Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Job-Based, Skill/competency-Based, Market-Based, or A Combination of
Job-Based, Skill/competency-Based, Market-Based, or A Combination of
Uploaded by
Cristina Crong Morgia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views9 pagesThis document discusses rewards management and compensation plans. It explains that total rewards consider both tangible and intangible rewards to motivate employees and boost productivity. Compensation includes direct monetary pay as well as indirect benefits and is determined by job evaluations and market factors. Effective compensation plans adhere to legal standards, sustain organizational goals, and induce employee loyalty through adequate, equitable and timely rewards.
Original Description:
Original Title
HRM Finals
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses rewards management and compensation plans. It explains that total rewards consider both tangible and intangible rewards to motivate employees and boost productivity. Compensation includes direct monetary pay as well as indirect benefits and is determined by job evaluations and market factors. Effective compensation plans adhere to legal standards, sustain organizational goals, and induce employee loyalty through adequate, equitable and timely rewards.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views9 pagesJob-Based, Skill/competency-Based, Market-Based, or A Combination of
Job-Based, Skill/competency-Based, Market-Based, or A Combination of
Uploaded by
Cristina Crong MorgiaThis document discusses rewards management and compensation plans. It explains that total rewards consider both tangible and intangible rewards to motivate employees and boost productivity. Compensation includes direct monetary pay as well as indirect benefits and is determined by job evaluations and market factors. Effective compensation plans adhere to legal standards, sustain organizational goals, and induce employee loyalty through adequate, equitable and timely rewards.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Chapter 5: Rewards Management
Objective based on the task & the
skills/knowledge of the employee
It involves a reward system containing
compensation and benefits with the intention of Motivating boosting morale & performance
improving performance.
Productivity- ensures happy employees,
Total Rewards Approach/ Model- considers all providing resulting in greater productivity
aspects of a reward; tangible and intangible
elements Equitable fair to all
Tangible Rewards - are monetary in nature and are
more enticing than intangible rewards, but it can be Non- free from prejudices
easily copied by competitors discriminating
Intangible Rewards - enhances tangible aspects and
inspires loyalty while giving satisfaction Sustaining provides for the employee’s needs
and is concerned with their
REMUNERATION welfare. It should also sustain the
organization’s goals & objectives
This is the computation of compensation & benefits,
which is the heart of the HR dept’s responsibilities. Adequate Legal adheres to the law
Compensation - tangible equivalent of work and the Compliance
primary reason why employees look for a job
Direct Compensation - monetary rewards Time-bound should be given on time
Indirect Compensation - benefits such as insurance,
days-off, outings, etc. Inducing induce employees to stay
Loyalty
Common Terminologies
Base Pay fixed and largest component of the Obligatory companies have the obligation to
compensation package. Factors pay their employees well, as
that determine the base pay are indicated by the employment
job-based, skill/competency-based, contract
market-based, or a combination of
the three. No Insecurity The pay should make the
employee feel secure and satisfy
Incentive incentives or bonuses are given to their basic needs
Compensation those who achieve objectives
External Factors ( influencing the compensation plans)
Allowances temporary add-ons to the basic 1. Demand and Supply of Labor
pay ● Highly specialized jobs = higher pay
● Fewer skills = lower salaries
Overtime Pay for work beyond the normal work
hours 2. Prevailing Economic Conditions
If it’s good, there will be satisfying &
Retirement for those have reached compulsory competitive wages.
Benefits retirement age (65 years old) ● High compensation packages may be
provided to keep up with the industry.
Equity for senior executives in the from of (TelCo, Pharmaceuticals, Hotels)
Compensation stock options 3. Government Intervention in Compensation
● Regulations such as price floors (minimum
Perquisites for members of senior wage)
management at the company’s
expense (travel, accommodations, Internal Factors (influencing the compensation
dinner meetings, etc.) plans)
1. Budget
2. Employee Motivation
Criteria for an Effective Compensation Plan 3. Employee Productivity
● An effective way to increase productivity is to
Cost based on the ability of the provide a good compensation package
Containment company to pay
Compensation Strategies Used by Firms 5. Special Surveys
1. Minimum / Average Level ★ Conducted by & focused on a particular
Best for small/medium firms who can only organization
afford minimum wage ★ Much time and effort is needed
2. Above Average Pay
Firms that believe that money is a good Pay and Grade Structures
motivator This enables the creation of a framework that
3. Competitive & Comparable Pay determines the levels of compensation
Involves the use of salary surveys and ➔ Grade Structure - determines the grade
studies hierarchy and job levels depending on difficulty
➔ Pay Structure - different pay levels for jobs
REWARDS ➔ A grade structure becomes a pay structure when pay
This entails deciding on compensations and ranges are attached
methods of payments
Developing Pay and Grade Structures
Job Evaluation Fixed Pay
➔ The process wherein the worth/value of a job is ➔ each grade is associated with a single pay
assessed ➔ Is simple, transparent, and unbiased
➔ Is usually done through employee interviews ➔ Can result in demotivation due to lack of salary
➔ Factors considered to determine the worth/value progression
of a job: skills required, responsibilities of the job, Salary Scales
working conditions, critical decision-making ➔ consists of incremental pay points and
functions of the job. progression
➔ Recognizes additional skills and motivates
Methods of Job Evaluation employees
1. Ranking ➔ Aren’t transparent
● Rank the jobs from simplest to most difficult
2. Grading System If salary scales are chosen, one must choose
● Use a grading system according to the level of between:
job difficulty ➔ Broadbands - more flexible with wide pay bands
3. Point System ➔ Narrowbands - provide comparison between
● Elements of a job are given specific points. jobs, thrive on expertise & experience, and are
How much of each factor is required per job is used for incremental progression
also identified.
