Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Domain Level Title Action Verbs Remember
Domain Level Title Action Verbs Remember
Uploaded by
saqib khalidOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Domain Level Title Action Verbs Remember
Domain Level Title Action Verbs Remember
Uploaded by
saqib khalidCopyright:
Available Formats
Please ensure that the questions of different assessment tools (assignments, quizzes, exam questions
etc.) are formulated at correct difficulty level. This can be done by using the action verbs that correspond
to the taxonomy level of the CLO to which the question is mapped.
A brief list of action verbs corresponding to different taxonomy levels in cognitive, affective and
psychomotor domains is given below. This list has been prepared using the guidance material available
on the PEC website. However, it is not exhaustive and relevant verbs can be added after seeing the
examples of other universities that are accredited under Washington Accord.
Domain Level Title Action Verbs
Remember:
Can the student recall Define, Duplicate, List, Memorize, Recall,
C1
or remember Repeat, Reproduce, State
information?
Understand:
Classify, Describe, Discuss, Explain,
Can the student
C2 Identify, Locate, Recognize, Report, Select,
explain ideas or
Translate, Paraphrase
concepts?
Apply:
Choose, Demonstrate, Dramatize, Employ,
Can the student use
C3 Illustrate, Interpret, Operate, Schedule,
the information in a
Sketch, Solve, Use, Write
new way?
Cognitive
Analyze:
Appraise, Compare, Contrast, Criticize,
Can the student
C4 Differentiate, Discriminate, Distinguish,
distinguish between
Examine, Experiment, Question, Test
the different parts?
Judge:
Can the student Appraise, Argue, Defend, Judge, Select,
C5
justify a stand or Support, Value, Evaluate
decision?
Create:
Can the student Assemble, Construct, Create, Design,
C6
create new product or Develop, Formulate, Write
point of view?
Receiving:
Accept, Acknowledge, Be aware, Listen,
A1 Selectively attends to
Notice, Pay Attention, Tolerate
stimuli
Agree to, Answer freely, Assist, Care for,
Communicate, Comply, Conform, Consent,
Responding:
A2 Contribute, Cooperate, Follow, Obey,
Responds to stimuli
Participate Willingly, Read Voluntarily,
Respond, Visit, Volunteer
Adopt, Assume Responsibility, Behave
Affective
Valuing: according to, Choose, Commit, Desire,
A3 Attaches value or Exhibit loyalty, Express, Initiate, Prefer,
worth to something Seek, Show Concern, Show continual
desire to, Use resources to
Organization:
Conceptualizes the Adapt, Adjust, Arrange, Balance, Classify,
A4 value and resolves Conceptualize, Formulate, Group,
conflict between it Organize, Rank, Theorize
and other values
Domain Level Title Action Verbs
Internalizing:
Act upon, Advocate, Defend, Exemplify,
Integrates the value
A5 Influence, Justify behavior, Maintain,
into a value system
Serve, Support
that controls behavior
Perception: Detect, Hear, Listen, Observe, Perceive,
P1 Senses cues that Recognize, See, Sense, Smell, Taste, View,
guide motor activity Watch
Set:
Achieve a posture, Assume a body stance,
Is mentally,
Establish a body position, Place hands,
P2 emotionally and
arms etc., Position the body, Sit, Stand,
physically ready to
Station
act
Guided Response:
Copy, Duplicate, Imitate, Manipulate with
Imitates and practices
P3 guidance, Operate under supervision,
skills, often in
Practice, Repeat, Try
discrete steps
Mechanism: Complete with confidence, Conduct,
Psychomotor
Performs acts with Demonstrate, Execute, Improve efficiency,
P4
increasing efficiency Increase speed, Make, Pace, Produce, Show
and proficiency dexterity
Complex Overt Act habitually, Advance with assurance,
Response: Control, Direct, Excel, Guide, Maintain
P5
Performs efficiency, Manage, Master, Organize,
automatically Perfect, Perform automatically, Proceed
Adaptation:
Adapts skill sets to
P6 Adapt, Reorganize, Alter, Revise, Change
meet a problem
situation
Definition: Design, Originate, Combine, Compose,
P7
Creates new patterns Construct
In addition, PEC requires adequate exposure to complex engineering problems and activities. For this
purpose, please ensure that some assessment tools (assignments, quizzes, labs, exam questions etc.)
meet the requirements of complex problem solving. The criteria for complex problem solving is
provided in Annex A of the PEC Manual of Accreditation 2014 v1.1. A checklist based on the
aforementioned annexure is given below which may be added in course folder with every question that
qualifies as a complex engineering problem. The related fields that help make that question a complex
engineering problem should be checked accordingly.
