Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Strategic Management Control (Best Summary)
Strategic Management Control (Best Summary)
Uploaded by
Laura Lo Priore0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pages1. There is tension between controlling employees to avoid excessive risk and empowering creativity and innovation. Strict measurement and standardization are expensive and inefficient. Relying on values and ethics is ideal but people are imperfect.
2. Effective control systems include diagnostic controls to monitor goals, beliefs systems to inspire values-driven behavior, and boundary systems with clear limits to avoid scandals. Interactive controls allow exploration of opportunities.
3. High-performance jobs are designed around four spans: control over resources, accountability for performance measures, influence over who to interact with to achieve goals, and available support from others. More accountability than control encourages entrepreneurship while compliance roles have narrower measures.
Original Description:
Best summary ever
Original Title
Strategic Management Control (best summary)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. There is tension between controlling employees to avoid excessive risk and empowering creativity and innovation. Strict measurement and standardization are expensive and inefficient. Relying on values and ethics is ideal but people are imperfect.
2. Effective control systems include diagnostic controls to monitor goals, beliefs systems to inspire values-driven behavior, and boundary systems with clear limits to avoid scandals. Interactive controls allow exploration of opportunities.
3. High-performance jobs are designed around four spans: control over resources, accountability for performance measures, influence over who to interact with to achieve goals, and available support from others. More accountability than control encourages entrepreneurship while compliance roles have narrower measures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesStrategic Management Control (Best Summary)
Strategic Management Control (Best Summary)
Uploaded by
Laura Lo Priore1. There is tension between controlling employees to avoid excessive risk and empowering creativity and innovation. Strict measurement and standardization are expensive and inefficient. Relying on values and ethics is ideal but people are imperfect.
2. Effective control systems include diagnostic controls to monitor goals, beliefs systems to inspire values-driven behavior, and boundary systems with clear limits to avoid scandals. Interactive controls allow exploration of opportunities.
3. High-performance jobs are designed around four spans: control over resources, accountability for performance measures, influence over who to interact with to achieve goals, and available support from others. More accountability than control encourages entrepreneurship while compliance roles have narrower measures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
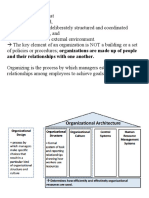
1 Control in an Age of Empowerment
Tension between providing flexibility/innovation/creativity/entrepreneurial flair to empower employees do redefine
according to their best knowledge AND exposure to excessive risk and/or behaviours than damage the company’s
integrity which used to be controlled by constant surveillance (50’s) + standardization (still in use nowadays) but
expensive, inefficient; also by only relying on good people with right values: idealistic
CONTROL (not only strict measurement of performance) VS CREATIVITY
o diagnostic control system (critical performance variables)
keep critical performance variables within present limits to monitor goals and measure progress
towards targets periodically, allowing for fine-tuning/adjustments only
can create failures (crises), as built-in danger (ex: audit control, false journal entries)
o beliefs systems (core values + purpose)
articulate concise, value-laden, inspirational values/directions to inspire commitment
how firms create value (best in the world), level of performance the organization strives
for (pursuit of excellence), how people should behave (respect)
works if only values are deeply rooted (actually walk the talk), provide guidance
more empowered/creative employees augment diagnostic control systems
o boundary system (risks to be avoided)
minimum standards (ethical behaviour, codes of conduct), should tell what to do discourage
creativity or what not to do allow innovation, but within clearly defined limits
temptation, pressure to bend the rule to achieve “unwanted/undesirable” goals
often instituted only after a public scandal/investigation, must be harsh/severe punishment
also clear the field of possible clients/market opportunities to pursue, and other to avoid
o interactive control system (strategic uncertainties - managerial)
if small: explore emerging threats and opportunities together, otherwise proper tools
formal information systems to influence decisions in an action plans/react accordingly
2 Designing High-Performance Jobs
Four basic spans of a job:
Control: “What resources do I control to accomplish my tasks?”
o E.g. Nestlé – reformulate for each country/taste
Manager regional – lots of control over pricing, distribution, sales
Manager HQ: limited decision-making logistic, supply chain
Accountability: “What measures will be used to evaluate my performance?”