● Is trusted more than ranking; more objective Jobs to Grades - job evaluation points are translated
4. Factor System into job grades
● Based on skills, degree of responsibility, Broadbanding -uses very wide grade ranges
physical effort, mental effort, and working
conditions Contingent Pay
This is a pay scheme on top of the base rate linked to
Market Rate Analysis - is popularly used to performance, competency, contribution, skills. It can be
determine job rates. applied to individual & group pay
Sources of Market Rate Data
1. General Published Surveys Individual Pay
★ Are readily accessible & available 1. Pay-for-performance Scheme
★ Are subdivided by location and have a wide ● Good performance is rewarded with a bonus
coverage ● May be subjective; should rely on quality and not
★ Is consistent, allowing trend analysis quantity
2. Online Data 2. Pay-for-competency Scheme
● Encourages competence enhancement
★ Limited, but easy to access and purchase
● Is difficult to assess and ignores output levels
3. Industrial Occupational Surveys 3. Pay-for-contribution Scheme
★ Done by job organizations and trade ● A combination of competence and output levels
associations ● May be difficult to manage
★ Better & more reliable than general surveys 4. Pay-for-skills Scheme
4. Consultant Databases ● Encourages employees to learn more skills
★ Is available upon purchase, but is expensive ● May be expensive due to paying for a skill that is
to obtain unnecessary/ unused
5. Pay for service ◆ Merit Pay (for outstanding performance)
● Paid yearly based on continued service Merit Pay - one-time payment
●
Merit Increase - addition to
●
Group Pay salary
1. Team-based Pay - given to groups who do ◆ Piece Rate Pay (paid per piece)
similar/ related jobs and measured in terms of ◆ Commission (on achieved sales quota)
achievement of a quota ◆ Group Incentive (given to a team that
2. Organization-wide Pay - based on achievement meets a sales target)
of performance/goals. Has two types: 4. Payments based on Skills
a. Gain-sharing ➔ Isn’t popular in the Philippines
Based on a bonus plan where employees can share 5. Payments based on Knowledge/ Credentials
in the financial gains of the company (sales ➔ Continuous learning is a motivation to attend
bonus) seminars and conferences, and this also
b. Profit-sharing improves one’s ranking
Given in the form of cash/shares of stock 6. Executive Payments
➔ For CEOs, chairpersons, or the BOD
Compensation for Special Groups 7. Special Payments
1. Directors/ Executives Pay a. Overtime Pay is based on additional hours
They receive basic salary, incentives & bonuses worked, and doesn’t include COLA
(% of basic salary), and stock options ● +25% of the hourly rate in excess of 8 hours
● +30% if excess is on a rest day/ special day/
2. Sales Staff Pay (4 basic schemes) regular holiday
a. Salary only
b. Salary + commission ( % of sales volume) b. Holiday Pay is payment for an unworked
regular holiday as long as they are present on the
c. Salary + bonus (given when a quota/ objective
workday before the holiday.
is met) ● 200% of daily rate if one works on a regular
d. Commission only (when employee isn’t holiday
involved in non-selling activities) c. Premium Pay is given if one works during rest
e. Other non-cash rewards (transpo days and special holidays
allowances, etc.) ● +30% of the basic pay if either one, +50% if
3. Manual Workers/ Laborers Pay both at the same time
Payments are made through time rates/ flat d. Night Differential Payments is an additional
rates, or also output produced 10% of the basic rate for work between 10PM to
6AM
Common Modes of Payment e. Service Charges :85% of it is given to
1. Payment for time worked employees, 15% goes to management. This is the
➔ Wages are paid on an hourly rate same with tips
➔ Salary is paid on a monthly basis f. Severance / Separation Pay is provided to
those terminated with authorized cause
➔ Monthly Paid are paid each day of a month
● You get half a month’s salary per year of
➔ Daily paid are paid on the basis of the days service if the cause is: retrenchment to prevent
they actually worked further losses, company closure, or employee
➔ Payment for the time worked are adjusted illness which prevents you to work.
based on: ● You get a month’s salary per year of service if
◆ Across-the-board increase (provided the cause is: imposition of labor-saving
to all employees with the same rate, devices, duplicate functions, abolition of a
regardless of rank) department without possible transfer.
◆ Merit increases (on performance) g. Retirement Pay is given to those 60 to 65 years
◆ Cost-of-Living Allowance (COLA) (to old as long as they had 5 years of continuous
cope with the standard of living) service
● You get half a month’s salary per year of
◆ Seniority Pay (based on length of service
service, but overall at least equivalent to 22.5
in the company) days for every year of service.