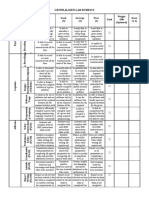
S# Attribute Complex Problems = 1 & (2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9)
Engineering problems which cannot be resolved
1 Preamble without in-depth engineering knowledge, and have ☐
some or all of the characteristics listed below:
Range of conflicting Involve wide-ranging or conflicting technical,
2 ☐
requirements engineering and other issues.
Have no obvious solution and require abstract
3 Depth of analysis required thinking, originality in analysis to formulate suitable ☐
models.
Requires research-based knowledge much of which is
Depth of knowledge at, or informed by, the forefront of the professional
4 ☐
required discipline and which allows a fundamentals-based,
first principles analytical approach.
5 Familiarity of issues Involve infrequently encountered issues ☐
Are outside problems encompassed by standards and
6 Extent of applicable codes ☐
codes of practice for professional engineering.
Extent of stakeholder
Involve diverse groups of stakeholders with widely
7 involvement and level of ☐
varying needs.
conflicting requirements
8 Consequences Have significant consequences in a range of contexts. ☐
Are high level problems including many component
9 Interdependence ☐
parts or sub-problems.
You might also like
- Reading Success 3 - Answer KeyDocument5 pagesReading Success 3 - Answer Keysanti600450% (4)
- Access Forklifts - Forklifts - Forklift 2 3T CM TCM FG25T3 - Operation Manual PDFDocument184 pagesAccess Forklifts - Forklifts - Forklift 2 3T CM TCM FG25T3 - Operation Manual PDFAmr El Saeed100% (2)
- Cot 3-Prepare AppetizersDocument5 pagesCot 3-Prepare AppetizersIvy Rosell Buayaban100% (3)
- Keys and Locks and Open DoorsDocument3 pagesKeys and Locks and Open DoorsGaby TaeidkashaniNo ratings yet
- Interview With An Ethical LeaderDocument7 pagesInterview With An Ethical LeaderKathryn StacyNo ratings yet
- The Principles and Techniques of Design Using Online Creation Tools, Platforms and Application Develop ICT ContentDocument4 pagesThe Principles and Techniques of Design Using Online Creation Tools, Platforms and Application Develop ICT Contentbilly jane ramosNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning (Iplan)Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning (Iplan)Nathalie Yvonne AliserNo ratings yet
- E-Tech DLLDocument4 pagesE-Tech DLLlawrenceNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Remembering: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP)Document4 pagesKnowledge Remembering: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP)billy jane ramosNo ratings yet
- IPlan DLP Format v.02Document5 pagesIPlan DLP Format v.02Alvin Cuandot100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJimmy VelascoNo ratings yet
- DLP Per DevDocument8 pagesDLP Per DevJeanne AndradeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningHelen LaurelNo ratings yet
- 1stQ Week2 DLLDocument6 pages1stQ Week2 DLLlawrenceNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- DLP Format Blank SheetDocument25 pagesDLP Format Blank SheetRhea Rose PelaezNo ratings yet
- DLP ArnisDocument6 pagesDLP ArnisFaith GesimNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJesson AlbaranNo ratings yet
- Ent 28ADocument3 pagesEnt 28AJeanne AndradeNo ratings yet
- Ent 20Document3 pagesEnt 20sabellonanamariaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planningamy faith susonNo ratings yet
- Fact and Opinion WorksheetDocument4 pagesFact and Opinion WorksheetMa Lou100% (1)
- ABM - BM11FO-Ia-1 GSAYDDLPQTR1-DAY 2Document4 pagesABM - BM11FO-Ia-1 GSAYDDLPQTR1-DAY 2Junard AsentistaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 - CS - RS12 - If-J-6Document6 pagesPractical Research 2 - CS - RS12 - If-J-6Lubeth Cabatu100% (1)
- IPlan DLP Format v.02Document4 pagesIPlan DLP Format v.02Julie Anne MacuseNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Jhiamae PiqueroNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: Daily Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesCurriculum Guide: Daily Lesson PlanJade ViloriaNo ratings yet
- SHS STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY DLP M11or12SP-IVd-1Document6 pagesSHS STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY DLP M11or12SP-IVd-1Thea BynzNo ratings yet
- C1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Document4 pagesC1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Jonathan Gabriel Nario Jr.No ratings yet
- IPLan TemplateDocument5 pagesIPLan TemplateSigrid Therese CañeteNo ratings yet
