Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Test 1 Matter
Physics Test 1 Matter
Uploaded by
prospire embeleCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Capillarity and Wetting PhenomenaDocument186 pagesCapillarity and Wetting Phenomenachkpcc1b1222No ratings yet
- Uganda Certificate of Education Physics Paper 4 Time: 2 HoursDocument4 pagesUganda Certificate of Education Physics Paper 4 Time: 2 HoursTamale John PaulNo ratings yet
- Physics Mock Exam 2017Document6 pagesPhysics Mock Exam 2017sulayajannyNo ratings yet
- BS1881-208 1996Document15 pagesBS1881-208 1996surangaNo ratings yet
- Porous Ceramics CA2014Document3 pagesPorous Ceramics CA2014Ahmad AnwarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Summary Notes PDFDocument322 pagesFluid Mechanics Summary Notes PDFLendo PosaraNo ratings yet
- Physics Test 1Document2 pagesPhysics Test 1kamalasish deb100% (1)
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Levelyuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Physics Past PaperDocument14 pagesPhysics Past PaperApplemeisterNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science: 2/3 Unit (Common)Document38 pagesEngineering Science: 2/3 Unit (Common)Tahmedul Hasan TanvirNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42afyNo ratings yet
- Aqa Phya2 W QP Jan09Document13 pagesAqa Phya2 W QP Jan09kiingkangNo ratings yet
- PHYU3JUNE2008Document20 pagesPHYU3JUNE2008api-3726022No ratings yet
- 9702 As Physics 12Document317 pages9702 As Physics 12Vinod RNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 2 Question PaperDocument16 pagesPhysics Unit 2 Question PaperqeoobyogNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence: On The Past, Present, and Future of Artificial IntelligenceDocument11 pagesA Brief History of Artificial Intelligence: On The Past, Present, and Future of Artificial IntelligenceTran Thi ThaoNo ratings yet
- 4bs Physics TestDocument2 pages4bs Physics TestRonaldo MohammedNo ratings yet
- PHY2 Jun06 QUESDocument16 pagesPHY2 Jun06 QUESapi-3743896No ratings yet
- Engineering Science: 3 Unit (Additional)Document22 pagesEngineering Science: 3 Unit (Additional)Tahmedul Hasan TanvirNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 20.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 20.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- MHT CET Question Papers 1Document17 pagesMHT CET Question Papers 1Pankaj Joshi100% (2)
- Edexcel Igcse January 2017 Physics p1Document28 pagesEdexcel Igcse January 2017 Physics p1Kriti0% (1)
- PHY3 Jan06 QUESDocument20 pagesPHY3 Jan06 QUESapi-3743896No ratings yet
- 12 Mathematics Ncert Ch09 Differential Equations 9.4 SolDocument11 pages12 Mathematics Ncert Ch09 Differential Equations 9.4 SolBhaskarjyoti Phukan100% (1)
- Differential Equations PaperDocument48 pagesDifferential Equations PaperVipul Meta100% (1)
- Unit 10 Regents Physics Test (Circuits Review)Document7 pagesUnit 10 Regents Physics Test (Circuits Review)aznblehtnNo ratings yet
- Class Vi Worksheet 1Document2 pagesClass Vi Worksheet 1abdul mutalib100% (1)
- Physics Practice Paper 1Document31 pagesPhysics Practice Paper 1Venus YauNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 2020Document24 pagesPhysics Paper 2 2020priyen bhuvaNo ratings yet
- 2 Class XII Chemistry CHSE Workbook 0Document305 pages2 Class XII Chemistry CHSE Workbook 0chithiraikumar83No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 GK Question Paper Set BDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 7 GK Question Paper Set BGayatriNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science Olympiad Achievers Section Practice PapersDocument5 pagesClass 8 Science Olympiad Achievers Section Practice PapersY_AZNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Merged QuestionsDocument142 pagesChemistry Merged QuestionsGanpat j muthaNo ratings yet
- Physics HSC Exam 2014 PDFDocument44 pagesPhysics HSC Exam 2014 PDFKevin KeNo ratings yet
- Nstse 7Document10 pagesNstse 7penumudi233No ratings yet
