Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis Instructor-Led Course: Answer Sheet On Back Do Not Discard
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis Instructor-Led Course: Answer Sheet On Back Do Not Discard
Uploaded by
Cristhian HuilcapazCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Automotive Electrical Diagnosis CourseDocument304 pagesAutomotive Electrical Diagnosis CoursePaul100% (17)
- Engine Management System Diagnosis II: EMSD2 Course GuideDocument87 pagesEngine Management System Diagnosis II: EMSD2 Course GuideCristhian Huilcapaz100% (4)
- Technical Service Bulletin: Installation of Additional Battery Ground Cable CautionDocument3 pagesTechnical Service Bulletin: Installation of Additional Battery Ground Cable CautionCristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- Engine Management System Diagnosis II: EMSD2 Course GuideDocument87 pagesEngine Management System Diagnosis II: EMSD2 Course GuideCristhian Huilcapaz100% (4)
- Pow Powertrain Products PDF enDocument67 pagesPow Powertrain Products PDF enJesse DavisNo ratings yet
- Universal RENAULT Injection ECU Decoding ToolDocument4 pagesUniversal RENAULT Injection ECU Decoding ToolvalkovNo ratings yet
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU) : Ankul GuptaDocument20 pagesElectronic Control Unit (ECU) : Ankul Guptadarkim ajahNo ratings yet
- Acupressure ChartDocument1 pageAcupressure Chartapi-3838398100% (9)
- EMSDI Course For KGIS June 2019Document235 pagesEMSDI Course For KGIS June 2019Cristhian Huilcapaz100% (1)
- Xtool Vag401 User ManualDocument21 pagesXtool Vag401 User ManualMichael KleinNo ratings yet
- Beat The Book: Automotive Electrical Diagnosis. Better Diagnosis, Faster RepairDocument14 pagesBeat The Book: Automotive Electrical Diagnosis. Better Diagnosis, Faster RepairEric RojasNo ratings yet
- Toyota-Lexus Automotive SRS Air bag Repair ManualFrom EverandToyota-Lexus Automotive SRS Air bag Repair ManualRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lin Bus PDFDocument9 pagesLin Bus PDFMuneeswaran AyyappanNo ratings yet
- Tata Indica v2 Xeta CarDocument89 pagesTata Indica v2 Xeta Carsantoshk165No ratings yet
- Toyota Electrical ConceptsDocument30 pagesToyota Electrical ConceptsNDD1959100% (3)
- Automotive Electronic SystemsDocument62 pagesAutomotive Electronic Systemsyusufsithik100% (3)
- Brochure Optima 2016Document12 pagesBrochure Optima 2016woofyNo ratings yet
- Technical Service Training Global Fundamentals Curriculum Training - TF1010011S Electrical Systems-FordDocument68 pagesTechnical Service Training Global Fundamentals Curriculum Training - TF1010011S Electrical Systems-FordAnonymous vcdqCTtS9No ratings yet
- Signal ProcessingDocument47 pagesSignal ProcessingAthira rcNo ratings yet
- As-T-T022 S11 Body Electric SystemDocument91 pagesAs-T-T022 S11 Body Electric SystemJunior Edder Aguilar Apolaya100% (1)
- Automatic Transmission (Diagnostics)Document136 pagesAutomatic Transmission (Diagnostics)testdamNo ratings yet
- 1982 Siliconix Analog Switch and IC Product Data Book PDFDocument436 pages1982 Siliconix Analog Switch and IC Product Data Book PDFevilmoistureNo ratings yet
- Engine Control SystemDocument766 pagesEngine Control Systemmortadaalsonni211No ratings yet
- Autodata Training - Course Guide - 2020Document24 pagesAutodata Training - Course Guide - 2020MMR100% (2)
- TPMS - 021709 LR5Document88 pagesTPMS - 021709 LR5juanNo ratings yet
- 600 ECU Installation Manual 2v01Document40 pages600 ECU Installation Manual 2v01LIMBERTOLEDONo ratings yet
- Manual Transmission and Differential (Diagnostics)Document38 pagesManual Transmission and Differential (Diagnostics)GURBZHNo ratings yet
- TR Auto Engine Rebuilding NC IIDocument83 pagesTR Auto Engine Rebuilding NC IIMichael V. MagallanoNo ratings yet
- Engine Diagnostic ManualDocument296 pagesEngine Diagnostic ManualAteeq SialNo ratings yet
- MAN-00555 EMS+Diagnostic+Manual Roxor Rev2Document392 pagesMAN-00555 EMS+Diagnostic+Manual Roxor Rev2amp divisionNo ratings yet
- ECU Designing and Testing Using National Instruments ProductsDocument7 pagesECU Designing and Testing Using National Instruments ProductsTYu4443No ratings yet
- (E Series) Truck Equipment Certification - Tests Study Guide 2021Document24 pages(E Series) Truck Equipment Certification - Tests Study Guide 2021Vương HoàngNo ratings yet
- ch46Document15 pagesch46jose perezNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis From The Drivers SeatDocument101 pagesDiagnosis From The Drivers Seatabul hussain100% (1)
- Reset Adaptive TransmissionDocument4 pagesReset Adaptive TransmissionGALERİ MUTLU EFENo ratings yet
- 14043.17D Passenger AWD PG R1.03 PDFDocument79 pages14043.17D Passenger AWD PG R1.03 PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis For in Vehicle NetworksDocument26 pagesDiagnosis For in Vehicle NetworksSayyedNo ratings yet
- Charging System: Engine Auxiliary SystemsDocument44 pagesCharging System: Engine Auxiliary SystemsMinh TuấnNo ratings yet
- PB SRS EngDocument18 pagesPB SRS EngMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- Read & Reset ECUDocument2 pagesRead & Reset ECUKároly Dávid NyulasiNo ratings yet
- ChemicalsDocument46 pagesChemicalsjuanowk05No ratings yet
- Ford Motor Company - Automotive Systems Training - Electrical SystemsDocument68 pagesFord Motor Company - Automotive Systems Training - Electrical SystemsjevulNo ratings yet
- Fuel Trim and Misfire Analysis Y: A "No Excuse" Approach PPDocument243 pagesFuel Trim and Misfire Analysis Y: A "No Excuse" Approach PPSalah Edeen Al-Ardah100% (1)
- KessDocument1 pageKessDarjanNo ratings yet
- SSP 820233-Electric-Drives-7 - 9 - 2013 - SMDocument62 pagesSSP 820233-Electric-Drives-7 - 9 - 2013 - SMaulin64_845645735No ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument22 pagesElectric Motorhmiwukcy100% (2)
- Different Types of VVT VTECDocument12 pagesDifferent Types of VVT VTECshahrizalNo ratings yet
- Student Workbook2Document52 pagesStudent Workbook2papipapiiNo ratings yet
- Body Repairs - General Body RepairsDocument49 pagesBody Repairs - General Body RepairsjomialheNo ratings yet
- Automotive Electricity and Electronics: A01 - HALD4428 - 06 - SE - FM - Indd 1 01/11/19 7:20 PMDocument22 pagesAutomotive Electricity and Electronics: A01 - HALD4428 - 06 - SE - FM - Indd 1 01/11/19 7:20 PMsa ltyNo ratings yet
- Signal Analysis - Crank Position Sensor PDFDocument29 pagesSignal Analysis - Crank Position Sensor PDFLui Koc100% (2)
- User Manual Abrites Commander For ToyotaDocument33 pagesUser Manual Abrites Commander For ToyotaMiguel VegaNo ratings yet
- Control Module: Testing and Inspection (FS5A-EL)Document7 pagesControl Module: Testing and Inspection (FS5A-EL)calumo938220100% (1)
- Lambda Sensors: Quick and Easy Testing and ReplacementDocument12 pagesLambda Sensors: Quick and Easy Testing and ReplacementChinh HuuNo ratings yet
- 01-273 Electrical Testing PDFDocument66 pages01-273 Electrical Testing PDFmefisto06cNo ratings yet
- Ecu Diagram Forester 2002Document7 pagesEcu Diagram Forester 2002Razvan MateiNo ratings yet
- 36 S 12 T 0Document28 pages36 S 12 T 0papipapii100% (1)
- Engine Mechanical Diagnosis CourseDocument147 pagesEngine Mechanical Diagnosis CoursePaul100% (8)
- Body Network Diagnosis 2016Document79 pagesBody Network Diagnosis 2016Paul100% (5)
- TS00E v1.2 Student Noteset PDFDocument303 pagesTS00E v1.2 Student Noteset PDFpatrick morris100% (1)
- Session 1 Photometric Measrement Based On CIE S 025Document82 pagesSession 1 Photometric Measrement Based On CIE S 025Marce MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Water: Ipeat Calibration Tool of SWATDocument17 pagesWater: Ipeat Calibration Tool of SWATCristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- EMSDI Course For KGIS June 2019Document235 pagesEMSDI Course For KGIS June 2019Cristhian Huilcapaz100% (1)
- TB008 - Fuel System Pressure Test - Low Pressure System - v2021Document1 pageTB008 - Fuel System Pressure Test - Low Pressure System - v2021Cristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- TSB FUE038 Air Drain Case Replacement Rev 1Document5 pagesTSB FUE038 Air Drain Case Replacement Rev 1Cristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- Technical Service Bulletin: Aftermarket Oil Filters and Oil Viscosity NoticeDocument2 pagesTechnical Service Bulletin: Aftermarket Oil Filters and Oil Viscosity NoticeCristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- Kia J2534 Reprogramming SystemDocument1 pageKia J2534 Reprogramming SystemCristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- TB018 Cylinder Compression Test v2021Document2 pagesTB018 Cylinder Compression Test v2021Cristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- TB008 - Fuel System Pressure Test - Low Pressure System - v2021Document1 pageTB008 - Fuel System Pressure Test - Low Pressure System - v2021Cristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- Taiwan Panorama 2023 NovDocument128 pagesTaiwan Panorama 2023 NovKwang HwaNo ratings yet
- Phylum Aschelminthes (Nemathelminthes / Nematoda)Document15 pagesPhylum Aschelminthes (Nemathelminthes / Nematoda)Aditya KaleNo ratings yet
- 100 Watts Power Amplifier Design PDFDocument47 pages100 Watts Power Amplifier Design PDFMark Kenneth ValerioNo ratings yet
- Page Proofs: Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument44 pagesPage Proofs: Continuous Probability DistributionsApoorva PanchalNo ratings yet
- Cost CurvesDocument2 pagesCost CurvesSumit Ray100% (1)
- 36 - 4 - New York - 08-91 - 1478Document8 pages36 - 4 - New York - 08-91 - 1478Ovo OjasNo ratings yet
- DIS 4.1 ExcavationDocument29 pagesDIS 4.1 ExcavationAshraf Ismail HassenNo ratings yet
- Things That Make You Go HMMDocument2 pagesThings That Make You Go HMMmckee_jemNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Elevated Temperature On ConcreteDocument204 pagesThe Effect of Elevated Temperature On Concretexaaabbb_550464353100% (1)
- Consumer Electronics Servicing Learning Module 130610203451 Phpapp02Document145 pagesConsumer Electronics Servicing Learning Module 130610203451 Phpapp02Maureen Pusing80% (10)
- WEF DibiDocument130 pagesWEF DibimanuelNo ratings yet
- Revised LRS BRS Booklet-2015-2016Document14 pagesRevised LRS BRS Booklet-2015-2016undyingNo ratings yet
- Book's SolutionsDocument20 pagesBook's SolutionsKodjo ALIPUINo ratings yet
- Space - The Final FrontierDocument51 pagesSpace - The Final FrontierAbdul Shakoor100% (1)
- Egg Drop NotesDocument2 pagesEgg Drop Notesapi-365288705No ratings yet
- Case Study On Development of Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis (PFMEA) - Issues and RecommendationsDocument8 pagesCase Study On Development of Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis (PFMEA) - Issues and RecommendationsSang BùiNo ratings yet
- Practice Question Ffor Module 7Document6 pagesPractice Question Ffor Module 7hemkumar DahalNo ratings yet
- IND110321USA6 Bayou CatDocument1 pageIND110321USA6 Bayou CatMichel MichelNo ratings yet
- Ivf NiceDocument22 pagesIvf NiceDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure, Bohr Model and IsotopesDocument17 pagesAtomic Structure, Bohr Model and IsotopeskushanNo ratings yet
- Nage Waza (Throwing) : HIP THROWS (Koshi Waza)Document5 pagesNage Waza (Throwing) : HIP THROWS (Koshi Waza)Stuart WalshNo ratings yet
- The Hamburger Ate Boy Isn't Acceptable (Odd) But The Boy Ate The Hamburger Is Hamburger Doesn't Have This Property and The Noun Boy DoesDocument6 pagesThe Hamburger Ate Boy Isn't Acceptable (Odd) But The Boy Ate The Hamburger Is Hamburger Doesn't Have This Property and The Noun Boy DoesDania SaviraNo ratings yet
- Lo2012 TPFDocument114 pagesLo2012 TPFramjoceNo ratings yet
- Ce503 RBTDocument2 pagesCe503 RBTTarang ShethNo ratings yet
- Portuguese Market Outlook Up To 2040: A Report To APRENDocument48 pagesPortuguese Market Outlook Up To 2040: A Report To APRENMiguel Chã AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Technical Information: Dpbs 90 E MeDocument3 pagesTechnical Information: Dpbs 90 E MeЛулу ТраедNo ratings yet
- Technoir Players GuideDocument16 pagesTechnoir Players GuideDerrick D. Cochran100% (1)
- NANO-REX Lubricant AdditiveDocument8 pagesNANO-REX Lubricant AdditiveProject Sales CorpNo ratings yet
- I/O Specifications: CPU Unit DescriptionsDocument10 pagesI/O Specifications: CPU Unit Descriptionsวรพงษ์ กอชัชวาลNo ratings yet
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis Instructor-Led Course: Answer Sheet On Back Do Not Discard
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis Instructor-Led Course: Answer Sheet On Back Do Not Discard
Uploaded by
Cristhian HuilcapazOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis Instructor-Led Course: Answer Sheet On Back Do Not Discard
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis Instructor-Led Course: Answer Sheet On Back Do Not Discard
Uploaded by
Cristhian HuilcapazCopyright:
Available Formats
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Kia Evaporative
System Diagnosis
Instructor-Led Course
Student Guide
Part Number: TT-KESD18-SG
Cover Sheet/Answer Sheet
Student Theory Workbook
Student Performance Assessment
Scorecard
Kia University Course Number: TEC-03-030-1
Print 1 / July 2018
ANSWER SHEET ON BACK
DO NOT DISCARD
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 1
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis (KESD)
Module 1: Course Guide
COURSE OVERVIEW This course will increase your skills and efficiency in
diagnosing evaporative system customer concerns.
