Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCL 140: Engineering Thermodynamics Tutorial-4
MCL 140: Engineering Thermodynamics Tutorial-4
Uploaded by
Masamune RutherfordOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MCL 140: Engineering Thermodynamics Tutorial-4
MCL 140: Engineering Thermodynamics Tutorial-4
Uploaded by
Masamune RutherfordCopyright:
Available Formats
MCL 140: Engineering Thermodynamics
Tutorial-4
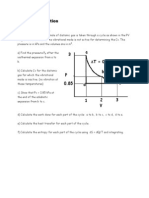
1. Air is trapped in a piston-cylinder machine (shown in figure). Initially 𝑃1 = 100 kPa,
𝑉1 = 2 × 10−3 m3 . The spring exerts no force on the piston in the initial position. The
atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa and the area of the piston is 0.018 m2. The air expands
slowly till its volume is 𝑉2 = 3 × 10−3 m3 . During the process, the spring exerts a force
on the piston 𝐹 = −𝑘𝑥, where 𝑘 = 16.2 × 103 N/m. Neglecting any friction between
piston and cylinder wall, determine the final pressure of air and the work done by the
air on the piston.
2. The heat capacity at constant pressure of a certain system is a function of temperature
only and may be expressed as
41.87
𝐶𝑃 = 2.093 + J/℃
𝑡 + 100
where t is the temperature of the system in ℃. The system is heated while it is
maintained at a pressure of 1 atm until its volume increases from 2000 cm3 to 2400 cm3
and its temperature increases from 0℃ to 100℃. (a) Find the magnitude of heat
interaction. (b) How much does the internal energy of the system increase?
3. In a gas turbine the gas enters at the rate of 5 kg/s with a velocity of 50 m/s and enthalpy
of 900 kJ/kg. The loss of heat from the gases to the surroundings is 25 kJ/kg. Assume
for gas R = 0.285 kJ/kgK and cp = 1.004 kJ/kgK and the inlet conditions to be at 100
kPa and 27℃. Determine the power output of the turbine and the diameter of the inlet
pipe.
4. Two bodies have heat capacities that depend on temperature as 𝐶 = 𝑎 + 𝑏𝑇 + 𝑐𝑇 2 ,
where 𝑎 = 8 J/K, 𝑏 = 2 × 10−2 J/K2 , 𝑐 = 3 × 10−5 J/K3 and 𝑇 is the temperature in
kelvin. The two bodies are initially at temperatures of 400 K and 300 K. If these bodies
are brought in contact with each other, what is the heat transferred between these two
bodies.
You might also like
- Assignment 1 & 2Document17 pagesAssignment 1 & 2Iyyan Paramanandam67% (3)
- 11 Heat TransferDocument3 pages11 Heat Transferjamesvita62No ratings yet
- ME3100 Solution Tut-2Document8 pagesME3100 Solution Tut-2B V V HANUMA GAYATHRINo ratings yet
- TDCE Question Bank - 2018 Unit IDocument11 pagesTDCE Question Bank - 2018 Unit IvinodNo ratings yet
- MAE 11 Thermodynamics Practice ProblemsDocument8 pagesMAE 11 Thermodynamics Practice ProblemsGuest SuiteNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3happy20212025No ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3asasNo ratings yet
- Processes and Carnot CycleDocument4 pagesProcesses and Carnot CycleRagh AhmedNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument1 pageBasicsRishi Raj100% (1)
- CH2043 - Tutorial 1Document1 pageCH2043 - Tutorial 1Ngọc ĐàoNo ratings yet
- ME214 BTD Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesME214 BTD Tutorial QuestionsKONDALRAONo ratings yet
- Problem Set#1Document2 pagesProblem Set#1ron ronnnNo ratings yet
- Our Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromDocument2 pagesOur Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromPradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet1Document4 pagesWork Sheet1Tesfa negaNo ratings yet
- THRM1001 Tutorial 4 1st Law of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesTHRM1001 Tutorial 4 1st Law of ThermodynamicsDimitri RamloganNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 QuestionsDocument2 pagesHomework 3 Questionsdaragh keaveneyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Akatew Haile MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 1Document1 pageAssignment 3 1shubham2395No ratings yet
- PHY 103 Lecture 4Document26 pagesPHY 103 Lecture 4oloruntishevictorNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Karthik RaoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Tutorial - QuestionsDocument11 pagesThermodynamics Tutorial - Questionsdinalamin195No ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument57 pagesThermodynamicsMei Lamfao100% (1)