o E.g. many trade-off – accountability; fewer trade-off – less accountability
Initiative/take risks: broad metrics (market share, customer satisfaction, …)
Compliance with standard operating procedures: narrow measures (employees, expense)
More accountability than control: become entrepreneurs/stimulate creativity
Influence: “Who do I need to interact with and influence to achieve my goals?”
o Wide: think outside the box, consolidate outside silos, counteract rigidity, cross functional teams,
The more the complex/interdependent job, the wider the span should be
P&G quote: “The circle of influences should be greater than circle of control”
Support: “How much support can I expect when I reach out to others for help?”
o Level of commitment from the other are required (low =
You might also like
- Organization and ManagementDocument88 pagesOrganization and ManagementJayMorales100% (1)
- Mcs SummaryDocument36 pagesMcs Summarypatrik stenbergNo ratings yet
- OB2 Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesOB2 Cheat SheetVeni GuptaNo ratings yet
- Management 1 - Gekürzte KarteikartenDocument51 pagesManagement 1 - Gekürzte KarteikartenGzg GebNo ratings yet
- Management Theory and PracticeDocument24 pagesManagement Theory and Practiceprvigneshkumar100% (1)
- Septemer 4: Rational IndividualDocument10 pagesSeptemer 4: Rational IndividualDyenNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ShortDocument13 pagesEntrepreneurship Shortali abbasNo ratings yet
- Summary Applied Psychology in Human Resource Management by CascioDocument46 pagesSummary Applied Psychology in Human Resource Management by CascioDaanNo ratings yet
- Blocks To and Aids For CreativityDocument4 pagesBlocks To and Aids For CreativityShahid RehmanNo ratings yet
- Notes For ReportingDocument4 pagesNotes For ReportingCharie Mae Gaurana BarbaNo ratings yet
- Organization CultureDocument12 pagesOrganization CultureRenu TutejaNo ratings yet
- MCS NotesDocument17 pagesMCS NotesNikhil JainNo ratings yet
- Commencment and ContractDocument6 pagesCommencment and Contractmehulj099No ratings yet
- RESOURCES ! Entrepreneurial Processes ! STRATEGIC POSITIONING ! Innovative Strategies Development ! INDUSTRY STRUCTUREDocument7 pagesRESOURCES ! Entrepreneurial Processes ! STRATEGIC POSITIONING ! Innovative Strategies Development ! INDUSTRY STRUCTUREkvakxeNo ratings yet
- Look and LearnDocument4 pagesLook and LearnNebi LezgizadehNo ratings yet
- Liam MCDocument18 pagesLiam MCFluid TrapsNo ratings yet
- Organization TheoryDocument7 pagesOrganization TheoryDiana MatviikoNo ratings yet
- Assignment #3Document3 pagesAssignment #3Ruby EstacioNo ratings yet
- Why and How To Manage Clinical PracticeDocument29 pagesWhy and How To Manage Clinical Practiceanon_526533404No ratings yet
- Chapter VIII. MEASURING RESULTS ORG.Document16 pagesChapter VIII. MEASURING RESULTS ORG.Arliz Ellaine SiquianNo ratings yet
- Stratman HB NotesDocument31 pagesStratman HB NotessaikyouNo ratings yet
- "70% of All Business Initiatives Fail." - Harvard Elearning AlertDocument6 pages"70% of All Business Initiatives Fail." - Harvard Elearning AlertVictor LimonNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1-2-3Document9 pagesChapters 1-2-3Jim ThiveosNo ratings yet
- Clayton Watters MSW Notes - Dec-2009Document25 pagesClayton Watters MSW Notes - Dec-2009SZANo ratings yet
- Npower Presentation 2Document24 pagesNpower Presentation 2ahmed umar bahagoNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: The Skills and CompetenciesDocument5 pagesOperations Management: The Skills and CompetenciesAnchit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Final Management 145revisionDocument24 pagesFinal Management 145revisionnahoai2004No ratings yet
- M&O SamenvattingDocument4 pagesM&O SamenvattingHoney ChangNo ratings yet
- PP-IT NotesDocument7 pagesPP-IT Notesmustabshirah.nayerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Extra Note The Internal Environment: ResourcesDocument15 pagesChapter 02 - Extra Note The Internal Environment: ResourcesjmhdeveNo ratings yet
