Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Dynamic and Adaptable City: Travel Choices Will Be Guided By
A Dynamic and Adaptable City: Travel Choices Will Be Guided By
Uploaded by
Vedant HingmireOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Dynamic and Adaptable City: Travel Choices Will Be Guided By
A Dynamic and Adaptable City: Travel Choices Will Be Guided By
Uploaded by
Vedant HingmireCopyright:
Available Formats
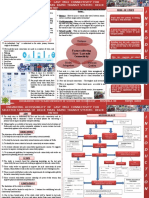
AJAY D-18 | YASH D-20 | PRATIK F-24 |
M E L B O U R N E , A U ST RA L I A PRADYUMNA G-26 | VEDANT-28
CHALLENGES The most space-efficient modes
A DYNAMIC AND Major project disruption
also produce the least emissions
ADAPTABLE CITY The benefits and risks of emerging technology are unclear.
Transport emissions are increasing and electric vehicles are not yet the
Melbourne is the capital and most-populous city of the Australian
state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in Australia. solution.
The city is focused around a central city, Greater Melbourne’s area Recharging requirements of electric cars.
of approximately 9900 km² of suburbs.
Transport inequality.
The City of Melbourne has a well established strategic direction
to create a city that puts people first and is connected and sus-
tainable.
Melbourne is a hub for intercity, intracity and regional travel.
OPPURTUNITIES
Public transport forms a key part of the transport system. Driverless cars could one day change cities
Melbourne is a busy regional transport hub for the statewide pas-
senger rail network. A forecast decline of road-related revenue
Transport pricing which doesn’t manage demand
Melbourne’s central city has the largest concentration of Victo-
ria’s key economic, social and cultural assets. It is the Centre of Road funding
the state’s transport network.
Protect and improve urban amenity as
REDUCED DELAY FOR PEOPLE USING driverless car technology develops.
EFFICIENT TRANSPORT An increased risk for vulnerable road users (for example, in the event of an ac-
Optimize traffic signals to reduce waiting times cident the vehicle protects the driver first, potentially risking the lives of others)
New or additional obligations for existing road users to protect themselves from
Reduce travel times and increase reliability of trams and buses automated vehicles
Increased congestion, rat-running or empty vehicles circulating the streets
Reduce incidences of vehicles blocking intersections to prevent
Any reduction to the permeability of the walking environment, such as additional
delays to all modes
fencing.
EQUITABLE AND EFFICIENT TRANSPORT
TRANSPORTATION MAP PRICING
NIGHT TRAIN NIGHT TRAM NIGHT BUS The way we pay for Transport will ensure an equitable and effi-
cient system which manages transport demand and reduces con-
gestion.
Travel choices will be guided by :-
Price to influence the number of trips.
At what time of day.
The route and the transport mode.
How do people pay
TRAM METRO NIGHT RIDER
for transport ?
Registration, licensing and fu-
SOURCES:
https://www.melbourne.vic.gov.au/Pages/home.aspx
Fairs based on travel distance,
discounts- concession fares
https://assets.weforum.org/article/image/imDJ_EHS4Nnm4-d1RmQRfrjxIV2-Zp1-o_gkkixGcSg.jpg
https://www.britannica.com/place/Melbourne
https://www.australia.com/en-in/places/melbourne-and-surrounds/guide-to-melbourne.html
https://youtu.be/mSwWS_r6u1I
Fares included in daily goods.
