Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PEC AC Resistance Reactance Table
PEC AC Resistance Reactance Table
Uploaded by
Erwin OsorioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PEC AC Resistance Reactance Table
PEC AC Resistance Reactance Table
Uploaded by
Erwin OsorioCopyright:
Available Formats
*
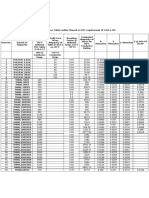
Table 9.1.1.9 Alternating-Current Resistance and Reactance for 600-Volt Cables,
9.1.1.9
-Phase, 60 Hz, 7S°C -Three Single Conductors in Conduit m
Conductor Size Ohms to Neutral per 305 m
X|, (Reactance) for All Alternating-Current Alternating-Current Effective Z at 0.85 PF for Effective Z at 0.85 PF for
Wires Resistance for Uncoated Resistance for Aluminum Uncoated Copper Wires Aluminum Wires
Copper Wires Wires
PVC, Aluminum Steel PVC Aluminum Steel PVC Aluminum Steel PVC Aluminum Steel PVC Aluminum Steel
Conduits Conduit Conduit Conduit Conduit Conduit Conduit Conduit Conduit Conduit Conduit Conduit Conduit Conduit
2.0 (1.6) 0,058 0.073 3.1 3.1 3.1 2.7 2.7 2.7 ----------- -----------
3.5 (2.0) 0.054 0.068 2.0 2.0 2.0 3.2 3.2 3.2 1.7 1,7 1.7 2.8 2.8 2.8
5.5(26) 0.050 0.063 1.2 1.2 1.2 2.0 2.0 2.0 1.1 1.1 1.1 1.8 1,8 1.8
8.0 (3.2) 0.052 0.065 0.78 0.78 0.78 1.3 1.3 1.3 0.69 0.69 0.70 1,1 1.1 1.1
14 0.051 0.064 0.49 0.49 0.49 0.81 0.81 0.81 0.44 0.45 0.45 0,71 0.72 0.72
CHAPTER 9 -TABLES
22 0.048 p. 060 0.31 0.31 0.31 0.51 0,51 0.51 0.29 0.29 0.30 0.46 0.46 0.46
30 0.045 0.057 0.19 0.20 0.20 0.32 0.32 0.32 0.19 0.19 0.20 0,30 0.30 0.30
38 0.046 0.057 0.15 0.16 0.16 0.25 0.26 0.25 0.16 0.16 0.16 0.24 0.24 0.25
50 0.044 0.055 0.12 0.13 0.12 0.20 0,21 0.20 0.13 0 13 0.13 0.19 0.20 0.20
60 0.043 0,054 0.10 0.10 0,10 0.16 0.16 0,16 0.11 0.11 0.11 0,16 0.16 0.16
80 0.042 0.052 0.077 0.082 0.079 0.13 0.13 0.13 0,088 0.092 0.094 0.13 0.13 0.14
100 0.041 0.051 0.062 0.067 0.063 0,10 0.11 0.10 0.074 0.078 0.080 0.1 1 0,11 0.1 1
125 0.041 0.052 0.052 0.057 0.054 0.085 0,090 0.086 0.066 0.070 0.073 0.094 0.098 0.10
150 0.041 0.051 0.044 0.049 0.045 0.071 0.076 0.072 0.059 0.063 0.065 0,082 0.086 0.088
175 0.040 0.050 0.038 0.043 0.039 0.061 0.066 0.063 0.053 0.058 0.060 0.073 0.077 0.080
200 0.040 0.049 0,033 0.038 0.035 0.054 0.059 0.055 0.049 0.053 0.056 0.066 0.071 0.073
250 0.039 0.048 0.027 0.032 0.029 0,043 0.048 0.045 0.043 0,048 0.050 0.057 0.061 0,064
325 0.039 0.048 0.023 0.028 0.025 0.036 0.041 0.038 0.040 0.044 0,047 0.051 0.055 0.058
375 0.038 0.048 0.019 0,024 0.021 0.029 0.034 0,031 0.036 0.040 0.043 0.045 0.049 0.052
400 0,038 0.048 0.019 0.024 0.021 0.029 0.034 0.031 0.036 0.040 0.043 0.045 0.049 0.052
500 0.037 0.046 0.015 0.019 0.018 0.023 0.027 0.025 0.032 0.036 0.040 0.039 0.042 0.046
Notes:
1. These values are based on the following constants: UL-type RHH wires with Class B stranding, in cradled configuration. Wire conductivities are 100 percent IACS
copper and 61 percent IACS aluminum, and aluminum conduit is 45 percent IACS. Capacitive reactance is ignored, since it is negligible at these voltages.
