Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML Syringe
Sodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML Syringe
Uploaded by
Hannah BuquironCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Allison HT HTB CLT CLBT Electronic Control Transmissions Tips ManualDocument51 pagesAllison HT HTB CLT CLBT Electronic Control Transmissions Tips ManualMauricio Gomez Gomez100% (1)
- Community Health Nursing Exam 2Document7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 2Hannah Buquiron100% (1)
- Drugs During PregnancyDocument9 pagesDrugs During Pregnancyjeelani saimaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateTempoNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)Document3 pagesCalcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)govind_soni_15No ratings yet
- High Risk Drugs Used in RTSKH AEDDocument41 pagesHigh Risk Drugs Used in RTSKH AEDYyan CwyNo ratings yet
- Abellar - Drug Study SpironolactoneDocument13 pagesAbellar - Drug Study SpironolactoneJeah Bearl AbellarNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument8 pagesSodium BicarbonateRaf AylaniNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia EclampsiaDocument10 pagesPreeclampsia EclampsiajasphergliponeoNo ratings yet
- Gel A PotDocument3 pagesGel A PotGela PielagoNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument3 pagesSodium BicarbonateAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument40 pagesEmergency Drugsmattheus101No ratings yet
- General Measure in The Management of PoisoningDocument43 pagesGeneral Measure in The Management of PoisoningCharlotte Anne Villero TiuNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 pagesEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument8 pagesGeneric NameRosaree Mae PantojaNo ratings yet
- Potassium Supplements ParenteralDocument3 pagesPotassium Supplements Parenteralcarl meiNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument5 pagesAcute Renal FailureSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNo ratings yet
- Pedoman Obat High AlertDocument6 pagesPedoman Obat High AlertErvinaOctavianiNo ratings yet
- Management of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticleDocument4 pagesManagement of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticlealeNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Crash CartDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs Crash CartEricson SomeraNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs - Cardiac DrugsDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs - Cardiac DrugsKookie JunNo ratings yet
- Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital Adult IV Medication MonographDocument3 pagesDepartment of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital Adult IV Medication MonographRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationDocument4 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationApril Joy MangsatNo ratings yet
- 19BCPDocument64 pages19BCPNinna Isabel VictorioNo ratings yet
- (UHL CHILDREN) Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) PDFDocument12 pages(UHL CHILDREN) Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) PDFRizki Ismi Arsyad IINo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Drug Monograph AssignmentDocument5 pagesDrug Monograph AssignmentAdam BannonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For ITPDocument25 pagesDrug Study For ITPMary Ann QuinonesNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Furosemide (Lasix)Document1 pageFurosemide (Lasix)E100% (3)
- Emergency MedsDocument24 pagesEmergency MedsNursyNurse100% (1)
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Document4 pagesHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument7 pagesEmergency DrugsMarie Angeline ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors Simple NursingDocument2 pagesAce Inhibitors Simple NursingMM J30No ratings yet
- Critical Care Drug CardsDocument10 pagesCritical Care Drug Cardsjcadiz211No ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Used in Different CasesDocument60 pagesEmergency Drugs Used in Different CasesEimhie Lee CasiNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCM 118Document14 pagesCase Study NCM 118Romzy BasañesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCharm LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Drug CardsDocument5 pagesWeek 13 Drug CardsPRECIOUS wardNo ratings yet
- 5 Emergency Drugs (Zacarias)Document7 pages5 Emergency Drugs (Zacarias)Joheina Cyndril L. ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyVal FielNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaNo ratings yet
- Digoxin Drug CardDocument1 pageDigoxin Drug CardMahsa Ahmadzadeh100% (2)
- Medici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Document18 pagesMedici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Andee SalegonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Capitol)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Capitol)Joy CalmerinNo ratings yet