https://www.visitmelbourne.com/Information/Getting-here-and-around/Public-transport
You might also like
- Proposed Intermodal TerminalDocument65 pagesProposed Intermodal TerminalArchito Ilot100% (1)
- Tim Hortons - Market EntryDocument18 pagesTim Hortons - Market EntryParas KatariaNo ratings yet
- Simplified CHSP For Two Storey Residential HouseDocument5 pagesSimplified CHSP For Two Storey Residential HouseMark Roger Huberit IINo ratings yet
- Tao Zhu Yin YuanDocument14 pagesTao Zhu Yin YuanVedant HingmireNo ratings yet
- Yellow Book: Presented by-H.V.Sithuruwan Fernando (Engineering Cadet)Document24 pagesYellow Book: Presented by-H.V.Sithuruwan Fernando (Engineering Cadet)piliyandalaleosNo ratings yet
- 52R 06Document14 pages52R 06Showki Wani100% (1)
- Exam 1 ReviewerDocument6 pagesExam 1 ReviewerGriffin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Umesh Sharma - TransEng.AssignmentDocument1 pageUmesh Sharma - TransEng.AssignmentUmesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Highway Engineering NotesDocument7 pagesHighway Engineering NotesYna MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Cost Benefit Analysis of Railway Electrification Case Study For Cairo Alexandria Railway Line PDFDocument12 pagesCost Benefit Analysis of Railway Electrification Case Study For Cairo Alexandria Railway Line PDFPABLO MAURONo ratings yet
- Gestion Du Trafic en Milieu Urbain - Web - Planches - ENDocument15 pagesGestion Du Trafic en Milieu Urbain - Web - Planches - ENMai Anh ThưNo ratings yet
- Multi Modal Interchange Hub: at RourkelaDocument63 pagesMulti Modal Interchange Hub: at RourkelaAr Nizya NoushadNo ratings yet
- Public Bus Accessibility and Its Implications in Energy and Environment: A Case Study of Kathmandu ValleyDocument8 pagesPublic Bus Accessibility and Its Implications in Energy and Environment: A Case Study of Kathmandu ValleyAmul ShresthaNo ratings yet
- BRT Tod Design BookletDocument67 pagesBRT Tod Design BookletAnoosha MansoorNo ratings yet
- Week 1 (Introduction To Highway and Railroad Engineering)Document10 pagesWeek 1 (Introduction To Highway and Railroad Engineering)Glenn PaaNo ratings yet
- Envision Utah Envision Utah: Submitted By: Aseem Arnav Tessy Varkey Vinay Kumar AryanDocument9 pagesEnvision Utah Envision Utah: Submitted By: Aseem Arnav Tessy Varkey Vinay Kumar AryanAseem ArnavNo ratings yet
- RUC Congestion Charging Pricing ENDocument24 pagesRUC Congestion Charging Pricing ENJuangga FarrizNo ratings yet
- The Kampala Mobility News Bite: Entambula YoDocument3 pagesThe Kampala Mobility News Bite: Entambula YoKISENYI RONALDNo ratings yet
- ARPL1010A 2023+Transport+LectureDocument20 pagesARPL1010A 2023+Transport+Lecturebbtrdxtq6zNo ratings yet
- Avoid Shift Improve - ENDocument2 pagesAvoid Shift Improve - ENAIILSG SataraNo ratings yet
- MageeanDocument16 pagesMageeanKerimcanNo ratings yet
- Ropeways in Urban TransportDocument20 pagesRopeways in Urban TransportbbkbkukbNo ratings yet
- Transportation System Operation: By: Engr. Kristelle Ann V. Ginez, MECEDocument52 pagesTransportation System Operation: By: Engr. Kristelle Ann V. Ginez, MECEKristelle GinezNo ratings yet
- Urban - Air - Mobility - Insights - Into - Potentials - and - Challenges: DesafiosDocument6 pagesUrban - Air - Mobility - Insights - Into - Potentials - and - Challenges: DesafiosLeonardo Simas DuarteNo ratings yet
- Tramways in Urban Areas: An Overview On Safety at Road IntersectionsDocument11 pagesTramways in Urban Areas: An Overview On Safety at Road IntersectionsMahdi kobeNo ratings yet
- PTE - Module 2Document4 pagesPTE - Module 2chavezjuliajaffaNo ratings yet
- Smart Green Brochure 2019 - en VersionDocument12 pagesSmart Green Brochure 2019 - en VersionLucia KarollNo ratings yet
- Reviewer HWDocument7 pagesReviewer HWSharline BerjuegaNo ratings yet
- PTV Vision Traffic Suite Innovation - 2018Document42 pagesPTV Vision Traffic Suite Innovation - 2018Saduddin NsNo ratings yet
- Gis Based Advanced Traveler Information System For Hyderabad Cit PDFDocument9 pagesGis Based Advanced Traveler Information System For Hyderabad Cit PDFMeet JaniNo ratings yet
- Urban Transportation Planning: Topic:IntroductionDocument14 pagesUrban Transportation Planning: Topic:IntroductionSesay AlieuNo ratings yet
