocument38 pages100 Ways To Motivate OthersonyejekweNo ratings yet
- Kelas Khusus Berbakat C Kelas 9: Pertemuan 6 Algebra Iii Materi Basic Concepts of FunctionDocument7 pagesKelas Khusus Berbakat C Kelas 9: Pertemuan 6 Algebra Iii Materi Basic Concepts of FunctionDari Mana KauNo ratings yet
- Functions - Operations On FunctionsDocument6 pagesFunctions - Operations On FunctionsMara ClaireNo ratings yet
- 6e. Operations On FunctionsDocument10 pages6e. Operations On FunctionsDexter CaroNo ratings yet
- Genmath Learning Packets Aug. 17 2022Document9 pagesGenmath Learning Packets Aug. 17 2022Ennik SomiNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Content: FUNCTIONDocument9 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Content: FUNCTIONLeopoldo MalicdemNo ratings yet
- M106 Worktext Ch2.Lesson 2Document16 pagesM106 Worktext Ch2.Lesson 2Raymond GarciaNo ratings yet
- Functions, Graphs, and Limits: By: Husni Tel: 0615257175 Alas Tel: 0615521558Document56 pagesFunctions, Graphs, and Limits: By: Husni Tel: 0615257175 Alas Tel: 0615521558Abdalla ShowNo ratings yet
- Preparation For Calculus and Functions: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoDocument7 pagesPreparation For Calculus and Functions: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoJhon Mark SantoniaNo ratings yet
- CompositefunctionsDocument39 pagesCompositefunctionsapi-296860619No ratings yet
- Gen-Math ReviewerDocument26 pagesGen-Math ReviewerElla DyNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: Mathematics 11 Evaluating FunctionsDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Mathematics 11 Evaluating Functionsashley magtotoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Functions: (Represents Real-Life Situations Using Rational Functions)Document33 pagesBasic Concepts of Functions: (Represents Real-Life Situations Using Rational Functions)Gerlie Jay-ann Ramos100% (1)
- q1 Genmath Module 2 3Document4 pagesq1 Genmath Module 2 3Angel MandigmaNo ratings yet
- GENMATH Lpt3 For SRDDocument10 pagesGENMATH Lpt3 For SRDEnnik SomiNo ratings yet
- Math 11: Calculus I Differential CalculusDocument9 pagesMath 11: Calculus I Differential CalculusKors Min YeolNo ratings yet
- GENERAL MATHEMATICS m2Document23 pagesGENERAL MATHEMATICS m2Victor Rey Dinorog MamonNo ratings yet
- LP DraftDocument51 pagesLP Draftnicole MenesNo ratings yet
- Math 11WORKSHEET 1Document3 pagesMath 11WORKSHEET 1nebiyutafesse543No ratings yet
- CC23 - Unit 1 Module - With SolutionsDocument8 pagesCC23 - Unit 1 Module - With SolutionsGemma AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.b Algeebra of FunctionDocument4 pagesLesson 1.b Algeebra of FunctionAniqah Mardi Macuja EscarianNo ratings yet
- Reminders: Attend The Gmeet Class For Complete DiscussionDocument16 pagesReminders: Attend The Gmeet Class For Complete DiscussionFaba, Froi Jastine T.No ratings yet
- General Mathematics MODULE 3 Part 1 OPERATIONS OF FUNCTIONSDocument16 pagesGeneral Mathematics MODULE 3 Part 1 OPERATIONS OF FUNCTIONSJohn Jericho U RosalesNo ratings yet
- 9426 - Some Suggestions For Review For Test2-PMT0101 (T3-1415)Document10 pages9426 - Some Suggestions For Review For Test2-PMT0101 (T3-1415)YoongHong ChoyNo ratings yet
- Composition of Functions Gen Math Mod 4Document5 pagesComposition of Functions Gen Math Mod 4King HarlequinNo ratings yet
- Mat 121-FunctionsDocument45 pagesMat 121-Functionsakinleyedavid2007No ratings yet
- Gen. Math Summary of Topics2Document7 pagesGen. Math Summary of Topics2Rann MNo ratings yet
- SLG 2.1.2 Definition of Functions and Operations On Functions (Session 2 of 3)Document6 pagesSLG 2.1.2 Definition of Functions and Operations On Functions (Session 2 of 3)jvvuvuuv lopezNo ratings yet
- Evaluating FunctionsDocument1 pageEvaluating FunctionsOfelia OredinaNo ratings yet
- Math 103 Take-Home Quiz 5Document4 pagesMath 103 Take-Home Quiz 5Brandon CabjuanNo ratings yet
- DIRECTION: Write All Answers and Required Solutions in The Test Booklet. Determine Whether Each Statement Is TRUE or FALSE. (1 Point Each)Document3 pagesDIRECTION: Write All Answers and Required Solutions in The Test Booklet. Determine Whether Each Statement Is TRUE or FALSE. (1 Point Each)MariaRebeccaObafialFloresNo ratings yet