- DRUGS PediatricsDocument42 pagesDRUGS PediatricsRAJ BADMERANo ratings yet
- Backup NclexDocument61 pagesBackup NclexSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive - ABCDDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive - ABCDTingCheung100% (1)
- Paramedic Drugs in EMSDocument12 pagesParamedic Drugs in EMSJim Hoffman100% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKristoff CamposNo ratings yet
- Potassium DisturbancesDocument23 pagesPotassium DisturbancesThien Nhan MaiNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument2 pagesOmeprazoleErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Document46 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Gabrielle Frances FernandezNo ratings yet
- Calcium Chloride: Additional InformationDocument4 pagesCalcium Chloride: Additional InformationnurchandraNo ratings yet
- GROUP 6 - Medications (HF)Document34 pagesGROUP 6 - Medications (HF)Sunshine CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Use of Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesGuidelines For The Use of Potassium ChlorideSallie NaomiNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis IntanDocument60 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Intandesi susantiNo ratings yet
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Document2 pagesMicro K (Potassium Chloride)ENo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Using Antimicrobial Agents To Control Mirobial Growth in VivoDocument39 pagesUsing Antimicrobial Agents To Control Mirobial Growth in VivoHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument52 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyHannah Buquiron100% (1)
- Infectious Diseases of Skin and EarDocument56 pagesInfectious Diseases of Skin and EarHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Rregular Heartbeats. Nausea. Vomiting. Anxiety. Headache. Chills. Goosebumps. Shortness of BreathDocument4 pagesRregular Heartbeats. Nausea. Vomiting. Anxiety. Headache. Chills. Goosebumps. Shortness of BreathHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Exam 3Document7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 3Hannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Lidocaine 100 MG 5ml Syringes Brand Name - DosageDocument2 pagesLidocaine 100 MG 5ml Syringes Brand Name - DosageHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Brand Name:: VasopressinDocument3 pagesBrand Name:: VasopressinHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 ReviewerDocument2 pagesChapter 12 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Exam 5: B. Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 5: B. Liver CirrhosisHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Exam 1Document7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 1Hannah Buquiron100% (2)
- Chapter 10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesChapter 10 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document24 pagesChapter 12Hannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 ReviewerDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 10 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 ReviewerDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 9 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document23 pagesChapter 11Hannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chem 205 Lecture 5 Nucleic AcidsDocument37 pagesChem 205 Lecture 5 Nucleic AcidsHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Validating and Documenting DataDocument14 pagesValidating and Documenting DataHannah Buquiron100% (1)
- Introduction To Cell Physiology Introduction To Cell PhysiologyDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Cell Physiology Introduction To Cell PhysiologyHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Collecting Subjective DataDocument18 pagesCollecting Subjective DataHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Collecting Objective DataDocument14 pagesCollecting Objective DataHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHEM 205 LECTUREs 7 8 9 CARBOHYDRATES and Carb MetabDocument136 pagesCHEM 205 LECTUREs 7 8 9 CARBOHYDRATES and Carb MetabHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHEM 205 LECTURE 4 Enzyme KineticsDocument47 pagesCHEM 205 LECTURE 4 Enzyme KineticsHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Nursing SkillDocument1 pageNursing SkillHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Thayer, Indo-Pacific Geopolitics and The South China Sea Disputes: Australian PerspectiveDocument21 pagesThayer, Indo-Pacific Geopolitics and The South China Sea Disputes: Australian PerspectiveCarlyle Alan ThayerNo ratings yet
- D N V T A C: ET Orske Eritas YPE Pproval ErtificateDocument3 pagesD N V T A C: ET Orske Eritas YPE Pproval ErtificateJason RobertsNo ratings yet