2. Flat Rates / Collective Bargaining Agreement h. 13th Month Pay is given before Dec. 24 to those
(CBA)-negotiated Rates who have worked for at least a month in a
➔ common to unionized firms calendar year
➔ Doesn’t consider skills & seniority
3. Compensation through Incentives
➔ Is based on output. Most popular forms
include:
RETENTION
Vacation Leaves Group Life Insurance
Non-financial benefits are given to motivate and
Unused days are forfeited Program
promote loyalty. The objectives are: and not carried over to the Benefits are given to
1. Attract & retain highly-skilled/ performing next year beneficiaries in the case of
employees a member’s death
2. Promote commitment and loyalty
3. Fulfill the employees’ needs Bonuses Christmas Party and
Package
Government-mandated Benefits
➔ SSS / GSIS (Government Service Insurance Cash Bonuses Emergency Loan
System)
◆ SSS is for private firms, GSIS is for government Free Uniform or Executive Perquisites
employees Clothing Allowance Also called executive perks,
◆ Both employee & employer pay. The former is given to top management
through salary deduction, while the latter usually
pays higher
➔ Employees’ Compensation Program Chapter 6: E
mployee Relations and Discipline
◆ Given in case of work-related injury, disability,
sickness, or death Employee Relations - balancing employee
➔ Pag-IBIG Benefits satisfaction and productivity
◆ Benefits include housing & salary loans, retirement Policies - labor relations
funds, and total disability benefits Practices - unions and CBAs
➔ PhilHealth Program Prevention - employee violations and disciplinary
◆ Given to all SSS members and their dependents, actions
providing financial assistance for in and
out-patient care
➔ Service Incentive Leave Four Essential Schools of Thought:
◆ All except gov’t employees, managerial 1. Mainstream Economics
employees, and house helpers get 5 days of ● Emphasizes free market competition
service incentive leave with pay as long as they ● Workers are free to resign
have provided at least 1 year of service. ● Unions restrict the supply of labor and threaten
◆ Unused credits may be converted to cash strikes, which slow productivity and output
➔ Maternity Leave levels
◆ For all SSS female members (married or not) 2. Human Resources Management
◆ 60 days for normal delivery/ miscarriage ● Personnel management; better management of
◆ 78 days for caesarean delivery human resources and effective handling of
➔ Paternity Leave employees
◆ For all married male employees in private firms ● If companies have effective HRM programs,
◆ Granted to the first 4 deliveries of the lawful wife workers will not seek unions
◆ 7 days after the wife’s delivery 3. Industrial Relations
➔ Special Leave for Women ● The great bargaining power of employers breed
◆ For female employees with gynecological inequality and is the primary cause of labor
disorders that involve surgical procedures problems
◆ 2 months leave with pay ● Employees can acquire their own power by
forming independent labor unions and collective
Voluntary Benefits bargaining
4. Marxis Industrial Relations
Hospitalization Sick Leaves ● Opposes mainstream economics
● Perpetuates strong militant unions to obtain
better working conditions
Emergency Leaves Summer Outings
POLICIES
Sports Fest Rice Subsidy Covers rules, rights, and procedures to be followed
Providing a monthly sack to maintain harmony
of rice
Employee Relations Framework
Meal Subsidy Shuttle Service This constitutes the main task of employee relations
personnel. The following elements must be present:
Stock Options Profit-sharing Scheme
For those who’ve rendered Portion of the profits are
over 10 years of service divided, regardless of rank
1. Drive for Commitment (to gain loyalty) ➔ Terms and conditions of employment - Policies
2. Harmonization of Terms and Conditions of on how this will be governed by CBAs should be
Employment (efforts of employees & conditions of decided
employment are united) ➔ Employee handbook - company policies should
3. Emphasis on Mutuality (teamwork) be stated and explained
4. Policies and Practices for Communication
(maintaining a harmonious relationship centers on Employee Handbook
communication; it is the solution) ➔ This guides employees on the vision, mission,
values, philosophy, history, policies, disciplinary
Basic Rights of Employees offenses, sanctions, and benefits
1. Equal opportunities for all ➔ It includes the key officers, management
2. Security of tenure - can’t be dismissed without standards and expectations
due process
➔ Employees are expected to sign the
3. Work days and hours - 8 hours is the normal
acknowledgement portion to show that they’ve
number, and they must be paid for all the hours they
worked. In excess, they are entitled to overtime pay read it
4. Wage and wage-related benefits
5. Safe working conditions Employee Voice
6. Rest days and holidays - Rest day is at least a day This is how much “say” employees have. Its
off from work. If they work, they’re entitled to coverage is a whole variety of processes and
holiday pay on these days structures enabling and empowering employees to
7. Leave - three types: service incentive, paternity, contribute to the decision-making power of the
and maternity firm. The forms include:
8. Right to self-organization and collective 1. Little Voice - little/ minimal say
bargaining - right to join any legit workers 2. Some - employees can give suggestions
association, free from employer interference 3. Two way - employees can be consulted
