Professional Documents
Culture Documents
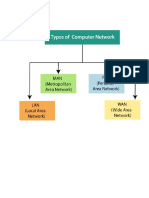
Personal Area Network (WPAN) Can Also Be Made Possible With
Personal Area Network (WPAN) Can Also Be Made Possible With
Uploaded by
Aneer RajeshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Personal Area Network (WPAN) Can Also Be Made Possible With
Personal Area Network (WPAN) Can Also Be Made Possible With
Uploaded by
Aneer RajeshCopyright:
Available Formats
A
personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used
for communication among computer devices, including telephones and personal digital assistants, in
proximity to an individual's body. The devices may or may not belong to the person in question. The
reach of a PAN is typically a few meters. PANs can be used for communication among the personal
devices themselves (intrapersonal communication), or for connecting to a higher level network and
the Internet (an uplink).
Personal area networks may be wired with computer buses such as USB and FireWire. A wireless
personal area network (WPAN) can also be made possible with wireless network technologies such
as IrDA, Bluetooth, UWB, Z-Wave and ZigBee
A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a large computer network that usually spans a city or a large
campus. A MAN usually interconnects a number of local area networks (LANs) using a high-capacity
backbone technology, such as fiber-optical links, and provides up-link services to wide area
networks (or WAN) and the Internet.
The IEEE 802-2001 standard describes a MAN as being[1]:
A MAN is optimized for a larger geographical area than a LAN, ranging from several blocks of
“ buildings to entire cities. MANs can also depend on communications channels of moderate-to-
high data rates. A MAN might be owned and operated by a single organization, but it usually will
be used by many individuals and organizations. MANs might also be owned and operated as
public utilities. They will often provide means for internetworking of local networks. ”
Authors Kenneth C. Laudon and Jane P. Laudon(2001) of Management Information Systems:
Managing the Digital Firm 10th ed. define a metropolitan area network as:
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a large computer network that spans a metropolitan area or
“ campus. Its geographic scope falls between a WAN and LAN. MANs provide Internet connectivity for
LANs in a metropolitan region, and connect them to wider area networks like the Internet
Question 8
Layer 1 = physical layer
Define the mecanisme for communicating with the transmission media and interface hardware.
Layer 2 = data link layer
Validates the integrity of the flow of data.
Layer 3 =network layer
Defines the protocols for data routing to ensure that information arrives at the correct destination.
Layer 4 = transport layer
Defines the protocol for structuring message.
Layer 5 =session layer
Coordinates communications and maintains the session for as long as needed including security and
log on function
Layer 6 = presentation layer
Defines the way data is formatted, converted and encoded.
Layer 7 = application layer
Defines the way that applications programs such as e-mail interact with the network.
You might also like
- Gas BillDocument2 pagesGas Billmohan100% (1)
- 2019-11-28 - HSBC UK Mobile Banking App Terms and ConditionsDocument13 pages2019-11-28 - HSBC UK Mobile Banking App Terms and ConditionsMarisac MihaiNo ratings yet
- Sim Swap Tutorial Verizon / At&T: Concep / Create Jac Sparrow Whatsapp +918954133645 Create: 2n Februar 2022Document6 pagesSim Swap Tutorial Verizon / At&T: Concep / Create Jac Sparrow Whatsapp +918954133645 Create: 2n Februar 2022Eduardo Sarmiento100% (2)
- Types of NetworksDocument5 pagesTypes of NetworksmmrmadhuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Network PDFDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Computer Network PDFPriyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Css3 Space Cuadra 2Document19 pagesCss3 Space Cuadra 2Dhanica PaynNo ratings yet
- Sir Kyle Perez 3Document2 pagesSir Kyle Perez 3Paulo CelisNo ratings yet
- Internet Technology:: Network Basics: Classification of NetworkDocument30 pagesInternet Technology:: Network Basics: Classification of NetworkAdibahNo ratings yet
- N 5Document19 pagesN 5visheshNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: by SatyendraDocument14 pagesComputer Networks: by SatyendraSatyendra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Networking On HDFCDocument9 pagesNetworking On HDFCAbhishek SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 1. What Is Computer Networks?Document9 pagesActivity 1 1. What Is Computer Networks?Katrina Mae VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Network, Is A Collection ofDocument8 pagesComputer Networks: Network, Is A Collection oftilak101No ratings yet
