Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The Body
A Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The Body
Uploaded by
SarthepandabearOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The Body
A Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The Body
Uploaded by
SarthepandabearCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOLOGY 1107K- Chapter 6
TERMS:
CELLS are the basic unit for LIFE
Organelles – a sub-cellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body.
Prokaryote – single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus or other organelles. Contains two of the three domains of life;
Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryote – plant, animals, fungi. Has a nucleus and other internal membrane bound organelles.
Archaea – single-called prokaryotic cells
Cytoplasm – interior of a prokaryotic cell, also region between the nucleus and plasma membrane in a eukaryotic cell
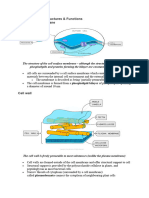
Plasma membrane – functions as a selective barrier that allows sufficient passage of molecules for cell
Nucleus – contains most of the genes in a eukaryotic cell
Chromosome – structures that carry the genetic material
Nucleolus – within the non-dividing nucleus, RNA is synthesized here
Ribosome – complexes made of ribosomal RNA and protein, carry out protein synthesis
Endoplasmic reticulum (both smooth and rough) – network of membranes, part of the nuclear envelope, network of tubules and sacs,
divided into two regions
Golgi apparatus – the center for manufacturing, warehousing, sorting and shipping, proteins are modified and stored and sent to other
destinations
Vesicle – small membrane sacs that transport proteins in the rough ER
Lysosome – membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes used to digest macromolecules
Vacuole – large vesicles produced from the ER and golgi. Found in plants and fungi. variety of functions, depending on the cell.
Cytoskeleton – network of protein fibers that extend throughout the cytoplasm and serve a variety of mechanical, transport, and
signaling functions. microtubules, intermediate filaments, microfilaments. Give the cell support.
Microtubules – Support cell structure and provide compression resistance. organelles are carried by motor proteins along
microtubules. transport vesicles also move along microtubules throughout the cells.
Microfilaments – also called actin filaments. smallest of the cytoskeleton proteins. rods that are 7nm in diameter. made of actin
monomers. bear tension forces in the cell.
Intermediate filaments – create the nuclear lamina. cytoplasmic ones are found only in animal cells.found in keratin, laming,
neurofilaments.
Concepts:
Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Edno-membrane system and the path a protein takes from synthesis to secretion from cell
Surface area to volume ratio
Functions of each organelle discussed in class
You might also like
- Comparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesComparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsmalathyNo ratings yet
- MCAT - Kaplan Biology OutlineDocument8 pagesMCAT - Kaplan Biology OutlineShum ChanNo ratings yet
- STM123 OutlineDocument19 pagesSTM123 OutlineNur-Aiza AlamhaliNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Cell StructureDocument31 pagesCh.4 Cell StructureEmma WisemanNo ratings yet
- Yr 11 Biology NotesDocument19 pagesYr 11 Biology Notesareebah.shahbaz1No ratings yet
- Unit 4 REVIEWDocument16 pagesUnit 4 REVIEWJuliana RiveraNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- CH 6 A Tour of The CellDocument7 pagesCH 6 A Tour of The Cellwil7verNo ratings yet
- CellDocument32 pagesCellSagita RahayuNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellDocument8 pagesGrade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellOlayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Organelles: Prepared By: SAPANA JHADocument14 pagesEukaryotic Cell Organelles: Prepared By: SAPANA JHAAppu JhaNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- Structure and TaxonomyDocument4 pagesStructure and Taxonomymhiee maaaNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument146 pagesCell TheoryGynewNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsDocument56 pagesTopic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsAhmed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Nature of CellsDocument7 pagesNature of CellsAdrian Lee VannorsdallNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Cells Structure and FunctionDocument56 pagesCells Structure and FunctionAnnisa DiyanabilaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SVDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SValkbbushra25No ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions FunctionsDocument4 pagesLesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions Functionskruyll vlogsNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Lec 2-Cell BiologyDocument48 pagesLec 2-Cell BiologyHowra KiyasdeenNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- BiotDocument13 pagesBiotJOSCEL SYJONGTIANNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2016 - 2017Document8 pagesReviewer 2016 - 2017VivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- OrganellesDocument13 pagesOrganellesjanaNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesCell OrganellesMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument36 pagesThe CellSam MumoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument28 pagesCellJanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2ALevels of Organization in Animal ComplexityDocument15 pagesLecture 2ALevels of Organization in Animal ComplexityElleNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalDocument6 pagesAnimal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalJohnson Macayan FernándezNo ratings yet
- The Cell FinalDocument48 pagesThe Cell FinalJuliane Caniele IndiongcoNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Document8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ReviewerDocument11 pagesEarth and Life Science ReviewerVicente MarkNo ratings yet
- Ploginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsDocument2 pagesPloginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsNelson De LimaNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 BioA 3201Document6 pagesAssign 2 BioA 3201Princess CabardoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.animal Cell StructureDocument25 pagesTopic 2.animal Cell StructureJanine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures 2: Hamilton High School Biology Chapter 3Document27 pagesCell Structures 2: Hamilton High School Biology Chapter 3PiereNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- UNIT-2-SHORT NOTES Biology ALEVElSDocument38 pagesUNIT-2-SHORT NOTES Biology ALEVElSMohammed HasnatNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction CellDocument48 pagesIntroduction CellabdNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypesDocument6 pagesLESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypessandraNo ratings yet
- Notes Science CellsDocument12 pagesNotes Science CellsHina SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelDocument56 pages2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelVe LinNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Document22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoNo ratings yet
- bsc2010 - Biology - 1 06-2010-10Document59 pagesbsc2010 - Biology - 1 06-2010-10RoxyLoreNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- 2 CellsDocument31 pages2 CellsRashed NadaNo ratings yet
- Crux - Cell Biology - 1680870050Document38 pagesCrux - Cell Biology - 1680870050Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- 2 Cell and TissueDocument45 pages2 Cell and Tissuemandefro2No ratings yet
- Chapter #1 Aishka NotesDocument5 pagesChapter #1 Aishka Notessales zfNo ratings yet
- BIO101 Eukaryotic CellDocument24 pagesBIO101 Eukaryotic CellAvani PatilNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Ncert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesNcert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeShah RukhNo ratings yet
- Biology Part - 1Document68 pagesBiology Part - 1SantoshNo ratings yet
- Type of Cell FunctionDocument3 pagesType of Cell FunctionDerek Pagsolingan0% (1)
- Biology Solved 1500 MCQs PDF Book With Answers Download PDFDocument367 pagesBiology Solved 1500 MCQs PDF Book With Answers Download PDFBaba Khan67% (3)
- Ilovepdf Merged 2 PDFDocument307 pagesIlovepdf Merged 2 PDFAhmed ZidanNo ratings yet
- Endobiosis or Blood Parasitism - The Teaching of Prof. G. EnderleinDocument47 pagesEndobiosis or Blood Parasitism - The Teaching of Prof. G. EnderleinrafaelNo ratings yet
- Essential Notes On Pathophysiology For Advanced Practice NursesDocument88 pagesEssential Notes On Pathophysiology For Advanced Practice NursesHaneenNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 - Module 7-MitosisandmeiosisDocument32 pagesGeneral Biology 1 - Module 7-Mitosisandmeiosisエアーア ラシブNo ratings yet
- 64212-08 RNA SplicingDocument41 pages64212-08 RNA SplicingKhadija MohammedNo ratings yet
- SBI3U - Genetics Processes-Meiosis and MitosisDocument3 pagesSBI3U - Genetics Processes-Meiosis and Mitosisapi-280363197No ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 1 To 5Document23 pagesBio Chapter 1 To 5QASIM jamilNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function Multiple Choice Quiz Questions and AnswersDocument32 pagesCell Structure and Function Multiple Choice Quiz Questions and AnswersAlyssa Kim Fernandez50% (4)
- Notes On Anatomy and Physiology For Yoga PDFDocument195 pagesNotes On Anatomy and Physiology For Yoga PDFPetar MogilskiNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 First Periodical Test TosDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology 1 First Periodical Test TosMA. HAZEL TEOLOGONo ratings yet
- Neural ApoptosisDocument6 pagesNeural ApoptosisJay HardkickNo ratings yet
- Physiology Biophysics and Biomedical EngDocument759 pagesPhysiology Biophysics and Biomedical EngLUIS DAVID ROJAS CARDENAS100% (4)
- BIOCHEM 1 Cell Biomolecules PDFDocument3 pagesBIOCHEM 1 Cell Biomolecules PDFHarold James AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Fifth Edition Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: GCSE Biology For YouDocument1 pageFifth Edition Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: GCSE Biology For YouclydeNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Quarter 1, Module 2aDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Quarter 1, Module 2aSam KimNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 1 PDFDocument32 pagesMeiosis 1 PDFSaurabh Raje67% (3)
- M1 Science Test-Cells: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesM1 Science Test-Cells: Multiple ChoiceBillD100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument8 pagesCell Structure and FunctionTshibambeNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument30 pagesTranscriptionAizelle TarataraNo ratings yet
- Bioptron Hyperpolarized Light - Brochure - EN - Low ResDocument23 pagesBioptron Hyperpolarized Light - Brochure - EN - Low ResMilica Popovic100% (1)
- Zinc, Copper and Selenium in ReproductionDocument15 pagesZinc, Copper and Selenium in ReproductionNéstor MirelesNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology and GeneticsDocument144 pagesCell Biology and GeneticsReka Kutasi100% (1)
- The Living CellDocument53 pagesThe Living CellDaniele Joseph HizonNo ratings yet
- Lupus ErythematosusDocument19 pagesLupus ErythematosusLakshya J Basumatary100% (2)
- 33 MANE-001 Human Genetics Block-3 Human Cytogenetics PDFDocument60 pages33 MANE-001 Human Genetics Block-3 Human Cytogenetics PDFArvindPathakNo ratings yet
- In Spermatogenesis, 4 Genetically Unique Sperm Cells Are Created. in Oogenesis, 1 Ovum Forms and 3 Polar BodiesDocument1 pageIn Spermatogenesis, 4 Genetically Unique Sperm Cells Are Created. in Oogenesis, 1 Ovum Forms and 3 Polar Bodiesscooter brewerNo ratings yet