- Math0861 FunctionNotationDocument4 pagesMath0861 FunctionNotationShane LambertNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 FunctionsDocument22 pagesChapter 1 FunctionsJeremy Chin Jun ChenNo ratings yet
- TOPIC DETAILS 4 POOL 3 Edited VersionDocument7 pagesTOPIC DETAILS 4 POOL 3 Edited VersionUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus Module 2Document3 pagesIntegral Calculus Module 2AldzNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Polynomial FunctionsDocument21 pagesWeek 1 Polynomial FunctionspotatersNo ratings yet
- GM Week 1 MELC 3Document17 pagesGM Week 1 MELC 3kierashleerafalloNo ratings yet
- Recommendation Letter ExampleDocument1 pageRecommendation Letter Examplerose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Career Portfolio - Bacus Merianne Yvon NicoleiDocument9 pagesCareer Portfolio - Bacus Merianne Yvon Nicoleirose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Signal WordsDocument1 pageSignal Wordsrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Infographic Sample 1Document4 pagesInfographic Sample 1rose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Guidelines v.2023Document8 pagesBusiness Plan Guidelines v.2023rose ynqueNo ratings yet
- 2 I Want FishDocument24 pages2 I Want Fishrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- 01 Last Name First Name Holland Code Career TestDocument2 pages01 Last Name First Name Holland Code Career Testrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Various Dimensionsof Philippine Literary HistoryDocument5 pagesModule 6 Various Dimensionsof Philippine Literary Historyrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Colorful Illustrative Back To School I Spy Ice Breaker Game PresentationDocument12 pagesColorful Illustrative Back To School I Spy Ice Breaker Game Presentationrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- RES01 Research Proposal Template Main BodyDocument11 pagesRES01 Research Proposal Template Main Bodyrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Reflection 1Document1 pagePhilosophical Reflection 1rose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Work Values - Paloma Anthony Nevin - Docx 1Document2 pagesWork Values - Paloma Anthony Nevin - Docx 1rose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Epic Fails in Global Branding: Intercultural CommunicationDocument9 pagesEpic Fails in Global Branding: Intercultural Communicationrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 10 Module 11 LLM HealthDocument10 pagesMAPEH 10 Module 11 LLM Healthrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- God Speaks: A. Human ExperienceDocument2 pagesGod Speaks: A. Human Experiencerose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Application LetterDocument1 pageApplication Letterrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Solve The Following. Show Your Complete Solution and Box Your Final AnswerDocument1 pageSolve The Following. Show Your Complete Solution and Box Your Final Answerrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Grade 10: QuarterDocument5 pagesGrade 10: Quarterrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument10 pagesStatistics and Probabilityrose ynque63% (8)
- Lesson Plan in SetsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in Setsrose ynque75% (4)
- Mean, VarianceDocument3 pagesMean, Variancerose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 ARTSDocument6 pagesGrade 7 ARTSrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math TGDocument2 pagesGen. Math TGrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts of LuzonDocument12 pagesArts and Crafts of Luzonrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument2 pagesArgumentative Essayrose ynque100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Functions: SolutionDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Functions: Solutionrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Functions and RelationsDocument35 pagesFunctions and Relationsrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Mean, VarianceDocument3 pagesMean, Variancerose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Art and Special EducationDocument8 pagesArt and Special EducationAli JenkinsNo ratings yet
