Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study: Generic Name
Drug Study: Generic Name
Uploaded by
Alyanna Alcazar CapateCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Drug NeurontinDocument1 pageDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- Migraine Thesis FinalDocument96 pagesMigraine Thesis FinalPranesh Peter84% (19)
- PREDNISONEDocument4 pagesPREDNISONECay SevillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NewDocument4 pagesDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- MirtazapineDocument3 pagesMirtazapineapi-37979410% (1)
- Irbesartan (Avapro)Document1 pageIrbesartan (Avapro)ENo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineVina Jane P Laurel92% (12)
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAdrianPaul Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyRamon Carlo Almiranez100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (FINAL)Document31 pagesDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Side Effects Intervention and EvaluationDocument3 pagesName of Drug Classification Action Indication Side Effects Intervention and EvaluationMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Clonidine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesClonidine Drug Studypoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Atenolol (Tenormin)Document2 pagesAtenolol (Tenormin)Amanda West100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studysnowyfingers100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug Studydelpozo100% (3)
- F. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Document5 pagesF. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Lopirts NiganiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMelody Forca FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Nacl Drug StudyDocument1 pageNacl Drug StudydyndzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Room 104)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Room 104)Maeshe Pryll TanamorNo ratings yet
- Brand Name Generic Name Indication and Contraindication Nursing Consideration Action of The Drug Dose and Administration Side EffectsDocument2 pagesBrand Name Generic Name Indication and Contraindication Nursing Consideration Action of The Drug Dose and Administration Side EffectsCarla Dana GozumNo ratings yet
- Name of The Drug Dosage Indication and Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsbilitiesDocument2 pagesName of The Drug Dosage Indication and Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsbilitiesMiguel Paolo Bastillo MercadoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studysuperhuman_mabz100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyMay Dianne Mansia Bautista100% (1)
- Losartan Potassium Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLosartan Potassium Drug StudyJonieP84100% (4)
- Paracetamol PODocument3 pagesParacetamol POSheena GallardoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudySuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyMaye HerbitoNo ratings yet
- DRUG FluimucilDocument1 pageDRUG FluimucilrholiboiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaNo ratings yet
- Felodipine CefuroximeDocument3 pagesFelodipine CefuroximecotyboyNo ratings yet
- HydrochlorothiazideDocument1 pageHydrochlorothiazideKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocument3 pagesDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Cetirizine 2Document2 pagesCetirizine 2ianNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument26 pagesDrug Studyrn msnNo ratings yet
- Vasotec EnalaprilDocument1 pageVasotec EnalaprilCassie100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyArmie Joy Embat CariazoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuNo ratings yet
- RosuvastatinDocument1 pageRosuvastatinJoshua KellyNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University: Institute of Nursing S.Y. 2018-2019Document1 pageFar Eastern University: Institute of Nursing S.Y. 2018-2019shendae cosmianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyBadgal BazingaNo ratings yet
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- Difflam Drug StudyDocument1 pageDifflam Drug StudyDanlee EstandaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument18 pagesDrug StudyAntonethe DemdamNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EditedDocument5 pagesDrug Study EditedfabtaciousVeelaNo ratings yet
- Micardis Indication CNS: DigoxinDocument1 pageMicardis Indication CNS: Digoxineric macabiogNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyuntoned100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- NCP1 CHFDocument2 pagesNCP1 CHFapi-27015740100% (5)
- Lactulose: (Enuluse, Kristalose, Duphalac, Chronulac Syrup)Document30 pagesLactulose: (Enuluse, Kristalose, Duphalac, Chronulac Syrup)Joanna Dela Torre100% (2)
- Name of Drug Content Class and Mechanism of Action (MOA) Indication/s Contraindication/s Side Effects (Pere System) Nursing ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesName of Drug Content Class and Mechanism of Action (MOA) Indication/s Contraindication/s Side Effects (Pere System) Nursing ConsiderationsJustin John NavarroNo ratings yet
- Allopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument9 pagesAllopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComifyNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Epoetin AlfaDocument4 pagesEpoetin AlfachoyuminNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudycarmaxetaNo ratings yet
- Los Art AnDocument2 pagesLos Art AnKersey Adricula RicaldeNo ratings yet
- Drug Name WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesDrug Name WPS OfficeCAMILLE GAIL HADJIRANINo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contra Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contra Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJessica FabroaNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument4 pagesDigoxinJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines in The Management of Diabetic Nerve Pain Clinical Utility of PregabalinDocument22 pagesGuidelines in The Management of Diabetic Nerve Pain Clinical Utility of PregabalinSuryana Marjuki0% (1)
- Gabapentin FDADocument37 pagesGabapentin FDAAnish NairNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic PainDocument13 pagesNeuropathic Paintita_leo2No ratings yet
- Perbedaan Efek Analgesik Amitriptilin, Gabapentin, Dan Pregabalin Pada Neuropati Diabetik Dan Neuralgia TrigeminalDocument7 pagesPerbedaan Efek Analgesik Amitriptilin, Gabapentin, Dan Pregabalin Pada Neuropati Diabetik Dan Neuralgia TrigeminalsalmaNo ratings yet
- Sympo POKDI 2 ADocument66 pagesSympo POKDI 2 AQisti AshariNo ratings yet
- A Narrative EssayDocument8 pagesA Narrative Essaymkiyvubaf100% (2)
- Sun Zi's Art of War and Business StrategiesDocument15 pagesSun Zi's Art of War and Business StrategiesKomalaa BalanNo ratings yet
- NeurontinDocument3 pagesNeurontinFesto HakiNo ratings yet
- 2007 Uremic Pruritis AJKD PDFDocument11 pages2007 Uremic Pruritis AJKD PDFDexter BluesNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care - Overview of Cough, Stridor, and Hemoptysis - UpToDateDocument19 pagesPalliative Care - Overview of Cough, Stridor, and Hemoptysis - UpToDateThaísa NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Mdical Darpan September 2018Document16 pagesMdical Darpan September 2018Sarathya GhoshalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Antiepileptic Drugs Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesChapter 14: Antiepileptic Drugs Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceMekeshia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology. Sedative HypnoticDocument16 pagesPharmacology. Sedative HypnoticJean FlorencondiaNo ratings yet
- Drlee - Restless Leg SyndromeDocument1 pageDrlee - Restless Leg SyndromeSouheila MniNo ratings yet
- Drugs GabapentinDocument8 pagesDrugs Gabapentinvinod reddyNo ratings yet
- Case Study Breast CancerDocument16 pagesCase Study Breast CancerDanica Lorine Robino TaguinodNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology ReviewDocument8 pagesNursing Pharmacology ReviewKevin Mikhail EstandarteNo ratings yet
- Product Brief VOWWAYSDocument15 pagesProduct Brief VOWWAYSvowcare salesNo ratings yet
- Migraine CorrectedDocument97 pagesMigraine CorrectedPranesh Peter100% (1)
- Ogrania: Pregabalin 75 MG CapsulesDocument9 pagesOgrania: Pregabalin 75 MG Capsulesمصطفى الجبوريNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudySoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- 03 - Neurotoxicity in OncologyDocument17 pages03 - Neurotoxicity in OncologygorklanNo ratings yet
- Gabapentin in Pain Management: Jianren Mao,,, and Lucy L. ChenDocument8 pagesGabapentin in Pain Management: Jianren Mao,,, and Lucy L. ChenBarbara Sakura RiawanNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathy - UpToDateDocument20 pagesTreatment of Diabetic Neuropathy - UpToDateKarina MilaréNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Final Exam NURS 6630N ..Document17 pagesWeek 11 Final Exam NURS 6630N ..troillerdrippyNo ratings yet
- Adjuvant Analgesics: Helena Knotkova, PHD, Marco Pappagallo, MDDocument12 pagesAdjuvant Analgesics: Helena Knotkova, PHD, Marco Pappagallo, MDCarlos ArbeláezNo ratings yet
- Chill Protogol To Manage Aggressive & Fearful DogsDocument3 pagesChill Protogol To Manage Aggressive & Fearful DogsdmantsioNo ratings yet
- Neurontin (Gabapentin)Document1 pageNeurontin (Gabapentin)E100% (3)
Drug Study: Generic Name
Drug Study: Generic Name
Uploaded by
Alyanna Alcazar CapateOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study: Generic Name
Drug Study: Generic Name
Uploaded by
Alyanna Alcazar CapateCopyright:
Available Formats
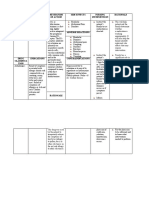
Drug Study
Drugs Action Indications Contraindications Adverse effects Nursing
Consideration
Generic An angiotensin Treatment of Hypersensitivity to Body as a Whole: Assessment &
Name: II receptor hypertension, valsartan or Arthralgia. Drug Effects:
Valsartan (type to lower blood losartan; CNS: Headache, dizziness.
