Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transformer: Aeronaves y Laboratorio
Transformer: Aeronaves y Laboratorio
Uploaded by
Angel Ferreyra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views2 pagesThis document discusses the basics of how a transformer works. It explains that a transformer consists of two coils of wire wound around an iron core. When voltage is applied to the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil. The ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the secondary coil determines the ratio of the voltages. For example, if there are 3 times as many turns in the primary coil, the secondary voltage will be one-third the primary voltage. The document provides examples to demonstrate how to calculate the turns ratio and secondary voltage given the primary voltage and coil turn ratios.
Original Description:
Original Title
TRANSFORMER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the basics of how a transformer works. It explains that a transformer consists of two coils of wire wound around an iron core. When voltage is applied to the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil. The ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the secondary coil determines the ratio of the voltages. For example, if there are 3 times as many turns in the primary coil, the secondary voltage will be one-third the primary voltage. The document provides examples to demonstrate how to calculate the turns ratio and secondary voltage given the primary voltage and coil turn ratios.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views2 pagesTransformer: Aeronaves y Laboratorio
Transformer: Aeronaves y Laboratorio
Uploaded by
Angel FerreyraThis document discusses the basics of how a transformer works. It explains that a transformer consists of two coils of wire wound around an iron core. When voltage is applied to the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil. The ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the secondary coil determines the ratio of the voltages. For example, if there are 3 times as many turns in the primary coil, the secondary voltage will be one-third the primary voltage. The document provides examples to demonstrate how to calculate the turns ratio and secondary voltage given the primary voltage and coil turn ratios.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Estudiante: Ferreyra Ríos, José Ángel Matrícula: 1850141 UNIVERSIDAD AUTÓNOMA DE NUEVO LEÓN
Materia: Sistemas electrónicos de Grupo: 005 Facultad de Ingeniería Mecánica y Eléctrica
aeronaves y laboratorio Ingeniería en Aeronáutica
Evidencia: TRANSFORMER No. evidencia: 6
Fecha:
Comentarios: Puntaje:
TRANSFORMER to convert this alternating magnetic field into
electrical power producing the required output
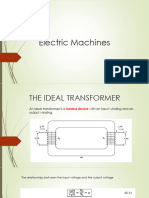
A transformer is an electrical apparatus voltage as shown.
designed to convert alternating current from
one voltage to another. It can be designed to Where:
"step up" or "step down" voltages and works on VP – is the Primary Voltage
the magnetic induction principle. A transformer
has no moving parts and is a completely static VS – is the Secondary Voltage
solid state device, which insures, under normal
NP – is the Number of Primary Windings
operating conditions, a long and trouble-free
life. It consists, in its simplest form, of two or NS – is the Number of Secondary Windings
more coils of insulated wire wound on a
Φ (phi) – is the Flux Linkage
laminated steel core. When voltage is
introduced to one coil, called the primary, it Transformers are all about “ratios”. The ratio of
magnetizes the iron core. A voltage is then the primary to the secondary, the ratio of the
induced in the other coil, called the secondary input to the output, and the turns ratio of any
or output coil. The change of voltage (or given transformer will be the same as its
voltage ratio) between the primary and voltage ratio. In other words for a transformer:
secondary depends on the turns ratio of the “turns ratio = voltage ratio”. The actual number
two coils. of turns of wire on any winding is generally not
important, just the turns ratio and this
Single Phase Voltage Transformer relationship is given as:
Assuming an ideal transformer and the phase
angles: ΦP ≡ ΦS
In other words, for a transformer there is no
direct electrical connection between the two Note that the order of the numbers when
coil windings, thereby giving it the name also of expressing a transformers turns ratio value is
an Isolation Transformer. Generally, the very important as the turns ratio 3:1 expresses
primary winding of a transformer is connected a very different transformer relationship and
to the input voltage supply and converts or output voltage than one in which the turns ratio
transforms the electrical power into a magnetic is given as: 1:3.
field. While the job of the secondary winding is
Transformer Basics Example No1 Transformer. (s. f.). Electronic Tutorials.
Recuperado 16 de octubre de 2020, de
A voltage transformer has 1500 turns of wire https://www.electronics-
on its primary coil and 500 turns of wire for its tutorials.ws/transformer/transformer-basics.html
secondary coil. What will be the turns ratio (TR)
of the transformer.
