Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Sheet 2 - Terminal Velocity
Tutorial Sheet 2 - Terminal Velocity
Uploaded by
TÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Sheet 2 - Terminal Velocity
Tutorial Sheet 2 - Terminal Velocity
Uploaded by
TÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnCopyright:
Available Formats
CH3083 Particle & Powder Technology
Tutorial 2 Sheet
Terminal Velocity
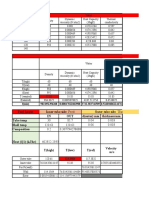
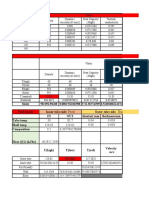
1. A particle of 2 mm in diameter and density of 2500 kg/m3 is settling in a stagnant
fluid in the Stokes’ flow regime.
(a) Calculate the viscosity of the fluid if the fluid density is 1000 kg/m 3 and the
particle falls at a terminal velocity of 4 mm/s.
(b) What is the drag force on the particle at these conditions?
(c) What is the particle drag coefficient at these conditions?
(d) What is the particle acceleration at these conditions?
(e) What is the apparent weight of the particle?
2. A particle of equivalent volume diameter 0.3 mm, density 2000 kg/m3 and sphericity
0.6 falls freely under gravity in a fluid of density 1.2kg/m3 and viscosity 2 x 10-5 Pa s.
Estimate the terminal velocity reached by the particle.
Ans. 0.089m/s
3. A particle of equivalent volume diameter 0.2 mm, density 2000 kg/m3 and sphericity
0.6 falls freely under gravity in a fluid of density 1.0kg/m3 and viscosity 2 x 10-5 Pa s.
Estimate the terminal velocity reached by the particle.
Ans. 0.075m/s
4. A spherical particle of density 1500 kg/m3 has a terminal velocity of 1 cm/s in a fluid
of density 800 kg/m3 and viscosity 0.001 Pa s. Estimate the diameter of the particle.
Ans. 175m
5. Estimate the largest diameter of spherical particle of density 2000 kg/m3 which
would be expected to obey Stokes’ law in air of density 1.2kg/m3 and viscosity 18 x
10-6 Pa s.
Ans. 42m
Settling
6. Spherical particles of density 2500 kg/m3 and in the size range 20–100 m are fed
continuously into a stream of water (density, 1000 kg/m3 and viscosity, 0.001 Pa s)
flowing upwards in a vertical, large diameter pipe. What maximum water velocity is
required to ensure that no particles of diameter greater than 60 m are carried
upwards with water?
Ans. 2.9 mm/s
7. Spherical particles of density 2000 kg/m3 and in the size range 20–100 m are fed
continuously into a stream of water (density, 1000 kg/m3 and viscosity, 0.001 Pa s)
flowing upwards in a vertical, large diameter pipe. What maximum water velocity is
required to ensure that no particles of diameter greater than 50 m are carried
upwards with the water?
Ans. 1.4 mm/s
Dr C. Mangwandi
Terminal Velocity & Settling
CH3083 Particle & Powder Technology
Dr C. Mangwandi
Terminal Velocity & Settling
CH3083 Particle & Powder Technology
Dr C. Mangwandi Terminal Velocity & Settling
CH3083 Particle & Powder Technology
Dr C. Mangwandi Terminal Velocity & Settling
You might also like
- Mamufacturing of Potassium ChlorideDocument16 pagesMamufacturing of Potassium Chloriderajesh100% (1)
- Jntuworld: R07 Set No. 2Document6 pagesJntuworld: R07 Set No. 2Dolly PriyaNo ratings yet
- Problems Collection-2018Document19 pagesProblems Collection-2018calvinNo ratings yet
- Mahmood Et Al. - 2011 - Comparison of Different Methods For The Point of Zero Charge Determination of NiODocument7 pagesMahmood Et Al. - 2011 - Comparison of Different Methods For The Point of Zero Charge Determination of NiOJefersonCorreiaNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Techniques Used For Wastewater TreatmentDocument11 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Techniques Used For Wastewater TreatmentGirish GuptaNo ratings yet
- CHE572 Chapter 2 Particle Size Characterization PDFDocument18 pagesCHE572 Chapter 2 Particle Size Characterization PDFMuhd FahmiNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL-on Absorption - 2018 - SolutionDocument2 pagesTUTORIAL-on Absorption - 2018 - SolutionMayank Prasad100% (1)