AT1 antagonist; pressure. pregnancy GI: Diarrhea, nausea. >Monitor BP
Brand Name: blocks the Lowering [(category C) first Respiratory: Cough, periodically; take
Diovan binding of blood pressure trimester, sinusitis. trough readings,
angiotensin II reduces the (category D) Metabolic: Hyperkalemia. just prior to the
Classification: to the risk of fatal second and third next scheduled
Angiotensin II AT1 receptors and nonfatal trimesters], dose, when
Receptor found in many cardiovascular lactation; severe possible.
Antagonists tissues (e.g., events, heart failure with >Lab tests:
(ARBs) vascular primarily compromised renal Monitor liver
smooth strokes and function. function tests,
Dosage: muscle, myocardial BUN and
Hypertension adrenal infarctions creatinine,
Adult: PO 80 glands). serum
mg q.d. (max: Angiotensin II potassium, and
320 mg q.d.) is a potent CBC with
vasoconstrictor differential,
Heart Failure and primary periodically.
Adult: PO Star vasoactive
t with 40 mg hormone of
b.i.d. and the renin–
titrate up to angiotensin–
160 mg b.i.d. aldosterone
system.
Drugs Action Indications Contraindications Adverse effects Nursing
Consideration
Generic Name: Selective Celexa Hypersensitivity Body as a >Watch closely
Citalopram serotonin (citalopram to citalopram; Whole: Asthenia, fatigue, for worsening
reuptake HBr) is concurrent use of fever, arthralgia, myalgia. of depression
Brand Name: inhibitor (SSRI) in indicated for MAOIs or use CV: Tachycardia, postural or emergence
Celexa the CNS. the treatment within 14 d of hypotension, of suicidal
Antidepressant of depression. discontinuing hypotension. ideations.
Classification: effect is MAOIs; pregnancy GI: Nausea, vomiting,
Central presumed to be The efficacy (category C); diarrhea, dyspepsia, >Monitor for
Nervous linked to its of Celexa in volume depleted; abdominal pain, dry therapeutic
System (CNS) inhibition of CNS the treatment lactation; children mouth, anorexia, effectiveness:
Agent; presynaptic of depression <18 y. flatulence. Indicated by
Psychotherapy neuronal uptake was CNS: Dizziness, insomnia, elevation of
Agent; of serotonin established in somnolence, agitation, mood; 1–4 wk
Selective which results in 4–6-week, tremor, anxiety, may be
Serotonin- antidepressant controlled paresthesia, migraine. needed before
Reuptake activity. Does not trials of Respiratory: URI, rhinitis, improvement
Inhibitor (SSRI) produce any outpatients sinusitis. is noted.
sympathomimetic whose Skin: Increased sweating.
Dosage: response or diagnosis Urogenital: Dysmenorrhea, >Lab tests:
Adult: PO Start anticholinergic corresponded decreased libido, Monitor
at 20 mg q.d., activity. most closely ejaculation disorder, periodically
may increase to the DSM-III impotence. hepatic
to 40 mg q.d. if and DSM-III-R functions, CBC,
needed category of serum sodium,
Geriatric: PO 2 major and lithium
0 mg q.d. depressive levels when
disorder the two drugs
are given
concurrently.
>Monitor
periodically HR
and BP, and
carefully
monitor
complete
cardiac status
in person with
known or
suspected
cardiac
disease.
>Monitor
closely older
adult patients
for adverse
effects
especially with
doses >20
mg/d.
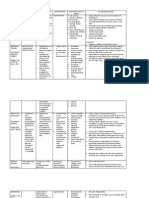
Drugs Action Indications Contraindications Adverse effects Nursing
Consideration
Generic Antagonist Benign prostatic Hypersensitivity Body as a Whole: Asthenia, back >Monitor for
Name: of the hyperplasia/urinar to tamsulosin; in or chest pain. signs of
Tamsulosin alpha1A- y retention conjunction with CNS: Headache, orthostatic
Hydrochlorid adrenergic another alpha1A- dizziness, insomnia. hypotension;
e receptors adrenergic CV: Orthostatic hypotension take BP lying
located in blocking agent; (especially with first dose). down, then
Brand Name: the lactation, GI: Diarrhea, nausea. upon
Flomax prostate. pediatric Respiratory: Rhinitis, pharyngitis, standing.