- Mba AssignmentDocument17 pagesMba AssignmentFatima AliNo ratings yet
- CN 3rd Year Unit 1notes by MasterDocument44 pagesCN 3rd Year Unit 1notes by MasterNikhil kumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 4.1 Understand The Overview of Networking:: Characteristics of A Computer NetworkDocument14 pagesUNIT-4 4.1 Understand The Overview of Networking:: Characteristics of A Computer NetworkArunNo ratings yet
- 100 Hrs ITTDocument35 pages100 Hrs ITTricha chauhanNo ratings yet
- DCN Chapter 1 - Part 2Document66 pagesDCN Chapter 1 - Part 2Esta AmeNo ratings yet
- 1 What Is A Computer NetworkDocument4 pages1 What Is A Computer NetworkMd. Abdullah ZishanNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Data Communication & Network (3) - RemovedDocument20 pagesCH - 1 Data Communication & Network (3) - Removedmubin.pathan765No ratings yet
- Hardware and Network Servicing Level III: Determine Best Fit TopologyDocument14 pagesHardware and Network Servicing Level III: Determine Best Fit TopologyDagneWalleNo ratings yet
- Lan Wan ManDocument40 pagesLan Wan ManmanafsulaimanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of A Network: What Is A Network?Document60 pagesFundamentals of A Network: What Is A Network?Sahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4 Communication NetworkDocument72 pages4 Communication Networkhsahu14No ratings yet
- Network 1Document15 pagesNetwork 1Gaurav MishraNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer NetworkDocument3 pagesData Communication and Computer NetworkKim VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Personal Area NetworkDocument5 pagesPersonal Area Networkshahed_mdbNo ratings yet
- Review of Network Fundamentals 1Document6 pagesReview of Network Fundamentals 1hilloNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument9 pagesComputer Networksmanjotsingh12artsNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: by Tilak.k & AbhishekDocument10 pagesComputer Networks: by Tilak.k & Abhishektilak101No ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer NetworkingDocument12 pagesData Communication and Computer NetworkingM. R. KHAN DIPUNo ratings yet
- Art IntegrationDocument5 pagesArt IntegrationHargun MakkarNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer NetworkingDocument46 pagesWhat Is Computer NetworkingramprasadNo ratings yet
- Management Development Program On Network Administration SkillsDocument43 pagesManagement Development Program On Network Administration SkillsJelamDavdaNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Arpa ArpanetDocument10 pagesPurpose: Arpa ArpanetSanchit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Network TLEDocument3 pagesNetwork TLEDian DasmariñasNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Swapnil JainDocument28 pagesPresented By: Swapnil JainSwapnil JainNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworksDocument16 pagesTypes of NetworksAshraf MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Notes On Hardware & NetworkingDocument56 pagesNotes On Hardware & Networkingsomag83100% (1)
- NetworkingDocument24 pagesNetworkingAli AmarNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks - S1Document28 pagesComputer Networks - S1AnandarajAnnaduraiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Overview of Internet and Network 1Document7 pagesUnit 1 Overview of Internet and Network 1Dudzayi KasiyoNo ratings yet
- CN Two MarksDocument4 pagesCN Two MarksSelva PalaniNo ratings yet
- ComputerDocument4 pagesComputerNEHA CHAHARNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument101 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworksFARIHA KARIM INAM UL KARIMNo ratings yet
- The Latest Development in Networks and CommunicationsDocument6 pagesThe Latest Development in Networks and CommunicationsadillahNo ratings yet
- UoK - Computer NetWorksDocument18 pagesUoK - Computer NetWorksaqsaanazir12No ratings yet
- Internet Fundamentals and Web Tools Unit-1 (Fundamentals of Internet)Document35 pagesInternet Fundamentals and Web Tools Unit-1 (Fundamentals of Internet)hemanNo ratings yet
- Coputer Network Assignment'sDocument4 pagesCoputer Network Assignment'sHariom ThakurNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument64 pagesProject ReportAJ JimmyNo ratings yet