9. Workers’ participation and tripartism - 4. Two way plus - they are consulted in the making
Tripartism is the cooperation of the employees, & implementation of a decision
employers, and government 5. A lot - they have the right to delay a decision
10. Social Legislation - social security benefits 6. Veto power - they have the power to reject/refuse
7. Substantial - they have an equal “say” as
Basic Rights of Employees
management
1. Closure of business - they can close when needed,
such as when bankrupt PRACTICES
2. Transfer of workers - from one dept to another Labor Organization - any union/ association for
3. Hire and fire - only when it arises from just/ collective bargaining of employment conditions.
authorized cause, meaning done after due process
Kinds include:
4. Impose employee discipline
● Independent Labor Union - w/o affiliation to a
5. Issue rules and regulations
national federation
6. Management prerogatives - there's leeway to ● Legitimate Labor Organization - registered
administer company affairs to maximize profits with the Bureau of Labor Relations
● Company Union - is unlawful since it is
Employee Policies
manipulated by the employer
The objective of this is to build a positive workforce ● Federation and National Union - a group of
and conducive workplace wherein all employees unions in an industry or area
maintain good relations with each other with top ● Trade Associations - formed by self-employed
management. They are covered by: individuals and those without definite employers
➔ Union Recognition - the company decides which or company affiliations
union represents the employees
➔ Collective Bargaining - the company should Individuals Eligible to Join/Form Labor Orgs
formulate policies of the coverage of CBAs 1. Rank-and-file employees
➔ Procedures on grievance handling and 2. Supervisory employees with their own union,
discipline - these should be formulated and not with rank-and-file unions
implemented 3. Government employees in civil service
➔ Communication policies - there should be 4. Employees of government corporations
policies that allow employees to voice out their 5. Aliens in the PH with valid employment
concerns and grievances permits, if they are nationals of a country
that has the same privileges, can join/assist
but not form labor organizations
Individuals Not Eligible to Join/Form Labor Orgs Forms of Strike
1. Managerial employees - the nature of their 1. Legal
work involves policy-making and implementation 2. Illegal
2. Subversive Organizations and their members 3. Economic - to compel employers to provide
-those engaged in rebellious seditious activities wages and economic concessions not required by
3. Employees of cooperatives - since they’re also law
members, they’re part-owners and cannot 4. Unfair Labor Practice Strike - include
bargain. However, this doesn’t apply if the violations of the CBA and union busting
employee is not a member/ co-owner 5. Slow-down Strike - not abandoning, but
4. Employees exempted from being union reducing their work output
members -
those who have access to confidential 6. Wildcat Strike - without formal filing of required
information that may be advantageous to the notice and majority approval
labor organization (accounting, radio & telegraph, 7. Sit-down Strike - stops working, but doesn’t
secretarial personnel) leave work areas
Collective Bargaining - the negotiation of certain Settlement of disputes - duty of labor conciliators to
T&C’s to enable workers to bargain more call the concerned parties after 48 hours
persuasively on the improvement of their working immediately upon valid notice for a strike/ lockout
conditions. Industrial peace & harmony is achieved if Picketing - protest outside the workplace that
it is done through friendly and fair dialogue should be done without intimidation, violence, or
Collective Bargaining Agreements (CBAs) - have a coercion
5-year effectivity. Other provisions must be National Labor Relations Commission - has the
renegotiated within 3 years of execution, and power to issue temporary injunctions/ restraining
enacted within 6 months from the date of expiry. orders, but cannot prevent peaceful picketing. The
These will be retroactive immediately after said date. President/ Secretary of Labor can give
Deadlock - when the contents of the provisions return-to-work orders when the work is of national
cannot be agreed on interest.
Unfair Labor Practice (ULP) - violates the rights of
the employees to self-organization PREVENTION
Union Busting - a form of ULP wherein militant The company’s ability to avert anything that could
union leaders are illegally dismissed tarnish their employee relationship, and to impose
discipline among its employees
A strike or lockout is valid on the grounds of bargaining
deadlock, ULP, and union busting. Employee Code of Conduct
This defines acceptable behavior, and an employee
Strike - temporary employee work stoppage, which must sign their acceptance as a legal agreement
includes sit-down strikes, slow-down strikes, and between them and the company. Common contents
mass leaves include:
Lockout - employer’s call to replace union members 1. Prohibition of illegal activities
with non-union employees 2. Prohibition of discrimination
3. Sexual harassment
Requirements for a strike/ lockout 4. Confidentiality expectations
5. Dress code and appearance
1. Notice must be filed with DOLE at least 15 days
6. Punctuality and absenteeism
before the staging of a strike/lockout, and 30 7. Procedures for sick and emergency leaves