COURSE GOAL Improve your Kia evaporative system diagnostic skills
and Fix It Right the First Time repairs.
COURSE OBJECTIVES After completing this performance-based course, you
will be able to (with 80% or greater accuracy):
Describe the purpose of the evaporative system
Identify and locate evaporative system components
and describe their operation
Use KGIS to locate evaporative system service
information
Perform basic evaporative system and component
tests
Describe the four evaporative system processes
Describe the benefits of following a logical
diagnostic plan
Use KDS to test evaporative system components
and diagnose EVAP concerns
Use the gas cap tester to inspect gas cap sealing
Use an evaporative emissions tester to locate
evaporative system leaks
EXPECTATIONS In this course, you will be expected to:
Follow diagnostic procedures and instructions to
safely service evaporative emission systems
Gain a technical understanding of evaporative
emission systems and their operation
TARGET AUDIENCE Kia Service Technicians who will be diagnosing and
repairing evaporative emission systems.
PREREQUISITES You must successfully pass prerequisite courses
containing knowledge that supports this course:
ILC: Diagnosing with GDS VE (GDS 6) Course
(TEC-03-035-1)
ILC: Automotive Electrical Diagnosis Course
(TEC-03-017-1)
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 2
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
THEORY A Theory Module presents information to increase
your working knowledge of the subject, which helps
guide you to successful diagnosis and repair.
GUIDED PRACTICE A Guided Practice Module allows you to practice
diagnostic skills through hands-on experience. The
tasks are instructor supervised and verified.
PERFORMANCE ASSESMENT The Performance Assessment Module will assess
what you have learned. Each technician will
independently prove that he or she has mastered the
subject.
COURSE ACHIEVEMENT A final score of 80% or greater on the Guided Practice
Activities and Performance Assessment is required to
receive credit for this course.
NOTE: Arriving late may result in a loss of points
and an incomplete achievement score.
PERFORMANCE SCORECARD The Performance Scorecard tracks your
performance on Guided Practices, diagnosis,
troubleshooting and the Performance Assessment.
SCORECARD ROUTING One copy of the Performance Scorecard is yours, and
one copy is used to update your Kia technical training
records. Should you not complete the course, the third
copy is forwarded to your Kia District Parts and Service
Manager.
ANSWER SHEET An answer sheet is provided to record your
Performance Assessment answers. You will return your
answer sheet to your instructor for grading. Your score
will be transferred to the scorecard.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 3
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
COURSE MATERIALS/TIMELINE
Performance
Module Title
Assessment
Practice
Number
Module
Guided
Theory
Course
Timing
01 Introduction and Course Guide 8:00 - 8:30
02 EVAP System Overview X 8:30 - 9:30
03 EVAP System Overview GP X 9:30 - 10:00
Break 10:00 - 10:15
04 EVAP System Leak Testing X 10:15 - 10:45
05 EVAP System Leak Testing GP X 10:45 - 11:30
Lunch 11:30 - 12:30
06 EVAP OBD-II Diagnosis X 12:30 - 1:30
07 EVAP OBD-II Diagnosis GP X 1:30 - 2:15
Break 2:15 - 2:30
08 EVAP Diagnostic Tips X 2:30 - 2:45
Clean-up 2:45 - 3:00
09 Performance Assessment (PA) X 3:00 - 5:00
COURSE MANAGEMENT The course and materials are for you to learn and keep.
Use them, and your time, in a way that will benefit you
upon returning to your dealership.
TAKE NOTES Take notes and highlight these materials to help you
remember important details. Each module is designed
with ample margins for your notes. Each Guided
Practice has a notes page at the end.
ASK QUESTIONS If you do not understand something in this course, ask
your instructor for clarification. Asking questions is
strongly encouraged to help you get the most out of
this course.
TEAMWORK During the hands-on Guided Practices, you will often be
working as a team. By actively engaging in each Guided
Practice, you will maximize your learning experience.
While in the lab, feel free to ask the instructor
questions at any time.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 4
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
PROFESSIONALISM Conduct yourself in a professional manner. This
includes:
Wearing your dealer uniform or Kia shop coat
Arriving to class on time
Returning from breaks on time
Not using profanity
Returning tools and vehicles to the location and
condition they were found
Keeping the classroom and shop clean
Completing the Performance Assessment on your
own
Failure to comply may result in deduction of Guided
Practice points and/or expulsion without course credit.
LEARN AT EVERY This course is an opportunity for you to learn in a
OPPORTUNITY controlled environment under the guidance of a trained
Kia instructor. Through active participation you can
build confidence in your abilities to diagnose customer
concerns right the first time, every time!
ICONS
NOTE
FEEDBACK:
CAUTION:
Activities
WARNING:
Wait for further instructions:
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 5
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
ACRONYMS CCV: Canister Close Valve
CO2: Carbon Dioxide
DLC: Data Link Connector
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code
DVOM: Digital Volt Ohm Meter
ECU: Electronic Control Unit
ECM: Electronic Control Module
ETM: Electronic Troubleshooting Manual
FTPS: Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor
GDS: Global Diagnostic System
HC: Hydrocarbons
KDS: Kia Diagnostic System
KGIS: Kia Global Information System
KOEO: Key On Engine Off
KOER: Key On Engine Running
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Light
NC: Normally Closed
NO: Normally Open
OBD: On-Board Diagnostics
ORVR: Onboard Refueling Vapor Recovery
OL: Out of Limits
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCSV: Purge Control Solenoid Valve
TSB: Technical Service Bulletin
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 6
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
NOTES:
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 7
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis (KESD)
Module 2: EVAP System Overview
To become familiar with Kia evaporative system
principles of operation and diagnostic and repair tools.
MODULE GOAL
MODULE OBJECTIVES After completing classroom theory instruction, guided
practice shop activities and a written test, you will be
able to complete the following with 80% or greater
accuracy:
Describe the purpose of the evaporative system
Identify and locate evaporative system components
and describe their operation
MODULE INSTRUCTIONS Carefully read the material, take notes based on the
classroom discussion, and study each illustration.
Answer the Progress Check questions at the end of the
module. You may use the information covered in this
module to answer the questions.
TIME TO COMPLETE 1.0 hour
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 8
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM A vehicle’s evaporative system collects and stores fuel tank
BASICS vapors in a charcoal-filled canister. The evaporative system
uses engine vacuum to draw fuel vapors from the canister
to the engine to be burned.
Gasoline in an open fuel tank can vaporize quickly,
especially when it is hot outside. This trait is bad for the
environment, with 20 percent of all automotive
hydrocarbon (HC) emissions coming from fuel evaporation.
In 1971, the Federal Government mandated that all
vehicles sold in the United States use a system to prevent
fuel tank vapors from escaping to the atmosphere.
This system is commonly known as the EVAPorative
Emission Control System (EVAP).
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 9
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM About 40 years ago, fuel tanks began getting more
BASICS complicated as emission controls were added to
prevent vapors from leaking into the atmosphere.
As shown above, fuel tanks have an unused portion to
allow for vapor expansion.
Filling the tank raises the liquid level, causing the vapor
space to decrease (vapors are compressed), which
causes the tank vapor pressure to increase.
Alternatively, as gasoline leaves the tank, the vapor
space increases and tank vapor pressure decreases.
If the tank is filled beyond the gas station pump’s
automatic shut-off, liquid fuel is pushed into the
vehicle’s charcoal canister, causing damage.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 10
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM
BASICS
The EVAP system allows fuel vapors to be pushed into the
engine (using tank pressure and engine vacuum) and
burned during the engine combustion process.
This process is known as “purging.” In addition, there are
processes that test EVAP system integrity and operation.
The EVAP system usually requires little maintenance, but
faults can illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
and prevent a vehicle from successfully completing the
OBD II monitor or passing a state vehicle emissions test.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 11
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM OPERATION
The EVAP system uses these four processes during
vehicle operation:
1. Refueling: Fueling and evaporation in the tank
create vapors that are pushed into the canister for
temporary storage.
2. Venting: Expanding air vents out of the fuel tank
without allowing gasoline vapors to escape; activated
charcoal in the canister absorbs hydrocarbons.