These resistance values are valid only at 75°C and for the parameters as given, but are representative for 600-volt wire types operating at 60 Hz.
2. Effective Z is defined as R cos(0) + X sin(0), where 0 is the power factor angle of the circuit. Multiplying current by effective impedance gives a good approximation
for line-to-neutral voltage drop. Effective impedance values shown in this table are valid only at 0.85 power factor.
1506
For another circuit power factor (PF), effective impedance (Ze) can be calculated from R and X L values given in this table as follows:
Z e - R x P F + Xt sin[arccos(PF)J.
You might also like
- Schedule of Loads ExcelDocument2 pagesSchedule of Loads ExcelClein Baltazar100% (6)
- Service Entrance - Meralco StandardsDocument1 pageService Entrance - Meralco StandardsMark Tristan Vallesteros85% (20)
- (2017) PEC Tables - FinalDocument13 pages(2017) PEC Tables - FinalJustin Jay Delos Reyes38% (8)
- Meralco StandardsDocument28 pagesMeralco StandardsBenj Alvarez Capistrano67% (3)
- Table of Ampacities For Wire Sizes, Conversion of AWG To Metric Sizes and Number of Conductors in A ConduitDocument17 pagesTable of Ampacities For Wire Sizes, Conversion of AWG To Metric Sizes and Number of Conductors in A ConduitJay Sunga Villan73% (11)
- Overall Pee Ter CombinedDocument509 pagesOverall Pee Ter CombinedRyan Anthony Umali100% (2)
- Philippine Electrical Code For RME HackedDocument99 pagesPhilippine Electrical Code For RME HackedRodel D Dosano92% (129)
- Space To Height RatioDocument4 pagesSpace To Height Ratiodabs_orangejuice92% (13)
- CCTV PlanDocument1 pageCCTV PlanMyto MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Loads PDFDocument5 pagesSchedule of Loads PDFmae_morano82% (28)
- Pec 1&2 - RmeDocument38 pagesPec 1&2 - RmeDor Sniper Mendoza94% (79)
- PEC Design RulesDocument31 pagesPEC Design RulesReymart Manablug100% (1)
- Philflex THHN 90c THWN 75c 600v Building WireDocument1 pagePhilflex THHN 90c THWN 75c 600v Building WireJM Arcilla100% (4)
- Technical Engineering PEEDocument3 pagesTechnical Engineering PEEMariano Acosta Landicho Jr.No ratings yet
- Electrical Design Analysis: 3 Storey Commercial BuildingDocument6 pagesElectrical Design Analysis: 3 Storey Commercial Buildingcjay ganir0% (1)
- GE Pricelist 2017Document2 pagesGE Pricelist 2017Rolando Cawaling100% (4)
- PEC (Phil Elec. Code) (By JVM) - Part-1Document56 pagesPEC (Phil Elec. Code) (By JVM) - Part-1aluism50% (2)
- Philippine Electrical Code Part 1 - Chapter 2. Wiring and Protection - GroundDocument31 pagesPhilippine Electrical Code Part 1 - Chapter 2. Wiring and Protection - GroundHarry King Corral Avenido100% (1)
- EE141 Dumlao Researched Electrical PlanDocument12 pagesEE141 Dumlao Researched Electrical PlanEme Dumlao100% (1)
- The Science of Ar K Crysta L SDocument19 pagesThe Science of Ar K Crysta L SLuana LaraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design Analysis: ProjectDocument3 pagesElectrical Design Analysis: ProjectMARKCHRISTMASNo ratings yet
- Philippine Electrical Code Table 9.1.1.9 AC Resistance Reactance TableDocument1 pagePhilippine Electrical Code Table 9.1.1.9 AC Resistance Reactance TableGlasee GoweeNo ratings yet
- Welding Machines Schedule of LoadsDocument2 pagesWelding Machines Schedule of LoadsRamled Rerref91% (11)
- Load ScheduleDocument1 pageLoad Schedulethirdy67% (3)
- Electrical Load ComputationDocument4 pagesElectrical Load ComputationAllen Velasquez Mangaoil87% (15)