days in the case of a bargaining deadlock 8. Sanctions for each violation
2. Strike should be supported by majority members.
Lockout should be supported by a majority of Objectives include:
management/ BOD via a secret meeting 1. To maintain peace & harmony
3. Vote should be reported to DOLE at least 7 days 2. To avoid litigation and lawsuits
before the intended event 3. To promote teamwork & transparency
4. In case of union busting, the union may take
action immediately
5. Non-compliance will render it illegal
Employee Discipline Three Types of Grievances
It enables employees to conform to standards, and 1. Factual -
based on facts or reality
corrects/ punishes them when rules are violated. 2. Imaginary - caused by misinterpretation of a rule
Common violations include: 3. Disguised - caused be pressure from the
● Personal habits of employees - those that may employee’s family and friends, or from a heavy
affect productivity, like tardiness & intoxication heart. (see example from book)
● Incompetence - non-performance of assigned
duties
● Misconduct - fraud, deceit, sleeping on duty, Classification of Grievances and Their Causes
sexual harassment Refer to Table 9, p.181
Positive Discipline - encourages participation by Grievance Handling in the Union
allowing employees to willingly conform. It applies In CBAs, a problem is “grievable” if some provisions
reason in the achievement of company objectives are not implemented. Grievance Handling is the
and allows self-expression. process of solving conflicts between a union member
The approach is as follows: and the management. They include the following:
1. Identify the problem - root cause ● CBA violations
2. Analyze the severity of the problem ● Violations of labor laws & occupational
3. Discuss the problem - including how it affects the health and safety standards
employee and the solution ● Unjust labor practices
4. Document the discussion - for easy follow-up ● Violations of union policies
5. Follow up on the correction - after an agreed time
General Grievance Handling Procedure
Negative Discipline - focuses on punishment 1. Interview - of those involved
(demotion, suspension, termination) and is used in 2. Investigation - interrogation of witnesses
severe forms of employee violation 3. Research and Documentation - legal research
4. Counseling
The Disciplinary Process 5. Drafting of necessary papers - position papers,
1. Identify the violator testimonies, and formal complaints
2. Identify the violation 6. Hearing
3. Consult the head/supervisor and make an 7. Settlement - whatever agreed upon must be
initial assessment documented in the minutes of the meeting. If not
4. Set a meeting with the head/supervisor settled, a third-party conciliation is done
5. Set a meeting with the above & the employee
6. Accord the employee due process Conciliation - a mild form of intervention by a
7. Plan and discuss the corrective action with neutral third party wherein the conciliator keeps the
the head/supervisor discussions calm and going
Mediation - mild intervention by a neutral third
Due Process of Law - encompasses all other party wherein the mediator starts advising and
employee rights, ensuring a fair hearing regarding offering solutions
their violation or a management decision. It provides
an objective investigation of the case, and allows Progressive Discipline - the most popular approach
management to impose disciplinary action. in implementing discipline, which promotes fairness
in handling cases and preventing lawsuits. Steps are:
Employee Grievances - any discontent, whether 1. Oral reprimand
expressed or not, valid or not, arising out of 2. Written warning
anything connected to the company which the 3. Final written warning or Suspension
employee finds unfair 4. Termination
Dissatisfaction - mental or emotional disturbance
which may or may not be expressed Hot-Stove Rule - immediate, impersonal, and
Complaint - spoken or written dissatisfaction that is consistent disciplinary actions. Characteristics are:
brought to a supervisor’s attention 1. Immediate
Grievance - formally presented to management or a 2. Consistent
union official 3. Impersonal
4. Early warning and notice
Chapter 7: Career Management ● Management should provide support and
guidance in career planning
This is ensuring that the organization has a steady 4. Self-Assessment Programs
flow of talent and can achieve its goals by developing ● Helps employees determine their career goals
their employees’ abilities and careers. It makes sure 5. Development Programs
the company retains people with talent ● Employees usually turn to their immediate
supervisors, who will give career advice
Career Management Framework ● Portfolio Career - people will change the
1. Career Management Policies direction of their careers during their
The company decides how often and to what working life
extent it’ll use the following internal moves: ● Protean Career - employees take
a. Promotion responsibility for their career paths
● This boost employee morale as they ● Career Anchors - employees’ own concept of
assume greater responsibility and their talents and abilities, and motives
authority for higher salaries and benefits related to their careers
● Plateaued Employees are those who will 6. Succession Planning
no longer advance in their careers ● An integrated approach of identifying
b. Demotion employees who will fill key areas, and honing
● Employees can be depressed and those employees’ skills
inefficient, so some companies just
discharge or transfer the employee Career Anchors
● It is caused by structural changes, 1. Technical and/or Functional Competence
disciplinary action, or employee inability They like to be challenged and to use their skills to
c. Transfer become experts. They may reject management
● It takes 9 months to adjust after a positions because they don’t want to stop
practicing their specialties. They want to be
promotion or transfer
appreciated for their technical skills.