3. Purging: During certain operating conditions, the
ECM uses intake manifold vacuum to purge
hydrocarbon vapors from the system, drawing them
out of the canister and into the engine where they are
burned during combustion.
4. Testing: The PCM tests the system’s integrity and
checks for any system leaks.
These four processes will be explained in Module 6.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 12
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
PCSV – Location varies by model
Engine Room Compartment
Fuel Cap Under vehicle (rear)
Fuel Tank Air Filter
FTPS
CCV
Canister
EVAP SYSTEM Typical components include:
COMPONENTS
Fuel tank
Onboard refueling vapor recovery (ORVR) valve
Fuel tank air filter
Fuel tank (gas) cap
Charcoal canister
Purge control solenoid valve (PCSV)
Fuel tank pressure sensor (FTPS)
Canister close valve (CCV)
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 13
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Canister Unleaded Restrictor Plate
ORVR
Valve Vapor
Stage II
Valve
Nozzle
Check
Valve
Liquid Seal
ONBOARD REFUELING Starting in 1998, vehicles were required to have an
VAPOR RECOVERY (ORVR) Onboard Refueling Vapor Recovery (ORVR) system to
SYSTEM control vapors created during refueling by routing them
to the canister.
The ORVR system can consist of the following:
Fill vent valve
Fuel shut off valve
Fuel cut/roll-over valve
Two-way valve for pressure/vacuum relief
Fuel liquid/vapor separator next to the filler pipe
Charcoal canister
Narrowing size fuel tank filler tube
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 14
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
ONBOARD REFUELING Fuel Filler Pipe: During refueling, a small amount of
VAPOR RECOVERY SYSTEM air is pushed into the filler pipe to prevent fuel vapors
(ORVR) from escaping into the air. The fill pipe diameter
narrows from the unleaded fuel restrictor plate,
creating a liquid seal that prevents fuel vapor from
escaping during fueling.
Check Valve: A spring loaded check valve at the end
of the filler pipe to prevent fuel backflow.
Vapor/2-Way/Cut Valve: Vents to the canister
through the ORVR valve, which has a float to close off
the vent when the tank is full.
ORVR Valve: Create an aspiration effect that draws air
into the fill tube. During refueling, the valve closes and
the fuel tank vents to the canister to capture escaping
vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there are no
fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere.
A faulty ORVR valve can stick closed and cause
difficulty fueling or early shut-off of the filler nozzle
when filling the tank. A faulty ORVR can also stick
open, filling the charcoal canister, tank vent line, and
fuel air filter with fuel.
Note: ORVR components vary in name and location. For
example, the vapor valve is also known as the 2-way or
fuel cut-off valve.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 15
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Fuel tank under pressure Fuel tank under vacuum
FUEL TANK CAP (GAS CAP) The gas cap is a fuel tank-sealing device and there are
different types of tightening procedures depending on
the cap type.
Most caps have a ratchet-type mechanism that causes
a clicking sound as the cap is tightened.
Gas caps are designed to hold vapor pressure up to
approximately 1.5-2 PSI and then relieve if needed
for safety.
If fuel tank vacuum becomes excessive, the cap
will vent at approximately 1.5” Hg vacuum to
prevent collapse of tank.
Most Kia models will illuminate the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) if the gas cap is loose or missing.
Some older Kia models use a “Check Fuel Cap” or a gas
cap symbol in the instrument cluster that can illuminate
after a fill-up if the cap is loose or missing.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 16
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Fuel Tank Air Filter
Fresh Air
To Canister Close Valve
The EVAP system uses an air filter to prevent dirt and
debris from entering the system during purge. Inspection
of the air filter is part of a vehicle’s regular maintenance
schedule.
When the purge valve opens, intake manifold low
pressure (vacuum) causes EVAP system pressure to
start dropping
Atmospheric pressure outside the filter allows air to
start flowing through the filter, the CCV, and the
canister
This airflow carries hydrocarbons through the open
purge valve and into the intake manifold.
The filter is usually located in the rear of vehicle near the
canister or on the fuel tank fill pipe (inside the left-rear
wheel well liner).
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 17
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
CANISTER CLOSE VALVE
(CCV)
To
Canister
To
Air
Filter
The canister close valve (CCV) is an ECM/PCM
controlled, normally open (NO) in-line, 12-volt solenoid
valve.
The CCV controls the airflow from the fuel tank air filter
to the canister during leak check. The ECM/PCM
provides a ground to close the valve. When normally
open, fresh air flows to the canister during engine
purge.
When diagnosing EVAP system concerns, visually check
the CCV, hoses, and clamps. Check for spider webs,
corrosion, or damage at the electrical terminals and
connector.
Using the KDS Actuation Test should cause the CCV
solenoid valve to “click,” actuating the valve.
NOTE: The CCV orifice is much larger than the PCSV
lines so flow is not restricted. The fresh air inlet
normally includes a serviceable air filter that helps
prevent contaminants from entering the EVAP system.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 18
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
CHARCOAL CANISTER
The canister contains activated charcoal to absorb and
store any gasoline vapors (not liquid) from the fuel
tank, as well as those created during refueling (ORVR).
Purging the canister of vapors recovers its absorbing
capability.
The charcoal canister does not require scheduled
maintenance.
When servicing the EVAP system, inspect the canister
for cracks, accident damage, broken mounts, poor hose
connections, and liquid fuel.
The OBD II EVAP monitor tests the canister for leaks
and adequate flow.
The canister is usually located in the rear of vehicle
near the fuel tank.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 19
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
PURGE CONTROL Charcoal Canister
SOLENOID VALVE (PCSV)
Intake Manifold
The purge control solenoid valve (PCSV) is a normally
closed (NC), duty-cycled 12-volt valve.
The PCSV controls the vacuum flow from the intake
manifold to the EVAP system. It is commanded open by
the PCM providing a ground. When open, it allows a
path for HC vapors to flow from the EVAP canister to
the low pressure (or vacuum) of the intake manifold.
The PCSV is usually located near the intake manifold.
NOTE: Some models may have a purge solenoid valve
with an integrated air filter.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 20
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
PURGE CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE (PCSV)
Various Styles of Kia Purge Control Solenoid Valves
Always check the PCSV for cracks, hose deterioration,
and contamination with charcoal granules. Inspect the
electrical terminals and connector for corrosion,
damage, and fit.
The PCSV should hold vacuum when applied with a
hand pump. Using the KDS Actuation test should cause
the solenoid to “click,” opening the valve, and bleeding
off vacuum.
The coil’s resistance specification varies by model.
Locate resistance specification with KGIS and check the
solenoid with an ohmmeter.
With the engine running, verify that vacuum from the
intake manifold is present at PCSV.
Note: Verify purge hoses are correctly installed on the
valve. Kia supplies PCSVs that can have a red line, a
red dot, an arrow, or the letters “CAN” on the fitting to
assist with correct hose installation.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 21
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
FUEL TANK PRESSURE Vent to atmosphere
SENSOR (FTPS)
Fuel Tank
The Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (FTPS) monitors
pressure levels affecting the entire EVAP system. This
3-wire, 5-volt sensor is usually located on top of the
fuel tank.
The FTPS output signal voltage changes as it measures
the difference between fuel tank pressure and outside
air pressure (atmospheric). The ECM/PCM relies on the
FTPS signal to complete the OBD-II EVAP system
monitor.
Note: The FTPS can measure both positive and
negative pressure changes in the EVAP system. The
PCM/ECM can use the FTPS pressure readings to detect
a blocked canister or fresh air vent.
This pressure vs. voltage scale compares the two types
of fuel tank pressure sensors used on Kia vehicles.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 22
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM ENGINE The EVAP system is controlled by the engine
MANAGEMENT CONTROL management system (ECM/PCM) and primarily uses a
combination of 2 solenoids and 1 sensor to
control/monitor the system:
PCSV
CCV
FTPS
12 volt power (B+) to the PCSV and CCV is supplied
from the engine control relay circuit through a fuse.
The PCSV is controlled using a pulse width
modulated (PWM) ground signal
The CCV is an ON/OFF solenoid
Each solenoid is controlled by the PCM, which
pulls the circuit down from 12 to 0 volts.
The FTPS uses a 5-volt supply directly from the PCM.
On most Kia vehicles, the FTPS circuit completes
its ground through the PCM
The FTPS signal voltage is sent to the PCM and
varies between 0.5 and 4.5 volts depending on
fuel tank pressure.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 23
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM ENGINE EVAP System Components 2015 Optima 2.4 Liter
MANAGEMENT CONTROL
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 24
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
LOCATING EVAP SYSTEM Locating EVAP system service information plays a
SERVICE INFORMATION critical role in diagnosis. There are several places you
can find this information:
KGIS (www.KDealer.com)
KDS Service Info Section
KGIS is updated weekly so it always contains the latest
service information.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 25
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
LOCATING EVAP SYSTEM Most service information needed to successfully
SERVICE INFORMATION diagnose EVAP concerns is located in KGIS under:
Service Materials
Service Info (Shop, ETM, DTC &
Component, Replace Manuals)
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 26
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
LOCATING EVAP SYSTEM EVAP system-related wiring diagrams are located in
SERVICE INFORMATION KGIS under:
ETM
Schematic Diagrams
Engine Control Systems
Schematic Diagrams
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 27
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
LOCATING EVAP SYSTEM EVAP system related DTCs are located in KGIS under:
SERVICE INFORMATION
DTC
Engine
Engine Control
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 28
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 2 SUMMARY In this module, you:
Learned why vehicles require an EVAP system
Identified EVAP system components
Reviewed EVAP system operation
Learned where to find EVAP Service Information
Using Service Information to identify EVAP
system components and diagnosis information to
develop a diagnostic plan will result in quicker
repairs with less intrusive testing for Fix It
Right the First Time results.
Diagnosis of the EVAP system begins with
understanding the system and how to test it. As
you continue on to the next section, you will find
that KDS and KGIS are valuable tools for solving
EVAP related concerns.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 29
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 2 PROGRESS 1. Technician A says the PCSV is Normally Open
CHECK (NO).
Technician B says the PCSV is Normally Closed
(NC) and the CCV is Normally Open.
Who is right?
A. A only
B. B only
C. Both A and B
D. Neither A nor B
2. Technician A says charcoal canisters are
normally replaced during the 30k service.
Technician B says the EVAP air filter is inspected
as part of the factory maintenance schedule.
Who is correct?
A. A only
B. B only
C. Both A and B
D. Neither A nor B
3. Technician A says the FTPS voltage on some Kia
vehicles is 1.5V with the gas cap OFF.
Technician B says the FTPS voltage on some Kia
vehicles is 2.5V with the gas cap OFF.
Who is correct?
A. A only
B. B only
C. Both A and B
D. Neither A nor B
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 30
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 2 PROGRESS 4. Technician A says the canister can exhaust
CHECK Hydrocarbon (HC) vapors not captured through a
fuel tank air filter during normal operation.
Technician B says the EVAP system prevents HC
vapors from being released into the atmosphere.
Who is correct?
A. A only
B. B only
C. Both A and B
D. Neither A nor B
5. Technician A says overfilling the fuel tank can
damage the FTPS.
Technician B says overfilling the fuel tank can
damage the charcoal canister.
Who is correct?
A. A only
B. B only
C. Both A and B
D. Neither A nor B
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 31
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis (KESD)
Module 3: EVAP System Overview Guided Practice
Tasks 1 to 3
GUIDED PRACTICE GOAL Provide you with hands-on experience with KGIS to
learn how to access EVAP system service information,
and discover how the EVAP system is constructed and
controlled.