Symptoms patients. increased cough, sinusitis. Report a
Classification: related to Urogenital: Decreased systolic
Autonomic benign libido, abnormal ejaculation. pressure drop
Nervous prostatic Special Senses: Amblyopia. of 15 mm
System hypertrophy Hg or a HR
Agent; Apha- (BPH) are 15 beats
Adrenergic related to upon
Antagonist bladder standing.
outlet
Dosage: obstruction. >Monitor
Adult: PO 0.4 patients on
mg q.d. 30 warfarin
min after a therapy
meal, may closely.
increase up to
0.8 mg q.d.
Drugs Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Nursing Consideration
effects
Generic Specific inhibitor of Benign prostatic Hypersensitivity to Urogenital: >Evaluate carefully
Name: the steroid 5-alpha- hypertrophy, finasteride; pregnancy Impotence, any sustained
Finasteride reductase, an male pattern (category X), lactation, decreased increase in serum
enzyme necessary hair loss and children. libido, PSA levels while
Brand Name: to convert (androgenetic decreased patient is taking
Propecia, testosterone into alopecia). volume of finasteride. It may
Proscar the potent ejaculate. indicate the
androgen 5-alpha- presence of
Classification: dihydrotestosterone prostate cancer or
Hormones (DHT) in the noncompliance with
and Synthetic prostate gland. the therapy.
Subtitutes;
Antiandrogen; >Monitor patients
5-Alpha with a large residual
Reductase urinary volume or
Inhibitor decreased urinary
flow. These patients
Dosage: may not be
Benign candidates for this
Prostatic therapy.
Hypertrophy
Adult: PO 5
mg/d
Male Pattern
Hair Loss
Adult: PO 1
mg q.d.
Drugs Action Indications Contraindications Adverse effects Nursing
Consideration
Generic Name: Atorvastati Adjunct to diet for Hypersensitivity Body as a >Monitor for
Atorvastatin Calcium n is an the reduction of LDL to atorvastatin, Whole: Back pain, therapeutic
inhibitor of cholesterol and myopathy, asthenia, effectiveness
Brand Name: reductase triglycerides in active liver hypersensitivity which is
Lipitor 3-hydroxy- patients with primary disease, reaction, myalgia, indicated by
3-methyl- hypercholesterolemi unexplained rhabdomyolysis. reduction in
Classification: glutaryl a and mixed persistent CNS: Headache. the level of
Cardiovascular Agent; coenzyme A dyslipidemia. transaminase GI: Abdominal pain, LDL-C.
Antilipemic Agent; HMG- (HMG-CoA), elevations, constipation,
COA; Reductase Inhibitor which is pregnancy diarrhea, dyspepsia, >Lab tests:
(Statin) essential to (category X), flatulence, increased Monitor lipid
hepatic lactation. liver function tests. levels within
Dosage: production Respiratory: Sinusitis 2–4 wk after
Adult: PO Start with 10– of , pharyngitis. initiation of
40 mg q.d., may increase cholesterol. Skin: Rash. therapy or
up to 80 mg/d Lipitor upon change
Child/Adolescent: PO 10 increases in dosage;
–17 y: Start with 10 mg the number monitor liver
q.d., may increase up to of hepatic functions at
20 mg/d low- 6 and 12 wk
density- after
lipid (LDL) initiation or
receptors, elevation of
thus dose, and
increasing periodically
LDL uptake thereafter.
and
catabolism >Assess for
of LDL. muscle pain,
tenderness,
or weakness;
and, if
present,
monitor CPK
level
(discontinue
drug with
marked
elevations of
CPK or if
myopathy is
suspected).
>Monitor
carefully for
digoxin
toxicity with
concurrent
digoxin use.
Drugs Action Indications Contraindications Adverse effects Nursing
Consideration
Generic Name: An Duodenal and Long-term use for CNS: Headache, >Lab tests:
Omeprazole antisecretory gastric ulcer. gastroesophageal dizziness, fatigue. Monitor urinalysis
compound Gastroesophageal reflux disease GI: Diarrhea, for hematuria and
Brand Name: that is a reflux disease (GERD), duodenal abdominal pain, proteinuria.
Losec, Prilosec, gastric acid including severe ulcers; proton nausea, mild transient Periodic liver
Prilosec OTC, pump erosive pump inhibitors increases in liver function tests with
Zegerid inhibitor. esophagitis (4 to (PPIs), function tests. prolonged use.
Suppresses 8 wk treatment). hypersensitivity; Urogenital: Hematuria,
Classification: gastric acid Long-term children <2 y; use of proteinuria.