● A lateral transfer requires 7.8 months 2. General Managerial Competence
d. Separation They like to solve problems, make decisions, and
● Termination may be traumatic, and old influence others. They feel satisfied with the
people who are laid off may take a longer general managerial position
time to get another job 3. Autonomy or Independence
● Retirement Age is 60 to 65 years old, and They like to work alone and become consultants or
some retirees may return to work as independent businesspeople
consultants 4. Security and Stability
● Resignation is when an employee quits. They like a stable and secure job, and will look for
a company that’ll make them economically stable
Types of resignees include:
5. Entrepreneurial Creativity
○ Impulsive quitters - resign on the spot
They’ll be fulfilled with creative efforts, and want
without planning what’s next for their something creative and innovative
career
6. Service and Dedication to a Cause
○ Comparison quitters - resign due to
7. Pure Challenge
better alternatives; they hold no bitter
feelings They get satisfaction from winning over
competitors
○ Pre-planned quitters - they can’t be
8. Lifestyle
prevented since they’ve already planned it
They want a balance between family and career,
○ Conditional quitters - leaves as soon as
and want jobs that jibe with their lifestyle
there’s a job offer that meets their
conditions
MAINTENANCE
2. Talent Audits This is where loyalty to the company is nurtured by
● The review of the talent pool available keeping employees satisfied all the time
3. Career Planning
● Defining the career path of people in the Career - one’s pattern of activities during their work
organization life. Stages are:
● Systematic matching of career goals, ➔ Formation Stage (the moment they get hired;
21-28 years old)
employee capabilities and opportunities to
➔ Enterprising Stage (when the employee sells
achieve them
their skills well, or pursue a master’s or graduate
● Career Ladder is a sequence of jobs with degree; 28-35 years old)
increasing levels of responsibility
➔ Maintenance Stage (marked by many Succession Planning - the structured approach of
achievements and recognitions, with the best of identifying, developing, and retaining employees to
both work and family life; 35-42 years old) fill key areas. The key principles are:
➔ Mid-Career Stage (mid-career crisis; there may ● It’s aligned to company objectives
be dissatisfaction with psychological or emotional ● It’s not limited to executive positions
conflicts; 42-48 years old) ● It ensures a pool of talents for key positions
➔ Fulfillment Stage (contemplation of retirement; ● A process that’s fair, well-communicated, and
48-60 years old) transparent
● It’s monitored and the progress is evaluated
MOTIVATION
Wherein the individual carers of employees are well Succession Planning Steps:
managed 1. Identify key areas and positions - key
positions are those critical to the strategic
Career Planning - the process of selecting career objectives of the organization
targets and paving the path to them. The company 2. Identify capabilities for the above -
identification of knowledge (information that
must provide growth opportunities until retirement.
allows a person to successfully perform a task),
It is the process of matching career goals and skills (level of proficiency), and abilities
individual capabilities with opportunities for their (enduring capacity to perform a task)
fulfillment. Steps include: 3. Identify employees who have potential for
1. Self-Assessment (a personal assessment of these key positions - the purpose is for these
one’s interests, skills, characteristics, and values) employees to acquire the needed skills once the
2. Exploration and Research (the company positions are available
provides a career path for every position, which 4. Develop and implement succession plans -
identifies the career opportunities available) they can be given assignments beyond their
3. Decision-Making (career goals are formulated) current abilities, or temporarily assume a key post
4. Taking Action (bridging of individual career if the incumbent is absent
goals with the prepared development programs) 5. Evaluate effectiveness - monitor the efforts and
5. Evaluation (a necessary periodic review to keep make adjustments when needed
track of the employee’s career progress)
MEASUREMENT
SODI Career Planning Model - a simple model of The ultimate measure is the feeling of satisfaction
career education with four concepts: and fulfillment. The company should be satisfied
1. Self-Awareness ( awareness of one’s skills, with the employee’s performance, the employee
petentials, and competencies) should be satisfied with their long stint in the
2. Opportunity Awareness (includes career company
possibilities and opportunities)
3. Decision-making and Planning (how to make
career decisions and an awareness of work
pressures and influences)
4. Implementing Plans (making it a reality)
Career Counseling - The process of helping
employees develop their careers. There are six
personality types:
1. Realistic - likes to work with animals, tools, or
machines. Dislikes social activities. Are technical
in nature
2. Investigative - like studying and solving
math/science problems. They’re precise and
intellectual
3. Artistic - like creative activities, dislike repetitive
or routine activities
4. Social - like helping others, avoids machines/
tools
5. Enterprising - likes selling products and
persuading people. They avoid analytical thinking
and are sociable and ambitious
6. Conventional - like to work with numbers and
machines; are systematic and orderly