- CATWOE - Developing A Robust Problem DefinitionDocument6 pagesCATWOE - Developing A Robust Problem DefinitionMario Ramón LópezNo ratings yet
- Innovation Management Realizing Value 0913 1Document13 pagesInnovation Management Realizing Value 0913 1lsfnknNo ratings yet
- Business Model InnovationDocument4 pagesBusiness Model InnovationJefferson Alzate CabobosNo ratings yet
- (Research Paper On Innovative Process) : K.Povenesan B.Eng (Hons) Mal, MSC (Adelaide)Document9 pages(Research Paper On Innovative Process) : K.Povenesan B.Eng (Hons) Mal, MSC (Adelaide)Povenesan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Key Differences Between Production and Operation ManagementDocument3 pagesKey Differences Between Production and Operation ManagementSiddhesh HirekarNo ratings yet
- Class 1 - An Introduction To ManagementDocument23 pagesClass 1 - An Introduction To ManagementThy Nguyen Ngoc BaoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Management: MAN101: Principles of Management Class 1Document192 pagesAn Introduction To Management: MAN101: Principles of Management Class 1Tố Quyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam RevisionDocument9 pagesMidterm Exam RevisionmaryamNo ratings yet
- MM 407 - Entrepreneurship DevelopmentDocument27 pagesMM 407 - Entrepreneurship DevelopmentPeter IllahNo ratings yet
- Notes On BAHR 508Document8 pagesNotes On BAHR 508Gurinder ParmarNo ratings yet
- LPO Final Exam FrameworkDocument11 pagesLPO Final Exam FrameworkthienlcapitalNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics Class 2 - Module 1Document42 pagesBusiness Ethics Class 2 - Module 1archit.chatterjee05No ratings yet
- Talent ManagementDocument33 pagesTalent ManagementPooja Rana100% (3)
- MNO Chapter 07 - Individual and Group Decision MakingDocument21 pagesMNO Chapter 07 - Individual and Group Decision MakingDouglas FongNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 ReviewDocument4 pagesQuiz 1 Reviewxan.orchidNo ratings yet
- OB Lecture NotesDocument60 pagesOB Lecture NotesHan XiangNo ratings yet
- HSM For BMS Students Kiu-WcDocument137 pagesHSM For BMS Students Kiu-Wcmugabe junior kabingiraNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Communication SkillsDocument23 pagesProblem Solving Communication SkillsSavitha KumarNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics NotesDocument19 pagesManagerial Economics NotesPavithra GovindarajNo ratings yet
- C D D: A T - P C A R W C: Heck The Rama at The OOR EN Oint Hecklist For Voiding and Esolving Orkplace OnflictDocument9 pagesC D D: A T - P C A R W C: Heck The Rama at The OOR EN Oint Hecklist For Voiding and Esolving Orkplace Onflictjustin76No ratings yet
- Project Management Midterm ReviewerDocument7 pagesProject Management Midterm ReviewerVergara Teffani Ishy GNo ratings yet
- Organizational Diagnosis: Current and Desired Performance and How It Can Achieve Its GoalsDocument3 pagesOrganizational Diagnosis: Current and Desired Performance and How It Can Achieve Its GoalstalakayutubNo ratings yet
- LPO NotesDocument16 pagesLPO NotesthienlcapitalNo ratings yet
- Alpha Leadership ViewpointDocument7 pagesAlpha Leadership Viewpointrazvan rotaru100% (1)
- Imp For Business ManagementDocument19 pagesImp For Business ManagementMaarijNo ratings yet
- The Critical Elements of An Entrepreneurial PhilosDocument8 pagesThe Critical Elements of An Entrepreneurial Philosmelaku solomonNo ratings yet
- Buiness Competitiveness AnaysisDocument14 pagesBuiness Competitiveness AnaysisElma UmmatiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledÉlida MarinhoNo ratings yet
- Uncommonly Observant Leadership; Overcoming 'Management by Ignorance'From EverandUncommonly Observant Leadership; Overcoming 'Management by Ignorance'No ratings yet
- Indian Agri Input CompaniesDocument2 pagesIndian Agri Input Companiespratima_uniyalNo ratings yet
- Fin 2 Prelim NotesDocument8 pagesFin 2 Prelim NotesChaNo ratings yet
- Southeast University: Submitted ToDocument15 pagesSoutheast University: Submitted ToNehal NirobNo ratings yet