GUIDED PRACTICE After completing these guided practice tasks, you will
OBJECTIVES be able to:
Access all EVAP related service information
Describe the electrical portion of the EVAP system
Describe how the EVAP system is controlled
GUIDED PRACTICE Carefully read and follow the instructions for the task.
INSTRUCTIONS Perform each step in each task. If you are unsure of
something, ask your instructor. When you finish,
have your instructor review and sign off your work.
REQUIRED MATERIALS Student Guide
Pen or Pencil
KDS/KGIS
TIME TO COMPLETE Approximately 30 minutes
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 32
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 1: FINDING EVAP SERVICE INFORMATION
Use a KDS or classroom computer connected to a
printer to perform this task.
Follow these steps to locate the EVAP System ETM
wiring diagrams:
1. Service Materials
2. Service Info(SI)
3. Select: 2015, Optima and 2.4 Liter (TF/QF)
4. Select: ETM
5. Select: Schematic Diagrams
6. Select: Engine Electrical System
7. Select: Engine Control System
8. Select: Schematic Diagrams
9. Navigate through the Engine Control System
page(s) and print if necessary.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 33
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 2: ANSWERING EVAP SYSTEM ETM QUESTIONS
Use the previously reviewed/printed vehicle Engine Control System diagram(s) to answer
the following questions.
1. Which fuse supplies power to the PCSV solenoid?
2. Which fuse supplies power to the CCV solenoid?
3. Is the PCSV controlled with a “pull up” or a “pull down” type of electrical circuit?
4. With the ignition in the “ON” position, what voltage should be available at
connector C200-B pin -86?
5. With the ignition in the “ON” position, what voltage should be available at
connector C200-B pin -87?
6. With the ignition in the “ON” position, what voltage should be available at
connector C200-A pin -12?
7. With the ignition in the “ON” position, what voltage should be available at
connector C200-A pin -20?
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 34
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 3: FINDING EVAP SYSTEM SERVICE INFORMATION IN KGIS
Use a KDS or classroom computer to perform this task.
Follow these steps to locate EVAP System DTC P0441:
1. Service Materials
2. Service Info(SI)
3. Select: 2015 Optima (QF) and 2.4 Liter
4. Select: DTC
5. Select: Engine > Engine Control
6. Find DTC: P0441
1. Does the DTC show the location of the PCSV solenoid?
YES NO
2. When testing the PCSV in the “OFF” position, what is the specification for the valve?
A. Should hold vacuum
B. Should release vacuum
3. How many drive cycles does it take for the MIL to turn on?
4. Does the DTC information include an electrical diagram of the PCSV circuit?
YES NO
5. Which test found under “Component Inspection” is required to test the PCSV and
EVAP system operation?
Feedback: Discuss the results with your instructor.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 35
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis (KESD)
Module 4: EVAP System Leak Testing
To become familiar with Kia evaporative system
diagnostic and repair tools.
MODULE GOAL
MODULE OBJECTIVES After completing classroom theory instruction, guided
practice shop activities and a written test, you will be
able to complete the following with 80% or greater
accuracy:
Describe basic evaporative system and component
tests
MODULE INSTRUCTIONS Carefully read the material, take notes based on the
classroom discussion, and study each illustration.
Answer the Progress Check questions at the end of the
module. You may use the information covered in this
module to answer the questions.
TIME TO COMPLETE 30 minutes
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 36
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM LEAKS This illustration shows how small a leak can be that
would allow the EVAP system to fail its leak test, set a
DTC, and ultimately illuminate the MIL.
The 0.020” (0.5 mm) diameter leak is very small
and is 25% of a 0.40” leak.
The 0.040” (1.0 mm) diameter leak is a small leak.
Gas cap OFF (>1.0mm.) is a large or Gross leak.
NOTE: KIA service materials might refer to leaks as
large, small and very small, but Diagnostic Trouble
Codes titles will always be correct - i.e., if you are
diagnosing a P0442 DTC, you are diagnosing a 1mm
leak regardless of what the words (large/small)
indicate.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 37
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
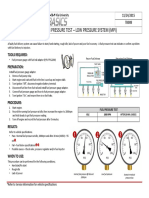
System Low High Vacuum
Tire and Wheel 28 psi 32 psi
Fuel Pressure NOT APPLICABLE
(Low Pressure System) 36 psi 75 psi
Air Conditioner 28 psi 350 psi 29 inHg
Fuel Tank Cap
0.2 psi 0.5 psi -0.5 psi
EVAP System
EVAP SYSTEM PRESSURES EVAP system operating pressures are extremely low.
This table compares typical EVAP operating pressures
to other automotive system operating pressures.
EVAP systems must be tested with low pressure as they
operate at pressures very close to atmospheric.
Positive pressure (above atmospheric) and negative
pressure (below atmospheric, also known as vacuum),
may never exceed 1.5-2 psi (positive) or -0.5 psi
(negative).
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 38
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
psi inHg kPa inH20 hPa/mBar
1.0 2 7 27.7 69
0.5 1 3.5 14 34
0.25 0.5 1.75 7 17
UNITS OF PRESSURE EVAP system operating pressures are very low, so
pounds per square inch (psi) is not an precise unit to
use for measurement. Using psi to measure EVAP
system pressure would be like measuring a crankshaft
journal diameter with a ruler instead of a micrometer.
Other units of measurement:
Inches of mercury (in.Hg) is a common unit of
measure for pressure. Automotive technicians use
vacuum gauges calibrated in inHg.
Kilopascals (kPa) is a lower measurement of
pressure best known for barometric pressure.
Inches of water (inH2O) is even more accurate for
measuring very small pressure variations. It is the
most commonly used unit for EVAP test equipment
in service bay testing.
Note: You may see inches of water shown as in.Aq.
depending upon the vehicle selected, KDS may use PSI,
Vac, mBar, or hPa to display pressure readings.
1 millibar (mBar) = 1 hectopascal (hPa).
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 39
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM TESTING As a part of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
OBD II emissions system regulations required on all
passenger vehicles sold in the U.S. since 1996, the
ECM/PCM must test the EVAP system for leaks,
adequate flow, and electrical faults.
This test, called an OBD-II monitor, automatically runs
based on conditions determined by the ECM/PCM.
Technicians can use KDS to “test” the EVAP system
when diagnosing an EVAP system DTC or to verify an
EVAP system repair.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 40
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM TESTER AND The best method for determining the location and
SMOKE MACHINE extent of a leak is to use an evaporative emissions
system tester, more commonly known as “a smoke
machine:”
DTC P0456 – 0.020” (0.5 mm) diameter leak
DTC P0442 – 0.040” (1.0 mm) diameter leak
DTC P0455 – >1.0mm.diameter leak
DTC P0497 – Evaporative Emission System No
Flow During Purge
NOTE: The smoke machine:
Can also be used to verify fuel tank pressure
(FTP) sensor performance
Must be used properly and consistently to
maintain accuracy
Requires calibration before each use
The majority of smoke machines feature two tools to
check and find for EVAP system leaks. The first tool
uses an inert gas such as nitrogen or CO2 to pressurize
the EVAP system and check for leaks.
The second tool is an actual “smoke” creating device
that fills the entire system with smoke to determine
where is the leak located in the system by watching the
smoke escape.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 41
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Test ports: Flow meter
Self-test
.040” orifice
Flow flag
.020” orifice
Flow ball
Fuel cap
adapters
Test hose
Smoke
Machine
Regulator
Nitrogen tank
Caution: Due to the possibility of combustion, DO
NOT use compressed shop air to test EVAP
systems. Always use an inert gas such as
nitrogen or carbon dioxide.
EVAP SYSTEM TESTER AND There are many different EVAP system testers
SMOKE MACHINE available, but most operate like the machine shown
above.
The tester components include:
Gas cap adaptor
Fuel tank filler adaptor
Nitrogen or carbon dioxide tank
Tank regulator
Calibration method
Test result gauge or meter
Smoke unit (12 volts)
The smoke solution can be scented. This solution can
also be sourced/purchased with tracer dye to help
locate leaks.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 42
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 4 SUMMARY In this module, you:
Learned about different sizes of EVAP system leaks
Identified critical EVAP system pressures
Reviewed EVAP smoke tester components
Using Service Information to identify EVAP
system components and diagnosis information to
develop a diagnostic plan will result in quicker
repairs with less intrusive testing for Fix It
Right the First Time results.
Diagnosis of the EVAP system begins with
understanding the system and how to test it. As
you continue on to the next section, you will find
that KDS and KGIS are valuable tools for solving
EVAP related concerns.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 43
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 4 PROGRESS 1. Which of the following sizes is NOT an actual
CHECK standard for an evaporative emission leak?
a. 0.000”
b. 0.020”
c. 0.040”
d. All of the above
2. After confirming a leak is present in the EVAP
system, all of the following are methods a
technician can use to find the leak EXCEPT:
A. Insert smoke into the system
B. Visual inspection
C. Use ultrasonic leak detector
D. Pressurize system and spray the joints
and lines with liquid nitrogen
3. Evaporative emissions can increase due to:
A. Low Fuel Temperatures
B. High Ambient Temperatures
C. Freezing Ambient Temperatures
D. All of the above
4. Technician A says if there is an EVAP failure you
should use the smoke machine first.
Technician B says you should use the smoke
machine if you have a leak and cannot spot it.
Who is correct?
A. A only
B. B only
C. Both A and B
D. Neither A nor B
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 44
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
5. A Kia vehicle comes into your shop with a loose
gas cap. Typically, what should the FTPS sensor
voltage be?
A. 0.5 volts
B. 2.5 volts
C. 5 to 12 volts
D. 12.0 volts
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 45
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis (KESD)
Module 5: EVAP Leak Testing Guided Practice
Tasks 4 to 8
GUIDED PRACTICE GOAL Provide you with hands-on experience with KDS and a
DVOM to learn how to test the EVAP system and its
components.
GUIDED PRACTICE After completing these guided practice tasks, you will
OBJECTIVES be able to:
Test the EVAP system with KDS
Test a fuel tank pressure sensor (FTPS) on the
simulator
Bench test a purge control solenoid valve (PCSV)
Bench test a canister close valve (CCV)
Bench test a fuel tank pressure sensor (FTPS)
GUIDED PRACTICE Carefully read and follow the instructions for the task.
INSTRUCTIONS Perform each step in each task. If you are unsure of
something, ask your instructor. When you finish,
have your instructor review and sign off your work.
REQUIRED MATERIALS Student Guide
Pen or Pencil
KDS/KGIS
DVOM and Leads
Hand Vacuum Pump
EVAP System Test Station
Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV)
Canister Close Valve (CCV)
Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (FTPS)
TIME TO COMPLETE Approximately 45 minutes
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 46
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 4: CONDUCTING A KDS EVAP SYSTEM TEST
Conduct an EVAP system test on a vehicle using KDS:
1. Using the KDS, select Engine, and then S/W Management
2. Select EVAP Leak Test
NOTE: Depending on the vehicle you are working on,
this test could have a different name.
3. Following the on-screen instructions, list the conditions
required to conduct the EVAP Test
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
4. Click OK to perform the test and list the test results:
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
Feedback: Discuss the results with your instructor.
Clean up your area as instructed.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 47
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 5: MEASURING FUEL TANK PRESSURE SENSOR (FTPS) VOLTAGES USING
THE EVAP SYSTEM TEST STATION
EVAP SYSTEM OPERATION Use the EVAP test station to measure FTPS output under
various pressures:
1. Make sure that the gas cap is tight.
2. Measure the FTPS Signal voltage at the FTPS Test
port.