You might also like
- HDFC Ergo Policy Renewal 2023 SelfDocument5 pagesHDFC Ergo Policy Renewal 2023 SelfGopivishnu KanchiNo ratings yet
- A - Level Project Work Insights & ReflectionsDocument3 pagesA - Level Project Work Insights & ReflectionsKou Uraki0% (1)
- Handjobs Mag 2010 SeptDocument84 pagesHandjobs Mag 2010 SeptGeorge Sy25% (12)
- Brand ArchetypesDocument14 pagesBrand ArchetypesCristina Crong MorgiaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On RTS Juice PlantDocument7 pagesProject Report On RTS Juice PlantEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Science NotesDocument19 pagesForm 1 Science NotesQQLove93% (14)
- Compensation Administration ReviewerDocument26 pagesCompensation Administration ReviewerprivsobelNo ratings yet
- Employee CompensationDocument9 pagesEmployee CompensationHemant AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Employee Compensation GuideDocument4 pagesHuman Resource Management: Employee Compensation Guideaqsa goharNo ratings yet
- Employee Compensation and Reward ManagementDocument4 pagesEmployee Compensation and Reward ManagementPrabhat AcharyaNo ratings yet
- CHP 8 - Compensation - BenefitDocument18 pagesCHP 8 - Compensation - BenefitFarah FarhathunNo ratings yet
- Compensation & Benefits SessionDocument65 pagesCompensation & Benefits Sessionahmed HammoudNo ratings yet
- HRM FinalDocument15 pagesHRM FinalAshhab NasimNo ratings yet
- CompensationDocument20 pagesCompensationKashif AnwerNo ratings yet
- G11 Org. MNGT Q2WK11 ABCDwithAnswerKeyDocument9 pagesG11 Org. MNGT Q2WK11 ABCDwithAnswerKeyMelanie Anaud Magro-AmosNo ratings yet
- CompensationDocument14 pagesCompensationAshrafulNo ratings yet
- CompensationDocument64 pagesCompensationDr. A John WilliamNo ratings yet
- Bda - Employee Pay and Rewards - Aug 13Document9 pagesBda - Employee Pay and Rewards - Aug 13drayeshanaseemsiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Compensating Human ResourcesDocument27 pagesChapter 8 Compensating Human ResourcesFaye YburanNo ratings yet
- Reward Management SystemDocument17 pagesReward Management SystemSiya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Compensation/wages and Performance Evaluation/appraisal: Group 3Document18 pagesCompensation/wages and Performance Evaluation/appraisal: Group 3Ellen BuddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-8Document6 pagesLecture 6-8kerynsantos026No ratings yet
- COMPENSATIONDocument19 pagesCOMPENSATIONkerynsantos026No ratings yet
- Compensation ManagementDocument32 pagesCompensation ManagementUrvi DodejaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource 08Document28 pagesHuman Resource 08Mainul HossainNo ratings yet
- Handout Slides Chapter 11Document12 pagesHandout Slides Chapter 11Sallu KabiaNo ratings yet
- Compensation Is Any Form of Payment Given To TheDocument24 pagesCompensation Is Any Form of Payment Given To TheRaghu Kishore SasanalaNo ratings yet
- Report Compensation BenefitsDocument21 pagesReport Compensation BenefitsmakNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 9 ReviewerDocument5 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 9 ReviewerNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- 20n71e0026-Evaluation of Wages and Salary AdministrationDocument16 pages20n71e0026-Evaluation of Wages and Salary Administrationsmartway projectsNo ratings yet
- HBO Chapter VI - Appraising and Rewarding PerformanceDocument53 pagesHBO Chapter VI - Appraising and Rewarding PerformanceDorisday Caballes EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- PSYINDUSTRIALDocument10 pagesPSYINDUSTRIALGerilyn SarileNo ratings yet
- Krystel Ann Tanawon BSCADocument1 pageKrystel Ann Tanawon BSCAChristelle Kaye BisnarNo ratings yet
- Financial and Non-Financial Rewards ActivityDocument3 pagesFinancial and Non-Financial Rewards ActivityAldrin CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Compensation Management: Examples of Financial & Non-Financial CompensationDocument21 pagesUnit 4 Compensation Management: Examples of Financial & Non-Financial CompensationRehan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Topic 8-11-SDocument66 pagesTopic 8-11-SsteyvohmannaNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - SPM - SISTEM PENGUKURAN KINERJA DAN KOMPENSASI MANAJEMENDocument8 pagesGroup 6 - SPM - SISTEM PENGUKURAN KINERJA DAN KOMPENSASI MANAJEMENHeli MamontoNo ratings yet
- Recognizing Employee Contribution With Pay & Employee BenefitseDocument15 pagesRecognizing Employee Contribution With Pay & Employee BenefitseNadya Jerrino100% (1)
- HRM 9 and 10Document37 pagesHRM 9 and 10kwamecalculusNo ratings yet
- 10 - Compensation ManagementDocument24 pages10 - Compensation ManagementTayyab AliNo ratings yet
- Week012 Staffing2Document9 pagesWeek012 Staffing2Joana MarieNo ratings yet
- Compensating People: DR Vaneeta AggarwalDocument42 pagesCompensating People: DR Vaneeta AggarwalJaya PradeepNo ratings yet
- Unit VI: Compensation Management: StructureDocument27 pagesUnit VI: Compensation Management: StructureOdirile MasogoNo ratings yet
- 5 Compensation and Reward ManagementDocument3 pages5 Compensation and Reward ManagementHeirron LugueNo ratings yet
- L11 StrategicPayPlanandIncentivePlansDocument57 pagesL11 StrategicPayPlanandIncentivePlansChíi KiệttNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Compensating HRDocument50 pagesChapter 8 Compensating HRarantonizhaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Compensation and Benefit ManagementDocument37 pagesHuman Resource Management: Compensation and Benefit Managementankesh_devNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Pay For PerformanceDocument29 pagesChapter 9 - Pay For PerformanceAnonymous Io54FfF0S100% (1)