Gastrointestinal secretion by treatment of OTC formulation in Skin: Rash.
Agent; Proton inhibiting the pathologic children <18 y or GI
Pump Inhibitor H+, K+-ATPase hypersecretory bleeding; pregnancy
enzyme conditions such (category C); use of
Dosage: system [the as Zollinger- Zegerid in metabolic
Gastroesophagea acid (proton Ellison syndrome, alkalosis,
l Reflux, Erosive H+) pump] in multiple hypocalcemia,
Esophagitis, the parietal endocrine vomiting, GI
Duodenal Ulcer cells. adenomas, and bleeding.
Adult: PO 20 mg systemic
once/d for 4–8 mastocytosis. In
wk combination with
clarithromycin to
Gastric Ulcer treat duodenal
Adult: PO 20 mg ulcers associated
b.i.d. for 4–8 wk with Helicobacter
pylori.
Hypersecretory
Disease
Adult: PO 60 mg
once/d up to 120
mg t.i.d.
Duodenal Ulcer
Associated
with H. pylori
Adult: PO 40 mg
once/d for 14 d,
then 20 mg/d for
14 d, in
combination with
clarithromycin
500 mg t.i.d. for
14 d
Drugs Action Indications Contraindications Adverse effects Nursing
Consideration
Generic Name: Vitamin B12 is a Vitamin History of Body as a Whole: Feeling >Lab tests: Before
Cyanocobalamin cobalt- B12 deficiency sensitivity to of swelling of initiation of
containing B due to vitamin B12, body, anaphylactic therapy,
Brand Name: complex malabsorption other shock, sudden death. reticulocyte and
Anacobin, Bedoz, vitamin syndrome as cobalamins, or CV: Peripheral vascular erythrocyte
Betalin 12, produced in pernicious cobalt; early thrombosis, pulmonary counts, Hgb, Hct,
Crystamine, by Streptomyce (Addison's) Leber's disease edema, CHF. vitamin B12, and
Cyanabin, s griseus. anemia, (hereditary optic GI: Mild transient serum folate levels
Cyanoject, Essential for sprue; GI nerve atrophy), diarrhea. should be
Kaybovite, normal growth, pathology, indiscriminate Hematologic: Unmasking determined; then
Nascobal, cell dysfunction, use in folic acid of polycythemia vera repeated between
Nascobal Redisol, reproduction, or surgery; deficiency. Safe (with correction of 5 and 7 d after
Rubion, Rubramin maturation of fish tapeworm use during vitamin B12 deficiency). start of therapy
PC RBCs, infestation, pregnancy Metabolic: Hypokalemia. and at regular
nucleoprotein and gluten [category A, Skin: Itching, rash, intervals during
Classification: synthesis, enteropathy. category C flushing. therapy. Monitor
Hormone and maintenance of Also used in (parenteral)], Special Senses: Severe potassium levels
Synthetic nervous system B12 deficiency lactation. optic nerve atrophy during the first 48
Substitute; (myelin caused by (patients with Leber's h. Conversion to
Vitamin B12 synthesis), and increased disease). normal
believed to be physiologic erythropoiesis
Dosage: involved in requirements increases
Vitamin protein and or inadequate erythrocyte
B12 Deficiency carbohydrate dietary intake, potassium
Adult: IM/Deep metabolism. and in vitamin requirement and
SC 30 mcg/d for 5– Also acts as B12 absorption can result in
10 d, then 100– coenzyme in (Schilling) severe
200 mcg/mo various biologic test. hypokalemia and
Child: IM/Deep reactions. sudden death.
SC 100 mcg doses Vitamin
to a total of 1–5 B12 deficiency >Obtain a careful
mg over 2 wk, results in history of
then 60 mcg/mo megaloblastic sensitivities.
anemia, Sensitization to
Pernicious Anemia dysfunction of cyanocobalamin
Adult: IM/Deep spinal cord with can take as long as
SC 100–1000 paralysis, GI 8 y to develop.
mcg/d for 2–3 wk, lesions. Monitor vital signs
then 100–1000 in patients with
mcg q2– cardiac disease
4wk Intranasal on and in those
e pump in one receiving
nostril once parenteral
weekly cyanocobalamin,
Child: IM 30–50 and be alert to
mcg/d times 2 wk symptoms of
to total of 1000 pulmonary edema,
mcg, then 100 which generally
mcg/mo occur early in
Infant: IM 1000 therapy.
mcg/d times at
least 2 wk, then 50 >Therapeutic
mcg/mo response to drug
therapy is usually
Diagnosis of dramatic,
Megaloblastic occurring within
Anemia 48 h. Effectiveness
Adult: IM/Deep is measured by
SC 1 mcg/d for 10 laboratory values
d while and improvement
maintaining a low in manifestations
folate and vitamin of vitamin
B12 diet B12 deficiency.