- Edecel GCSE Physics P2 Topic 1 and Topic 2 TS Test 13 - 14Document17 pagesEdecel GCSE Physics P2 Topic 1 and Topic 2 TS Test 13 - 14Paul BurgessNo ratings yet
- Kinematics DPP 04Document6 pagesKinematics DPP 04ROHANNo ratings yet
- 1 General Physics PDFDocument39 pages1 General Physics PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Number 01Document3 pagesChapter Number 01RAO UMAIRNo ratings yet
- Science Book - 10 - OnlineDocument266 pagesScience Book - 10 - OnlineShrestha PratikNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument8 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsNighin NazerNo ratings yet
- 00 PhysicsDocument64 pages00 PhysicsWing Hong Antony LukNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22 May/June 2020Document14 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22 May/June 2020junk filesNo ratings yet
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced 2022 Set-2Document7 pagesBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced 2022 Set-2Vaishnavi SuppalaNo ratings yet
- Skill Test Math CL3 D3Document3 pagesSkill Test Math CL3 D3rks9rksNo ratings yet
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-10Document7 pagesBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-10ASHISH NAIKNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 CHEMISTRY Previous Year Question Paper 2010Document8 pagesICSE Class 10 CHEMISTRY Previous Year Question Paper 2010Madhu SudanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 11 Introduction To Differential Equation V3Document2 pagesTutorial 11 Introduction To Differential Equation V3Movanniish Singh100% (1)
- Current Electricity - JEE Main 2023 January Chapter Wise Questions by MathonGoDocument24 pagesCurrent Electricity - JEE Main 2023 January Chapter Wise Questions by MathonGoRavi RajNo ratings yet
- Work and Power - AnsDocument32 pagesWork and Power - AnsSurbhi DungraniNo ratings yet
- The Scope of Physics PDFDocument2 pagesThe Scope of Physics PDFMeer MomiNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 - DensityDocument27 pagesPhysics 2 - DensitySimple ScienceNo ratings yet
- CHEM 121 Midterm Practice Questions 2013Document13 pagesCHEM 121 Midterm Practice Questions 2013Kathryn CruzNo ratings yet
- Questionpaper Paper1P June2017 PDFDocument36 pagesQuestionpaper Paper1P June2017 PDFMishka WajeedNo ratings yet
- Smart Artificial Intelligence Based Online Proctoring SystemDocument5 pagesSmart Artificial Intelligence Based Online Proctoring SystemDivyanshu TiwariNo ratings yet
- L6 U3 SNC1D NotesDocument6 pagesL6 U3 SNC1D NotesabhieNo ratings yet
- BSC MPCs Course StructureDocument3 pagesBSC MPCs Course Structurepuli sai kumarNo ratings yet
- 11th Chem MCQs Full Book Final PDF With Answer KeyDocument38 pages11th Chem MCQs Full Book Final PDF With Answer KeyHassan Abbas100% (1)
- QP Physics Sample PapersDocument116 pagesQP Physics Sample PapersShireen SuhailNo ratings yet
- Airforce Group X Model Question Papers PDF DownloadDocument11 pagesAirforce Group X Model Question Papers PDF DownloadTechie Harry90% (10)
- Physics Q Paper HSC Apr 2021 Kubal AcademyDocument4 pagesPhysics Q Paper HSC Apr 2021 Kubal AcademyRAVINDRA WAYKOLENo ratings yet
- Worksheet IIDocument2 pagesWorksheet IIgiziew belayNo ratings yet
- Physics: The Ambitious Combined Entry Test 2019 (Etea/Fmdc/Nums/Uhs-Mdcat)Document19 pagesPhysics: The Ambitious Combined Entry Test 2019 (Etea/Fmdc/Nums/Uhs-Mdcat)MUHAMMAD NOMAN SALEEMNo ratings yet
- XI-2nd Peridoic TestDocument4 pagesXI-2nd Peridoic TestKotyada ParthivNo ratings yet
- S.4 Physics - Electrostatics - O-Level NotesDocument12 pagesS.4 Physics - Electrostatics - O-Level Notesprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- f4 Second Term 2022Document6 pagesf4 Second Term 2022prospire embeleNo ratings yet
- E MockDocument6 pagesE Mockprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Lower Sixth Further MathematicsDocument1 pageLower Sixth Further Mathematicsprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Phy F4Document1 pagePhy F4prospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Scans Worksheet - 0Document1 pageUltrasound Scans Worksheet - 0prospire embeleNo ratings yet
