Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AdultTachycardiaWithPulse Algorithm
AdultTachycardiaWithPulse Algorithm
Uploaded by
Ismail SlimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AdultTachycardiaWithPulse Algorithm
AdultTachycardiaWithPulse Algorithm
Uploaded by
Ismail SlimCopyright:
Available Formats
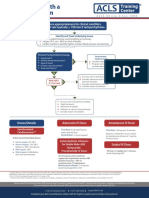
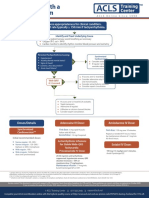
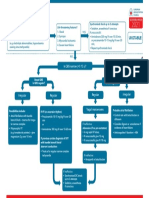
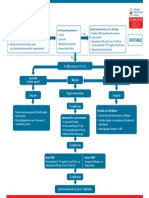
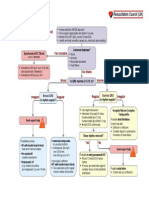
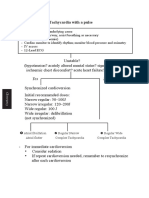
Adult Tachycardia (with Pulse)
1 Identify SVT
(Heart rate >150)
2 Establish and Treat
Possible Causes
Secure patient airway, assist with respirations
as needed
Administer oxygen if hypoxic
Attach cardiac monitor, monitor BP and SPO2
3 Hypotension?
Shock?
No Ischemic Chest Pain? Yes Synchronized Cardioversion
AMS? Starting Doses:
Heart Failure? Narrow regular: 50-100 J
Narrow irregular: 120-200 J biphasic
or 200 J monophasic
Wide regular: 100 J
Wide irregular: defibrillation dose
(Not synchronized)
4 QRS Wide? 5 Immediate Synchronized
Yes Adenosine
(>
_ 0.12 sec) Cardioversion
6 mg rapid IV push,
If regular narrow complex,
follow with NS flush
consider Adenosine
2nd Dose: 12 mg
6 Establish vascular access
Antiarrhythmic Infusions
Run 12-Lead ECG if possible
Consider adenosine only if (Stable Wide-Complex)
No monomorphic and regular
Consider antiarrhythmic infusion Amiodarone:
Seek expert consult 150 mg over 10 min
Repeat as necessary if VT recurs
Procainamide:
20-50 mg/min until arrhythmia is
7 Establish vascular access suppressed, hypotension ensues,
Run 12-Lead ECG if possible QRS duration increases >50%, or
Consider vagal maneuvers maximum dose of 17 mg/kg is reached
Adenosine (if regular rhythm)
Administer -Blocker or
Calcium Channel Blocker
Sotalol:
100 mg (1.5 mg/kg) over 5 min
Seek expert consult
You might also like
- Cardiac Arrest QuestionsDocument2 pagesCardiac Arrest Questionsmine251580% (5)
- Bojar PediatricDocument123 pagesBojar PediatricLuqman AlwiNo ratings yet
- Ecg MCQSDocument2 pagesEcg MCQSZafar Iqbal Manj100% (2)
- Assess Appropriateness For Clinical Condition. Heart Rate Typically 150/min If TachyarrhythmiaDocument1 pageAssess Appropriateness For Clinical Condition. Heart Rate Typically 150/min If TachyarrhythmiaSiti Nur R Firda FauziyahNo ratings yet
- Algo Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageAlgo Tachycardia PDFYudhistira AdiNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612Document1 pageAlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612YassarNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmRyggie ComelonNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia (With Pulse) AlgorithmDocument1 pageAdult Tachycardia (With Pulse) AlgorithmJames ChoiNo ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFPlabber JuneNo ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFibbs91No ratings yet
- Tachycardia AlgorythmDocument1 pageTachycardia AlgorythmUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLStachycardiawithapulse PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithmACLStachycardiawithapulse PDFDendy Frannuzul RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Assess Appropriateness For Clinical ConditionDocument1 pageTachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Assess Appropriateness For Clinical ConditionDendy Frannuzul RamadhanNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612Document1 pageAlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612must dietNo ratings yet
- Managemen Disritmia: Dr. Rofika Hanifa, SPPDDocument20 pagesManagemen Disritmia: Dr. Rofika Hanifa, SPPDavivlabirdNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsDocument1 pageAdult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsDocument1 pageAdult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsZakiyahulfahdwNo ratings yet
- With A Pulse and Poor Perfusion: Pediatric TachycardiaDocument1 pageWith A Pulse and Poor Perfusion: Pediatric TachycardiaIin-Ignasia Diahayujulindah Mujiman0% (1)