Schilling Test >Characteristically,
Adult: IM/Deep reticulocyte
SC 1000 mcg times concentration
1 dose rises in 3–4 d,
peaks in 5–8 d,
Nutritional and then gradually
Supplement declines as
Adult: PO 1–25 erythrocyte count
mcg/d and Hgb rise to
Child: PO <1 y: 0.3 normal levels (in
mcg/d; 1 y: 1 4–6 wk).
mcg/d
>Obtain a
complete diet and
drug history and
inquire into
alcohol drinking
patterns for all
patients receiving
cyanocobalamin to
identify and
correct poor
habits.
Drugs Action Indications Contraindications Adverse effects Nursing Consideration
Generic Long-acting Relief of Hypersensitivity to CNS: Dizziness, >Assess carefully for
Name: antihistamine symptoms of loratadine. dry mouth, and report
Loratadine with selective seasonal fatigue, distressing or
peripheral H1- allergic rhinitis; headache, dangerous S&S that
Brand Name: receptor idiopathic somnolence, occur after initiation
Claritin, sites, thus chronic altered salivation of the drug. A variety
Alavert, blocking urticaria. and lacrimation, of adverse effects,
Claritin histamine thirst, flushing, although not
Reditabs release. anxiety, common, are
depression, possible. Some are
Classification: impaired an indication to
Antihistamine; concentration. discontinue the drug.
H1- Receptor CV: Hypotension,
Antagonist; hypertension, >Monitor
Nonsedating palpitations, cardiovascular status
syncope, and report significant
Dosage: tachycardia. changes in BP and
Adult: PO 10 GI: Nausea, palpitations or
mg once/d on vomiting, tachycardia.
an empty flatulence,
stomach; start abdominal
patients with distress,
liver disease constipation,
with 10 mg diarrhea, weight
every other gain, dyspepsia.
day Body as a
Child: PO <30 Whole: Arthralgia,
kg, 5 mg q.d.; myalgia.
>30 kg, 10 mg Special
q.d. Senses: Blurred
vision, earache,
eye pain,
tinnitus.
Skin: Rash,
pruritus,
photosensitivity.
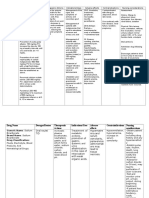
Drugs Action Indications Contraindications Adverse effects Nursing
Consideration
Generic Name: Gabapentin is a Adjunctive Hypersensitivity to CNS: Drowsiness, >Monitor for
Gabapentin GABA therapy for gabapentin; fatigue, dizziness, therapeutic
neurotransmitter partial seizures pregnancy tremor, slurred effectiveness;
Brand Name: analog; however, with or (category C), speech, impaired may not occur
Neurontin, it does not without lactation. concentration, until several
Gabarone interact with secondary headache, weeks following
GABA receptors, generalization increased initiation of
Classification: and it does not in adults, post- frequency of therapy.
Central Nervous inhibit GABA herpetic partial seizures.
System Agent; uptake or neuralgia. Endocrine: Weigh >Assess
Anticonvulsant, degradation. t gain. frequency of
GABA Analog Mechanism of GI: Nausea, seizures: In rare
action is gastric upset, cases, the drug
Dosage: unknown. An vomiting. has increased the
Adult/Child: PO >1 effect of Special frequency of
2 y, Initiate with gabapentin on Senses: Blurred partial seizures.