- Thickener Design and Theory ProblemsDocument9 pagesThickener Design and Theory ProblemsRodrigo GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Froth Stability in Froth Flotation PDFDocument6 pagesDynamic Froth Stability in Froth Flotation PDFMonica Ulloa LamasNo ratings yet
- Densitometer PrincipleDocument2 pagesDensitometer Principlebhavin1780% (1)
- Celda Flash Site Skim Air Test Procedure With PhotosDocument9 pagesCelda Flash Site Skim Air Test Procedure With Photosealfaro6580No ratings yet
- A Parametric Study of Froth Stability and Its EffectDocument19 pagesA Parametric Study of Froth Stability and Its EffectJuan OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Scope:: About The Ballbal - Direct Spreadsheet ..Document14 pagesScope:: About The Ballbal - Direct Spreadsheet ..alonsogonzalesNo ratings yet
- Acid Digestion ProcedureDocument2 pagesAcid Digestion ProcedureSolehah OmarNo ratings yet
- Anion-Cation BalancesDocument4 pagesAnion-Cation BalancesFikri Adam DermawanNo ratings yet
- Makanza Flotation (2008)Document23 pagesMakanza Flotation (2008)Richard CookNo ratings yet
- Che65: Introduction To Particle Technology: Reporters: Billy Jhones A Adaya Ercille Mae O PacamoDocument31 pagesChe65: Introduction To Particle Technology: Reporters: Billy Jhones A Adaya Ercille Mae O Pacamoکبری ادریس رسولNo ratings yet
- Process Copper LeachingDocument84 pagesProcess Copper LeachingLopezNgelekaNo ratings yet
- Filtration Unit Report: Index Terms-Pressure, Flow, Pump, Filtration, ParticleDocument4 pagesFiltration Unit Report: Index Terms-Pressure, Flow, Pump, Filtration, Particlejuan francoNo ratings yet
- On Paratacamite and Some Related Copper ChloridesDocument12 pagesOn Paratacamite and Some Related Copper ChloridesHJKB1975No ratings yet
- Final TrimexDocument46 pagesFinal Trimexmanojkumarchowdari382No ratings yet
- Sodium Chlorate - Properties and Reactions PDFDocument5 pagesSodium Chlorate - Properties and Reactions PDFangelofglory100% (1)
- 6 Copper Ores Bio LeachingDocument45 pages6 Copper Ores Bio LeachingSrdjan StankovicNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Mohr's MethodDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Mohr's MethodKingsley WongNo ratings yet
- Use of Coagulants To Reduce Crud by Colloidal SilicaDocument11 pagesUse of Coagulants To Reduce Crud by Colloidal SilicaJose Eduardo Osuna AraizaNo ratings yet
- ION - CCP - LAB INSTRUCTIONS - Dr. NEUMANN - 2008 - 07 - 10 PDFDocument40 pagesION - CCP - LAB INSTRUCTIONS - Dr. NEUMANN - 2008 - 07 - 10 PDFRahul Khandelwal100% (2)
- Gold Cyanidation: Cairo Universty Faculty of Engineering 3 Year Mining DepartmentDocument11 pagesGold Cyanidation: Cairo Universty Faculty of Engineering 3 Year Mining DepartmentMourad HosniNo ratings yet
- Mineral Processing Circuits - Detection of The Appropriate Sampling SchemeDocument19 pagesMineral Processing Circuits - Detection of The Appropriate Sampling SchemeTsakalakis G. KonstantinosNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Standard Humidity Cell Test ResultsDocument8 pagesInterpretation of Standard Humidity Cell Test Resultsomar TahaNo ratings yet
- Stuart SaichDocument27 pagesStuart Saichavca65No ratings yet
- Mass Balancing Examples 1Document49 pagesMass Balancing Examples 1Amnart L. JantharasukNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Bentonite Clay PDFDocument6 pagesCharacterization of Bentonite Clay PDFHafiz Mudaser AhmadNo ratings yet
- Contributions To An Improved Understanding of The Flotation ProcessDocument70 pagesContributions To An Improved Understanding of The Flotation Process4943900No ratings yet
- Lab Report GCDocument8 pagesLab Report GCAyish MataNo ratings yet
- Froth Floatation CellDocument3 pagesFroth Floatation CellinstrutechNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Exercise On Measurement of QuantitiesDocument3 pagesLecture 3: Exercise On Measurement of Quantitiesjr_satishNo ratings yet
- A Review On Pyrrhotite OxidationDocument12 pagesA Review On Pyrrhotite OxidationDaniela LobarinhasNo ratings yet
- IPL Engineering Design Report For CEMI427Document320 pagesIPL Engineering Design Report For CEMI427fieryfrostburn0% (1)
- NMDTM PhosphoricAcidDocument10 pagesNMDTM PhosphoricAcidacas35No ratings yet