- Electrical Design Analysis (Oppo Ayale Feliz) ) Dec. 21,2017Document5 pagesElectrical Design Analysis (Oppo Ayale Feliz) ) Dec. 21,2017Angelica Tungpalan Domingo100% (2)
- Electrical Design AnalysisDocument8 pagesElectrical Design Analysismaria cristina santos67% (3)
- Two Storey Load ScheduleDocument17 pagesTwo Storey Load ScheduleChristian Benedict SolomonNo ratings yet
- Floor Plan Floor Plan: Schedule of Loads PB1Document1 pageFloor Plan Floor Plan: Schedule of Loads PB1Lady Mae BrigoliNo ratings yet
- Allowable Ampacities of Insulated ConductorsDocument2 pagesAllowable Ampacities of Insulated ConductorsJohn Paks100% (2)
- Royu Wires Devices Price List APR 2017Document6 pagesRoyu Wires Devices Price List APR 2017Reymond IgayaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Bulletin - Table of Contents PDFDocument2 pagesEngineering Bulletin - Table of Contents PDFMark Anthony Baes Enoy71% (7)
- 222 M TC 106 TC Heat ExchangerDocument211 pages222 M TC 106 TC Heat ExchangerpragatheeskNo ratings yet
- Schleich Motor AnalyzerDocument12 pagesSchleich Motor AnalyzerHenry CruzNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design Analysis PDF FreeDocument2 pagesElectrical Design Analysis PDF FreeJonathan Feruelo100% (1)
- Kaic Rating (From Edison)Document1 pageKaic Rating (From Edison)Francisco M. RamosNo ratings yet
- Wiring Calculations For Single Family Dwelling UnitDocument12 pagesWiring Calculations For Single Family Dwelling UnitCastro Farfans100% (2)
- Electrical Design AnalysisDocument2 pagesElectrical Design AnalysisMaritel Sumatra100% (1)
- Typical Meter Center Set-Up For CT-Rated MeteringDocument1 pageTypical Meter Center Set-Up For CT-Rated Meteringmontgomery100% (2)
- Schedule of Load PreparationDocument3 pagesSchedule of Load PreparationTeodoro Quintana100% (2)
- Schedule of LoadDocument3 pagesSchedule of LoadCab VicNo ratings yet
- PEE REE RME RequirementsDocument28 pagesPEE REE RME RequirementsBer Salazar Jr90% (21)
- Design AnalysisDocument10 pagesDesign AnalysisRyan RamosNo ratings yet
- Iiee HymnDocument1 pageIiee HymnElvie Marian PerezNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectrical Design AnalysisJerome Virgo Catipay67% (3)
- Wire Ampacity TableDocument3 pagesWire Ampacity TablePaul YstianNo ratings yet
- 1.2.7.10 Line To Neutral 400Y-230 VDocument50 pages1.2.7.10 Line To Neutral 400Y-230 VedvirNo ratings yet
- Emt Pipe Pricelist PDFDocument1 pageEmt Pipe Pricelist PDFJules Milar Paguia80% (5)
- PEC 2017 Short Circuit Calculation SampleDocument8 pagesPEC 2017 Short Circuit Calculation SamplemarvinNo ratings yet
- ROMEO P. DELA PEÑA-Registered Electrical EngineerDocument6 pagesROMEO P. DELA PEÑA-Registered Electrical EngineerDELA PEÑA ROMEO PARDILLONo ratings yet
- Mercalco PDFDocument33 pagesMercalco PDFBethylGo100% (1)
- PEC Definition of Terms FOR ESDDocument2 pagesPEC Definition of Terms FOR ESDkelleyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design Analysis RevisionDocument3 pagesElectrical Design Analysis RevisionMarlon Habon67% (3)
- Wires Philflex Pricelist Aiti - 1620795576Document1 pageWires Philflex Pricelist Aiti - 1620795576MLB Account100% (1)
- Provide Atleast Two (2) 15A Lighting Circuits: Single Family Dwelling Service Load Calculation General LightingDocument10 pagesProvide Atleast Two (2) 15A Lighting Circuits: Single Family Dwelling Service Load Calculation General LightingRyan RamosNo ratings yet
- 2010 BurndyDocument99 pages2010 BurndycarloscaduNo ratings yet