- Human Resource Management 14 Edition Chapter 9 & 10 CompensationDocument43 pagesHuman Resource Management 14 Edition Chapter 9 & 10 CompensationTanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our PresentationDocument21 pagesWelcome To Our PresentationArafatNo ratings yet
- Compensation Management - Session 1Document17 pagesCompensation Management - Session 1IrfaN TamimNo ratings yet
- Module 6 (Chapter 25)- Executive Performance Measures & CompensationDocument16 pagesModule 6 (Chapter 25)- Executive Performance Measures & Compensationpia8mmNo ratings yet
- Motivation in PracticeDocument2 pagesMotivation in Practiceabrar mahir SahilNo ratings yet
- Incentive SchemesDocument6 pagesIncentive SchemesCharlien LabangcopNo ratings yet
- Compensation HRMDocument27 pagesCompensation HRMAkshat SinghNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8: Compensating Human ResourcesDocument41 pagesCHAPTER 8: Compensating Human Resourcesshane50% (2)
- Com Ben T & D - HboDocument5 pagesCom Ben T & D - Hbo22-72418No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document30 pagesChapter 9Iez LinNo ratings yet
- Compensation and BenefitsDocument58 pagesCompensation and BenefitsSushmaNo ratings yet
- Compensation ManagementDocument56 pagesCompensation ManagementShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Business Financial Motivators TableDocument3 pagesBusiness Financial Motivators TabledarwisyNo ratings yet
- Compensation and Benefits Compensation and BenefitsDocument34 pagesCompensation and Benefits Compensation and BenefitsKirti ShivakumarNo ratings yet
- Employee Compensation PlanDocument17 pagesEmployee Compensation PlanInquisitor SultanNo ratings yet
- CompensationDocument55 pagesCompensationJeeta Sarkar100% (1)
- Model Answer: Literature review on Employee motivation, rewards and performanceFrom EverandModel Answer: Literature review on Employee motivation, rewards and performanceNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 - Morgia - March 9, 2022Document2 pagesQuiz 4 - Morgia - March 9, 2022Cristina Crong MorgiaNo ratings yet
- Econ FinalsDocument7 pagesEcon FinalsCristina Crong MorgiaNo ratings yet
- SOEN Chapter 1-6 Lecture NotesDocument34 pagesSOEN Chapter 1-6 Lecture NotesCristina Crong MorgiaNo ratings yet
- Higher Productivity Means Higher Standard of Living: Chapter 1: Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument4 pagesHigher Productivity Means Higher Standard of Living: Chapter 1: Ten Principles of EconomicsCristina Crong MorgiaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control Basic Course: Exercises 2021Document124 pagesAutomatic Control Basic Course: Exercises 2021Duc-Duy Pham NguyenNo ratings yet
- 2442 4348 2 PBDocument8 pages2442 4348 2 PBdev iNo ratings yet
- NT TR 459 - Guideline For The Validation of Functional Safety According To IEC 61508 - Nordtest Technical ReportDocument54 pagesNT TR 459 - Guideline For The Validation of Functional Safety According To IEC 61508 - Nordtest Technical ReportManish MehtaNo ratings yet
- Trial Salary SlipDocument5 pagesTrial Salary SlipTvs12346No ratings yet
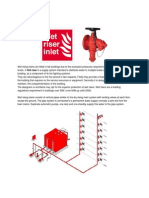
- Wet RisersDocument3 pagesWet RisersNur Amirah Abdul JamilNo ratings yet
- A Review On Ultra High Performance Concrete Part II. Hydration, Microstructure and Properties PDFDocument10 pagesA Review On Ultra High Performance Concrete Part II. Hydration, Microstructure and Properties PDFNocifLyesNo ratings yet
- Criticism Herzberg TheoryDocument3 pagesCriticism Herzberg TheoryCaroline NerbasNo ratings yet
- Class 11 English Notes Studyguide360Document272 pagesClass 11 English Notes Studyguide360IsnatainiNo ratings yet
- Wear Solutions BrochureDocument16 pagesWear Solutions BrochureOkan KalendarNo ratings yet
- Altitude, Cloud Cover and LatitudeDocument64 pagesAltitude, Cloud Cover and LatitudeIsarra AmsaluNo ratings yet
- Sago Pudding - Recipes - Poh's KitchenDocument2 pagesSago Pudding - Recipes - Poh's KitchenXuxu TooNo ratings yet
- BWT - HandbookDocument16 pagesBWT - HandbookDarko DuiloNo ratings yet
- Natural Rubber WikiDocument9 pagesNatural Rubber WikiMyra Wardati SNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Primary Sources: Books:: Marie-Curie-Speech - HTMLDocument11 pagesBibliography Primary Sources: Books:: Marie-Curie-Speech - HTMLapi-130099490No ratings yet
- Group3 Dilemmac pr6031Document8 pagesGroup3 Dilemmac pr6031api-576539858No ratings yet
- T N M M T N M M: HE EW Essies Anual HE EW Essies AnualDocument8 pagesT N M M T N M M: HE EW Essies Anual HE EW Essies AnualMunna100% (1)
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument43 pagesEmotional IntelligenceMelody ShekharNo ratings yet
- Bicycle ProjectDocument4 pagesBicycle Projectgaming channelNo ratings yet
- Silvestres Grupo 5Document39 pagesSilvestres Grupo 5Juliana DiazNo ratings yet
- Distribution Network of Coca-ColaDocument16 pagesDistribution Network of Coca-ColaRahul panditaNo ratings yet
- VBIED Attack July 31, 2007Document1 pageVBIED Attack July 31, 2007Rhonda NoldeNo ratings yet
- Riko Technical Brochure PDFDocument29 pagesRiko Technical Brochure PDFGrigoreOzonNo ratings yet
- Compact Evaporators: New Buffalo Trident GaccDocument16 pagesCompact Evaporators: New Buffalo Trident GaccPreeti gulatiNo ratings yet
- Gothic Arch Tracing PDFDocument9 pagesGothic Arch Tracing PDFSimran SahniNo ratings yet
- FEEDS and FEEDING - FEED FORMULATIONDocument55 pagesFEEDS and FEEDING - FEED FORMULATIONJane LabradorNo ratings yet