- BBMP Glossary Built Up Area Plinth AreaDocument44 pagesBBMP Glossary Built Up Area Plinth AreaRakesh S India100% (1)
- Felcom 15 Servi̇s ManualDocument236 pagesFelcom 15 Servi̇s ManualAnıl Kahya75% (8)
- Cuprins: State of The Art LivingDocument15 pagesCuprins: State of The Art LivingBogdan IonițăNo ratings yet
- Ecg Post TestDocument11 pagesEcg Post TestScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 HandoutsDocument8 pagesUnit 4 HandoutsRegan rautNo ratings yet
- Unit II - MCMTDocument50 pagesUnit II - MCMTSai RamNo ratings yet
- Lenovo t430 NZM4H-7 r7.54Document97 pagesLenovo t430 NZM4H-7 r7.54norberto100% (1)
- Ac 19-Aircraft LeasingDocument8 pagesAc 19-Aircraft LeasingKINGDOEMSELYNo ratings yet
- Dr. Anil MishraDocument1 pageDr. Anil MishraAyush BishtNo ratings yet
- Articles A-An-The 1Document1 pageArticles A-An-The 1api-249605888No ratings yet
- Explain FOUR Measures Which Governments Can Use To Encourage Entrepreneurial Activities in The Caribbean Region.Document2 pagesExplain FOUR Measures Which Governments Can Use To Encourage Entrepreneurial Activities in The Caribbean Region.Bridget SequeaNo ratings yet
- MCQon PM PDFDocument11 pagesMCQon PM PDFKathirrveluSubramainanNo ratings yet
- Face 4Document9 pagesFace 4Marius SirbuNo ratings yet
- 01 PDFDocument2 pages01 PDFezrawidian99No ratings yet
- Basics of Capital BudgetingDocument26 pagesBasics of Capital BudgetingChaitanya JagarlapudiNo ratings yet
- MFC-L9570CDW Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesMFC-L9570CDW Brochure PDFAnonymous n80oQosNo ratings yet
- OS Lesson+Plan+and+ObjectivesDocument4 pagesOS Lesson+Plan+and+ObjectivesNikitha Rathnakar0% (2)
- Buckling and Ultimate Strength Assessment For Offshore Structures APRIL 2004Document5 pagesBuckling and Ultimate Strength Assessment For Offshore Structures APRIL 2004Flávio RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Galcon Manual UsuarioDocument65 pagesGalcon Manual Usuariopedro1981No ratings yet
- Fronius Datamanager 2.0Document88 pagesFronius Datamanager 2.0JohnNo ratings yet
- ARM COM 2010 11 TacticalRadios-v2Document32 pagesARM COM 2010 11 TacticalRadios-v2maruka33No ratings yet
- Nelson Stud Welding - CJL Reduced Base StudsDocument1 pageNelson Stud Welding - CJL Reduced Base StudsStefan IonitaNo ratings yet
- EprDocument8 pagesEprcyrimathewNo ratings yet
- Technical Instruction ABB RED670Document10 pagesTechnical Instruction ABB RED670Iqball ArdiyanNo ratings yet
- 381 - Real Time Communication Between Dumb, Deaf and Blind People Using Voice & Gesture With MatlabDocument4 pages381 - Real Time Communication Between Dumb, Deaf and Blind People Using Voice & Gesture With MatlabBhaskar Rao PNo ratings yet
- CoaDocument6 pagesCoaCarlo CariasoNo ratings yet
- Women Security Assistance System With GPS Tracking and Messaging SystemDocument4 pagesWomen Security Assistance System With GPS Tracking and Messaging Systemhamed razaNo ratings yet
Sodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML Syringe
Sodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML Syringe
Uploaded by
Hannah BuquironOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML Syringe
Sodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML Syringe
Uploaded by
Hannah BuquironCopyright:
Available Formats
BENITO, A.
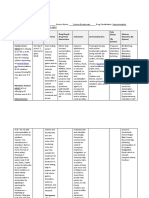
Sodium bicarbonate 50mEq/50 ml syringe Calcium chloride 1gm/10 ml syringe
Brand Name Brand Name
Alka-Seltzer CaCl or CaCl2
Dosage Dosage
Cardiac arrest. Adults: 200-300mEq given rapidly as a 7.5% or 8.4% solution Adult: 0.5-1g
Severe metabolic acidosis: 90-180mEq/L at a rate of 1-1.5L during the first hour Pediatric: 25mg/kg (0.2mL/kg up to 1-10mL/kg) given slowly
Less severe metabolic acidosis. 2-5mEq/kg Frequency
Frequency Adult: every 1-3 days (given at a rate not to exceed 13.6-27.3mg/min)
Less severe metabolic acidosis: given over a 4-8hr period Indications
Indications For the treatment of hypocalcemia in those conditions requiring a prompt increase in blood
Treatment of hyperacidity. plasma calcium levels
Treatment of acute mild to moderate metabolic acidosis due to shock, severe dehydration, Contraindications
anoxia, uncontrolled diabetes, renal disease, cardiac arrest, extracorporeal circulation of Use to treat hypocalcemia of renal insufficiency.
blood, severe primary lactic acidosis. Side Effects
Contraindications Most common – peripheral vasodilation with moderate decreases in BP
Chloride loss due to vomiting or from continuous GI suction. Adverse Effects
Side Effects Rapid injection may cause the patient to complain of tingling sensations, a calcium taste, a
Most common – rebound hyperacidity, milk-alkali syndrome sense of oppression or “heat wave”.
Adverse Effects Injections of calcium chloride are accompanied by peripheral vasodilatation as well as a local
Edema, Aggravated CHF, Cerebral hemorrhage “burning” sensation and there may be a moderate fall in blood pressure.