3. Record the FTPS signal voltage: __________volts.
4. Measure and record the FTPS Signal voltage at the
FTPS test port with the gas cap removed:
______________volts.
5. Re-install the gas cap and make sure it is tight.
6. Turn the vacuum pump ON (ENGINE SWITCH).
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 48
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
7. Turn the CCV ON.
8. Turn the PCSV ON.
9. Wait about 10 seconds and measure the FTPS
voltage: ______________volts
10. Turn the Engine OFF (vacuum).
11. Turn the PCSV OFF.
12. Wait about 10 seconds and measure the FTPS
voltage again: ______________volts
13. Did the voltage reading remain the same or did it
change?
Changed No change
14. If the voltage changed, which of the following
could be the cause?
a. Bad CCV
b. Bad PCSV
c. System has a leak
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
15. Turn the CCV OFF.
Feedback: Discuss the results with your instructor.
Clean up your area as instructed.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 49
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
NOTES:
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 50
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 6: BENCH TESTING A PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE (PCSV)
If no power supply is
available, use E/R
JUNCTION BOX
to Supply B+
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 51
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
SERVICE INFORMATION Using KDS, look up and record the PCSV resistance
specification for the vehicle assigned by your instructor:
PCSV: ___________
Using a DVOM, measure and record the resistance
below:
PCSV: ____________ Results: Good No Good
PURGE CONTROL Connect and apply vacuum to the PCSV engine side
SOLENOID VALVE (PCSV) fitting. Record the results with and without battery
voltage applied to the red (B+) and black (Ground)
terminals.
1. With no voltage applied, vacuum is:
Released Maintained
2. With voltage applied, vacuum is:
Released Maintained
3. Was a faint click heard from the solenoid?
YES NO
4. The solenoid is:
Good No Good
5. Will it affect the long-term operation of the valve
if the hoses are connected backwards?
YES NO
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 52
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 7: BENCH TESTING A CANISTER CLOSE VALVE (CCV)
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 53
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
SERVICE INFORMATION Using KDS, look up and record the CCV resistance
specification for the vehicle assigned by your instructor:
CCV: _____________
Using a DVOM, measure and record the resistance
below:
CCV: _____________
Results: Good No Good
The system operates at low (atmospheric) pressure.
Apply low vacuum pressure to the canister fitting.
Record the results with and without battery voltage and
ground applied.
Do NOT apply excessive pump pressure as this
could result in damage to the valve
1. With no voltage applied, vacuum is:
Released Maintained
2. With voltage applied, vacuum is:
Released Maintained
3. Was a faint click heard from the solenoid?
YES NO
4. The solenoid is:
Good No Good
5. Will it affect the long-term operation of the valve
if the hoses are connected backwards?
YES NO
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 54
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 8: BENCH TESTING THE FUEL TANK PRESSURE SENSOR (FTPS)
SORENTO FUEL TANK Connect 5 volts to pin 1 (red) and ground to pin 3
PRESSURE SENSOR (FTPS) (black). Use a hand pump to apply very low pressure
(2 psi maximum). Measure and record the pin 2 (signal
port) output voltage below.
Change the hand pump to vacuum. Apply very low
vacuum pressure (5 in.Hg maximum) and record the
voltage below.
No - pressure
+ pressure
pressure (vacuum)
Signal
Voltage:
The sensor is: Good No Good
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 55
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
SEDONA FUEL TANK Connect 5 volts to pin 1 (red) and ground to pin 3
PRESSURE SENSOR (FTPS) (black). Use a hand pump to apply very low pressure (2
psi maximum). Measure and record the pin 2 (signal
port) output voltage below.
Change the hand pump to vacuum. Apply very low
vacuum pressure (5 inHg maximum) and record the
voltage below.
No - pressure
+ pressure
pressure (vacuum)
Signal
Voltage:
The sensor is: Good No Good
INSTRUCTOR SIGN-OFF: ___________________________________________
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 56
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 5 SUMMARY In this module, you:
Learned why vehicles require an EVAP system
Identified EVAP system components
Reviewed EVAP system operation
Learned where to find EVAP Service Information
Learned how to perform basic EVAP system and
component tests
Using Service Information to identify EVAP
system components and diagnosis information to
develop a diagnostic plan will result in quicker
repairs with less intrusive testing for Fix It
Right the First Time results.
Diagnosis of the EVAP system begins with
understanding the system and how to test it. As
you continue on to the next section, you will find
that KDS and KGIS are valuable tools for solving
EVAP related concerns.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 57
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis (KESD)
Module 6: EVAP System Diagnosis
Demonstrate your knowledge of EVAP system operation
and perform system diagnosis.
MODULE GOAL
MODULE OBJECTIVES After completing classroom theory instruction, guided
practice shop activities and a written test, you will be
able to complete the following with 80% or greater
accuracy:
Describe the four evaporative system processes
Describe the benefits of following a logical
diagnostic plan
Use KDS to test evaporative system components
and diagnose EVAP concerns
Use the gas cap tester to inspect gas cap sealing
Use a smoke machine to locate evaporative system
leaks
MODULE INSTRUCTIONS Carefully read the material, take notes based on the
classroom discussion, and study each illustration.
Answer the Progress Check questions at the end of the
module. You may use the information covered in this
module to answer the questions.
TIME TO COMPLETE 1.0 Hour
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 58
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
FUEL SYSTEM OPERATION The EVAP system uses the following four processes of
PROCESSES operation:
5. Refueling: Along with regular fueling, fuel
evaporation in the tank creates vapors which are
drawn into the canister for temporary storage.
6. Venting: Expanding air vents out of the fuel tank
without allowing gasoline vapors to escape.
7. Purging: During certain operating conditions, the
ECM uses intake manifold vacuum to purge gasoline
vapors from the system, drawing them out of the
canister and into the engine where they are burned
during combustion.
8. Testing: The PCM tests the system’s integrity and
checks for system leaks.
The following pages describe each of these processes in
more detail.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 59
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM OPERATION Fueling displaces hydrocarbons (fuel vapors) when
PROCESSES: FUELING pumping liquid fuel into the tank.
As fuel enters the tank, the fuel level increases, and
begins to move vapors out of the tank into the
canister.
The canister absorbs fuel vapors and temporarily
stores them until the purging process can begin.
During refueling, there is a large flow rate of vapors
throughout the system. If a gas station pump
dispenses 10 gallons per minute, as fast as that fuel
enters the tank, the same volume of fuel vapors
have to be moved out of the tank. These vapors are
sent to the canister where the fuel is removed and
the remaining air is passed through the normally
open canister close valve (CCV), then through the
air filter to the atmosphere.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 60
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM OPERATION Venting is similar to refueling as it prevents
PROCESSES: VENTING unwanted vapor pressure build-up in the tank.
Vapors are generated as fuel tank temperature
increases, so system pressure increases. At this
point, the canister vents to the atmosphere allowing
hydrocarbons (fuel vapors) to be “captured” in the
charcoal canister. The charcoal removes the fuel
and the remaining air passes through the normally
open CCV, then through the air filter to the
atmosphere.
Problems with the EVAP system such as tampering,
lack of maintenance, and vehicle damage result in
evaporative system failures that can also cause the
unintended release (venting) of vapors.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 61
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM OPERATION Purging occurs when the engine is running. The
PROCESSES: PURGING CCV is normally open, and the PCSV is commanded
open at a predetermined purge flow rate. This
allows atmospheric pressure to push air into the
canister, forcing air and fuel vapors toward the
engine.
During the purging process, a slight increase in
EVAP system vacuum takes place. This increase can
be monitored by viewing a very small FTPS voltage
change on the KDS Data Analysis screen.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 62
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM OPERATION The KDS Data Analysis screen above (2016 Soul 2.0
PROCESSES: PURGING Liter) shows the EVAP system during purging with
the engine running.
The PCSV is running at 57.9% duty cycle allowing
engine vacuum to draw fuel vapors from the
canister. This can be seen by monitoring the FTPS
voltage and pressure which shows 2.353 volts and -
3 mmHg (-0.0580psi) negative tank pressure
(vacuum).
This test is also an easy method to test the tank
vent/filter for restriction. If voltage continues to
drop to <1.5V (2.5V style sensor) or rise >1.9V
(1.5V style sensor), this indicates a vent restriction
and further testing/inspection is required.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 63
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM As a part of the OBD II emissions system required on
MONITORING: TESTING all passenger vehicles sold in the U.S. since 1996, the
EVAP system is required to test for leaks, adequate
flow, and electrical faults.
The PCM/ECM automatically runs this test, known as an
OBD-II monitor.
To make the test results reliable and consistent, the
monitor only runs when meeting certain Enable
Criteria conditions.
Enable criteria conditions may include:
Fuel tank level between 15%-85%
Cold startup (less than 180°F)
12 hours since monitor last ran
Drive cycle type operation
If the PCM/ECM detects an EVAP fault during a driving
cycle, a Pending DTC is stored in memory. If the same
fault occurs again during the next driving cycle, the
system stores a DTC, records Freeze Frame Data, and
illuminates the MIL.
Most EVAP system DTC ON conditions require 2 driving
cycles (trips). However, some conditions, such as a
large leak (P0455) only require 1 trip (a loose or
missing gas cap, for example).
The EVAP monitor is non-continuous, meaning that the
monitor only runs when certain enable criteria items
have been met (see bullet points above). On the other
hand, the EVAP electrical circuits (such as PCSV, CCV,
and FTPS) are continuously monitored for opens,
shorts, and out-of-range.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 64
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM The EVAP system testing process has 4 stages:
MONITORING: TESTING
Stage 1: Compensation gradient mode (fuel
vapor generation)
Stage 2: Building vacuum (evacuation)
Stage 3: Gross leak detection mode
Stage 4: Small leak detection mode
As seen on the following page, before testing can
begin the system opens the PCSV to determine if
there are any signal voltage fluctuations from the
FTPS. If it calculates that vapors in the tank are
above a certain threshold (excessive), the test
monitor is aborted.
Testing begins by closing both the PCSV and CCV
valves to stabilize the tank pressure.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 65
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM During the 1st stage, the vapor generation period, the PCSV
MONITORING: VAPOR and CCV are closed to seal the fuel tank and the system
GENERATION PERIOD pressure is measured with the FTPS:
At DP_A to establish the starting pressure
Again at DP_B after a defined time period (T1)
The pressure difference (DP_B – DP_A) is calculated, and if
the system has no problems there should be a slight
increase in pressure. The test will abort if the pressure rise
exceeds threshold, and no code will set.
If this calculated difference indicates that the system
developed vacuum in this stage, the PCSV is leaking vacuum
when it should be closed. The system will set DTC P0441 for
Purge Flow and testing will be aborted.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 66
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM The 2nd stage is building vacuum (evacuation). At
MONITORING: this point, the Normally Open CCV is commanded to
EVACUATION close and the PCSV is duty cycled from 0-100% to
build vacuum in the EVAP system.
During this stage, the PCM/ECM monitors the FTPS
signal to calculate the pressure difference from
DP_B.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 67
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM MONITORING: The 3rd stage is gross leak detection mode, which
GROSS LEAK DETECTION also occurs during the building vacuum (evacuation)
stage.
The building vacuum stage continues with an
increase of the PCSV duty cycle to create a specific
level of vacuum. If pressure does not decrease
below a predetermined threshold, the system
determines that there is gross leak due to
component failure (or a loose gas cap), a pending
DTC P0455 is set, and testing is aborted.