This ratio of 3:1 (3-to-1) simply means that
there are three primary windings for every one
secondary winding. As the ratio moves from a
larger number on the left to a smaller number
on the right, the primary voltage is therefore
stepped down in value as shown.
Transformer Basics Example No2
If 240 volts rms is applied to the primary
winding of the same transformer above, what
will be the resulting secondary no load voltage.
Again confirming that the transformer is a
“step-down” transformer as the primary voltage
is 240 volts and the corresponding secondary
voltage is lower at 80 volts.
So now we know that the main purpose of a
transformer is to transform voltages at preset
ratios and we can see that the primary winding
has a set amount or number of windings (coils
of wire) on it to suit the input voltage.
REFERENCES
Tyco Electronics. (s. f.). Potential Transformer.
Cromptonusa. Recuperado 16 de octubre de 2020,
de http://www.cromptonusa.com/Potential
%20Transformers.pdf
You might also like
- NET AM2 Pre Assessment Manual 21 02Document13 pagesNET AM2 Pre Assessment Manual 21 02Alin GutaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Voltage Regulators - Smart Grid Solutions - SiemensDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Voltage Regulators - Smart Grid Solutions - SiemenstusarNo ratings yet
- Specificatii Tehnice Vensys 77-70 PDFDocument7 pagesSpecificatii Tehnice Vensys 77-70 PDFBarastean Arsenie NicuNo ratings yet
- Aim For Cash ManualDocument74 pagesAim For Cash ManualyiutkmvjkqNo ratings yet
- Foundation Fieldbus Segment Design CalculatorDocument2 pagesFoundation Fieldbus Segment Design CalculatorMahesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Transformer BasicsDocument14 pagesTransformer BasicsJohn Brix BalisterosNo ratings yet
- Transformer BasicsDocument10 pagesTransformer BasicsRaja DesinguNo ratings yet
- Transformer Basics A Typical Voltage TraDocument13 pagesTransformer Basics A Typical Voltage Trarotimi olalekan fataiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Basics: Register To Download Premium Content!Document12 pagesTransformer Basics: Register To Download Premium Content!Venkatesh PeruthambiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Basics and Transformer Principles of OperationDocument14 pagesTransformer Basics and Transformer Principles of Operationengsamir296No ratings yet
- Full Transformer PDFDocument158 pagesFull Transformer PDFPratik K AnandparaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Basics and Principles of OperationDocument6 pagesTransformer Basics and Principles of Operationmkeen85No ratings yet
- Me 2Document7 pagesMe 2shayma ahmedNo ratings yet
- Transformers Single Phase Voltage TransformerDocument7 pagesTransformers Single Phase Voltage TransformerStephen VillaruzNo ratings yet
- Transformer:: Date:02-04-2019 Power Distribution Lab Assignment No:01Document9 pagesTransformer:: Date:02-04-2019 Power Distribution Lab Assignment No:01Rasheed ShahNo ratings yet
- Single Phase T'MerDocument4 pagesSingle Phase T'Merjay shahNo ratings yet
- University Physics Lab Report (UWI)Document10 pagesUniversity Physics Lab Report (UWI)VanoiMariaStylesWilkinsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - TransformersDocument25 pagesChapter 2 - TransformersYousab CreatorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Transformers PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 2 - Transformers PDFAmmar Safwt0% (1)
- Transformers (ALL TOPICS)Document22 pagesTransformers (ALL TOPICS)Ramprakash100% (13)
- Eec 147Document38 pagesEec 147pokemal gomalNo ratings yet
- Transformers Part 1 147Document38 pagesTransformers Part 1 147joevane escrupoloNo ratings yet
- Transformer: Mahindra École Centrale EE101: Basic Electrical Engineering (Fall 2015) Experiment 10Document6 pagesTransformer: Mahindra École Centrale EE101: Basic Electrical Engineering (Fall 2015) Experiment 10nirmalaNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERS LectureDocument9 pagesTRANSFORMERS LectureDarylNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document40 pagesChapter 5Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- E283C2Document22 pagesE283C2Steven YuNo ratings yet
