Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost Reduction in File Manufacturing by Using Special Purpose Resistance Heating: A Case Study
Cost Reduction in File Manufacturing by Using Special Purpose Resistance Heating: A Case Study
Uploaded by
Karthik JayaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cost Reduction in File Manufacturing by Using Special Purpose Resistance Heating: A Case Study
Cost Reduction in File Manufacturing by Using Special Purpose Resistance Heating: A Case Study
Uploaded by
Karthik JayaCopyright:
Available Formats
Volume IV, Issue II, February 2015 IJLTEMAS ISSN 2278 - 2540
Cost Reduction in File Manufacturing by using
Special Purpose Resistance Heating: A Case Study
Sameer S. Gajmal1, Prof. Santosh Rane2, Prof. Sudhir.G Bhatwadekar3
1
Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Gharda Institute of Technology, Lavel
2
Associate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, SPCE, Mumbai
3
Associate Professor, Department of Production Engineering, K.I. T.’s college of Engineering, Kolhapur.
Abstract: File manufacturing industry is having a tremendous II. TYPES OF FILES
scope in the market. There is a large variety of files which are
manufactured in mass production. Out of 11 nos. of operations, A. Depending on the Type of Cut:
one of the operation is tang forging operation. The raw
material is heated and is made undergo through open die
1. Extra Rough Cut and Rough Cut Files
forging process. In the present paper a case study of an small
scale industry is discussed. For the tang forging operation the
source used for heating the raw material was Gas heating.
Both these types of files are used for the initial filing where
the amount of material removed is quite a lot while
Special Purpose Resistance Heating Furnace was replaced
precision is not a concern since it is normally carried out at
instead of Gas heating. It was found that the cost of tang
the beginning of a filing operation.
forging operation was reduced to almost 80%. Also it was
found that the operator was put into a comfortable and safe
2. Middle Cut, Bastard Cut and Second Cut Files
work environment due to replacement of Gas Fired Furnace by
Resistance heating Furnace. These types of files are used for intermediate operations
after the heavy material removal is complete and before
Keywords: File, Gas Heating ,Resistance Heating.
finishing the final smoothening out operation.
I. INTRODUCTION
3. Smooth Cut and Dead Smooth Cut Files
A file is a metalworking, woodworking and plastic working
These files are used for finishing the filing operation by
tool used to cut fine amounts of material from a work piece.
smoothening out the irregularities which are left by the
It most commonly refers to the hand tool style, which takes
previous two operations.
the form of a steel bar with a case hardened surface and a
series of sharp, parallel teeth. The file is one of the most
In the above file classification is must be noted that the
basic and essential tools found in the any type of industry.
various types of cuts are made possible with the variation of
The proper file can rough out a shape rapidly or refine and
teeth density of the file. A rough cut file and other coarse
smooth the finest of details. Having a good selection of files
files have relatively less number of teeth per inch while the
will enhance your creative potential. While files seem so
smoother files have the maximum number of teeth. The cut
common, they are actually quite amazing tools. The first
of the file refers to how fine its teeth are. They are defined
files were made completely by hand with each tooth formed
as (from roughest to smoothest): rough, middle, bastard,
by striking a chisel at the proper angle and interval. The
second cut, smooth, and dead smooth. A single-cut file has
first successful file cutting machines came into use in the
one set of parallel teeth while a cross-cut or double-cut file
mid eighteenth century. This, along with improvements in
has a second set of cuts forming diamond teeth.
the refining of iron ore into steel and better heat treating
Some of the important files types are listed as follows
processes, led to the development of the modern files. Figure 2: Types of Files Depending upon cut
Figure 1. Basic Parts of a File
www.ijltemas.in Page 134
Volume IV, Issue II, February 2015 IJLTEMAS ISSN 2278 - 2540
B. Types Of Files Depending On The Shape Of The Shank:
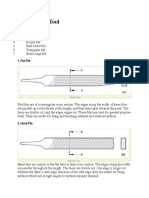
1. Flat Files: As the name itself suggests, these files 5. Band Saw
have flat shank shape which have teeth on both 6. Band Saw Blunt
sides and are mostly used for level filing work 7. Heavy Taper
involving straight surfaces. 8. Regular Taper
9. Slim Taper
Figure No-03: Flat File 10. Extra Slim Taper
11. Double Extra Taper
12. Double-Ender
13. Pit Saw
14. Cross Cut
15. Cant Saw
16. Rotary Mower
17. Round Chain Saw
2. Round Files: The blade or the shank of this type of 18. Farmers Own
files is round in shape and the teeth are formed on 19. Double Edge Saw
that round surface. The diameter of the whole shaft 20. Feather Edge Saw
is uniform towards one end, while it slightly tapers
at the outward end. These files are very useful in II. Machinists' Files
filing round shapes such as round holes or
enlarging them.