Gross leaks are relatively large (loose gas cap, gas
cap O-ring sealing, detached hose, or large crack),
and will allow hydrocarbons (HC) to escape into the
atmosphere.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 68
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM The 4th and final stage is the small leak detection mode,
MONITORING: SMALL which checks for .040” (small leak) and .020” (very small
LEAK DETECTION leak).
During this mode, the system measures system pressures
over a period of time while the system is sealed. If the
system does not maintain vacuum, pending DTC P0442
(.040”) is generated and testing is aborted.
If the .040” test passes, the system will then test for a .020”
leak from DP_C to DP_D. The earlier DP_A/DP_B values will
be used to make sure vapor generation does not create a
false test result. If the system does not maintain vacuum,
pending DTC P0456 (.020”) is set.
These small leaks can be caused by small component
failures (crack, pin-sized hole, or bad seal) and will allow HC
to leak into the atmosphere.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 69
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS Following a logical and organized diagnostic plan will
help you determine the root cause of the customer’s
concern. The basic approach is as follows:
1. Confirm the customer’s concern (MIL is ON)
Determine if it is an EVAP related code
2. If so, select the appropriate action(s) from the
following:
Enhanced Search in KGIS
Preparation with KDS (Hot Fix with GDS)
Print related service information
Review warranty history for previous repairs
Determine if you need to open a TechLine case*
3. Review the specific DTC diagnostic guide
Review code setting information
Inspect detecting conditions
Perform step-by-step inspection
4. Repair the vehicle
5. Verify the repair with a drive cycle
*Open a TechLine case if this is a repeat repair, or if
30+ minutes have been spent diagnosing the confirmed
concern without a conclusion.
NOTE: An example of a software-related issue is found
in Technical Service Bulletin ENG 025 for the 2006
Sedona (VQ) with a DTC P0441.
Not all DTC faults are component-related. The above
TSB addresses a concern that cannot be fixed by
repairing the circuit or replacing the component.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 70
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP DIAGNOSTIC FLOWCHART
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 71
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
GAS CAP SEALING A gas tank cap can cause an EVAP system leak, set a
INSPECTION DTC, and cause a vehicle to fail a state emissions test.
Use the Kia Special Service Tool (SST) Cap Tester to
determine if the cap can hold pressure.
Test result documentation is required to replace the cap
under warranty.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 72
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TESTING EVAP As shown above, the PCSV can be tested with KDS to
SYSTEM COMPONENTS determine if the electrical portion of the solenoid is
WITH KDS (PCSV) working properly. This test shows the output from the
PCM.
NOTE: This test does not check the sealing
integrity of the PCSV.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 73
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Canister Shut Off (Toggle On/Off) Canister Shut Off Valve (leak test)
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 74
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TESTING EVAP SYSTEM On certain models, KDS can perform two types of CCV
COMPONENTS WITH KDS actuations tests:
(CCV)
Canister Shut Off Toggling (OBD-2 only) – This
actuation test toggles the CVV on/off.
Canister Shut Off Valve (leak test) – This test
can be useful when performing test procedures
that require the CCV to be closed for a long
period (for example, using the smoke machine to
test the EVAP system for leaks).
NOTE: The Canister Shut Off Valve (leak test) is not
available on all Kia models or it could have a different
name.
NOTE: Conducting the above tests for more than 5
minutes may damage the solenoid valve.
NOTE: These tests do not check the sealing
integrity of the CCV.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 75
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
PCSV
Hose
from
charcoal
canister
Vacuum
hand pump
connected to
PCSV hose
from
charcoal
canister
TESTING EVAP SYSTEM You can quickly check FTPS operation by monitoring
COMPONENTS WITH KDS the sensor voltage and fuel tank pressure on KDS Data
(FTPS) Analysis while applying positive pressure (or vacuum)
at the PCSV hose from the charcoal canister:
1. Disconnect the PCSV valve hose from the
charcoal canister and connect a vacuum hand
pump to the hose.
2. Select Data Analysis and Actuation Test (shown
above) and choose the following parameters:
Fuel Tank Pressure Value (Option)
Fuel Tank Pressure Voltage (Option)
Canister Shut Off Valve (leak test)
NOTE: The word “Option” means that this
parameter might not be available on the vehicle
you are testing.
3. Select the Canister Shut Off Valve (Leak test),
and press Start.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 76
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TESTING EVAP SYSTEM 4. Use the hand pump to either put the EVAP
COMPONENTS WITH KDS system into a negative pressure (vacuum) or
(FTPS)- CONTINUED positive pressure condition.
5. The Fuel Tank Pressure and Fuel tank Pressure
Voltage parameters should begin to change (as
shown above).
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 77
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
OBD-II vehicles have “monitors,” a series of on-board
tests that confirm a vehicle has been adequately
EVAP SYSTEM MONITORING - checked for concerns so it can be emissions-tested.
KDS CARB OBD-II
MONITOR STATUS The KDS CARB OBD-II tool can display EVAP system
monitor status as “Completed” or “Not Completed.”
This status can be found in both the “Readiness Test”
and “Current Data” lists. This information can be useful
when diagnosing EVAP concerns.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 78
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Another tool within the CARB OBD-II section is
Monitoring Test Results (also known as Mode 6). Mode
EVAP SYSTEM MONITORING - 6 shows the test results of the monitors as PASS or
KDS CARB OBD-II MODE 6 FAIL. The test results may help narrow down the cause
of an EVAP concern, and TechLine may ask you to
complete record this data if a vehicle is harder to
diagnose.
The EVAP system is tested in sequence. If it fails the
0.040” leak test, it aborts the remaining portion of the
monitor and may still show a “PASS” for the 0.020” leak
because it did not run that test again.
Note: These tests may vary by model and year of
manufacture.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 79
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
This illustration shows a failed EVAP Monitor gas cap
test. This result could be caused by a missing gas cap
EVAP SYSTEM MONITORING - or an EVAP system gross leak (EVAP system hose
KDS CARB OBD-II MODE 6 disconnected).
Even after repairing all significant leaks and performing
functional tests on the components with EVAP DTCs,
the only way to know the MIL will remain off is by
performing a full EVAP drive cycle.
Instead of a test drive (for a long period of time to
allow the drive cycle to complete), you can conduct the
full EVAP drive cycle test by performing the KDS EVAP
system test.
NOTE: Under certain conditions, the KDS EVAP system
test does not perform a complete test or “full drive
cycle.” It usually stops at P0455 or P0442 – not reliable
for P0456 or restriction codes.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 80
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 6 SUMMARY In this module you:
Reviewed the four EVAP system processes
Used KDS and manual tests to diagnose EVAP
concerns
Used the CARB OBD-II monitoring test results to
help you diagnose EVAP concerns
Received tips to help you diagnose EVAP system
concerns
Used the smoke machine to verify and locate
system leaks
Used KDS and KGIS to solve EVAP related
concerns
Using KGIS Service Information for EVAP system
service and diagnosis information to develop a
diagnostic plan will result in quicker repairs with
less intrusive testing for Fix It Right the First
Time results.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 81
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 6 PROGRESS 2. When following the EVAP flowchart, it is always
CHECK necessary to contact TechLine and advise them
that you have an EVAP problem.
A. True
B. False
3. All of the following are EVAP system operating
modes, EXCEPT:
A. Testing
B. Fueling
C. Recapture
D. Purging
E. Venting
4. The EVAP monitor runs when certain specific
conditions are met. All of the following are
conditions, EXCEPT:
A. Fuel tank level
B. Engine coolant startup temperature
C. Time since monitor ran last
D. Drive wheels off the ground
5. Which of the 4 EVAP processes tests the
system’s integrity and checks for system leaks?
A. Refueling
B. Purging
C. Testing
D. Venting
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 82
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 6 PROGRESS 6. All of the following statements are true EXCEPT:
CHECK
A. The OBD II monitor tests the EVAP system
for leaks
B. The OBD II monitor tests the EVAP system
electrical components for faults
C. A vehicle owner can cause an EVAP DTC to
be set after refueling the vehicle
D. The OBD II monitor operates the EVAP
system during normal operation, and Kia
TechLine should always be consulted when
an EVAP DTC is set
6. Technician A says visually inspecting hoses and
connectors is a good place to start when
diagnosing an EVAP system failure.
Technician B says checking EVAP system
electrical and mechanical operation is a good
place to start diagnosing a failed EVAP
component.
Who is correct?
A. Technician A only
B. Technician B only
C. Both Technician A and B
D. Neither Technician A nor B
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 83
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 6 PROGRESS 7. Technician A says CARB OBD-II should only be
CHECK used when instructed by TechLine.
Technician B says CARB OBD-II can provide
additional diagnostic information to help you
diagnose an EVAP concern.
Who is correct?
A. Technician A only
B. Technician B only
C. Both Technician A and B
D. Neither Technician A nor B
8. The KDS Actuation Test is the best method to
test the sealing integrity of the PCSV or CCV
solenoids.
A. True
B. False
9. Purging operates when the engine is not
running.
A. True
B. False
10. To make the ORVR a two-stage vapor recovery
system, certain states require?
A. That the vehicle remain running during
refueling
B. That the engine is shut off during refueling
C. That all fuel sold has a minimum of 10%
ethanol
D. The pump nozzle recover HC vapors during
fueling
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 84
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis (KESD)
Module 7: EVAP System Diagnosis Guided Practice
Tasks 9 to 13
GUIDED PRACTICE GOAL Provide you with hands-on practice using KDS and
other tools to diagnose EVAP systems and components.
GUIDED PRACTICE After completing these guided practice tasks, you will
OBJECTIVES be able to:
Review EVAP monitoring test results
Test FTPS operation
Inspect gas cap sealing
Use a smoke machine to check for EVAP system
leaks
Check ORVR function on the bench
GUIDED PRACTICE Carefully read and follow the instructions for the task.
INSTRUCTIONS Perform each step in each task. If you are unsure of
something, ask your instructor. When you finish,
have your instructor review and sign off your work.
REQUIRED MATERIALS Student Guide
Pen or Pencil
KDS
Gas Cap Tester
Smoke Machine
DVOM and Leads
Hand Vacuum Pump
ORVR Valve
TIME TO COMPLETE Approximately 45 minutes
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 85
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 9: REVIEWING OBD-II EVAP MONITORING TEST RESULTS
Assigned Vehicle:______________________________
Set an EVAP system “ACTIVE” DTC and review the
OBD-II EVAP monitoring test results:
1. Loosen the gas cap
2. Using the KDS, select System - Engine, then
select S/W Management > Inspection/Test
3. Select EVAP Leak Test
4. Follow the on-screen instructions, and once all
the test conditions are met, proceed to the EVAP
Leak test.
5. Did the EVAP test show a “Pass” or a “Fail?”
If “FAIL” Continue to step 6
NOTE: If KDS displays a “PASS,” please consult with
your instructor.
6. Check for DTCs. Does the KDS display a
“pending” DTC?
YES NO
7. If yes, note the DTC:___________________
8. Turn the vehicle ignition and VCI OFF for approx.
15 seconds.
9. Turn the vehicle ignition and VCI back ON.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 86
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
10. Repeat Steps 3-5 until the DTC changes from
“Pending” to “Active.”
11. Select CARB OBD-II.
12. Select “Monitoring Test results.”
13. Which EVAP system tests show “PASS” and
which show “FAIL?”
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
14. Why did the gas cap test “FAIL” but the other
tests displayed “PASS?”