Special Precautions Special Precautions
Use with caution in impaired renal function, toxemia of pregnancy, with oliguria or anuria, Use usually restricted in children due to significant irritation and possible tissue necrosis and
during lactation, in edema, CHF, liver cirrhosis, with low-salt diets, and in geriatric or post-op sloughing caused by IV calcium chloride.
clients with renal or CV insufficiency with or without CHF Nursing Considerations
Nursing Considerations Never administer IM or SC
Assess for edema, which may indicate inability to utilize NaHCO 3 May give undiluted IV push
BENITO, A.I
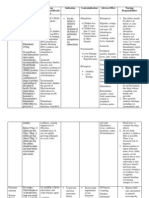
Naloxone
Brand Name
Narcan
Dosage (IM, IV, SC)
Narcotic overdose. Initial dose: 0.4-2mg IV
To reverse post-op narcotic depression. Adults initial dose: 0.1-0.2mg increments at 2-3min
intervals then repeat at 1-2hr intervals if necessary.
Frequency
To reverse post-op narcotic depression: At 2-3min intervals then repeat at 1-2hr intervals if
necessary
Indications
Complete or partial reversal of narcotic depression, including respiratory depression induced
by natural or synthetic narcotics, propoxyphene, methadone, nalbuphine, butorphanol, and
pentazocine.
Contraindications
Sensitivity to drug. Narcotic addicts (drug may cause severe withdrawal symptoms). Use in
neonates
Side Effects
Most common: virtually no pharmacologic effects in the absence of opioids
N&V, sweating, hypertension, tremors, sweating due to reversal of narcotic depression.
If used post-op, excessive dose may cause VT and fibrillation, hypo/hypertension, pulmonary
edema and seizures (infrequent).
Adverse Effects
Fever, sweating, runny nose, sneezing, goose bumps, yawning, weakness, shivering or
trembling, nervousness, restlessness or irritability, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, stomach
cramps, fast heartbeat, and increased blood pressure
Special Precautions
If given during labor, may cause severe hypertension in the mother with mild to moderate
hypertension.
Nursing Considerations
Do not confuse with naloxone with naltrexone
You might also like
- Allison HT HTB CLT CLBT Electronic Control Transmissions Tips ManualDocument51 pagesAllison HT HTB CLT CLBT Electronic Control Transmissions Tips ManualMauricio Gomez Gomez100% (1)
- Community Health Nursing Exam 2Document7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 2Hannah Buquiron100% (1)
- Drugs During PregnancyDocument9 pagesDrugs During Pregnancyjeelani saimaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateTempoNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)Document3 pagesCalcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)govind_soni_15No ratings yet
- High Risk Drugs Used in RTSKH AEDDocument41 pagesHigh Risk Drugs Used in RTSKH AEDYyan CwyNo ratings yet
- Abellar - Drug Study SpironolactoneDocument13 pagesAbellar - Drug Study SpironolactoneJeah Bearl AbellarNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument8 pagesSodium BicarbonateRaf AylaniNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia EclampsiaDocument10 pagesPreeclampsia EclampsiajasphergliponeoNo ratings yet
- Gel A PotDocument3 pagesGel A PotGela PielagoNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument3 pagesSodium BicarbonateAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument40 pagesEmergency Drugsmattheus101No ratings yet
- General Measure in The Management of PoisoningDocument43 pagesGeneral Measure in The Management of PoisoningCharlotte Anne Villero TiuNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 pagesEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument8 pagesGeneric NameRosaree Mae PantojaNo ratings yet
- Potassium Supplements ParenteralDocument3 pagesPotassium Supplements Parenteralcarl meiNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument5 pagesAcute Renal FailureSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNo ratings yet
- Pedoman Obat High AlertDocument6 pagesPedoman Obat High AlertErvinaOctavianiNo ratings yet
- Management of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticleDocument4 pagesManagement of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticlealeNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Crash CartDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs Crash CartEricson SomeraNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs - Cardiac DrugsDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs - Cardiac DrugsKookie JunNo ratings yet
- Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital Adult IV Medication MonographDocument3 pagesDepartment of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital Adult IV Medication MonographRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationDocument4 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationApril Joy MangsatNo ratings yet
- 19BCPDocument64 pages19BCPNinna Isabel VictorioNo ratings yet