1. Flat
Figure N0-04: Round File 2. Hand
3. Half
4. Square
5. Round
6. Three Square
7. Pillar
Table No.-01 Various Sizes of Round File
8. Warding
04 05 06 08 10 12 14 16 18
9. Knife
Code No. RD RD RD RD RD RD RD RD RD
III. Rasp Files
Inches 4 5 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
Size
mm 100 125 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Thic 3.8 5 6.3 7.1 9.2 12 16 19 22 1. Flat Rasp
knes mm 5 5 2. Half Round Rasp
s
3. Round Rasp
4. Cabinet Rasp
3. Square Files: These files are very similar in
5. Horse Rasp - Plain
construction to the above mentioned round files
with the only difference that the cross-section of 6. Horse Rasp - Tanged
the shaft is of square shape which is uniform 7. Shoe Rasp
towards the handle end but gets slightly tapered 8. File and Rasp Combination
towards the outside end while maintaining its
square shape. IV. Needle Files:
Figure N0-05: Square File
1. Hand
2. Flat
3. Three Square
4. Square
5. Half Round
6. Round
C. Commercial Types Of Files: 7. Knife
8. Barrette
I. Saw Files: 9. Crossing
10. Slitting
1. Mill Regular 11. Crochet
2. Mill Blunt – One Round 12. Hand With Round Edge
3. Mill Blunt – Two Round
4. Mill Blunt - Two Square
www.ijltemas.in Page 135
Volume IV, Issue II, February 2015 IJLTEMAS ISSN 2278 - 2540
V. Diamond Coated Needle Files Before Study:
1. Hand Machine Used for Forging:
2. Flat Auto Forging Hammer (Hammer of 15 Kg, 25 Kg.)
3. Three Square Gas Furnace:
4. Square Fuel: LPG
5. Half Round Temperature required: 550°C
6. Round Job Holding Tools:
7. Knife (Pair of tongs, Hand Gloves, etc
Figure No-07:Tang Forging Set Up with Gas Fired Furnace
III. APPLICATION OF FILES
Files are often used to put the finishing touches on a
machined work piece, either to remove burrs or sharp edges
or as a final fitting operation. Intricate parts or shapes are
often produced entirely by skilled workers using files.
IV. CASE STUDY
In this paper a case study from a small scale industry named
Sharda Maa Engineering Located at MIDC Gane-Khadpoli,
Taluka- Chiplun District- Ratnagiri is discussed. The
component under consideration is Round File 06 inch Size.
The Raw material for files is File Steel.
V. LIST OF MANUFACTURING OPERATION IN FILE
MANUFACTURING
1. Raw Material Cropping
2. Tang Forging
3. Tang Cutting
4. Annealing
5. Grinding
6. Teeth Cutting
7. Inspection
8. Stamping
9. Hardening
10. Scoring
11. Proving & Packing
VI. TANG FORGING OPERATION
Out these operations the Tang Forging Operation of Round
File (06 Inch) was taken was study.
The details of the operations before study and modification
are as follows:
Figure No-06: Tang Forged Round File
After Study:
Machine Used for Forging:
Auto Forging Hammer (Hammer of 15 Kg, 25 Kg.)