300 mg on day 1, central serotonin vision,
300 mg b.i.d. on metabolism has nystagmus, >Assess safety:
day 2, 300 mg t.i.d. been postulated. Skin: Rash, Vision,
on day 3, and eczema. concentration,
continue to and coordination
increase over a may be impaired
week to an initial by gabapentin.
total dose of 400
mg t.i.d. (1200
mg/d); may
increase to 1800–
2400 mg/d
depending on
response (most
patients receive
900–1800 mg/d in
3 divided doses)
400 mg t.i.d. (1200
mg/d)
Child: PO 3–12
y Initiate with 10–
15 mg/kg/d in 3
divided doses,
titrate q3d to
target dose of 40
mg/kg/d in pts 3–4
y or 25–35 mg/kg/d
in pts 5 y in 3
divided doses
Post-Herpetic
Neuralgia
Adult: PO Initiate
with 300 mg day 1,
300 mg b.i.d. day 2,
and 300 mg t.i.d.
day 3; may increase
up to 600 mg t.i.d.
if needed
Renal Impairment
Clcr >60 mL/min:
400 mg t.i.d.; 30–
60 mL/min: 300 mg
b.i.d.; 15–30
mL/min: 300 mg
q.d.; <15 mL/min:
300 mg q.o.d.;
hemodialysis: 200–
300 mg following
dialysis
You might also like
- Drug NeurontinDocument1 pageDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- Migraine Thesis FinalDocument96 pagesMigraine Thesis FinalPranesh Peter84% (19)
- PREDNISONEDocument4 pagesPREDNISONECay SevillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NewDocument4 pagesDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- MirtazapineDocument3 pagesMirtazapineapi-37979410% (1)
- Irbesartan (Avapro)Document1 pageIrbesartan (Avapro)ENo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineVina Jane P Laurel92% (12)
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAdrianPaul Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyRamon Carlo Almiranez100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (FINAL)Document31 pagesDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Side Effects Intervention and EvaluationDocument3 pagesName of Drug Classification Action Indication Side Effects Intervention and EvaluationMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Clonidine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesClonidine Drug Studypoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Atenolol (Tenormin)Document2 pagesAtenolol (Tenormin)Amanda West100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studysnowyfingers100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug Studydelpozo100% (3)
- F. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Document5 pagesF. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Lopirts NiganiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMelody Forca FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Nacl Drug StudyDocument1 pageNacl Drug StudydyndzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Room 104)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Room 104)Maeshe Pryll TanamorNo ratings yet
- Brand Name Generic Name Indication and Contraindication Nursing Consideration Action of The Drug Dose and Administration Side EffectsDocument2 pagesBrand Name Generic Name Indication and Contraindication Nursing Consideration Action of The Drug Dose and Administration Side EffectsCarla Dana GozumNo ratings yet
- Name of The Drug Dosage Indication and Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsbilitiesDocument2 pagesName of The Drug Dosage Indication and Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsbilitiesMiguel Paolo Bastillo MercadoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studysuperhuman_mabz100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyMay Dianne Mansia Bautista100% (1)
- Losartan Potassium Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLosartan Potassium Drug StudyJonieP84100% (4)
- Paracetamol PODocument3 pagesParacetamol POSheena GallardoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudySuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyMaye HerbitoNo ratings yet
- DRUG FluimucilDocument1 pageDRUG FluimucilrholiboiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaNo ratings yet
- Felodipine CefuroximeDocument3 pagesFelodipine CefuroximecotyboyNo ratings yet
- HydrochlorothiazideDocument1 pageHydrochlorothiazideKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocument3 pagesDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Cetirizine 2Document2 pagesCetirizine 2ianNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument26 pagesDrug Studyrn msnNo ratings yet
- Vasotec EnalaprilDocument1 pageVasotec EnalaprilCassie100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyArmie Joy Embat CariazoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuNo ratings yet
- RosuvastatinDocument1 pageRosuvastatinJoshua KellyNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University: Institute of Nursing S.Y. 2018-2019Document1 pageFar Eastern University: Institute of Nursing S.Y. 2018-2019shendae cosmianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyBadgal BazingaNo ratings yet
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- Difflam Drug StudyDocument1 pageDifflam Drug StudyDanlee EstandaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument18 pagesDrug StudyAntonethe DemdamNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EditedDocument5 pagesDrug Study EditedfabtaciousVeelaNo ratings yet