- (UHL CHILDREN) Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) PDFDocument12 pages(UHL CHILDREN) Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) PDFRizki Ismi Arsyad IINo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Drug Monograph AssignmentDocument5 pagesDrug Monograph AssignmentAdam BannonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For ITPDocument25 pagesDrug Study For ITPMary Ann QuinonesNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Furosemide (Lasix)Document1 pageFurosemide (Lasix)E100% (3)
- Emergency MedsDocument24 pagesEmergency MedsNursyNurse100% (1)
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Document4 pagesHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument7 pagesEmergency DrugsMarie Angeline ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors Simple NursingDocument2 pagesAce Inhibitors Simple NursingMM J30No ratings yet
- Critical Care Drug CardsDocument10 pagesCritical Care Drug Cardsjcadiz211No ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Used in Different CasesDocument60 pagesEmergency Drugs Used in Different CasesEimhie Lee CasiNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCM 118Document14 pagesCase Study NCM 118Romzy BasañesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCharm LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Drug CardsDocument5 pagesWeek 13 Drug CardsPRECIOUS wardNo ratings yet
- 5 Emergency Drugs (Zacarias)Document7 pages5 Emergency Drugs (Zacarias)Joheina Cyndril L. ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyVal FielNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaNo ratings yet
- Digoxin Drug CardDocument1 pageDigoxin Drug CardMahsa Ahmadzadeh100% (2)
- Medici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Document18 pagesMedici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Andee SalegonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Capitol)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Capitol)Joy CalmerinNo ratings yet
- DRUGS PediatricsDocument42 pagesDRUGS PediatricsRAJ BADMERANo ratings yet
- Backup NclexDocument61 pagesBackup NclexSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive - ABCDDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive - ABCDTingCheung100% (1)
- Paramedic Drugs in EMSDocument12 pagesParamedic Drugs in EMSJim Hoffman100% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKristoff CamposNo ratings yet
- Potassium DisturbancesDocument23 pagesPotassium DisturbancesThien Nhan MaiNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument2 pagesOmeprazoleErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Document46 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Gabrielle Frances FernandezNo ratings yet
- Calcium Chloride: Additional InformationDocument4 pagesCalcium Chloride: Additional InformationnurchandraNo ratings yet
- GROUP 6 - Medications (HF)Document34 pagesGROUP 6 - Medications (HF)Sunshine CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Use of Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesGuidelines For The Use of Potassium ChlorideSallie NaomiNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis IntanDocument60 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Intandesi susantiNo ratings yet
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Document2 pagesMicro K (Potassium Chloride)ENo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Using Antimicrobial Agents To Control Mirobial Growth in VivoDocument39 pagesUsing Antimicrobial Agents To Control Mirobial Growth in VivoHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument52 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyHannah Buquiron100% (1)
- Infectious Diseases of Skin and EarDocument56 pagesInfectious Diseases of Skin and EarHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Rregular Heartbeats. Nausea. Vomiting. Anxiety. Headache. Chills. Goosebumps. Shortness of BreathDocument4 pagesRregular Heartbeats. Nausea. Vomiting. Anxiety. Headache. Chills. Goosebumps. Shortness of BreathHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Exam 3Document7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 3Hannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Lidocaine 100 MG 5ml Syringes Brand Name - DosageDocument2 pagesLidocaine 100 MG 5ml Syringes Brand Name - DosageHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Brand Name:: VasopressinDocument3 pagesBrand Name:: VasopressinHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 ReviewerDocument2 pagesChapter 12 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Exam 5: B. Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 5: B. Liver CirrhosisHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Exam 1Document7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 1Hannah Buquiron100% (2)