Resistance Heating Furnace:
Specification: 03 Phase, AC Voltage 440 V,
www.ijltemas.in Page 136
Volume IV, Issue II, February 2015 IJLTEMAS ISSN 2278 - 2540
Temperature required: 550°C Low Power Consumption
Job Holding Tools: Fully Automatic
Not required. Thyristorised Electronic Precision control ensures
accuracy
Figure No-08:Tang Forging Set Up with Special Purpose Resistance Absolutely eco-friendly compared to conventional
Heating Furnace gas heating
Precise localized heating pattern ensures superior
product quality
Table N0.-02: Machine Description:
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFORMER
KVA 15 KVA to 30 KVA
COOLING WATER
INSULATION CLASS-F
POWER SUPPLY 415 V – 1 Ph
MACHINE SPECIFICATIONS
OVERALL DIMENSIONS 400W X 650DX800H
(mm)
WEIGHT (kg) 150
During the study it was found that the tang forging operation
with Gas Fired Furnace was not efficient, also the operator
was not comfortable with the hot environment because of
the Gas Fired Furnace nearby the workplace.
For one shift about 06-07 Kg of LPG was consumed for
forging 600- 650 Nos. of files.
VII. ABOUT SPECIAL PURPOSE RESISTANCE Table N0.-03: Cost of Gas Heating
HEATING FURNACE: Sr
. LPG
The Furnace used is fully automatic, Water-cooled heavy Particulars Production of Files
N Consumed
duty ESR Transformer suitable for different sizes of o.
furnishing rods, with suitable clamping and water cooled 600-650 Nos. of Files
heavy duty thyristorised, Latest heat sequence electronic 1 For One Shift 06-07 Kgs.
control panel, Electronic control system consists of water-
cooled thyristor assembly, necessary sensors for automation For Three 1800 Nos. of Files
2 18-19 Kgs
and protection & for achieving maximum productivity. Shift
FIRST TIME IN INDIA – special purpose Resistance Rs. 1600/- +
Cost of LPG required per day
Heating Machine which is very useful for Engineers’ File Transport Charges
manufacturers has been used. This machine is used in place
of existing Gas Burners for heating the file ends before After carrying out a deep study, it was suggested to carry
forging. The special design used in this machine helps to out the Tang Forging operation with Special Purpose
heat the job faster with considerable less current. Since the Resistance Heating Furnace instead of Gas Fired Furnace.
Time and Current is less, the electrical energy consumption, Salient features of resistance Heating Furnace;
which is proportional to the time and square of current, is Compact
considerably reduced and hence the operation cost of this Water Cooled Electrode
machine is negligible compared to gas heating. Apart from Pneumatic Clamping
the financial benefits, this machine is absolutely Eco Timer for adjusting the heating time period.
friendly compared to gas heating.
Salient Features:
www.ijltemas.in Page 137
Volume IV, Issue II, February 2015 IJLTEMAS ISSN 2278 - 2540
Table N0.-04: Cost of Resistance Heating REFERENCES
Sr
. Electricity Cost of Electricity [1] Professor em. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Ehrlenspiel, Dr.-Ing. Alfons Kiewert,
Particulars Professor Dr.-Ing. Udo Lindemann, “Cost-Efficient Design”, Springer
N Consumed Consumed
Berlin Heidelberg, 2007 ,pp 143-384.
o. [2] Philip K. Freakley, “Rubber Processing and Production Organization”
For One 10 Units 10 X 8 =Rs.80 , Springer US, 1985, pp 353-395
1 P. Selvaraj, P. Radhakrishnan , M. Adithan, “An integrated approach
Shift [3]
to design for manufacturing and assembly based on reduction of
For Three 30 Units 30 X 8 =Rs.320/-
product development time and cost”, International Journal of
2
Shift Advance Manufacturing technology, June 2008,pp 13-29
Cost of Resistance Heating [4] Sanjay Sharma, “ Effects of an increase in manufacturing rate in the
Rs. 320/- Only context of cyclic production”, The International Journal of Advanced
per shift Manufacturing Technology, November 2008, Volume 39, Issue 7-8,
pp 821-827.
VIII. RESULTS AND FINDINGS
By replacing Gas Fired Furnace by Special Purpose
Resistance Heating Furnace , the net saving in Tang
Forging Operation Cost was Rs.1280/- Per shift.
Machine Operator got relief from the hot environment
which improved his overall efficiency. The file can be
handled without using any of the work holding devices,
which was required in the previous case of Gas
Heating.
Figure No-09: Manual Handling of heated File
Workplace became safe since Gas Fired Furnace was
eliminated.