- Presentation On TransformerDocument80 pagesPresentation On TransformerGodlisten NyariNo ratings yet
- HHHHHHHHHDocument21 pagesHHHHHHHHHjameswovelee7No ratings yet
- The Ideal Transformer: Load Impedance Apparent PowerDocument6 pagesThe Ideal Transformer: Load Impedance Apparent PowerRoshan EkkaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Theory: Mutual InductionDocument20 pagesTransformer Theory: Mutual InductionJayz Sii ReshegNo ratings yet
- SrabanDocument10 pagesSrabanTenz WastonNo ratings yet
- CH3 TransformerDocument57 pagesCH3 TransformerDoktor CintaNo ratings yet
- Project On ACTransformer Class XIIDocument20 pagesProject On ACTransformer Class XIIDevi TalariNo ratings yet
- TransformersDocument26 pagesTransformersgireeshNo ratings yet
- What Is TertiarDocument84 pagesWhat Is TertiarChala DameNo ratings yet
- 4,5. Transformers (1 Phase & 3 Phase)Document48 pages4,5. Transformers (1 Phase & 3 Phase)nakkasrinuNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Ii EEEN 221 Single-Phase Transformers Pako Oteng 19000839 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engineering Ii EEEN 221 Single-Phase Transformers Pako Oteng 19000839 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringPako OtengNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 TransformersDocument39 pagesUnit 1 TransformersAyush Khandelwal100% (1)
- The Ideal TransformerDocument18 pagesThe Ideal TransformerlegendmahenNo ratings yet
- What Is A Transformer?: Mutual InductionDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Transformer?: Mutual InductionYaser QadeerNo ratings yet
- TransformersDocument24 pagesTransformersMonique ReidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 TransformersDocument17 pagesLecture 05 Transformersyiyej11346No ratings yet
- Transformers: Mochammad Ariyanto, ST, MTDocument84 pagesTransformers: Mochammad Ariyanto, ST, MTAmran WiratmaNo ratings yet
- Chater-2 TransformersDocument59 pagesChater-2 TransformersEZRA MOHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- Transformers PDFDocument23 pagesTransformers PDFVageesha Shantha Veerabhadra SwamyNo ratings yet
- Ac TransformerDocument10 pagesAc Transformermpravin kumarNo ratings yet
- Chater-2 Transformers PDFDocument59 pagesChater-2 Transformers PDFTofiqe AdamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 1: TransformersDocument21 pagesElectrical Machines 1: Transformerspawan fartyalNo ratings yet
- 325 04 TransformersDocument31 pages325 04 TransformersNurullah MertelNo ratings yet
- Project On Transformers Class XIIDocument20 pagesProject On Transformers Class XIIDevi TalariNo ratings yet
- Tran Sfor Mato R: Fakultas Teknik Universitas IndonesiaDocument24 pagesTran Sfor Mato R: Fakultas Teknik Universitas IndonesiaHaris SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Transform Ad orDocument26 pagesTransform Ad ormamanNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMER FinalDocument19 pagesTRANSFORMER FinalI'M POPZSHA GAMERNo ratings yet
- Chater-2 TransformerrsDocument62 pagesChater-2 TransformerrsAman BazeNo ratings yet
- EES612 Lab2Document19 pagesEES612 Lab2kombat13_708353334No ratings yet
- TransformerDocument28 pagesTransformerAMANNo ratings yet
- DC TransformerDocument25 pagesDC TransformerUmair100% (1)
- Lecture 07 TransformerDocument16 pagesLecture 07 TransformerSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08Document13 pagesLecture 08muhammadarsalank01No ratings yet
- PT2 (18 Pages)Document19 pagesPT2 (18 Pages)sampath kumarNo ratings yet
- Clase Engine SystemDocument31 pagesClase Engine SystemAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- AF 3. SDOF General Forced Response Example Report.: José Ángel Ferreyra Ríos 1850141Document5 pagesAF 3. SDOF General Forced Response Example Report.: José Ángel Ferreyra Ríos 1850141Angel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- Activity#1 Report On Recent Advances in Structural DynamicsDocument3 pagesActivity#1 Report On Recent Advances in Structural DynamicsAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier: Aeronaves y LaboratorioDocument3 pagesOperational Amplifier: Aeronaves y LaboratorioAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- Comparator Operational Amplifier: Aeronaves y LaboratorioDocument3 pagesComparator Operational Amplifier: Aeronaves y LaboratorioAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Aeronaves y LaboratorioDocument5 pagesTransistor: Aeronaves y LaboratorioAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- AF 3 - Reporte Casos Resistencia A La Flexión y TorsiónDocument20 pagesAF 3 - Reporte Casos Resistencia A La Flexión y TorsiónAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- What Is A Diode? and What Is Its Function?