- School: New Century Institute of Learning Subject: Physics Class: Form OneDocument2 pagesSchool: New Century Institute of Learning Subject: Physics Class: Form Oneprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- O.level Physics P1 MockDocument9 pagesO.level Physics P1 Mockprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Phy F4 2ND TermDocument4 pagesPhy F4 2ND Termprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Phy LSS 2ND TermDocument4 pagesPhy LSS 2ND Termprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument55 pagesFluidsdanena88No ratings yet
- Retention, Stability and SupportDocument57 pagesRetention, Stability and SupportYuvraj Kapoor100% (1)
- Question Paper 3 (Topic 4 - Heat P3)Document15 pagesQuestion Paper 3 (Topic 4 - Heat P3)Nur Syidah100% (1)
- Penetrant PresentationDocument20 pagesPenetrant PresentationJayesh100% (3)
- CE 521 - Reaction Paper On Introduction To Properties of FluidsDocument8 pagesCE 521 - Reaction Paper On Introduction To Properties of FluidsHipolito RarangolNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document23 pagesLecture 1meku44No ratings yet
- MM Candy ChartDocument6 pagesMM Candy ChartAliNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 5 Surface Tension: Capillary Rise Method de Leon, Kiara Justine C., Medrano, Jeffrey B., Merelos, Samantha B., Ong, Pedro Paolo NDocument7 pagesExperiment # 5 Surface Tension: Capillary Rise Method de Leon, Kiara Justine C., Medrano, Jeffrey B., Merelos, Samantha B., Ong, Pedro Paolo Nunlocks by xijiNo ratings yet
- Astm D-1266 PDFDocument11 pagesAstm D-1266 PDFDzia RizqiNo ratings yet
- 02 Mechanical Properties of Fluids One Shot (LMR Series)Document110 pages02 Mechanical Properties of Fluids One Shot (LMR Series)ashunaik409No ratings yet
- HPC Unit. 1x PDFDocument21 pagesHPC Unit. 1x PDFSaix CreationsNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension 2Document11 pagesSurface Tension 2Fozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 HYDRA325 DiscussionDocument34 pagesMODULE 1 HYDRA325 DiscussionCyruz HimenezNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Soil Water PlantDocument91 pages1.2 Soil Water PlantALINDA BRIANNo ratings yet
- Cohesion and Adhesion in LiquidsDocument1 pageCohesion and Adhesion in LiquidsjmlagumbayNo ratings yet
- 06.applied Science LabDocument9 pages06.applied Science LabkarthikNo ratings yet
- Moisture ManagementDocument5 pagesMoisture ManagementSombis2011No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Lecture 1: Introduction and Properties of FluidsDocument19 pagesFluid Mechanics: Lecture 1: Introduction and Properties of FluidsEleanor Caguimbal100% (1)
- Que Papers For Cbse Class 12Document3 pagesQue Papers For Cbse Class 12Bhagyaraj PandabNo ratings yet
- GPL 212 Determination of Surface Tension of A LiquidDocument28 pagesGPL 212 Determination of Surface Tension of A LiquidyasintharaNo ratings yet
- FM & F Machines 2013 PDFDocument355 pagesFM & F Machines 2013 PDFChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Properties of FluidsDocument55 pagesLesson 1 Properties of Fluidsjavarice653No ratings yet
- HT Heat ExchangerDocument17 pagesHT Heat Exchangerpatel jatinNo ratings yet
- CE 261 - Part Class NoteDocument16 pagesCE 261 - Part Class NoteAL-AMIN AHMED MOBIN 1801015No ratings yet
- Assignment Fluid Mechanics 3rd WeekDocument2 pagesAssignment Fluid Mechanics 3rd Weekchristos032No ratings yet
- Colegio de San Sebastian Sablayan, Occidental Mindoro: Fluid MechanicsDocument16 pagesColegio de San Sebastian Sablayan, Occidental Mindoro: Fluid MechanicsSanta mariaNo ratings yet
Physics Test 1 Matter
Physics Test 1 Matter
Uploaded by
prospire embeleOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Test 1 Matter
Physics Test 1 Matter
Uploaded by
prospire embeleCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS TEST BY MR. OBANDE P.