- Blank Detailed Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesBlank Detailed Lesson PlanJames Arnold PanilagaoNo ratings yet
- M11 GM-Ic-1Document5 pagesM11 GM-Ic-1Dan Albert AbesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAnonymous HJlXukJrNo ratings yet
- 10.2.4 DLP GealonDocument4 pages10.2.4 DLP GealonGlad Norman LimoconNo ratings yet
- Ent 05Document7 pagesEnt 05Jeanne AndradeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Evaluates The Effectiveness of An Oral Communication Activity EN11/12OC-Ibe-14Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Evaluates The Effectiveness of An Oral Communication Activity EN11/12OC-Ibe-14Zeen DeeNo ratings yet
- OC 10 Watches and Listens To Sample Oral Communication ActivitiesDocument4 pagesOC 10 Watches and Listens To Sample Oral Communication ActivitiesZeen Dee86% (7)
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRendyNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Kojiki Creation TheoryDocument32 pagesUnderstanding The Kojiki Creation TheoryShyrra AndersonNo ratings yet
- OC 13 Identifies Strategies Used by Each Speaker To Convey Hisher Ideas EffectivelyDocument4 pagesOC 13 Identifies Strategies Used by Each Speaker To Convey Hisher Ideas EffectivelyZeen Dee100% (1)
- Organizes Dance Event For A Target Health Issue or Concern: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument4 pagesOrganizes Dance Event For A Target Health Issue or Concern: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatLuda Cababan SanesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningRomeo LibanNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJeger JbTattoo BaguioNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- 21st Century-LC-Q124Document5 pages21st Century-LC-Q124Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm 1Document7 pagesOral Comm 1Theresa B.No ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument28 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanAlexis V. LarosaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument28 pagesDetailed Lesson Planmecky100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan For Submission No 1Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan For Submission No 1Dharyl BallartaNo ratings yet
- IPlan DLP Format English-VersionDocument5 pagesIPlan DLP Format English-VersionDina ArcenalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningEdgar Jr. SenarloNo ratings yet
- Per Dev Week 2Document4 pagesPer Dev Week 2Andrey DyNo ratings yet
- DLP FBS 1Document5 pagesDLP FBS 1Christine Rose Villanueva VargasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJulia Maria LoviteNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Various Models of CommunicationDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Various Models of CommunicationZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Saqib KhalidDocument2 pagesSaqib Khalidsaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Analyses of China-Pakistan Economic Corridor: Pakistan's PerspectiveDocument21 pagesDescriptive Analyses of China-Pakistan Economic Corridor: Pakistan's Perspectivesaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Boost Converter Fed DC Motor: Cleevan Deepak Britto Pradeep KumarDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Boost Converter Fed DC Motor: Cleevan Deepak Britto Pradeep Kumarsaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Ijepes 2019 02 045Document11 pages10 1016@j Ijepes 2019 02 045saqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Bidirectional Hybrid HVDC CB With A Single HV ValveDocument9 pagesBidirectional Hybrid HVDC CB With A Single HV Valvesaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Global Speed Control of Separately Excited DC MotorDocument6 pagesGlobal Speed Control of Separately Excited DC Motorsaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- boost+DC MotorDocument7 pagesboost+DC Motorsaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy and Neuro-Fuzzy Designs of Boost Converter Supplying DCDocument4 pagesFuzzy and Neuro-Fuzzy Designs of Boost Converter Supplying DCsaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Topology, Control and Fault Analysis of A New Type HVDC Breaker For HVDC SystemsDocument6 pagesTopology, Control and Fault Analysis of A New Type HVDC Breaker For HVDC Systemssaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power and Energy Systems: Shuai Li, Jiyuan Zhang, Jianzhong Xu, Chengyong Zhao TDocument10 pagesElectrical Power and Energy Systems: Shuai Li, Jiyuan Zhang, Jianzhong