- Micardis Indication CNS: DigoxinDocument1 pageMicardis Indication CNS: Digoxineric macabiogNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyuntoned100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- NCP1 CHFDocument2 pagesNCP1 CHFapi-27015740100% (5)
- Lactulose: (Enuluse, Kristalose, Duphalac, Chronulac Syrup)Document30 pagesLactulose: (Enuluse, Kristalose, Duphalac, Chronulac Syrup)Joanna Dela Torre100% (2)
- Name of Drug Content Class and Mechanism of Action (MOA) Indication/s Contraindication/s Side Effects (Pere System) Nursing ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesName of Drug Content Class and Mechanism of Action (MOA) Indication/s Contraindication/s Side Effects (Pere System) Nursing ConsiderationsJustin John NavarroNo ratings yet
- Allopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument9 pagesAllopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComifyNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Epoetin AlfaDocument4 pagesEpoetin AlfachoyuminNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudycarmaxetaNo ratings yet
- Los Art AnDocument2 pagesLos Art AnKersey Adricula RicaldeNo ratings yet
- Drug Name WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesDrug Name WPS OfficeCAMILLE GAIL HADJIRANINo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contra Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contra Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJessica FabroaNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument4 pagesDigoxinJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines in The Management of Diabetic Nerve Pain Clinical Utility of PregabalinDocument22 pagesGuidelines in The Management of Diabetic Nerve Pain Clinical Utility of PregabalinSuryana Marjuki0% (1)
- Gabapentin FDADocument37 pagesGabapentin FDAAnish NairNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic PainDocument13 pagesNeuropathic Paintita_leo2No ratings yet
- Perbedaan Efek Analgesik Amitriptilin, Gabapentin, Dan Pregabalin Pada Neuropati Diabetik Dan Neuralgia TrigeminalDocument7 pagesPerbedaan Efek Analgesik Amitriptilin, Gabapentin, Dan Pregabalin Pada Neuropati Diabetik Dan Neuralgia TrigeminalsalmaNo ratings yet
- Sympo POKDI 2 ADocument66 pagesSympo POKDI 2 AQisti AshariNo ratings yet
- A Narrative EssayDocument8 pagesA Narrative Essaymkiyvubaf100% (2)
- Sun Zi's Art of War and Business StrategiesDocument15 pagesSun Zi's Art of War and Business StrategiesKomalaa BalanNo ratings yet
- NeurontinDocument3 pagesNeurontinFesto HakiNo ratings yet
- 2007 Uremic Pruritis AJKD PDFDocument11 pages2007 Uremic Pruritis AJKD PDFDexter BluesNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care - Overview of Cough, Stridor, and Hemoptysis - UpToDateDocument19 pagesPalliative Care - Overview of Cough, Stridor, and Hemoptysis - UpToDateThaísa NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Mdical Darpan September 2018Document16 pagesMdical Darpan September 2018Sarathya GhoshalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Antiepileptic Drugs Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesChapter 14: Antiepileptic Drugs Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceMekeshia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology. Sedative HypnoticDocument16 pagesPharmacology. Sedative HypnoticJean FlorencondiaNo ratings yet
- Drlee - Restless Leg SyndromeDocument1 pageDrlee - Restless Leg SyndromeSouheila MniNo ratings yet
- Drugs GabapentinDocument8 pagesDrugs Gabapentinvinod reddyNo ratings yet
- Case Study Breast CancerDocument16 pagesCase Study Breast CancerDanica Lorine Robino TaguinodNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology ReviewDocument8 pagesNursing Pharmacology ReviewKevin Mikhail EstandarteNo ratings yet
- Product Brief VOWWAYSDocument15 pagesProduct Brief VOWWAYSvowcare salesNo ratings yet
- Migraine CorrectedDocument97 pagesMigraine CorrectedPranesh Peter100% (1)
- Ogrania: Pregabalin 75 MG CapsulesDocument9 pagesOgrania: Pregabalin 75 MG Capsulesمصطفى الجبوريNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudySoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- 03 - Neurotoxicity in OncologyDocument17 pages03 - Neurotoxicity in OncologygorklanNo ratings yet
- Gabapentin in Pain Management: Jianren Mao,,, and Lucy L. ChenDocument8 pagesGabapentin in Pain Management: Jianren Mao,,, and Lucy L. ChenBarbara Sakura RiawanNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathy - UpToDateDocument20 pagesTreatment of Diabetic Neuropathy - UpToDateKarina MilaréNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Final Exam NURS 6630N ..Document17 pagesWeek 11 Final Exam NURS 6630N ..troillerdrippyNo ratings yet
- Adjuvant Analgesics: Helena Knotkova, PHD, Marco Pappagallo, MDDocument12 pagesAdjuvant Analgesics: Helena Knotkova, PHD, Marco Pappagallo, MDCarlos ArbeláezNo ratings yet
- Chill Protogol To Manage Aggressive & Fearful DogsDocument3 pagesChill Protogol To Manage Aggressive & Fearful DogsdmantsioNo ratings yet
- Neurontin (Gabapentin)Document1 pageNeurontin (Gabapentin)E100% (3)