- Skills Framework For Air Transport BookDocument72 pagesSkills Framework For Air Transport BookMartin GohNo ratings yet
- Investiiccii PDFDocument24 pagesInvestiiccii PDFMilena KrstevaNo ratings yet
- Innovation Strategies and Performance - Are They Truly Linked PDFDocument17 pagesInnovation Strategies and Performance - Are They Truly Linked PDFEdward LumentaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing NotesDocument65 pagesPrinciples of Marketing NotesYanai ManyongaNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Overcoming Barriers To The Reuse of Construction Waste Material in Australia A Review of The LiteratureDocument11 pages2017 - Overcoming Barriers To The Reuse of Construction Waste Material in Australia A Review of The LiteratureShadab NoorNo ratings yet
- AITPN6389G - Issue Letter - 1053923881 (1) - 23062023Document2 pagesAITPN6389G - Issue Letter - 1053923881 (1) - 23062023Peddaiah KarthiNo ratings yet
- Eye Care LeadersDocument20 pagesEye Care LeadersStacy ThomasNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Policy Agenda, GovernanceDocument85 pagesModule 2 - Policy Agenda, Governancenalumino naluminoNo ratings yet
- J Cole - Marx Final EssayDocument8 pagesJ Cole - Marx Final EssayBryan PongNo ratings yet
- Case Study - 1 A-Strategic - Deep-Dive-Into-Pricing-To-Capture-Unrealized-Profit-Across-Business-Units-2020Document2 pagesCase Study - 1 A-Strategic - Deep-Dive-Into-Pricing-To-Capture-Unrealized-Profit-Across-Business-Units-2020Dr.Lalitha B S “Dr.LalithaBS SSMRV” SSMRVNo ratings yet
- TAX PlanningDocument56 pagesTAX PlanningSangram PandaNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Analysis: Introduction: ReadingDocument8 pagesDemand and Supply Analysis: Introduction: ReadingSatishNo ratings yet
- Bfsi SummitDocument1 pageBfsi SummitAamish PriyamNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 1 - Section 3 MicroEconomicsDocument34 pagesCFA Level 1 - Section 3 MicroEconomicsapi-3763138No ratings yet
- Public Goods and Externalities, by Tyler Cowen - The Concise Encyclopedia of Economics - Library of Economics and LibertyDocument3 pagesPublic Goods and Externalities, by Tyler Cowen - The Concise Encyclopedia of Economics - Library of Economics and LibertyMonikankana BoraNo ratings yet
- A Basic Primer Relative To Managed Buy/Sell Trade Programs: MT 799, MT 999 AND MT 199 Bank Swift MessagesDocument4 pagesA Basic Primer Relative To Managed Buy/Sell Trade Programs: MT 799, MT 999 AND MT 199 Bank Swift MessagesMuhammad Affendi100% (1)
- DMB 207Document8 pagesDMB 207Tirthraj SinghNo ratings yet
- MarxismDocument16 pagesMarxismKristle Jane VidadNo ratings yet
- Chap 03 - Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis-Breakeven Analysis-V1Document16 pagesChap 03 - Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis-Breakeven Analysis-V1Thanh ThưNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Education: What Do The Poor Really Want? A Look at Education Needs and Aspirations of The Bottom 40 Percent of Households in MalaysiaDocument22 pagesMalaysian Education: What Do The Poor Really Want? A Look at Education Needs and Aspirations of The Bottom 40 Percent of Households in MalaysiaIDEASMalaysiaNo ratings yet
- P3-Too Much Oil - How A Barrel Came To Be Worth Less Than Nothing - The New York TimesDocument4 pagesP3-Too Much Oil - How A Barrel Came To Be Worth Less Than Nothing - The New York Timeslê hiếuNo ratings yet
- Economics ProjectDocument7 pagesEconomics ProjectMadhusmita BeheraNo ratings yet
- Amazon CaseDocument6 pagesAmazon CaseRoopanjali JasrotiaNo ratings yet
- First American Corporation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesFirst American Corporation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDileep BhatNo ratings yet
- AAII Dividend Investing - User GuideDocument27 pagesAAII Dividend Investing - User Guideyounghack32100% (1)
- G7 HRM 3Document16 pagesG7 HRM 3Lê Minh TuấnNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Taxation PDFDocument6 pagesGeneral Principles of Taxation PDFDara CompuestoNo ratings yet