Now with Special Purpose Resistance Heating Furnace
the component is heated only for the required tang
length of 15 mm, excessive heating (along the length)
of component is avoided.
Since the net cost saving in the Tang Forging operation
was Rs.33,280/- per month, the capital investment of
Rs.1,50,000/- done in procuring the Special Purpose
Resistance Heating Furnace was going to be recovered
in 4.5 months which was acceptable by the industry.
IX. CONCLUSION
The cost of Tang Forging operation was reduced down to
almost 80 % (Initial Cost Rs.1600/- Per shift, Cost After
Modification Rs.320/- per shift for the Monthly Production
of 1800 Nos. of Round File of 06 Inch Length) which was
appreciated by the industry where the study was carried out.
www.ijltemas.in Page 138
You might also like
- Shop Practice No.2 Inside and Outside Caliper: Mapúa UniversityDocument12 pagesShop Practice No.2 Inside and Outside Caliper: Mapúa UniversitymarisonNo ratings yet
- Carpentry Report - Engineering Workshop Lab - Second/2004Document10 pagesCarpentry Report - Engineering Workshop Lab - Second/2004ahm531100% (2)
- FittingDocument7 pagesFittingAniz Farznor SariffuddinNo ratings yet
- TOOL MAKING.-Bench WorkDocument175 pagesTOOL MAKING.-Bench Workpbkamatar17944100% (2)
- Aircraft ToolsDocument98 pagesAircraft ToolsAdrian Aquino100% (4)
- Osprey Masterclass Panzer ModellingDocument129 pagesOsprey Masterclass Panzer ModellingJoppito100% (8)
- C00100Document24 pagesC00100Jimmy Deswidawansyah NasutionNo ratings yet
- Files Tools and Its TypesDocument6 pagesFiles Tools and Its Typesruth akoNo ratings yet
- Files Tools and Its TypesDocument8 pagesFiles Tools and Its TypesAJDominicNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT of Filling OperationDocument4 pagesLAB REPORT of Filling OperationAhtisham AmjadNo ratings yet
- Files and FilingDocument11 pagesFiles and FilingRaphaelNo ratings yet
- Topic 3-Hand Tools2Document12 pagesTopic 3-Hand Tools2samuelmutinda750No ratings yet
- File QuestionsDocument14 pagesFile QuestionsDipankar DasNo ratings yet
- TVET 1 - Worksheet 9Document5 pagesTVET 1 - Worksheet 9Abrigondo, Vindel J.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Hand ToolsDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Hand ToolsNEF RIDERSNo ratings yet
- Shop Practice Number 2Document13 pagesShop Practice Number 2JantzenCaliwliwNo ratings yet
- Shop Practice No. 2 Inside and Divider CaliperDocument15 pagesShop Practice No. 2 Inside and Divider CaliperLeslie CatindigNo ratings yet
- Nicholson - Guide To Filing 2014Document14 pagesNicholson - Guide To Filing 2014crm102b100% (1)
- EMG 2103 Workshop Processes and Practice IDocument24 pagesEMG 2103 Workshop Processes and Practice Iconc oxygenNo ratings yet
- Design Feature of NiTi Rotary FilesDocument64 pagesDesign Feature of NiTi Rotary FilesArmanThamanNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Single Point Cutting ToolDocument46 pagesDesign and Analysis of Single Point Cutting ToolkarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- 04 FileDocument103 pages04 FilerameshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Hand ToolsDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Hand ToolsMohd HapisNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Different Progressive ToolsDocument8 pagesDesign and Simulation of Different Progressive ToolsAnnaNo ratings yet
- LEC.4 Intracanal InstrumentsDocument6 pagesLEC.4 Intracanal InstrumentsDr-Ibrahim GhanimNo ratings yet
- Cons 9 - Rotary Instruments (1)Document9 pagesCons 9 - Rotary Instruments (1)khaNo ratings yet
- Endodontics: Classification of Intracanal InstrumentsDocument4 pagesEndodontics: Classification of Intracanal InstrumentsYasir AlnakibNo ratings yet
- Endodontic InstrumentsDocument63 pagesEndodontic Instrumentsitsme543210100% (1)