- 450 Bittern SeparationDocument5 pages450 Bittern SeparationJussier VitorianoNo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: Michel Shengo Lutandula, Banza MalobaDocument6 pagesJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: Michel Shengo Lutandula, Banza MalobaJordan Ulloa BelloNo ratings yet
- CHA CHA: Thickener DesignDocument1 pageCHA CHA: Thickener DesignKumar RajeshNo ratings yet
- Pervaporation of Ethanol-Water Solutions: Matthew Graham, Tsung-Ming Yeh, Benjamin Hsiao and Devinder MahajanDocument8 pagesPervaporation of Ethanol-Water Solutions: Matthew Graham, Tsung-Ming Yeh, Benjamin Hsiao and Devinder MahajanAnaclara LeitesNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0892687512001239 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0892687512001239 MainMiguel FrezNo ratings yet
- Biofilter DecisionsDocument23 pagesBiofilter DecisionsBokJrNo ratings yet
- Particle Size AnalysisDocument29 pagesParticle Size Analysisاشرفاللسامي100% (1)
- Solid Liquid Extraction Prac RepDocument7 pagesSolid Liquid Extraction Prac RepSlindile Hlambisa100% (1)
- Slip Casting of Kaolin-Quartz CeramicsDocument47 pagesSlip Casting of Kaolin-Quartz CeramicsCarlos SerranoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Introducction To Thermal Unit OperationDocument34 pagesLecture 2-Introducction To Thermal Unit Operationyemane gadaNo ratings yet
- 409 S05 PDFDocument46 pages409 S05 PDFRobert ZhangNo ratings yet
- AOT QuestionsDocument3 pagesAOT Questionsunni kNo ratings yet
- Application of Superconducting High Gradient Magnetic Separation Technology On Silica Extraction From Iron Ore BeneDocument7 pagesApplication of Superconducting High Gradient Magnetic Separation Technology On Silica Extraction From Iron Ore BeneLuanna MouraNo ratings yet
- Chapter One - Mecanical Unit OperationDocument17 pagesChapter One - Mecanical Unit OperationBizuayehu GeroNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Salt Deposits From Keana LGA, Nassarawa State, NigeriaDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Salt Deposits From Keana LGA, Nassarawa State, NigeriaMusa Balarabe AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- RheologyDocument18 pagesRheologyAjay YadavNo ratings yet
- 1 - Particle Size and Distribution AnalaysisDocument52 pages1 - Particle Size and Distribution AnalaysisMekonnen BirhaneNo ratings yet
- Pyrometallurgical Extraction of PGM AssignmentDocument10 pagesPyrometallurgical Extraction of PGM Assignmentprincekamutikanjore100% (2)
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Latihan Kelompok Mekanika Fluida Dan PartikelDocument2 pagesLatihan Kelompok Mekanika Fluida Dan PartikelrizkaNo ratings yet
- Momentum Transfer PDFDocument5 pagesMomentum Transfer PDFonyxNo ratings yet
- Feed Heater IN OUT D (Outer) MM Thickness MM Tube Temp Shell Temp Composition Inner Tube Side: Feed Outer Tube Side: WaterDocument57 pagesFeed Heater IN OUT D (Outer) MM Thickness MM Tube Temp Shell Temp Composition Inner Tube Side: Feed Outer Tube Side: WaterTÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Official Acrylic Acid 0712docxDocument42 pagesOfficial Acrylic Acid 0712docxTÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Feed Heater IN OUT D (Outer) MM Thickness MM Tube Temp Shell Temp Composition Inner Tube Side: Feed Outer Tube Side: WaterDocument57 pagesFeed Heater IN OUT D (Outer) MM Thickness MM Tube Temp Shell Temp Composition Inner Tube Side: Feed Outer Tube Side: WaterTÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Polyethylene (PE) : Is A Thermoplastic Polymer: (Image)Document7 pagesPolyethylene (PE) : Is A Thermoplastic Polymer: (Image)TÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 EvaporationDocument134 pagesChapter 9 EvaporationTÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Titrimetric Methods of Analysis: AC1 - Chap7Document66 pagesTitrimetric Methods of Analysis: AC1 - Chap7TÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Membrane Technology & ApplicationsDocument44 pagesMembrane Technology & ApplicationsTÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Methods of Analysis: AC1 - CHP 6Document24 pagesGravimetric Methods of Analysis: AC1 - CHP 6TÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Conditional Equilibrium Constant of ReactionDocument60 pagesConditional Equilibrium Constant of ReactionTÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Constant of ReactionDocument55 pagesEquilibrium Constant of ReactionTÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Review of Stoichiometric CalculationsDocument17 pagesReview of Stoichiometric CalculationsTÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- P1 Chp1Document23 pagesP1 Chp1TÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnNo ratings yet
- 2021-ME-54 Lab ReportDocument31 pages2021-ME-54 Lab ReportAbdullah ArshadNo ratings yet
- Supreme Agri 2021Document1 pageSupreme Agri 2021Mukesh HalpaniNo ratings yet
- REF - Chapter 05Document4 pagesREF - Chapter 05Jeffrey RebonquinNo ratings yet
- CompressorDocument33 pagesCompressorfvaefaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Equation Sheet: K A H ADocument31 pagesHeat Transfer Equation Sheet: K A H ABeydaNo ratings yet
- Domestic Wastewater TreatmentDocument20 pagesDomestic Wastewater TreatmentShayan SohailNo ratings yet
- Q - Bank - CHEM - AST - SEM VI - 2022Document15 pagesQ - Bank - CHEM - AST - SEM VI - 2022Patel DhruvilNo ratings yet
- Food Science 4txtDocument2 pagesFood Science 4txtSabreenNo ratings yet
- SUMP-CAISSON BrochureDocument2 pagesSUMP-CAISSON BrochurekawmawNo ratings yet
- Cascade Aerator: How It WorksDocument29 pagesCascade Aerator: How It WorksMahaveer ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Enhancing The Flow and HeatDocument13 pagesEnhancing The Flow and Heatmntbyun03No ratings yet
- Lab 7Document4 pagesLab 7Talha JuttNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow Notes - BasicDocument9 pagesPipe Flow Notes - BasicMwine Isaac NormanNo ratings yet
- Peerless - Process - 116 - 118 CurvasDocument6 pagesPeerless - Process - 116 - 118 CurvasedwinsazzzNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge of Sheet MetalDocument36 pagesBasic Knowledge of Sheet MetalHemang Shah33% (3)
- Form Request OvertimeDocument21 pagesForm Request OvertimeAndika ArdaNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry and Conservation of Energy Lab ReportDocument5 pagesCalorimetry and Conservation of Energy Lab ReportKali stringsNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal OperationsDocument26 pagesSheet Metal Operationssomu.cpNo ratings yet
- Pump NPSH - Accounting For Dissolved GasesDocument13 pagesPump NPSH - Accounting For Dissolved GasesSarelys ZavalaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Forced CirculationDocument7 pagesExperimental Study of Forced CirculationAadarshNo ratings yet
- Hidrotreating PDFDocument10 pagesHidrotreating PDFM Fariz YasminNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes On CatalysisDocument12 pagesAdditional Notes On CatalysisomoljavanNo ratings yet
- Flashover and Instabilities in Fire Behavior: P. H. Thomas and M. L. BullenDocument13 pagesFlashover and Instabilities in Fire Behavior: P. H. Thomas and M. L. BullenMihaNo ratings yet
- How Pressure Regulators WorkDocument22 pagesHow Pressure Regulators WorkAdeel QaiserNo ratings yet
- Design of Steam Generators Numerical Calculation Program ForDocument18 pagesDesign of Steam Generators Numerical Calculation Program ForTriambakeshwarNo ratings yet
- CLP301 Policy ScheduleDocument3 pagesCLP301 Policy ScheduleKhushii NaamdeoNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layers Integral Approach 1 - 2024Document16 pagesBoundary Layers Integral Approach 1 - 2024adityagolewar2003No ratings yet
- Single Stage DistillationDocument15 pagesSingle Stage DistillationFatimah MauludiyahNo ratings yet
- 18ee2128 Waste To EnergyDocument1 page18ee2128 Waste To Energys sNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1750583621001997 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S1750583621001997 MainAbdul ZahirNo ratings yet