06/28/2019
PHYSICS TEST 1
SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS: Tick the correct answer
1. The graph shown was plotted in an experiment on a metal wire. The shaded area represents
the total strain energy stored in stretching the wire. How should the axes be labelled?
X Y y
A Force Extension
B Mass Extension
C Stress Energy
D Stress strain
X
2. The variation with applied force of the extension of a spring is shown in the graph. When
there is no force applied to the spring, it has a length of 1.0cm. What is the increase in the
strain energy stored in the spring when its length is increased from 2.0cm to 3.0cm?
A) 0.020J B) 0.030J C ) 0.040J D) 0.050J
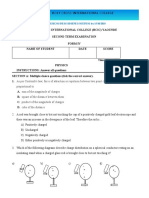
3. The air-filled bubbles X and Y shown in figure 2 are formed at the ends of the tube with the
tap T, closed.
When the tap, T, is opened T
A) X would increase in diameter.
B) The diameter of X would be equal to the diameter of Y.
C) X and Y would coalesce. Figure
Y 2
X
PHYSICS TEST BY MR. OBANDE P. 06/28/2019
D) Y would increase in diameter.
4. Which two substances are normally both crystalline?
A) copper and diamond B) copper and glass C)diamond and glass D) diamond
and rubber
5. The modulus of elasticity is dimensionally equivalent to
A) Strain B) stress C) surface tension D) force
6. The work done in stretching a wire by 1 mm is 2 J. What will be the work in joules necessary
to stretch another wire of the same material but with double the radius of cross-section and
half the length by 1 mm?
A) 16 B) 8 C) 4 D) ¼
7. According to Hooke’s law of elasticity, within the elastic limit, if the stress is increased, the
ratio of stress to strain
A) Increases B) decreases C) becomes zero D) remains
constant
8. The energy stored per unit volume of a strained wire is
1
A) × ( load ) × ( extension )
2
1 E
B) 2 2
( strain)
1
C) E( srain)2
2
D) stress× strain
9. The property due to which sheets can be prepared from materials is called
A) Elasticity B) malleability C) brittleness D) ductility
10. Choose the wrong statement from the following
A) Small droplets of a liquid are spherical due to surface tension
B) Oil rises through the wick due to capillarity
C) In drinking a cold drink through the straw, we use the phenomenon of capillarity
D) Gum is used to stick two surfaces. In this process, we use the property of adhesion
11. The angle of contact between a glass capillary tube of length 10 cm and a liquid is 90o. If the
capillary tube is dipped vertically in the liquid, then the liquid will
A) Rise in the tube
PHYSICS TEST BY MR. OBANDE P. 06/28/2019
B) Get depressed in the tube
C) Rise up to 10 cm in the tube and will overflow
D) Neither rise nor fall in the tube
12. The height of water in a capillary tube of radius 2 cm is 4 cm. What should be the radius of
the capillary tube if the water rises to 8 cm in the tube?
A) 1 cm B) 0.1 cm C) 2 cm D) 4 cm
13. Given that the surface tension of soap solution is 1,6 N/m, the excess pressure in a soap
bubble of diameter 5 mm is
A) 2560 Pa B) 3720 Pa C) 1208 Pa D) 10132 Pa
14. Two soap bubbles of radii 3 cm and 4 cm coalesce under isothermal conditions to form a
single bubble. What is the radius of the new single bubble?