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
15. Reinstall the gas cap and clear the DTC.
Feedback: Discuss the results with your instructor.
Clean up your area as instructed.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 87
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 88
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 10: USING KDS AND A VACUUM PUMP TO CHECK FUEL TANK PRESSURE SENSOR
(FTPS) OPERATION
Assigned Vehicle:______________________________
1. Using the KDS, select System - Engine, followed
by Current Data and Actuation Test.
2. Select the following Current Data parameters
in Graph mode:
a. Fuel Tank Pressure Value (Option)
b. Fuel Tank Pressure Voltage (Option)
c. Canister Shut off Valve Closed
3. Select Actuation Test. Select the following test:
a. Canister Shut off Valve (Leak test).
NOTE: If this test is not available on your
vehicle, use a pair of hose pinch pliers to
close the flow of air to the CCV.
DO NOT START THE ACTUATION TEST AT
THIS TIME
4. Find the PCSV valve.
5. Disconnect PCSV valve hose from the charcoal
canister.
6. Connect a hand pump to the PCSV hose from
the charcoal canister.
a. Select Start on the Canister Shut off Valve
(Leak test) Actuation Test.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 89
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
7. Using the hand pump, begin pumping to create
a vacuum in the system.
Alternatively, you can start the engine and
use the engine vacuum to achieve the
same effect.
8. While pumping, monitor both the FTPS voltage
and fuel tank pressure.
9. Pump until the FTPS voltage reaches
approximately 1.5 volts
10. Once you have reached 1.5 volts (or -32Mb
pressure), stop pumping but do not release the
vacuum in the system.
11. If the voltage in the FTPS does not change, what
does this indicate? _______________________
_______________________________________
12. Change the hand pump from vacuum to positive
pressure and repeat steps 6 and 7.
13. Pump until the FTPS voltage reaches
approximately 3.0 volts (15Mb pressure).
14. Once you have reached 3.0 volts (15Mb
pressure), stop pumping but do not release the
pressure in the system.
15. If the voltage in the FTPS does not change, what
does this indicate? _______________________
Feedback: Discuss the results with your instructor.
Clean up your area as instructed.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 90
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 11: USING THE GAS CAP TESTER TO INSPECT GAS CAP SEALING
Assigned Vehicle: _______________________
Attach the correct cap adapter to the tester.
Check gas cap for leaks using the cap tester.
1. Install gas cap onto the cap adaptor.
2. Press start to initiate auto-zero. Green LED ON.
3. Steady red LED ON, unit ready, install fuel cap.
4. Pump the handle until the green STOP LED is ON.
5. Wait up to 15 seconds until an LED comes ON.
Result of cap test:
GOOD NO GOOD
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 91
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 12: USING A SMOKE MACHINE TO LOCATE EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM LEAKS
Assigned Vehicle: ______________________________
Follow the instructions for the Evaporative Emissions
Tester KLI9210 machine and perform the following:
1. Self-test the machine
2. Calibrate and Test the machine for 0.020”
and a 0.040” leaks
3. Test a vehicle with the vehicle and fuel
cap test hoses.
NOTE: If you do not self-test and calibrate the
Evaporative Emissions Tester KLI9210 correctly, you
will probably misdiagnose the concern.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 92
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
1. Connect the test adaptors to gas cap and filler
neck.
2. Close the CCV using the KDS CCV (Leak Test)
actuation test.
3. Turn control knob to “TEST” position and allow
system to pressurize:
If the flow ball rises above preset level, the
system has a leak
If the flow ball falls below preset level, the
system passes
Leak __________ No Leak_________
If leak is found, proceed to step 4
4. Power the smoke machine by connecting it to
the vehicle’s battery. Push the button to activate
smoke. Allow fuel system to fill with smoke and
visually look for leaks using a 12V leak detection
spot light.
Record your results:
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
Feedback: Locate the leak and review with your
instructor.
Clean up your area as instructed.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 93
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
TASK 13: BENCH TESTING AN ORVR VALVE
Conduct a bench test of an ORVR valve :
1. Using the KGIS, locate the Inspection Test procedure
for an ORVR valve on a 2016 Cadenza 3.3 Liter
2. In which of the following KGIS Service Information
manuals did you find the ORVR Inspection procedure
(Select all that apply):
A. Shop Manual
B. ETM
C. DTC
D. Replace
E. Component
F. Body
3. Following the KGIS inspection procedure, bench test
the ORVR valve.
4. After testing the valve it was found to be:
GOOD NO GOOD
Feedback: Discuss the results with your instructor.
Clean up your area as instructed.
INSTRUCTOR SIGN-OFF: ___________________________________________
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 94
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
NOTES:
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 95
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis (KESD)
Module 8: EVAP System Diagnostic Tips
Improve your Kia evaporative system diagnostic skills
and Fix It Right the First Time Repairs.
MODULE GOAL
MODULE OBJECTIVES After completing classroom theory instruction, you will
be able to complete the following with 80% or greater
accuracy:
Describe diagnosis tips for six types of EVAP
concerns
MODULE INSTRUCTIONS Carefully read the material, take notes based on the
classroom discussion, and study each illustration.
TIME TO COMPLETE 15 Minutes
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 96
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
FTPS
O-Ring
ORVR gasket
Fuel Cap gasket
When diagnosing an EVAP system leak, always check
and be aware of the following:
EVAP SYSTEM
DIAGNOSTIC TIPS - LEAKS Check for cracked lines, nicker or cut O-rings, or
non-sealing gaskets.
Use care when moving or removing lines.
When replacing lines, take care with connected
parts to avoid damaging them.
Use caution when moving EVAP lines to access
other components or when wiggling lines during
inspection as this can cause cracks, bends, or kinks
in the lines.
A system with a very small leak may not set a DTC,
but two or more small leaks can set a DTC.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 97
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
Sedona Optima Sportage
The FTPS converts EVAP system pressure to a
proportional voltage signal allowing the PCM to
EVAP SYSTEM evaluate EVAP system operation. Therefore, it is
DIAGNOSTIC TIPS - FTPS important the FTPS is reading correctly (baseline).
Test the FTPS by removing the gas cap and
reading atmospheric pressure voltage using KDS
with the KOEO.
KOEO signal voltage for most FTPS should be
approximately 2.5 ± 0.3 volts.
Check to see if fuel is inside the sensor due to
over-filling the fuel tank.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 98
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
From Canister
To Intake
These are simple checks for diagnosing a PCSV flow or
a leak concern:
EVAP SYSTEM A new, incorrectly connected PCSV will operate but
DIAGNOSTIC TIPS - PCSV have a reduced service life
Inspect system hoses and ensure they are
connected correctly and are in good condition, with
no leaks
Inspect the PCSV plastic housing for cracks
Unplug the purge valve to verify the engine vacuum
source is good
Test the resistance value of the solenoid
Check for charcoal granules or other debris in the
PCSV and diagnose the root cause of contamination
During the beginning stage of the EVAP test, the
system is sealed. If vacuum leak develops in the
system, the likely cause could be a leaking PCSV. This
type of fault will set a P0441 Purge Flow DTC.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 99
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM
DIAGNOSTIC TIPS - CCV
The CCV is Normally Open (NO) to fresh air through the
fuel tank air filter, including during canister purging. It
is commanded closed during leak detection.
Here are simple CCV checks to make when there are
flow or leak concerns:
Inspect the hoses and clamps
Visually inspect the CCV exterior for damage
Test the resistance value of the CCV
Check for flow with the CCV at rest (de-energized)
Energize the CCV and check for sealing
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 100
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 101
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
ORVR Valve Vent Valve
Catch Can
ORVR system failures may result in:
EVAP SYSTEM The nozzle clicking off causing difficulty refueling
Fuel odor around the vehicle.
DIAGNOSTIC TIPS – ORVR AND
The tank vent valve can fail due to:
VENT VALVE
Clogging or sticking closed, causing fill problems
Stuck open vent allowing sloshing fuel to be drawn
into the canister
NOTE: To make the ORVR a two-stage vapor recovery
system, certain states recover HC vapors at the pump
nozzle during fueling.
NOTE: The 2011 Sportage has the ORVR and vent
valve located inside the tank connected to the fuel
pump assembly with a flex hose. Removing the fuel
pump assembly without disconnecting the flex hose will
dislodge the valves. Always replace the valves on the
top of the tank.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 102
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
EVAP SYSTEM The fuel tank filter filters the air flowing through the
DIAGNOSTIC TIPS – FUEL CCV and canister.
TANK AIR FILTER
Inspection intervals vary based on model and mileage,
but the filter has to be inspected to help prevent DTC
P2422. When the vacuum increases to the threshold
value, the system indicates a restricted flow, setting
this code.
Check the fuel tank air filter for blockage or reduced
air flow
The fuel tank air filter is sold and serviced
separately from the canister assembly
NOTE: The fuel tank air filter is also called the canister
air filter.
NOTE: Depending on the model and year, the fuel tank
air filter material may be a different size and thickness.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 103
Kia Evaporative System Diagnosis
MODULE 8 SUMMARY In this module you:
Learned about diagnosis tips for six types of
EVAP concerns
Using these tips along with KGIS diagnosis
information to develop a diagnostic plan will
result in quicker repairs with less intrusive testing
for Fix It Right the First Time results.