- Files MECH QB III ME6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument15 pagesFiles MECH QB III ME6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsAnantha Kumar0% (1)
- 1 First Law of Thermodynamics PDFDocument5 pages1 First Law of Thermodynamics PDFBharat BhushanNo ratings yet
- Singh - Applied Thermodynamics PDFDocument8 pagesSingh - Applied Thermodynamics PDFHectorCabzNo ratings yet
- Homework 4. Evaluating Properties.: Constant. TheDocument2 pagesHomework 4. Evaluating Properties.: Constant. TheLUISRONo ratings yet
- Chn-201 Tutorial 2 - Autumn 16-17-1Document2 pagesChn-201 Tutorial 2 - Autumn 16-17-1Prashant RajNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology RoorkeeDocument2 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Roorkeepushkal0% (2)
- DPP1 Thermodynamic (24feb2022)Document2 pagesDPP1 Thermodynamic (24feb2022)Shubham MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document1 pageChapter 5Train DiskenthNo ratings yet
- QB Unit 1Document6 pagesQB Unit 1Gaurav GadhesariaNo ratings yet
- MMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet6 - 1st Law Steady FlowDocument3 pagesMMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet6 - 1st Law Steady Flowgrandw9524No ratings yet
- 1st Law ProbDocument2 pages1st Law ProbShashank SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment FileDocument2 pagesAssignment FileMallesham DevasaneNo ratings yet
- AE-664A Assignment 1Document2 pagesAE-664A Assignment 1Saurav SonawaneNo ratings yet
- TD Tutorial 2018 EditedDocument34 pagesTD Tutorial 2018 EditedRochakNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Question Set ADocument4 pagesThermodynamics Question Set AVivek NegiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment SheetDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Assignment SheetSatwikMohantyNo ratings yet
- Assume Ideal Behavior Unless Stated Otherwise. 1.: CY11001 (Physical Chemistry) Tutorial 3Document2 pagesAssume Ideal Behavior Unless Stated Otherwise. 1.: CY11001 (Physical Chemistry) Tutorial 3Krityapriya BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document3 pagesTutorial 4joeltanwbNo ratings yet
- Question 2Document8 pagesQuestion 2mkbNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1Vinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Questions and AnswersMD SHOEBUDDIN0% (1)
- HT Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesHT Practice QuestionsVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- TD Thermo GTIERDocument14 pagesTD Thermo GTIERAHMED AL MERSNo ratings yet
- ME331 Thermodynamics: PS #3 Solutions: Numeric 1Document14 pagesME331 Thermodynamics: PS #3 Solutions: Numeric 1Crimson MorangeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document11 pagesLecture 2ahmed el-sayedNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1, Autumn 2023Document2 pagesAssignment 1, Autumn 2023cocodarshi2022No ratings yet
- Assignment1 MEL140 - 2013 PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment1 MEL140 - 2013 PDFSanaNo ratings yet
- PHYS242 Thermodynamics and HeatDocument4 pagesPHYS242 Thermodynamics and Heatmcspt117No ratings yet
- Ae708 Question Bank 2Document5 pagesAe708 Question Bank 2pRoBoTRoGe OPNo ratings yet
- NCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 12 ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesNCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 12 ThermodynamicsUday KhanalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 VannessDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 2 VannessMekeilah AgustinNo ratings yet
- Tarea No 7 ExergiaDocument3 pagesTarea No 7 ExergiaAndres RomeroNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Physics - ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesClass 11 - Physics - ThermodynamicsSha HNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesII B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsAshok DaraNo ratings yet
- Heat & Mass Transfer Tutorial Sheet: Force ConvectionDocument2 pagesHeat & Mass Transfer Tutorial Sheet: Force Convectionp KumarNo ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)