A) 3 cm B) 4 cm C) 5 cm D) 6 cm
15. When the inter molecular distance increases due to tensile forces,
A) There is no force between the molecules
B) There is a repulsive force between the molecules
C) There is a zero resultant force between the molecules
D) There is an attractive force between the molecules
16. Stress can be measured in:
A. N/m2
B. N·m2
C. N/m
D. N·m
17. Young’s modulus can be correctly given in:
A. N·m
B. N/m2
C. N·m/s
D. N/m
18. Young’s modulus is a proportionality constant that relates the force per unit area applied
perpendicularly at the surface of an object to:
A. the shear
B. the fractional change in volume
PHYSICS TEST BY MR. OBANDE P. 06/28/2019
C. the fractional change in length
D. the pressure
19. Young’s modulus can be used to calculate the strain for a stress that is:
A. just below the ultimate strength
B. just above the ultimate strength
C. well below the yield strength
D. well above the yield strength
20. The ultimate strength of a sample is the stress at which the sample:
A. returns to its original shape when the stress is removed
B. remains underwater
C. breaks
D. bends 180
21. A certain wire stretches by 0.90 cm when outward forces with magnitude F are applied to
each end. The same forces are applied to a wire of the same material but with three times the
diameter and three times the length. The second wire stretches by:
A. 0.10 cm
B. 0.30 cm
C. 0.90 cm
D. 2.7 cm
22. Solids having regular a arrangement of molecules through its structure is called:
A. Amorphous Solids
B. Polymeric Solids
C. Glassy Solids
D. Crystalline Solids
23. Which type of solids have definite melting point:
A. Crystalline Solids
B. Amorphous Solids
C. Polymeric Solids
D. Glassy Solids
24. Amorphous solids are also called:
A. Polymeric Solids
PHYSICS TEST BY MR. OBANDE P. 06/28/2019
B. Glassy Solids
C. Crystalline Solids
D. Brittle Solids
25. Which of the following is polymeric solid:
A. Glass
B. Iron
C. Steel
D. Nylon
SECTION B: ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. (a) With respect to either force and kinetic energy or separation and motion of particles,
differentiate between the different states of matter. (3 marks)
(b) The density of a solid is 1.2 ×103 Kgm−3 and its molar mass is 0.090 kg.
i. Calculate the average volume occupied by a single molecule of the solid.
ii. Estimate the distance between the centers of two adjacent molecules of the solid
stating any assumption that you make.
(The Avogadro constantN A =6.0 ×1023 mol−1 ) (3 marks)
(c) Materials could be classified as crystalline, amorphous or polymeric.
Define the terms in italics giving one example of each. (6 marks)
2. The net force F between two particles in a solid varies with their separation, r, according to
the equation
8.0× 10−20 2.0× 10−96
F= −
r2 r 10
a. Calculate, r 0 , the equilibrium separation. (3 marks)
b. The energy of the particles at this equilibrium position is called bonding energy.
Explain the meaning of the phrase in bold italics. (1 mark)
c. Sketch a graph showing how the force F between two adjacent particles varies with
their separation, r. (3 marks)
d. How can the graph in (b) above be used to explain Hookian behaviour of matter? (2
marks)
e. What is the physical significance of the area under the graph in (b) above? (1 mark)
PHYSICS TEST BY MR. OBANDE P. 06/28/2019
3. Define surface tension (2 marks)
ii) Describe an experiment to measure the surface tension at different temperatures of a
liquid. (7 marks)
b) Explain the following phenomena (2 marks)
i) A pond skater is able to walk over the surface of water without sinking
ii) A detergent dissolve in water will easily remove dirt from a greasy plate
iii) The molecules at the surface of a liquid have a higher potential energy than those
in the bulk
4. The figure above shows the force-extension graph for a metal specimen.
Calculate
a. The force constant of the speciment. (2 marks)
b. The work done in stretching the speciment up to
i. The proportionality limit
ii. Fracture (5 marks)
c. A steel bar is of length 0.5 m and has a rectangular cross-section 15 mm by 30 mm. If a
tensile forceof 36 KN produces an extension of 0.20 mm, calculate Young’s modulus for
steel. Assume that the limit of proportionality is not exceeded. (3 marks)
PHYSICS TEST BY MR. OBANDE P. 06/28/2019
GOOD LUCK!!!!!