- Algoritma Ambulance - PHCDocument11 pagesAlgoritma Ambulance - PHCYassarNo ratings yet
- Obat-Obatan Dalam Bantuan Hidup LanjutDocument16 pagesObat-Obatan Dalam Bantuan Hidup LanjutTheresia SihotangNo ratings yet
- AdenosineDocument2 pagesAdenosinegovind_soni_150% (1)
- 3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates CombinedDocument5 pages3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates Combinedamanrup randhawa100% (1)
- Adenosine: Scheduling BLS (CPR/First Aid) Acls PalsDocument4 pagesAdenosine: Scheduling BLS (CPR/First Aid) Acls PalsPhilippe Ceasar C. BascoNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Exam 2 - Lecture Notes: Treating Adult BradycardiaDocument5 pagesCardiology Exam 2 - Lecture Notes: Treating Adult BradycardiaAddieNo ratings yet
- Algoritmos AHA ACLS AdultoDocument4 pagesAlgoritmos AHA ACLS AdultoChristianFelipePorrasCastroNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument37 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life SupportRoy Acosta GumbanNo ratings yet
- Ecg ReadingsDocument11 pagesEcg ReadingsAnton Laurenciana100% (5)
- ALS Algorithms LS Tachycardia 2.0Document1 pageALS Algorithms LS Tachycardia 2.0Lucian Alin DinuNo ratings yet
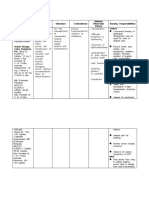
- Name of Drug Dosage/ Frequency / Timing/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesName of Drug Dosage/ Frequency / Timing/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesphoebeNo ratings yet
- Website Tachycardia Algorithm DiagramDocument1 pageWebsite Tachycardia Algorithm Diagramcolette zgheibNo ratings yet
- 5.ALS Algorithms TachycardiaDocument1 page5.ALS Algorithms TachycardiaMassimo Di BenedettoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Yes NoDocument1 pagePediatric Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Yes NoRatna TambaNo ratings yet
- Peri-Arrest ArrythmiaDocument14 pagesPeri-Arrest Arrythmiamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
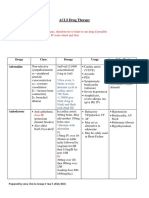
- ACLS Drug TherapyDocument8 pagesACLS Drug TherapySahrensNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification of AmlodepineDocument5 pagesDrug Classification of Amlodepineshai raNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Adult: IVDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Adult: IVBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Format Drug StudyDocument5 pagesFormat Drug StudykizpirinNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Generic NameDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Generic NameMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation - Student ResidencyDocument6 pagesAtrial Fibrillation - Student Residencyapi-404356063No ratings yet
- Tachycardia Algorithm 2021Document1 pageTachycardia Algorithm 2021Ravin DebieNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndromes - HandoutDocument4 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromes - Handoutapi-641524095No ratings yet
- ACLS 2015 Guidelines Upate Nov 2016 For PostingDocument2 pagesACLS 2015 Guidelines Upate Nov 2016 For PostingOana - Andreea CristeaNo ratings yet
- Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pagePals TachycardiadarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Bradycardia With A Pulse and Poor Perfusion AlgorithmDocument1 pagePediatric Bradycardia With A Pulse and Poor Perfusion AlgorithmRadhiatul MardhiahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument28 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmsDocument16 pagesAlgorithmsirish laglevaNo ratings yet
- Sop NCTDocument4 pagesSop NCTاحمد بلالNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia Algorithm: (With Pulse)Document1 pageAdult Tachycardia Algorithm: (With Pulse)ITSimplyNo ratings yet
- U.M.F. "Gr. T. Popa" Ia Ş IDocument37 pagesU.M.F. "Gr. T. Popa" Ia Ş Ij.doe.hex_87No ratings yet
- ACLS Drug Therapy RevisedDocument4 pagesACLS Drug Therapy RevisedpaveethrahNo ratings yet
- RLEdrugstudy 1Document6 pagesRLEdrugstudy 1Jayson Ray AbellarNo ratings yet