Xu, Chengyong Zhao Tsaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 11 04493 v3Document15 pagesSustainability 11 04493 v3saqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Concentrated Solar Power-Cover PageDocument1 pageConcentrated Solar Power-Cover Pagesaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Basic Topology, Modeling and Evaluation of A T-Type Hybrid DC Breaker For HVDC GridDocument10 pagesBasic Topology, Modeling and Evaluation of A T-Type Hybrid DC Breaker For HVDC Gridsaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Concentrated Solar PowerDocument8 pagesConcentrated Solar Powersaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Control of HVDC - Cover PageDocument1 pageCoordinated Control of HVDC - Cover Pagesaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Projet Report ACDC-1Document9 pagesProjet Report ACDC-1saqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Lab Rubrics v1.5 WorkbookDocument2 pagesLab Rubrics v1.5 Workbooksaqib khalidNo ratings yet
- Ice Breaking AIS655 OCT2020: Ir DR Mohd Badrulhisham IsmailDocument10 pagesIce Breaking AIS655 OCT2020: Ir DR Mohd Badrulhisham IsmailFirdaus YahyaNo ratings yet
- Gold Exp B1P U4to6 Review Lang Test ADocument4 pagesGold Exp B1P U4to6 Review Lang Test AarianaNo ratings yet
- LA1 Descriptive StatisticsDocument1 pageLA1 Descriptive StatisticsEhron RiveraNo ratings yet
- Méndez Et Al., 2015Document12 pagesMéndez Et Al., 2015Martin MarchiNo ratings yet
- MCGRATH MCGRATH Alister E Teologia Sistematica Historica e Filosofica QUESTIONARIODocument6 pagesMCGRATH MCGRATH Alister E Teologia Sistematica Historica e Filosofica QUESTIONARIORobert CollinsNo ratings yet
- AncientRuins1 FAQDocument2 pagesAncientRuins1 FAQsg 85No ratings yet
- Effects Nof Students' Alcoholism On Their Academic Performance in Jose Rizal Memotial State University, Dipolog CampusDocument5 pagesEffects Nof Students' Alcoholism On Their Academic Performance in Jose Rizal Memotial State University, Dipolog CampusbengNo ratings yet
- 31 Samss 009Document8 pages31 Samss 009BHAVEESHNo ratings yet
- Unified Application Form For New Business Permit (Online) : Male Male Female FemaleDocument2 pagesUnified Application Form For New Business Permit (Online) : Male Male Female Femaleflashpower fuelNo ratings yet
- On RussellDocument36 pagesOn Russelluzairhabib459No ratings yet
- Ethics: Moral Principles That Govern A Person's Behaviour or The Conducting of An Activity (His Guide 1) To DistinctDocument73 pagesEthics: Moral Principles That Govern A Person's Behaviour or The Conducting of An Activity (His Guide 1) To DistinctMonis KhanNo ratings yet
- Victoria's Secret PresentationDocument26 pagesVictoria's Secret PresentationSuren Theannilawu100% (1)
- Kia Sportage Remote StartDocument22 pagesKia Sportage Remote StartJONATHAN100% (1)
- Assignment of Indian Ethos & Business EthicsDocument6 pagesAssignment of Indian Ethos & Business EthicstarunNo ratings yet
- History Syllabus PDFDocument24 pagesHistory Syllabus PDFR K MeenaNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id2317650 PDFDocument12 pagesSSRN Id2317650 PDFOutage StoppedNo ratings yet
- Software Requirement SpecificationDocument3 pagesSoftware Requirement SpecificationKumara SNo ratings yet
- Historical Mosque Orientationin TurkeyDocument14 pagesHistorical Mosque Orientationin TurkeyTablet TabletNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Central Sales TaxDocument4 pagesSalient Features of Central Sales TaxPallavi SaxenaNo ratings yet
- The First-Timer's Guide To Hiring A Virtual Assistant: by Nick LoperDocument15 pagesThe First-Timer's Guide To Hiring A Virtual Assistant: by Nick LopermfaglaNo ratings yet
- Requirements Analysis Document TemplateDocument11 pagesRequirements Analysis Document TemplateGiovanbattista CelatoNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy and Driving in Europe Final Report v2 enDocument46 pagesEpilepsy and Driving in Europe Final Report v2 enskyclad_21No ratings yet
- Consensus On The Pathological Definition and Classification of Poorly Cohesive Gastric CarcinomaDocument9 pagesConsensus On The Pathological Definition and Classification of Poorly Cohesive Gastric CarcinomaMariangel FloresNo ratings yet
- Information Theory and LanguageDocument246 pagesInformation Theory and LanguageTherfer WarnNo ratings yet
- Perception: According To RobbinsDocument7 pagesPerception: According To RobbinsDibyaranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- EVoting SDS DocumentDocument58 pagesEVoting SDS DocumentKahfulwara MuhammadNo ratings yet