You might also like
- Capillarity and Wetting PhenomenaDocument186 pagesCapillarity and Wetting Phenomenachkpcc1b1222No ratings yet
- Uganda Certificate of Education Physics Paper 4 Time: 2 HoursDocument4 pagesUganda Certificate of Education Physics Paper 4 Time: 2 HoursTamale John PaulNo ratings yet
- Physics Mock Exam 2017Document6 pagesPhysics Mock Exam 2017sulayajannyNo ratings yet
- BS1881-208 1996Document15 pagesBS1881-208 1996surangaNo ratings yet
- Porous Ceramics CA2014Document3 pagesPorous Ceramics CA2014Ahmad AnwarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Summary Notes PDFDocument322 pagesFluid Mechanics Summary Notes PDFLendo PosaraNo ratings yet
- Physics Test 1Document2 pagesPhysics Test 1kamalasish deb100% (1)
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Levelyuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Physics Past PaperDocument14 pagesPhysics Past PaperApplemeisterNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science: 2/3 Unit (Common)Document38 pagesEngineering Science: 2/3 Unit (Common)Tahmedul Hasan TanvirNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42afyNo ratings yet
- Aqa Phya2 W QP Jan09Document13 pagesAqa Phya2 W QP Jan09kiingkangNo ratings yet
- PHYU3JUNE2008Document20 pagesPHYU3JUNE2008api-3726022No ratings yet
- 9702 As Physics 12Document317 pages9702 As Physics 12Vinod RNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 2 Question PaperDocument16 pagesPhysics Unit 2 Question PaperqeoobyogNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence: On The Past, Present, and Future of Artificial IntelligenceDocument11 pagesA Brief History of Artificial Intelligence: On The Past, Present, and Future of Artificial IntelligenceTran Thi ThaoNo ratings yet
- 4bs Physics TestDocument2 pages4bs Physics TestRonaldo MohammedNo ratings yet
- PHY2 Jun06 QUESDocument16 pagesPHY2 Jun06 QUESapi-3743896No ratings yet
- Engineering Science: 3 Unit (Additional)Document22 pagesEngineering Science: 3 Unit (Additional)Tahmedul Hasan TanvirNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 20.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 20.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- MHT CET Question Papers 1Document17 pagesMHT CET Question Papers 1Pankaj Joshi100% (2)
- Edexcel Igcse January 2017 Physics p1Document28 pagesEdexcel Igcse January 2017 Physics p1Kriti0% (1)
- PHY3 Jan06 QUESDocument20 pagesPHY3 Jan06 QUESapi-3743896No ratings yet
- 12 Mathematics Ncert Ch09 Differential Equations 9.4 SolDocument11 pages12 Mathematics Ncert Ch09 Differential Equations 9.4 SolBhaskarjyoti Phukan100% (1)
- Differential Equations PaperDocument48 pagesDifferential Equations PaperVipul Meta100% (1)
- Unit 10 Regents Physics Test (Circuits Review)Document7 pagesUnit 10 Regents Physics Test (Circuits Review)aznblehtnNo ratings yet
- Class Vi Worksheet 1Document2 pagesClass Vi Worksheet 1abdul mutalib100% (1)
- Physics Practice Paper 1Document31 pagesPhysics Practice Paper 1Venus YauNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 2020Document24 pagesPhysics Paper 2 2020priyen bhuvaNo ratings yet
- 2 Class XII Chemistry CHSE Workbook 0Document305 pages2 Class XII Chemistry CHSE Workbook 0chithiraikumar83No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 GK Question Paper Set BDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 7 GK Question Paper Set BGayatriNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science Olympiad Achievers Section Practice PapersDocument5 pagesClass 8 Science Olympiad Achievers Section Practice PapersY_AZNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Merged QuestionsDocument142 pagesChemistry Merged QuestionsGanpat j muthaNo ratings yet
- Physics HSC Exam 2014 PDFDocument44 pagesPhysics HSC Exam 2014 PDFKevin KeNo ratings yet
- Nstse 7Document10 pagesNstse 7penumudi233No ratings yet