- Sheet Metal ShopDocument35 pagesSheet Metal ShopAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- ME137L-2 Exercise1Document7 pagesME137L-2 Exercise1Andrew PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Care and Use: Hand FileDocument5 pagesCare and Use: Hand FileAngel Julian HernandezNo ratings yet
- Assignment No - IDocument3 pagesAssignment No - Ivikas.thoratNo ratings yet
- Department of Petrochemical Engineering College of Technical Engineering University of Polytechnic-DuhokDocument12 pagesDepartment of Petrochemical Engineering College of Technical Engineering University of Polytechnic-DuhokWalid AdnanNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Part 1 / Intra Canal Instruments Classification of Intracanal InstrumentsDocument7 pagesLec 6 Part 1 / Intra Canal Instruments Classification of Intracanal InstrumentsFlorida ManNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Instruments Endodontic InstrumentsDocument11 pagesEndodontic Instruments Endodontic InstrumentsMubashir ZamanNo ratings yet
- Mapúa Institute of Technology: School of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringDocument10 pagesMapúa Institute of Technology: School of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringJoseph ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of Wood Lathe: Poonam Diwan, Amrita SinghDocument11 pagesNumerical Analysis of Wood Lathe: Poonam Diwan, Amrita SinghRitik GaudwalNo ratings yet
- Tools, Equipment and Processes 1Document8 pagesTools, Equipment and Processes 1Osei Kwadwo Hyiamang KorantengNo ratings yet
- Instruments Used in EndodonticsDocument40 pagesInstruments Used in EndodonticsFlynn RiderNo ratings yet
- Design Engineer Basics FudamentalsDocument34 pagesDesign Engineer Basics FudamentalssandeepNo ratings yet
- UNIT OF COMPETENCE: - Perform Bench Work MODULE TITLE: Performing Bench Work LO1: Lay-Out and Mark Dimensions/ Features On Work PieceDocument63 pagesUNIT OF COMPETENCE: - Perform Bench Work MODULE TITLE: Performing Bench Work LO1: Lay-Out and Mark Dimensions/ Features On Work Pieceahmed jemal100% (1)
- Properties of InstrumentDocument13 pagesProperties of InstrumentAnciya NazarNo ratings yet
- GE8261-Engineering Practices Lab - CIVILDocument36 pagesGE8261-Engineering Practices Lab - CIVILraghaviNo ratings yet
- Rotary Workshop 5-5-2016 File Design & Guidlines DR - Elham SenanDocument52 pagesRotary Workshop 5-5-2016 File Design & Guidlines DR - Elham SenanRashed AlmasoodyNo ratings yet
- TOOL DESIGN AssignmentDocument2 pagesTOOL DESIGN Assignmentwaseem siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Hand ToolsDocument19 pagesChapter 1-Hand ToolsHarizNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal ShopDocument43 pagesSheet Metal ShopBhaskar KandpalNo ratings yet
- Amp-I: Chapter - Hand FilesDocument16 pagesAmp-I: Chapter - Hand FilesRahul KumawatNo ratings yet
- ME8451 QB 01 - Part A&BDocument61 pagesME8451 QB 01 - Part A&BAthithanNo ratings yet
- Endodontic File-Tip VS TaperDocument18 pagesEndodontic File-Tip VS TaperDrAditya Bansal100% (1)
- A Concise Note On Workshop Technology: Nepal Students' Union Purwanchal Campus CommitteeDocument14 pagesA Concise Note On Workshop Technology: Nepal Students' Union Purwanchal Campus CommitteeAashiz PoudelNo ratings yet
- Files and FilingDocument12 pagesFiles and FilingPremal ZinzuwadiaNo ratings yet
- Design of Polypropylene Random Co-Polymer Pipe CutterDocument6 pagesDesign of Polypropylene Random Co-Polymer Pipe CutterInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Me2252 MT1 Unit1Document23 pagesMe2252 MT1 Unit1saisenthNo ratings yet
- Files BiblographyDocument13 pagesFiles BiblographyFurqan AlamNo ratings yet
- Me137 Lab2Document6 pagesMe137 Lab2Dan Rhoie MagcalasNo ratings yet
- TM3000C VS Gop 300 Bosch PDFDocument11 pagesTM3000C VS Gop 300 Bosch PDFAnonymous lSEnEklZ7No ratings yet