- Wireless Detection of End-To-End Passenger Trips On Public Transport BusesDocument8 pagesWireless Detection of End-To-End Passenger Trips On Public Transport BusesataNo ratings yet
- Distance Distance: I N T R O D U C T I O NDocument3 pagesDistance Distance: I N T R O D U C T I O NMoushila DeNo ratings yet
- Urban Mobility: UNTIL 2050 UNTIL 2050Document2 pagesUrban Mobility: UNTIL 2050 UNTIL 2050Lánczos NorbertNo ratings yet
- 10415-Article Text PDF-32578-2-10-20180221 PDFDocument7 pages10415-Article Text PDF-32578-2-10-20180221 PDFanon_532474481No ratings yet
- GIZ SUTP FS Non Motorised Transport Policy in India enDocument4 pagesGIZ SUTP FS Non Motorised Transport Policy in India ensuranjanacNo ratings yet
- Transportation - IIIDocument2 pagesTransportation - IIITamim Ahmed Sakib B-81, R-112No ratings yet
- Towards Sustainable Urban Transportation Case Studies: R. M. R. HusseinDocument9 pagesTowards Sustainable Urban Transportation Case Studies: R. M. R. HusseinModeresa GopalNo ratings yet
- 06 Activity 1Document3 pages06 Activity 1andrea malazarteNo ratings yet
- Bus Rapid Transit System in Madurai Terminuses: R.ManimalaDocument9 pagesBus Rapid Transit System in Madurai Terminuses: R.Manimalasenthur kumarNo ratings yet
- TSTC A Way Forward CPreport 1.4.18 MediumDocument12 pagesTSTC A Way Forward CPreport 1.4.18 MediumSiska Riantini ArifNo ratings yet
- Road User Effects Related To Pavement Degradation Based On The HDM Tools (Mikolaj, 2019)Document9 pagesRoad User Effects Related To Pavement Degradation Based On The HDM Tools (Mikolaj, 2019)Mario SolanoNo ratings yet
- CH 25Document27 pagesCH 25Sujit MalikNo ratings yet
- Notes Transport PlanningDocument6 pagesNotes Transport PlanningFatimahHamidNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Transport + TSM + TDMDocument64 pagesSustainable Transport + TSM + TDMAshabul KahfiNo ratings yet
- Choices: A. Traffic Congestion and Parking DifficultiesDocument3 pagesChoices: A. Traffic Congestion and Parking DifficultiesgailNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - 22Document7 pagesLecture 9 - 22Hussein OmranNo ratings yet
- Seoul Transportation 2030Document53 pagesSeoul Transportation 2030First Sem Integrated BatchNo ratings yet
- Frida Youssef-UnctadDocument12 pagesFrida Youssef-Unctadlilikwbs9334No ratings yet
- Sustainable Urban Transport: Avoid-Shift-Improve (A-S-I) : iNUA #9: Implementing The New Urban AgendaDocument4 pagesSustainable Urban Transport: Avoid-Shift-Improve (A-S-I) : iNUA #9: Implementing The New Urban AgendaHeymar AndresNo ratings yet
- Bce - Mass TransportationDocument13 pagesBce - Mass Transportationtawkaya68No ratings yet
- Presentation The French Dis Case StudyDocument20 pagesPresentation The French Dis Case StudyezzatNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 14 02915 v2Document16 pagesSustainability 14 02915 v2Mihai AndreiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - TransportationDocument6 pagesLesson 1 - Transportationdummya790No ratings yet
- Sustainable Non-Motorized Transport For GaRankuwa and Rossylyn Transport Corridor, City of Tswane, South Africa - Icadi16pp281-288Document8 pagesSustainable Non-Motorized Transport For GaRankuwa and Rossylyn Transport Corridor, City of Tswane, South Africa - Icadi16pp281-288ADEYEMI ADEBOJENo ratings yet
- Urban Transport Planning: Piter BiswasDocument22 pagesUrban Transport Planning: Piter BiswasIhsanullahNo ratings yet
- Appendix: Transportation AnalysisDocument42 pagesAppendix: Transportation AnalysisM-NCPPCNo ratings yet
- Sustainability: Avoid, Shift, Improve ExternalitiesDocument1 pageSustainability: Avoid, Shift, Improve ExternalitiesJose Antonio Rodriguez AgredaNo ratings yet
- Executive Sum. A (Tarlac Terminal and Commercial Complex)Document2 pagesExecutive Sum. A (Tarlac Terminal and Commercial Complex)M.E .CNo ratings yet
- Transafrica - Efforts To Improve Public Transport in Africa - Smart Cities Dive2Document3 pagesTransafrica - Efforts To Improve Public Transport in Africa - Smart Cities Dive2afsdFsdfNo ratings yet
- Addressing The Challenges of Traffic Growth: The Solution: Road Tech Innovation On The Road Surface 5G NetworksDocument1 pageAddressing The Challenges of Traffic Growth: The Solution: Road Tech Innovation On The Road Surface 5G NetworksJamey DAVIDSONNo ratings yet
- Alinda BailyDocument5 pagesAlinda Bailynabawenda. joan.2019No ratings yet