KESD COURSE GUIDE 01 104
You might also like
- Automotive Electrical Diagnosis CourseDocument304 pagesAutomotive Electrical Diagnosis CoursePaul100% (17)
- Engine Management System Diagnosis II: EMSD2 Course GuideDocument87 pagesEngine Management System Diagnosis II: EMSD2 Course GuideCristhian Huilcapaz100% (4)
- Technical Service Bulletin: Installation of Additional Battery Ground Cable CautionDocument3 pagesTechnical Service Bulletin: Installation of Additional Battery Ground Cable CautionCristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- Engine Management System Diagnosis II: EMSD2 Course GuideDocument87 pagesEngine Management System Diagnosis II: EMSD2 Course GuideCristhian Huilcapaz100% (4)
- Pow Powertrain Products PDF enDocument67 pagesPow Powertrain Products PDF enJesse DavisNo ratings yet
- Universal RENAULT Injection ECU Decoding ToolDocument4 pagesUniversal RENAULT Injection ECU Decoding ToolvalkovNo ratings yet
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU) : Ankul GuptaDocument20 pagesElectronic Control Unit (ECU) : Ankul Guptadarkim ajahNo ratings yet
- Acupressure ChartDocument1 pageAcupressure Chartapi-3838398100% (9)
- EMSDI Course For KGIS June 2019Document235 pagesEMSDI Course For KGIS June 2019Cristhian Huilcapaz100% (1)
- Xtool Vag401 User ManualDocument21 pagesXtool Vag401 User ManualMichael KleinNo ratings yet
- Beat The Book: Automotive Electrical Diagnosis. Better Diagnosis, Faster RepairDocument14 pagesBeat The Book: Automotive Electrical Diagnosis. Better Diagnosis, Faster RepairEric RojasNo ratings yet
- Toyota-Lexus Automotive SRS Air bag Repair ManualFrom EverandToyota-Lexus Automotive SRS Air bag Repair ManualRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lin Bus PDFDocument9 pagesLin Bus PDFMuneeswaran AyyappanNo ratings yet
- Tata Indica v2 Xeta CarDocument89 pagesTata Indica v2 Xeta Carsantoshk165No ratings yet
- Toyota Electrical ConceptsDocument30 pagesToyota Electrical ConceptsNDD1959100% (3)
- Automotive Electronic SystemsDocument62 pagesAutomotive Electronic Systemsyusufsithik100% (3)
- Brochure Optima 2016Document12 pagesBrochure Optima 2016woofyNo ratings yet
- Technical Service Training Global Fundamentals Curriculum Training - TF1010011S Electrical Systems-FordDocument68 pagesTechnical Service Training Global Fundamentals Curriculum Training - TF1010011S Electrical Systems-FordAnonymous vcdqCTtS9No ratings yet
- Signal ProcessingDocument47 pagesSignal ProcessingAthira rcNo ratings yet
- As-T-T022 S11 Body Electric SystemDocument91 pagesAs-T-T022 S11 Body Electric SystemJunior Edder Aguilar Apolaya100% (1)
- Automatic Transmission (Diagnostics)Document136 pagesAutomatic Transmission (Diagnostics)testdamNo ratings yet
- 1982 Siliconix Analog Switch and IC Product Data Book PDFDocument436 pages1982 Siliconix Analog Switch and IC Product Data Book PDFevilmoistureNo ratings yet
- Engine Control SystemDocument766 pagesEngine Control Systemmortadaalsonni211No ratings yet
- Autodata Training - Course Guide - 2020Document24 pagesAutodata Training - Course Guide - 2020MMR100% (2)
- TPMS - 021709 LR5Document88 pagesTPMS - 021709 LR5juanNo ratings yet
- 600 ECU Installation Manual 2v01Document40 pages600 ECU Installation Manual 2v01LIMBERTOLEDONo ratings yet
- Manual Transmission and Differential (Diagnostics)Document38 pagesManual Transmission and Differential (Diagnostics)GURBZHNo ratings yet
- TR Auto Engine Rebuilding NC IIDocument83 pagesTR Auto Engine Rebuilding NC IIMichael V. MagallanoNo ratings yet
- Engine Diagnostic ManualDocument296 pagesEngine Diagnostic ManualAteeq SialNo ratings yet
- MAN-00555 EMS+Diagnostic+Manual Roxor Rev2Document392 pagesMAN-00555 EMS+Diagnostic+Manual Roxor Rev2amp divisionNo ratings yet
- ECU Designing and Testing Using National Instruments ProductsDocument7 pagesECU Designing and Testing Using National Instruments ProductsTYu4443No ratings yet
- (E Series) Truck Equipment Certification - Tests Study Guide 2021Document24 pages(E Series) Truck Equipment Certification - Tests Study Guide 2021Vương HoàngNo ratings yet
- ch46Document15 pagesch46jose perezNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis From The Drivers SeatDocument101 pagesDiagnosis From The Drivers Seatabul hussain100% (1)
- Reset Adaptive TransmissionDocument4 pagesReset Adaptive TransmissionGALERİ MUTLU EFENo ratings yet
- 14043.17D Passenger AWD PG R1.03 PDFDocument79 pages14043.17D Passenger AWD PG R1.03 PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis For in Vehicle NetworksDocument26 pagesDiagnosis For in Vehicle NetworksSayyedNo ratings yet
- Charging System: Engine Auxiliary SystemsDocument44 pagesCharging System: Engine Auxiliary SystemsMinh TuấnNo ratings yet
- PB SRS EngDocument18 pagesPB SRS EngMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- Read & Reset ECUDocument2 pagesRead & Reset ECUKároly Dávid NyulasiNo ratings yet
- ChemicalsDocument46 pagesChemicalsjuanowk05No ratings yet
- Ford Motor Company - Automotive Systems Training - Electrical SystemsDocument68 pagesFord Motor Company - Automotive Systems Training - Electrical SystemsjevulNo ratings yet
- Fuel Trim and Misfire Analysis Y: A "No Excuse" Approach PPDocument243 pagesFuel Trim and Misfire Analysis Y: A "No Excuse" Approach PPSalah Edeen Al-Ardah100% (1)
- KessDocument1 pageKessDarjanNo ratings yet
- SSP 820233-Electric-Drives-7 - 9 - 2013 - SMDocument62 pagesSSP 820233-Electric-Drives-7 - 9 - 2013 - SMaulin64_845645735No ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument22 pagesElectric Motorhmiwukcy100% (2)
- Different Types of VVT VTECDocument12 pagesDifferent Types of VVT VTECshahrizalNo ratings yet
- Student Workbook2Document52 pagesStudent Workbook2papipapiiNo ratings yet
- Body Repairs - General Body RepairsDocument49 pagesBody Repairs - General Body RepairsjomialheNo ratings yet
- Automotive Electricity and Electronics: A01 - HALD4428 - 06 - SE - FM - Indd 1 01/11/19 7:20 PMDocument22 pagesAutomotive Electricity and Electronics: A01 - HALD4428 - 06 - SE - FM - Indd 1 01/11/19 7:20 PMsa ltyNo ratings yet
- Signal Analysis - Crank Position Sensor PDFDocument29 pagesSignal Analysis - Crank Position Sensor PDFLui Koc100% (2)
- User Manual Abrites Commander For ToyotaDocument33 pagesUser Manual Abrites Commander For ToyotaMiguel VegaNo ratings yet
- Control Module: Testing and Inspection (FS5A-EL)Document7 pagesControl Module: Testing and Inspection (FS5A-EL)calumo938220100% (1)
- Lambda Sensors: Quick and Easy Testing and ReplacementDocument12 pagesLambda Sensors: Quick and Easy Testing and ReplacementChinh HuuNo ratings yet
- 01-273 Electrical Testing PDFDocument66 pages01-273 Electrical Testing PDFmefisto06cNo ratings yet
- Ecu Diagram Forester 2002Document7 pagesEcu Diagram Forester 2002Razvan MateiNo ratings yet
- 36 S 12 T 0Document28 pages36 S 12 T 0papipapii100% (1)
- Engine Mechanical Diagnosis CourseDocument147 pagesEngine Mechanical Diagnosis CoursePaul100% (8)
- Body Network Diagnosis 2016Document79 pagesBody Network Diagnosis 2016Paul100% (5)
- TS00E v1.2 Student Noteset PDFDocument303 pagesTS00E v1.2 Student Noteset PDFpatrick morris100% (1)
- Session 1 Photometric Measrement Based On CIE S 025Document82 pagesSession 1 Photometric Measrement Based On CIE S 025Marce MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Water: Ipeat Calibration Tool of SWATDocument17 pagesWater: Ipeat Calibration Tool of SWATCristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- EMSDI Course For KGIS June 2019Document235 pagesEMSDI Course For KGIS June 2019Cristhian Huilcapaz100% (1)
- TB008 - Fuel System Pressure Test - Low Pressure System - v2021Document1 pageTB008 - Fuel System Pressure Test - Low Pressure System - v2021Cristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- TSB FUE038 Air Drain Case Replacement Rev 1Document5 pagesTSB FUE038 Air Drain Case Replacement Rev 1Cristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- Technical Service Bulletin: Aftermarket Oil Filters and Oil Viscosity NoticeDocument2 pagesTechnical Service Bulletin: Aftermarket Oil Filters and Oil Viscosity NoticeCristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- Kia J2534 Reprogramming SystemDocument1 pageKia J2534 Reprogramming SystemCristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- TB018 Cylinder Compression Test v2021Document2 pagesTB018 Cylinder Compression Test v2021Cristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- TB008 - Fuel System Pressure Test - Low Pressure System - v2021Document1 pageTB008 - Fuel System Pressure Test - Low Pressure System - v2021Cristhian HuilcapazNo ratings yet
- Taiwan Panorama 2023 NovDocument128 pagesTaiwan Panorama 2023 NovKwang HwaNo ratings yet
- Phylum Aschelminthes (Nemathelminthes / Nematoda)Document15 pagesPhylum Aschelminthes (Nemathelminthes / Nematoda)Aditya KaleNo ratings yet
- 100 Watts Power Amplifier Design PDFDocument47 pages100 Watts Power Amplifier Design PDFMark Kenneth ValerioNo ratings yet
- Page Proofs: Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument44 pagesPage Proofs: Continuous Probability DistributionsApoorva PanchalNo ratings yet
- Cost CurvesDocument2 pagesCost CurvesSumit Ray100% (1)
- 36 - 4 - New York - 08-91 - 1478Document8 pages36 - 4 - New York - 08-91 - 1478Ovo OjasNo ratings yet
- DIS 4.1 ExcavationDocument29 pagesDIS 4.1 ExcavationAshraf Ismail HassenNo ratings yet
- Things That Make You Go HMMDocument2 pagesThings That Make You Go HMMmckee_jemNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Elevated Temperature On ConcreteDocument204 pagesThe Effect of Elevated Temperature On Concretexaaabbb_550464353100% (1)
- Consumer Electronics Servicing Learning Module 130610203451 Phpapp02Document145 pagesConsumer Electronics Servicing Learning Module 130610203451 Phpapp02Maureen Pusing80% (10)
- WEF DibiDocument130 pagesWEF DibimanuelNo ratings yet
- Revised LRS BRS Booklet-2015-2016Document14 pagesRevised LRS BRS Booklet-2015-2016undyingNo ratings yet
- Book's SolutionsDocument20 pagesBook's SolutionsKodjo ALIPUINo ratings yet
- Space - The Final FrontierDocument51 pagesSpace - The Final FrontierAbdul Shakoor100% (1)
- Egg Drop NotesDocument2 pagesEgg Drop Notesapi-365288705No ratings yet
- Case Study On Development of Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis (PFMEA) - Issues and RecommendationsDocument8 pagesCase Study On Development of Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis (PFMEA) - Issues and RecommendationsSang BùiNo ratings yet
- Practice Question Ffor Module 7Document6 pagesPractice Question Ffor Module 7hemkumar DahalNo ratings yet
- IND110321USA6 Bayou CatDocument1 pageIND110321USA6 Bayou CatMichel MichelNo ratings yet
- Ivf NiceDocument22 pagesIvf NiceDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure, Bohr Model and IsotopesDocument17 pagesAtomic Structure, Bohr Model and IsotopeskushanNo ratings yet
- Nage Waza (Throwing) : HIP THROWS (Koshi Waza)Document5 pagesNage Waza (Throwing) : HIP THROWS (Koshi Waza)Stuart WalshNo ratings yet
- The Hamburger Ate Boy Isn't Acceptable (Odd) But The Boy Ate The Hamburger Is Hamburger Doesn't Have This Property and The Noun Boy DoesDocument6 pagesThe Hamburger Ate Boy Isn't Acceptable (Odd) But The Boy Ate The Hamburger Is Hamburger Doesn't Have This Property and The Noun Boy DoesDania SaviraNo ratings yet
- Lo2012 TPFDocument114 pagesLo2012 TPFramjoceNo ratings yet
- Ce503 RBTDocument2 pagesCe503 RBTTarang ShethNo ratings yet
- Portuguese Market Outlook Up To 2040: A Report To APRENDocument48 pagesPortuguese Market Outlook Up To 2040: A Report To APRENMiguel Chã AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Technical Information: Dpbs 90 E MeDocument3 pagesTechnical Information: Dpbs 90 E MeЛулу ТраедNo ratings yet
- Technoir Players GuideDocument16 pagesTechnoir Players GuideDerrick D. Cochran100% (1)
- NANO-REX Lubricant AdditiveDocument8 pagesNANO-REX Lubricant AdditiveProject Sales CorpNo ratings yet
- I/O Specifications: CPU Unit DescriptionsDocument10 pagesI/O Specifications: CPU Unit Descriptionsวรพงษ์ กอชัชวาลNo ratings yet