- DifferentialCalculusCover PDFDocument2 pagesDifferentialCalculusCover PDFahmad nazirNo ratings yet
- Incorporating Sign Language To An Inclusive Classroom Setting A Meta-SynthesisDocument9 pagesIncorporating Sign Language To An Inclusive Classroom Setting A Meta-SynthesisIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Embracing Diverse Communities Conference Program FinalDocument3 pagesEmbracing Diverse Communities Conference Program Finalapi-521849429No ratings yet
- Arlene Perez ResumeDocument3 pagesArlene Perez Resumeapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Tienganh 10 Unit1 16Document168 pagesTienganh 10 Unit1 16snow1330% (1)
- Lived Experiences of Teachers in Far Flung Teaching Community in West Malungon District, Sarangani DivisionDocument9 pagesLived Experiences of Teachers in Far Flung Teaching Community in West Malungon District, Sarangani DivisionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Career Summary: Peeyush JainDocument3 pagesCareer Summary: Peeyush Jainshannbaby22No ratings yet
- AUDIO VISUAL AIDS MSCDocument7 pagesAUDIO VISUAL AIDS MSCPriyaNo ratings yet
- Oral Reading Verification Sheet School Reading Profile: School: Lungsodaan Elem. District: MABINIDocument3 pagesOral Reading Verification Sheet School Reading Profile: School: Lungsodaan Elem. District: MABINIRecil N. JugarapNo ratings yet
- CS 2305 - UT Dallas - SyllabusDocument7 pagesCS 2305 - UT Dallas - SyllabusTrí Minh CaoNo ratings yet
- Materi Report B.inggrisDocument5 pagesMateri Report B.inggrisYusrilNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Sistem Peredaran DarahDocument14 pagesJurnal Internasional Sistem Peredaran DarahLuluk Imasnuna100% (3)
- XXIV International Symposium On Morphological Sciences Abstract Book 3-9-2015Document241 pagesXXIV International Symposium On Morphological Sciences Abstract Book 3-9-2015Prof. Hesham N. MustafaNo ratings yet
- Psycholinguistic Correlates of Progress in Literature at Russian Vocational Training School: A Snap Shot From Selected PaperDocument5 pagesPsycholinguistic Correlates of Progress in Literature at Russian Vocational Training School: A Snap Shot From Selected PaperREILA Journal of Research and Innovation in LanguageNo ratings yet
- Research Philosophy and Practice: Course HandbookDocument5 pagesResearch Philosophy and Practice: Course HandbookAshlinNo ratings yet
- CV DivyanshiDocument2 pagesCV DivyanshiSanaya Rohit WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- 02.14 T He Nursing Role in Integrated Care ModelsReflecting On The United States ExperienceDocument19 pages02.14 T He Nursing Role in Integrated Care ModelsReflecting On The United States Experiencemehara1920No ratings yet
- Year 2 - Push and Pull Design BriefDocument5 pagesYear 2 - Push and Pull Design BriefRebecca LNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 26: Domain and Range of Logarithmic FunctionsDocument19 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 26: Domain and Range of Logarithmic FunctionsTeds TVNo ratings yet
- What Professors Do: Matthew N.O. Sadiku, Kolawole Olasupo, and Sudarshan R. NelaturyDocument2 pagesWhat Professors Do: Matthew N.O. Sadiku, Kolawole Olasupo, and Sudarshan R. NelaturyJose Leonardo Simancas GarciaNo ratings yet
- CVDocument15 pagesCVRajeshNo ratings yet
- MC Fil 101 Estruktura at Gamit NG Wikang FilipinoDocument18 pagesMC Fil 101 Estruktura at Gamit NG Wikang FilipinoReniel AsneNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management and Leadership PlanDocument5 pagesClassroom Management and Leadership Planapi-301728453No ratings yet
- TG KPWKP 2019 1st QuarterDocument109 pagesTG KPWKP 2019 1st QuarterDM Camilot II100% (1)
- Proof of English Language Skills PDFDocument2 pagesProof of English Language Skills PDFSylvaster maxim sNo ratings yet
- 614d6999779c8 Quarter 3 Module 6 Use Parallel Structures PDF Final EditedDocument10 pages614d6999779c8 Quarter 3 Module 6 Use Parallel Structures PDF Final EditedGerry Mae CastilloNo ratings yet
- FP002OR EvaluationDocument8 pagesFP002OR Evaluationpradensen100% (1)
- Grade Thresholds - November 2017: Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry (0620)Document2 pagesGrade Thresholds - November 2017: Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry (0620)helloNo ratings yet