- Chapter 10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesChapter 10 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document24 pagesChapter 12Hannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 ReviewerDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 10 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 ReviewerDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 9 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document23 pagesChapter 11Hannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chem 205 Lecture 5 Nucleic AcidsDocument37 pagesChem 205 Lecture 5 Nucleic AcidsHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Validating and Documenting DataDocument14 pagesValidating and Documenting DataHannah Buquiron100% (1)
- Introduction To Cell Physiology Introduction To Cell PhysiologyDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Cell Physiology Introduction To Cell PhysiologyHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Collecting Subjective DataDocument18 pagesCollecting Subjective DataHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Collecting Objective DataDocument14 pagesCollecting Objective DataHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHEM 205 LECTUREs 7 8 9 CARBOHYDRATES and Carb MetabDocument136 pagesCHEM 205 LECTUREs 7 8 9 CARBOHYDRATES and Carb MetabHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHEM 205 LECTURE 4 Enzyme KineticsDocument47 pagesCHEM 205 LECTURE 4 Enzyme KineticsHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Nursing SkillDocument1 pageNursing SkillHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Thayer, Indo-Pacific Geopolitics and The South China Sea Disputes: Australian PerspectiveDocument21 pagesThayer, Indo-Pacific Geopolitics and The South China Sea Disputes: Australian PerspectiveCarlyle Alan ThayerNo ratings yet
- D N V T A C: ET Orske Eritas YPE Pproval ErtificateDocument3 pagesD N V T A C: ET Orske Eritas YPE Pproval ErtificateJason RobertsNo ratings yet
- BBMP Glossary Built Up Area Plinth AreaDocument44 pagesBBMP Glossary Built Up Area Plinth AreaRakesh S India100% (1)
- Felcom 15 Servi̇s ManualDocument236 pagesFelcom 15 Servi̇s ManualAnıl Kahya75% (8)
- Cuprins: State of The Art LivingDocument15 pagesCuprins: State of The Art LivingBogdan IonițăNo ratings yet
- Ecg Post TestDocument11 pagesEcg Post TestScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 HandoutsDocument8 pagesUnit 4 HandoutsRegan rautNo ratings yet
- Unit II - MCMTDocument50 pagesUnit II - MCMTSai RamNo ratings yet
- Lenovo t430 NZM4H-7 r7.54Document97 pagesLenovo t430 NZM4H-7 r7.54norberto100% (1)
- Ac 19-Aircraft LeasingDocument8 pagesAc 19-Aircraft LeasingKINGDOEMSELYNo ratings yet
- Dr. Anil MishraDocument1 pageDr. Anil MishraAyush BishtNo ratings yet
- Articles A-An-The 1Document1 pageArticles A-An-The 1api-249605888No ratings yet
- Explain FOUR Measures Which Governments Can Use To Encourage Entrepreneurial Activities in The Caribbean Region.Document2 pagesExplain FOUR Measures Which Governments Can Use To Encourage Entrepreneurial Activities in The Caribbean Region.Bridget SequeaNo ratings yet
- MCQon PM PDFDocument11 pagesMCQon PM PDFKathirrveluSubramainanNo ratings yet
- Face 4Document9 pagesFace 4Marius SirbuNo ratings yet
- 01 PDFDocument2 pages01 PDFezrawidian99No ratings yet
- Basics of Capital BudgetingDocument26 pagesBasics of Capital BudgetingChaitanya JagarlapudiNo ratings yet
- MFC-L9570CDW Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesMFC-L9570CDW Brochure PDFAnonymous n80oQosNo ratings yet
- OS Lesson+Plan+and+ObjectivesDocument4 pagesOS Lesson+Plan+and+ObjectivesNikitha Rathnakar0% (2)
- Buckling and Ultimate Strength Assessment For Offshore Structures APRIL 2004Document5 pagesBuckling and Ultimate Strength Assessment For Offshore Structures APRIL 2004Flávio RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Galcon Manual UsuarioDocument65 pagesGalcon Manual Usuariopedro1981No ratings yet
- Fronius Datamanager 2.0Document88 pagesFronius Datamanager 2.0JohnNo ratings yet
- ARM COM 2010 11 TacticalRadios-v2Document32 pagesARM COM 2010 11 TacticalRadios-v2maruka33No ratings yet
- Nelson Stud Welding - CJL Reduced Base StudsDocument1 pageNelson Stud Welding - CJL Reduced Base StudsStefan IonitaNo ratings yet
- EprDocument8 pagesEprcyrimathewNo ratings yet
- Technical Instruction ABB RED670Document10 pagesTechnical Instruction ABB RED670Iqball ArdiyanNo ratings yet
- 381 - Real Time Communication Between Dumb, Deaf and Blind People Using Voice & Gesture With MatlabDocument4 pages381 - Real Time Communication Between Dumb, Deaf and Blind People Using Voice & Gesture With MatlabBhaskar Rao PNo ratings yet
- CoaDocument6 pagesCoaCarlo CariasoNo ratings yet
- Women Security Assistance System With GPS Tracking and Messaging SystemDocument4 pagesWomen Security Assistance System With GPS Tracking and Messaging Systemhamed razaNo ratings yet