- 24UTP Railway GBDocument8 pages24UTP Railway GBwpsssamsungNo ratings yet
- Technical DataDocument17 pagesTechnical Datat_syamprasadNo ratings yet
- Welding Technology Steelconstr - EngDocument32 pagesWelding Technology Steelconstr - EngLukman Tarigan SumatraNo ratings yet
- Wear and RepairDocument12 pagesWear and RepairmtonellyNo ratings yet
- N, BNDocument1 pageN, BNmomenziNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Corrosion Resisting SteelDocument10 pagesAtmospheric Corrosion Resisting SteelCarlos PadillaNo ratings yet
- SCH-00-J-7000 Inst. Cable Schedule Rev - 3Document28 pagesSCH-00-J-7000 Inst. Cable Schedule Rev - 3Kishore KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Cembre: Copper Tube Straight Lugs (Low Stranded)Document1 pageCembre: Copper Tube Straight Lugs (Low Stranded)Zankar R ParikhNo ratings yet
- IC65N Schneider BreakersDocument4 pagesIC65N Schneider Breakersdabs_orangejuice0% (1)
- Warehouse LED High Bay - 3 - Rev.102015 PDFDocument2 pagesWarehouse LED High Bay - 3 - Rev.102015 PDFdabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Warehouse: Lighting Layout Guide SeriesDocument2 pagesWarehouse: Lighting Layout Guide Seriesdabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Right PV VoltageDocument1 pageChoosing The Right PV Voltagedabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- BY471P InstallationDocument2 pagesBY471P Installationdabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Innovative Solutions 2011 Diagnostic Imaging Accessories & SuppliesDocument236 pagesInnovative Solutions 2011 Diagnostic Imaging Accessories & Suppliesdabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Circuit Breaker CatalogueDocument11 pagesVacuum Circuit Breaker Cataloguedabs_orangejuice0% (1)
- The IEEE Standard 1459: What and Why?Document7 pagesThe IEEE Standard 1459: What and Why?dabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Renewables 2015 Global Status Report PDFDocument251 pagesRenewables 2015 Global Status Report PDFdabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Liquid Brochure PDFDocument16 pagesLiquid Brochure PDFRigeNo ratings yet
- Power Cables YJV22Document30 pagesPower Cables YJV22dabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Parscoop Wallwashers/ceiling WashlightsDocument3 pagesParscoop Wallwashers/ceiling Washlightsdabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Powerbalance LED For HospitalsDocument5 pagesPowerbalance LED For Hospitalsdabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Cepalco Notice - July 27 To Aug 2Document5 pagesCepalco Notice - July 27 To Aug 2dabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- SmartForm LED 44W For HospitalsDocument3 pagesSmartForm LED 44W For Hospitalsdabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Luxspace LED For HospitalsDocument27 pagesLuxspace LED For Hospitalsdabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Coreline Downlight PDFDocument7 pagesCoreline Downlight PDFdabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Defini Um 5000 BrochureDocument4 pagesDefini Um 5000 Brochuredabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- C.A 6413 EARTH CLAMPS Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesC.A 6413 EARTH CLAMPS Datasheet PDFdabs_orangejuice100% (2)
- Transformer Fusing Tables For Power Line Construction and Maintenance Mz132005enDocument2 pagesTransformer Fusing Tables For Power Line Construction and Maintenance Mz132005enRiven ExileNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Dynamics of MachinesDocument60 pagesUnit 4 - Dynamics of MachinessadasivanNo ratings yet