- Note: Dosage May Be Gradually Increased Over: AmlodipineDocument4 pagesNote: Dosage May Be Gradually Increased Over: Amlodipineanette katrinNo ratings yet
- Dx. StudyDocument3 pagesDx. Studymayumitanaka8042No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument49 pagesDrug StudyMitz BaldizarNo ratings yet
- TachycardiaDocument7 pagesTachycardiaArvind SahniNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyVanessa Belmonte AzurinNo ratings yet
- Ecg Dysrythmias Nursing Responsibilitu Sinus Node 1.) Sinus BradycardiaDocument2 pagesEcg Dysrythmias Nursing Responsibilitu Sinus Node 1.) Sinus BradycardiaNickha LazoNo ratings yet
- Initial Recommended Doses NarrowDocument1 pageInitial Recommended Doses NarrowwisgeorgekwokNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- 71Document27 pages71onuchukwu chibuzorNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease Pathophysiologyjethro sanchez100% (1)
- HistoryandPhysicalExamDocument105 pagesHistoryandPhysicalExamsilentscream0618No ratings yet
- Atrioventricular - Septal - Defects-1 PCICSDocument8 pagesAtrioventricular - Septal - Defects-1 PCICSAdrian KhomanNo ratings yet
- Polyclinic AllDocument92 pagesPolyclinic AllFatima ShahNo ratings yet
- Bradycardia and TachycardiaDocument50 pagesBradycardia and Tachycardialiu_owen17No ratings yet
- Journal On HIEDocument19 pagesJournal On HIEMohammad Misbahul IslamNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument35 pagesRheumatic Heart DiseaseSAYMABANUNo ratings yet
- ##Default - Genres.article## 28348 2 10 20210116Document14 pages##Default - Genres.article## 28348 2 10 20210116Vega VirlyNo ratings yet
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) : The Calm Before The StormDocument31 pagesTransient Ischemic Attack (TIA) : The Calm Before The StormAnonymous mFKwUNNo ratings yet
- ARRHYTHMIADocument82 pagesARRHYTHMIAjiluNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Left-to-Right Shunt LesionsDocument17 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Left-to-Right Shunt LesionsAgustinaNo ratings yet
- Cardio-Cerebral Infarction Syndrome: Definition, Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and TreatmentDocument6 pagesCardio-Cerebral Infarction Syndrome: Definition, Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and TreatmentDina RyantiNo ratings yet
- Management of Thoracic Aortic DissectionDocument2 pagesManagement of Thoracic Aortic DissectionKarina ResendeNo ratings yet
- ECG Discussion: Wellens Syndrome: A Subtle ECG FindingDocument1 pageECG Discussion: Wellens Syndrome: A Subtle ECG FindingEINSTEIN2DNo ratings yet
- Cardio Quiz Answer KeyDocument6 pagesCardio Quiz Answer KeyMark MasbadNo ratings yet
- History of Palpitation: Editing LinkDocument6 pagesHistory of Palpitation: Editing LinkTouseef Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of IMADocument32 pagesDiagnosis of IMARamón Ruesta BerdejoNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument3 pagesAngina PectorisKhalid Mahmud Arifin100% (2)
- INTERPRETASI EKG MahasiswaDocument43 pagesINTERPRETASI EKG MahasiswaMartin Susanto, MDNo ratings yet
- Acute Ischemia of The Lower Limb (LL) : Sudden Occlusion of A Previously Patent Artery Supplying A LimbDocument4 pagesAcute Ischemia of The Lower Limb (LL) : Sudden Occlusion of A Previously Patent Artery Supplying A LimbOmar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block - A Diagnostic DilemmaDocument4 pagesIntermittent Left Bundle Branch Block - A Diagnostic DilemmaCorina GrosuNo ratings yet
- Verapamil HCL Drug StudyDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCL Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- ECG TeachingDocument5 pagesECG Teachingmeyyappan nachiappanNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal DefectDocument6 pagesVentricular Septal DefectPrem AnandNo ratings yet
- MOH Pocket Manual in Emergency MedicineDocument244 pagesMOH Pocket Manual in Emergency MedicineAli Al-Brahim (AlucardAli)No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Problem 2Document8 pagesUnit 3 Problem 2Adoub AlderaziNo ratings yet