- Edecel GCSE Physics P2 Topic 1 and Topic 2 TS Test 13 - 14Document17 pagesEdecel GCSE Physics P2 Topic 1 and Topic 2 TS Test 13 - 14Paul BurgessNo ratings yet
- Kinematics DPP 04Document6 pagesKinematics DPP 04ROHANNo ratings yet
- 1 General Physics PDFDocument39 pages1 General Physics PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Number 01Document3 pagesChapter Number 01RAO UMAIRNo ratings yet
- Science Book - 10 - OnlineDocument266 pagesScience Book - 10 - OnlineShrestha PratikNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument8 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsNighin NazerNo ratings yet
- 00 PhysicsDocument64 pages00 PhysicsWing Hong Antony LukNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22 May/June 2020Document14 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22 May/June 2020junk filesNo ratings yet
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced 2022 Set-2Document7 pagesBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced 2022 Set-2Vaishnavi SuppalaNo ratings yet
- Skill Test Math CL3 D3Document3 pagesSkill Test Math CL3 D3rks9rksNo ratings yet
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-10Document7 pagesBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-10ASHISH NAIKNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 CHEMISTRY Previous Year Question Paper 2010Document8 pagesICSE Class 10 CHEMISTRY Previous Year Question Paper 2010Madhu SudanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 11 Introduction To Differential Equation V3Document2 pagesTutorial 11 Introduction To Differential Equation V3Movanniish Singh100% (1)
- Current Electricity - JEE Main 2023 January Chapter Wise Questions by MathonGoDocument24 pagesCurrent Electricity - JEE Main 2023 January Chapter Wise Questions by MathonGoRavi RajNo ratings yet
- Work and Power - AnsDocument32 pagesWork and Power - AnsSurbhi DungraniNo ratings yet
- The Scope of Physics PDFDocument2 pagesThe Scope of Physics PDFMeer MomiNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 - DensityDocument27 pagesPhysics 2 - DensitySimple ScienceNo ratings yet
- CHEM 121 Midterm Practice Questions 2013Document13 pagesCHEM 121 Midterm Practice Questions 2013Kathryn CruzNo ratings yet
- Questionpaper Paper1P June2017 PDFDocument36 pagesQuestionpaper Paper1P June2017 PDFMishka WajeedNo ratings yet
- Smart Artificial Intelligence Based Online Proctoring SystemDocument5 pagesSmart Artificial Intelligence Based Online Proctoring SystemDivyanshu TiwariNo ratings yet
- L6 U3 SNC1D NotesDocument6 pagesL6 U3 SNC1D NotesabhieNo ratings yet
- BSC MPCs Course StructureDocument3 pagesBSC MPCs Course Structurepuli sai kumarNo ratings yet
- 11th Chem MCQs Full Book Final PDF With Answer KeyDocument38 pages11th Chem MCQs Full Book Final PDF With Answer KeyHassan Abbas100% (1)
- QP Physics Sample PapersDocument116 pagesQP Physics Sample PapersShireen SuhailNo ratings yet
- Airforce Group X Model Question Papers PDF DownloadDocument11 pagesAirforce Group X Model Question Papers PDF DownloadTechie Harry90% (10)
- Physics Q Paper HSC Apr 2021 Kubal AcademyDocument4 pagesPhysics Q Paper HSC Apr 2021 Kubal AcademyRAVINDRA WAYKOLENo ratings yet
- Worksheet IIDocument2 pagesWorksheet IIgiziew belayNo ratings yet
- Physics: The Ambitious Combined Entry Test 2019 (Etea/Fmdc/Nums/Uhs-Mdcat)Document19 pagesPhysics: The Ambitious Combined Entry Test 2019 (Etea/Fmdc/Nums/Uhs-Mdcat)MUHAMMAD NOMAN SALEEMNo ratings yet
- XI-2nd Peridoic TestDocument4 pagesXI-2nd Peridoic TestKotyada ParthivNo ratings yet
- S.4 Physics - Electrostatics - O-Level NotesDocument12 pagesS.4 Physics - Electrostatics - O-Level Notesprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- f4 Second Term 2022Document6 pagesf4 Second Term 2022prospire embeleNo ratings yet