- Lumped Heat Capacity AnalysisDocument7 pagesLumped Heat Capacity AnalysisSaumyajit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Grounding Electrode Conductors - Bonding & GroundingDocument6 pagesGrounding Electrode Conductors - Bonding & GroundingMenaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - FST559Document10 pagesExperiment 2 - FST559JAZMINA AZMANNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance Manual For WYJ 250 Series Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Gearless Traction MachineDocument20 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual For WYJ 250 Series Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Gearless Traction MachineJULIONo ratings yet
- Low-Voltage Products-Contactors, Relays, StartersDocument179 pagesLow-Voltage Products-Contactors, Relays, StartersjjbentesNo ratings yet
- Condenser Water Pump Design Guide PDFDocument31 pagesCondenser Water Pump Design Guide PDFMelaku TamiratNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document56 pagesChapter 02Samaria Mitchell100% (9)
- Second Order Circuits PDFDocument25 pagesSecond Order Circuits PDFDony AjieNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: Power / Phase Angle / Power Factor TransducerDocument44 pagesOperating Manual: Power / Phase Angle / Power Factor TransducerpadmawarNo ratings yet
- Eex5453 Tma01 2020-2021Document4 pagesEex5453 Tma01 2020-2021amilapradeepsarangaNo ratings yet
- SPD Design StepDocument1 pageSPD Design StepDEADMANNo ratings yet
- Wind Load & Blow Off Calculation NMML1Document14 pagesWind Load & Blow Off Calculation NMML1Ankit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Revisi Boq 4 Unit Solar PanelDocument3 pagesRevisi Boq 4 Unit Solar Panelahmad kusumaNo ratings yet
- DC Transient AnalysisDocument206 pagesDC Transient Analysisasanithanair35No ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionDocument14 pagesColligative Properties of SolutionJescil Ann OriolNo ratings yet
- Chapterwise Board QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapterwise Board QuestionsMirza SabeelNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: The Digital Multimeter: 1.1 ObjectiveDocument50 pagesLab 1: The Digital Multimeter: 1.1 ObjectiveWarishaNo ratings yet
- AP7301-Electromagnetic Interference and CompatibilityDocument13 pagesAP7301-Electromagnetic Interference and CompatibilitySaadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Basic Concept: 1.0 Intended Learning OutcomesDocument29 pagesUnit 1: Basic Concept: 1.0 Intended Learning OutcomesMark BerioNo ratings yet
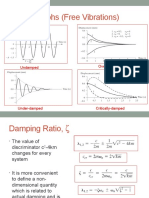
- Graphs (Free Vibrations) : Over-Damped UndampedDocument7 pagesGraphs (Free Vibrations) : Over-Damped UndampedaftabNo ratings yet
- Charge Density in MOSDocument68 pagesCharge Density in MOSJay Chandra DharNo ratings yet
- IRENA RE Auctions Status and Trends 2019Document104 pagesIRENA RE Auctions Status and Trends 2019Ricardo Marques DutraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Resistive Circuits-EditadoDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - Resistive Circuits-EditadojoeNo ratings yet
- Mov-10Dxxxk Series - Metal Oxide Varistor: Features ApplicationsDocument4 pagesMov-10Dxxxk Series - Metal Oxide Varistor: Features ApplicationsNguyên NghĩaNo ratings yet
- Questions 1 33Document33 pagesQuestions 1 33dileepNo ratings yet