- Green BookDocument68 pagesGreen BookAnoosha MansoorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Highway and Railroad EngineeringDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Highway and Railroad EngineeringRussel TorrenteNo ratings yet
- Experiential Learning Based Biophilic DesignDocument14 pagesExperiential Learning Based Biophilic DesignVedant HingmireNo ratings yet
- Experiance Certificate FormatDocument1 pageExperiance Certificate FormatVedant HingmireNo ratings yet
- ARCHITECTURE FOR AUTISM B Arch DissertatDocument62 pagesARCHITECTURE FOR AUTISM B Arch DissertatVedant HingmireNo ratings yet
- Tokyo Mass TransitDocument7 pagesTokyo Mass TransitVedant HingmireNo ratings yet
- A Dimension of Biophilia in Urban DesignDocument8 pagesA Dimension of Biophilia in Urban DesignVedant HingmireNo ratings yet
- Badminton Court LightingDocument9 pagesBadminton Court LightingVedant HingmireNo ratings yet
- Badminton Court LightingDocument9 pagesBadminton Court LightingVedant HingmireNo ratings yet
- Street Furniture: Vedant Hingmire 29B CP Sem 5Document7 pagesStreet Furniture: Vedant Hingmire 29B CP Sem 5Vedant HingmireNo ratings yet
- Thasaamah Technology Profile - Dubai, UAEDocument10 pagesThasaamah Technology Profile - Dubai, UAEAvcom TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Water ActDocument4 pagesSalient Features of Water Actparth sarthi100% (2)
- Advisory Circular: U.S. Department of TransportationDocument22 pagesAdvisory Circular: U.S. Department of TransportationlocoboeingNo ratings yet
- Kosambi Marxism and Indian HistoryDocument4 pagesKosambi Marxism and Indian Historyroopeshkappy9315No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ins200Document11 pagesChapter 3 Ins2002024985375No ratings yet
- WHO - Safe Management of Wastes From Healthcare ActivitiesDocument328 pagesWHO - Safe Management of Wastes From Healthcare ActivitiesMITRA TEHNIKNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 2 of 2 Portfolio and Written Questions: Submission InformationDocument28 pagesAssessment Task 2 of 2 Portfolio and Written Questions: Submission InformationDiego Grecco100% (1)
- Fundamental Concepts: Engineering Economy 1Document10 pagesFundamental Concepts: Engineering Economy 1Andre BocoNo ratings yet
- Project Presentation (142311004) FinalDocument60 pagesProject Presentation (142311004) FinalSaad AhammadNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 AReading Tieng Anh 12 GoodDocument44 pagesUnit 4 AReading Tieng Anh 12 GoodXuân Hòa HoàngNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 7942Document42 pagesRepublic Act No. 7942Paul John Page PachecoNo ratings yet
- File-4 (Chapter-3) PDFDocument136 pagesFile-4 (Chapter-3) PDFabc654No ratings yet
- Footwear - PattensDocument100 pagesFootwear - PattensThe 18th Century Material Culture Resource Center100% (6)
- Nokia Deploying 5G Networks White Paper ENDocument16 pagesNokia Deploying 5G Networks White Paper ENIyesusgetanew100% (1)
- SBI Gold LoanDocument12 pagesSBI Gold Loan1208059010100% (1)
- 6.2 Making My First DecisionsDocument7 pages6.2 Making My First Decisionschuhieungan0729No ratings yet
- My First Two Thousand Years - The Autobio - George Sylvester ViereckDocument392 pagesMy First Two Thousand Years - The Autobio - George Sylvester Viereckglencbr100% (1)
- AIM Vs AIM Faculty AssociationDocument2 pagesAIM Vs AIM Faculty AssociationAgnes Lintao100% (1)
- UPSE Securities Limited v. NSE - CCI OrderDocument5 pagesUPSE Securities Limited v. NSE - CCI OrderBar & BenchNo ratings yet
- Disaster Waste Management in Malaysia: Significant Issues, Policies & StrategiesDocument7 pagesDisaster Waste Management in Malaysia: Significant Issues, Policies & Strategiesmuhamadrafie1975No ratings yet
- (Stephen Burt, Hannah Brooks-Motl) Randall JarrellDocument197 pages(Stephen Burt, Hannah Brooks-Motl) Randall JarrellAlene Saury100% (2)
- RSLogix 5000 Fatal Error 0x80042008Document2 pagesRSLogix 5000 Fatal Error 0x80042008Thandayudhapani VeeraputhiranNo ratings yet
- Bipa Newletter 2011Document10 pagesBipa Newletter 2011JP RajendranNo ratings yet
- WWW - Pscnet.in Kerala PSC Staff Nurse Previous Questions 1Document47 pagesWWW - Pscnet.in Kerala PSC Staff Nurse Previous Questions 1VR VlogsNo ratings yet
- 117 Class 12th EnglishDocument2 pages117 Class 12th EnglishPushpendra PatelNo ratings yet
- AnyDocument35 pagesAnyAashutosh SinghalNo ratings yet