- Workshop ManualDocument68 pagesWorkshop ManualrisNo ratings yet
- Fitting ShopDocument11 pagesFitting Shopsaraswatishruti1982No ratings yet
- Carpentry Shop Updated - Ver 2Document16 pagesCarpentry Shop Updated - Ver 2Divyansh GargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cutting ToolsDocument33 pagesChapter 2 Cutting Toolskaleab hintsaNo ratings yet
- Workshop ManualDocument68 pagesWorkshop ManualAkanksha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Reporters: Sabang, Mary Wrestly M. Miro, Michelle TDocument21 pagesReporters: Sabang, Mary Wrestly M. Miro, Michelle TJose Lapera Jr.No ratings yet
- Endodontics: Classification of Intracanal InstrumentsDocument8 pagesEndodontics: Classification of Intracanal InstrumentsHaider F YehyaNo ratings yet
- Turning Wood with Carbide Tools: Techniques and Projects for Every Skill LevelFrom EverandTurning Wood with Carbide Tools: Techniques and Projects for Every Skill LevelRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Nota MEM160 PDFDocument146 pagesNota MEM160 PDFArefiq ShafikNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Hack SawmachineDocument93 pagesPneumatic Hack Sawmachinesanthosh saravananNo ratings yet
- Module No. 1: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Public Technical - Vocational High SchoolsDocument211 pagesModule No. 1: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Public Technical - Vocational High SchoolszNo ratings yet
- Mould PolishingDocument4 pagesMould PolishingArun PrasadNo ratings yet
- PepsistoveDocument5 pagesPepsistoveMark Anthony T. PadilNo ratings yet
- Herramienta Afila MechasDocument4 pagesHerramienta Afila MechasLalo LeloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Basic Hand Tools and 5S 2Document47 pagesLesson 3 Basic Hand Tools and 5S 2hiiamaj03No ratings yet
- Plumbing and Pipe Line Work PDFDocument248 pagesPlumbing and Pipe Line Work PDFLoren ViejayNo ratings yet
- Paper - 2 - Question Bank With Answer PDFDocument274 pagesPaper - 2 - Question Bank With Answer PDFnithinib_007100% (1)
- TVET 1 - Worksheet 9Document5 pagesTVET 1 - Worksheet 9Abrigondo, Vindel J.No ratings yet
- IC Workshop Materials 09 - Marking Out, Measurement, Fitting & AssemblyDocument24 pagesIC Workshop Materials 09 - Marking Out, Measurement, Fitting & AssemblybabunrajunNo ratings yet
- DNT NotesDocument9 pagesDNT NotesPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Exterior Technik 2020 GB WebDocument92 pagesExterior Technik 2020 GB WebJura OkrešaNo ratings yet
- Fixing Guards - Rob BrownDocument5 pagesFixing Guards - Rob BrownleandroNo ratings yet
- 2b. Fitting Trade 27112020Document29 pages2b. Fitting Trade 27112020Jeevan MandalaNo ratings yet
- Carpentry Shop FinalDocument36 pagesCarpentry Shop FinalRakesh Kumar Shukla KECNo ratings yet
- Bench WorkingDocument11 pagesBench WorkingMonica MagdyNo ratings yet
- GegasDocument6 pagesGegasambatarNo ratings yet
- Basic Manufacturing Systems (ME1083) : School of Mechanical Engineering KIIT Deemed To Be UniversityDocument38 pagesBasic Manufacturing Systems (ME1083) : School of Mechanical Engineering KIIT Deemed To Be UniversityDiKshya PahariNo ratings yet
- Guide To Jewelry TechniquesDocument22 pagesGuide To Jewelry TechniquesJill Krahling80% (5)
- Cutting ToolsDocument150 pagesCutting ToolsSiwapol Charykaew100% (1)
- Aluminium Mig WeldingDocument5 pagesAluminium Mig WeldingManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Batangas State UniversityDocument6 pagesBatangas State UniversityEnchanting BerryNo ratings yet
- 1st & 2nd Sem Manual 2022Document33 pages1st & 2nd Sem Manual 2022Dipanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Work Book For 1st Year Mechanical WorkshopDocument82 pagesWork Book For 1st Year Mechanical WorkshopVishal KumarNo ratings yet