- E MockDocument6 pagesE Mockprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Lower Sixth Further MathematicsDocument1 pageLower Sixth Further Mathematicsprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Phy F4Document1 pagePhy F4prospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Scans Worksheet - 0Document1 pageUltrasound Scans Worksheet - 0prospire embeleNo ratings yet
- School: New Century Institute of Learning Subject: Physics Class: Form OneDocument2 pagesSchool: New Century Institute of Learning Subject: Physics Class: Form Oneprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- O.level Physics P1 MockDocument9 pagesO.level Physics P1 Mockprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Phy F4 2ND TermDocument4 pagesPhy F4 2ND Termprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Phy LSS 2ND TermDocument4 pagesPhy LSS 2ND Termprospire embeleNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument55 pagesFluidsdanena88No ratings yet
- Retention, Stability and SupportDocument57 pagesRetention, Stability and SupportYuvraj Kapoor100% (1)
- Question Paper 3 (Topic 4 - Heat P3)Document15 pagesQuestion Paper 3 (Topic 4 - Heat P3)Nur Syidah100% (1)
- Penetrant PresentationDocument20 pagesPenetrant PresentationJayesh100% (3)
- CE 521 - Reaction Paper On Introduction To Properties of FluidsDocument8 pagesCE 521 - Reaction Paper On Introduction To Properties of FluidsHipolito RarangolNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document23 pagesLecture 1meku44No ratings yet
- MM Candy ChartDocument6 pagesMM Candy ChartAliNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 5 Surface Tension: Capillary Rise Method de Leon, Kiara Justine C., Medrano, Jeffrey B., Merelos, Samantha B., Ong, Pedro Paolo NDocument7 pagesExperiment # 5 Surface Tension: Capillary Rise Method de Leon, Kiara Justine C., Medrano, Jeffrey B., Merelos, Samantha B., Ong, Pedro Paolo Nunlocks by xijiNo ratings yet
- Astm D-1266 PDFDocument11 pagesAstm D-1266 PDFDzia RizqiNo ratings yet
- 02 Mechanical Properties of Fluids One Shot (LMR Series)Document110 pages02 Mechanical Properties of Fluids One Shot (LMR Series)ashunaik409No ratings yet
- HPC Unit. 1x PDFDocument21 pagesHPC Unit. 1x PDFSaix CreationsNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension 2Document11 pagesSurface Tension 2Fozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 HYDRA325 DiscussionDocument34 pagesMODULE 1 HYDRA325 DiscussionCyruz HimenezNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Soil Water PlantDocument91 pages1.2 Soil Water PlantALINDA BRIANNo ratings yet
- Cohesion and Adhesion in LiquidsDocument1 pageCohesion and Adhesion in LiquidsjmlagumbayNo ratings yet
- 06.applied Science LabDocument9 pages06.applied Science LabkarthikNo ratings yet
- Moisture ManagementDocument5 pagesMoisture ManagementSombis2011No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Lecture 1: Introduction and Properties of FluidsDocument19 pagesFluid Mechanics: Lecture 1: Introduction and Properties of FluidsEleanor Caguimbal100% (1)
- Que Papers For Cbse Class 12Document3 pagesQue Papers For Cbse Class 12Bhagyaraj PandabNo ratings yet
- GPL 212 Determination of Surface Tension of A LiquidDocument28 pagesGPL 212 Determination of Surface Tension of A LiquidyasintharaNo ratings yet
- FM & F Machines 2013 PDFDocument355 pagesFM & F Machines 2013 PDFChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Properties of FluidsDocument55 pagesLesson 1 Properties of Fluidsjavarice653No ratings yet
- HT Heat ExchangerDocument17 pagesHT Heat Exchangerpatel jatinNo ratings yet
- CE 261 - Part Class NoteDocument16 pagesCE 261 - Part Class NoteAL-AMIN AHMED MOBIN 1801015No ratings yet
- Assignment Fluid Mechanics 3rd WeekDocument2 pagesAssignment Fluid Mechanics 3rd Weekchristos032No ratings yet
- Colegio de San Sebastian Sablayan, Occidental Mindoro: Fluid MechanicsDocument16 pagesColegio de San Sebastian Sablayan, Occidental Mindoro: Fluid MechanicsSanta mariaNo ratings yet