- Trabalho Redes 2Document5 pagesTrabalho Redes 2Vinicius FreitasNo ratings yet
- Write A Detail On Types of Computer NetworkDocument39 pagesWrite A Detail On Types of Computer NetworkramzanNo ratings yet
- CSE Computer NetworksDocument14 pagesCSE Computer NetworksSree MahaNo ratings yet
- Types of Networks 2Document5 pagesTypes of Networks 2Ramel OñateNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument15 pagesComputer NetworkingKatongo JamesNo ratings yet
- Types of Computer Networks Personal Area NetworkDocument3 pagesTypes of Computer Networks Personal Area Networkchapatatatenda_45863No ratings yet
- History of InternetDocument1 pageHistory of InternetTushar ShahNo ratings yet
- Networking HandbookDocument28 pagesNetworking Handbookrf telecomNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument4 pagesComputer Networkbalaji bysaniNo ratings yet
- National ESIA/ekspertisaDocument19 pagesNational ESIA/ekspertisaSimbhu Ashok CNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks (2-3)Document17 pagesComputer Networks (2-3)younas125No ratings yet
- San TiDocument5 pagesSan TiYogesh KadamNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal On Improving QualityDocument4 pagesProject Proposal On Improving Qualityzakuan79100% (2)
- Neslo Tours BrochureDocument2 pagesNeslo Tours BrochureSam NatoNo ratings yet
- Bhartiya Post Feb 09Document32 pagesBhartiya Post Feb 09K V Sridharan General Secretary P3 NFPENo ratings yet
- Senior Citizen's Act 2010 RA 9994: Alman-Najar Namla XU-College of Law Zamboanga Social Legislation and Agrarian ReformDocument15 pagesSenior Citizen's Act 2010 RA 9994: Alman-Najar Namla XU-College of Law Zamboanga Social Legislation and Agrarian ReformlazylawstudentNo ratings yet
- Indian School of Business (ISB) PGP (Intended Major: Finance) - GMAT: 740Document1 pageIndian School of Business (ISB) PGP (Intended Major: Finance) - GMAT: 740Suprateek BoseNo ratings yet
- AIA Employer's StatementDocument1 pageAIA Employer's StatementChad IMS CalambaNo ratings yet
- Internship Humayun IuDocument65 pagesInternship Humayun IuYouth ViralNo ratings yet
- Fee Structure For KUCCPS BACHELOR OF COMMERCEDocument1 pageFee Structure For KUCCPS BACHELOR OF COMMERCEFrank MweneNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Financial Accounting Canadian 3Rd Edition Phillips Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesFundamentals of Financial Accounting Canadian 3Rd Edition Phillips Test Bank Full Chapter PDFjocastahaohs63k100% (12)
- Report 2021 Aug 15 145917Document9 pagesReport 2021 Aug 15 145917dina beniniNo ratings yet
- Biznet Corporate Fact Sheet 2021Document3 pagesBiznet Corporate Fact Sheet 2021heri lerokNo ratings yet
- BSNL Bill - December PDFDocument1 pageBSNL Bill - December PDFAlak MajumderNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On VK Mart ApplicationDocument4 pagesA Review Paper On VK Mart ApplicationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Bank Rakyat - Internet BankingDocument2 pagesBank Rakyat - Internet BankingMazuin Mohd AriffNo ratings yet
- Alumni Fee Voucher UpdatedDocument1 pageAlumni Fee Voucher UpdatedHassan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Universal Health Coverage in 'One ASEAN': Are Migrants Included?Document1 pageUniversal Health Coverage in 'One ASEAN': Are Migrants Included?Renzo R. GuintoNo ratings yet
- Invoice Form 9606099Document4 pagesInvoice Form 9606099Xx-DΞΛDSH0T-xXNo ratings yet
- Malaysia E Commerce Market by Revenue - Report by Ken ResearchDocument12 pagesMalaysia E Commerce Market by Revenue - Report by Ken Researchkenresearch12No ratings yet
- 1569997233671Document2 pages1569997233671Brant RingsrudNo ratings yet
- MT Slides Logistics (14 NovDocument24 pagesMT Slides Logistics (14 NovRyan Tw ChoumingNo ratings yet
- Pedestrian Safety in Road TrafficDocument9 pagesPedestrian Safety in Road TrafficMaxamed YusufNo ratings yet
- HSBC Email Update FormDocument1 pageHSBC Email Update Formpalashsarkar8773No ratings yet
- Zdde Challan Receiptform PDFDocument1 pageZdde Challan Receiptform PDFmailtajinderNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Chapter 14 - Wireless LANsDocument29 pagesLecture 2 - Chapter 14 - Wireless LANsosamazeway22No ratings yet
- Telehealth ApplicationsDocument3 pagesTelehealth ApplicationsJILLIAN MARIE BARREDONo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 (I)Document43 pagesChapter 5 (I)mania fendiNo ratings yet
- Vanguard North America Cfs Hours of Operation 27mar2020Document16 pagesVanguard North America Cfs Hours of Operation 27mar2020Atlas SNo ratings yet