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Diode? and What Is Its Function?Angel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- AF 6 Reporte de Casos Sobre Resist. en Uniones Estruc. AeroespDocument4 pagesAF 6 Reporte de Casos Sobre Resist. en Uniones Estruc. AeroespAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- Estabilizadores Más Usados en AerotransportesDocument40 pagesEstabilizadores Más Usados en AerotransportesAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- ECE 405 Presentation Team 1Document14 pagesECE 405 Presentation Team 1Eric Quan TranNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka 2017 May PMRDocument46 pagesSri Lanka 2017 May PMRlutfiNo ratings yet
- 3M™ U/UTP Category 6 Cable Vol-6Aupn4 / Vol-6Auln4: DatasheetDocument2 pages3M™ U/UTP Category 6 Cable Vol-6Aupn4 / Vol-6Auln4: Datasheetosama_munir12No ratings yet
- Brushless DC Motor ReportDocument6 pagesBrushless DC Motor ReportSaumik HeronNo ratings yet
- Return On Equity Calculations: Yellow Cells Are User Inputs. Please Do Not Change Any Other CellDocument4 pagesReturn On Equity Calculations: Yellow Cells Are User Inputs. Please Do Not Change Any Other CellMohammad YaqoobNo ratings yet
- The Basics of ETAP For The BeginnersDocument4 pagesThe Basics of ETAP For The Beginnersjhon MethewNo ratings yet
- Portable Accommodation For Beach Cleaning Robot With Solar ChargingDocument3 pagesPortable Accommodation For Beach Cleaning Robot With Solar ChargingVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines I - 2019/2020: Amir Dillawar Msc. (Eng), MIETDocument31 pagesElectrical Machines I - 2019/2020: Amir Dillawar Msc. (Eng), MIETOneil Prettyboyswagg LeitchNo ratings yet
- Products Catalog Index: Part No. Manufacturer Description URL PriceDocument9 pagesProducts Catalog Index: Part No. Manufacturer Description URL PricePedro IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Chapter 4 Capacitor HWDocument21 pagesUnit 4 - Chapter 4 Capacitor HWcontact typicalNo ratings yet
- MCB Auxiliary Load ScheduleDocument1 pageMCB Auxiliary Load ScheduleKevin Lexter OcayNo ratings yet
- APsystems Microinverter DS3D-L For Brazil Datasheet - Rev1.0 - 2022!08!03Document2 pagesAPsystems Microinverter DS3D-L For Brazil Datasheet - Rev1.0 - 2022!08!03Conrado MoraesNo ratings yet
- Time Relay Off Delay Datasheet - 3rp1540-1an30 - enDocument3 pagesTime Relay Off Delay Datasheet - 3rp1540-1an30 - enJUAN CARLOS BERNAL MEJIANo ratings yet
- Challan No. H3241Document1 pageChallan No. H3241SANJAY PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- HBC-260单页 12.17Document2 pagesHBC-260单页 12.17Área de IngenieríaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Solar Energy System CompleteDocument5 pagesAutomatic Solar Energy System CompleteRameswaran BalasubramaniamNo ratings yet
- BC210 1224Document1 pageBC210 1224Jose M. AvellanedaNo ratings yet
- Static Transfer Switch Design by NoelDocument4 pagesStatic Transfer Switch Design by Noeldarshan chirkeNo ratings yet
- Installation Procedure T5MaxDocument2 pagesInstallation Procedure T5MaxCarlos Alberto RuedaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power and Machines - Three-Phase Induction MotorsDocument17 pagesElectrical Power and Machines - Three-Phase Induction MotorsDhanis ParamaguruNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Model 175 Autoranging MultimeterDocument67 pagesInstruction Manual Model 175 Autoranging Multimetervmilano1No ratings yet
- ESS2200Document4 pagesESS2200Rasith NimnaNo ratings yet
- Powerflex 700h PDFDocument120 pagesPowerflex 700h PDFEvandro PavesiNo ratings yet
- Speakers CircuitDocument3 pagesSpeakers CircuitSantosh TalankarNo ratings yet
- Triplex Service DropDocument3 pagesTriplex Service DropEvan Merkel0% (1)