Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Perspectives On Community Education and Implications For Social Work Education and Practice
Perspectives On Community Education and Implications For Social Work Education and Practice
Uploaded by
Maria Gie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views2 pagesCommunity education is a key component of social work and aims for mutual learning between community members and social workers. It utilizes participatory methods where learners are active participants. The goals are to raise critical awareness, encourage questioning of dominant forces, and empower communities. Community development is related to community education as it is led by community members and aims to redistribute power and address inequality through collective action and equipping communities with skills.
Original Description:
Original Title
Perspectives on Community Education and Implications for Social Work Education and Practice
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCommunity education is a key component of social work and aims for mutual learning between community members and social workers. It utilizes participatory methods where learners are active participants. The goals are to raise critical awareness, encourage questioning of dominant forces, and empower communities. Community development is related to community education as it is led by community members and aims to redistribute power and address inequality through collective action and equipping communities with skills.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views2 pagesPerspectives On Community Education and Implications For Social Work Education and Practice
Perspectives On Community Education and Implications For Social Work Education and Practice
Uploaded by
Maria GieCommunity education is a key component of social work and aims for mutual learning between community members and social workers. It utilizes participatory methods where learners are active participants. The goals are to raise critical awareness, encourage questioning of dominant forces, and empower communities. Community development is related to community education as it is led by community members and aims to redistribute power and address inequality through collective action and equipping communities with skills.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
processes, and community education techniques reflect a given
society's socially constructed reality.
LESSON 3: 10. In utilizing a strengths perspective, the knowledge already exists in
a community is extended to become assets that fortify
Framework for Social Work and Community Education and Training communities' human, social, and identity capital.
11. Activities such as participation and empowerment mean sharing,
working together, and enhancing mutual learning in community
education.
Perspectives on Community Education and Implications for Social
A participatory and Liberating concept of training
Work Education and Practice
/ PARTICIPATORY TRAINING is an educational strategy in
1. A social work response to risk issues such as AIDS, poverty,
which learners are active participants in the educational process.
economic, social, political, environmental, and security matters
Their needs and questions, their reflection and analysis, and their
will include community education components.
strategy for change carry the process forward. This approach to
2. Community education has been a general social responsibility
Training aims at freeing people from patterns of thinking imposed
throughout history. Still, present risk issues compel the social work
upon them by dominant forces. Its methodology is learner-
profession to consciously accept co-responsibility for community
centered, experience-based, and open-ended.
education within the broader context of community development.
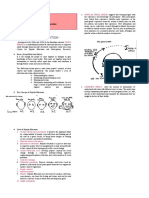
/ Five Core Elements in Development Work
3. The theoretical underpinning of the social work profession can be
o Conscientization is based on the ideas of Paolo Freire.
utilized to construct an ideal type of community education.
According to Freire, conscientization is the process of
4. The ideal type of community education is based on a mutual
raising people's critical awareness of reality.
exchange of knowledge, skills, and ideas with the community,
which implies horizontal learning. Freire’s Perspective:
5. Community education is a function of social work on a macro-
level and an identifiable role of the social worker in partnership Domestic Education emphasizes passivity,
with the community. acceptance, and submissiveness.
6. Community education is a precondition for action by the Liberating Education encourages people to
community, and therefore it is inherent in all other social work take risks, to be curious, and to question. It is
activities. seen as a process of empowerment that allows
7. Community education is not an isolated, single occurrence, but it is individuals to function as being in and with the
process-driven. Prevention, awareness, and consciousness-raising world.
are pursued as process goals. o Adult Education viewed adults as active learners. They
8. Community education is mainly non-formal, lifelong, open-ended, have specific characteristics (e.g., years of experience,
never completed, applied from a people-centered perspective, and maturity, sensitiveness to failure, etc.) that must be
aimed at sustainable social development. considered to identify more effective learning methods.
9. The social worker's response is situation-relevant and related to
local culture and indigenous knowledge. All activities, ideas, The concern for more experiential and dialogical teaching
methods has several advantages:
Learning is based on shared experiences / a holistic approach grounded in principles of empowerment,
Self-analysis/reflection is facilitated since human rights, inclusion, social justice, self-determination, and
students are treated as adults; and collective action.
Methods used contribute to excellent retention / considers community members to be experts in their lives and
or learning experiences. communities and values community knowledge and wisdom.
o Participatory Development views development training / community development programs are led by community members
as: at every stage - from deciding on issues to selecting and
A crucial step in the social preparation for more implementing actions and evaluation
critical and responsible participation; and / has an explicit focus on redistributing power to address the causes
A continuing effort to strengthen local of inequality and disadvantage.
capabilities to sustain such actions. / educating community people is central to community development.
o Empowerment of the Poor is one of the fundamental goals / aims to equip communities with the knowledge and skills they
of empowerment is to enable people to make themselves need for collective action.
better than before they were trained. It involves capacity / a process whereby learning is used for both the betterment of the
building, changes in its management, democratic individual and the community.
processes, change agents acting as capability builders and / characterized by:
enablers, and technical soundness as crucial as the human o Involvement of people of all ages
process. o The use of community learning, resources, and research to
o Community Organizing as an element regards training as bring about community change
an integral part of raising people's consciousness and o The recognition that people can learn through, with, and
facilitating collective action. for each other to create a better society.
Central to community organizing is the Micro to
Macro Approach that merges individual
concerns with group interests, gradually moving
from immediate to community issues.
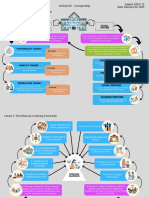
Relationship of Community Education and Community Development
COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT
/ designed to empower the people in a targeted geographical area
with the knowledge, skills, and motivation to improve their
surrounding environment and economic circumstances.
/ a transformational approach to change that concentrates on
creating embedded competencies rather than just giving people a
handout.
You might also like
- First Grade Math Lesson - MoneyDocument7 pagesFirst Grade Math Lesson - Moneyapi-383249099No ratings yet
- Framework of Community Education and TrainingDocument9 pagesFramework of Community Education and Trainingfedro cruz100% (1)
- Module 1 - Introduction To Community EducationDocument17 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Community EducationRonn Serrano100% (5)
- Chapter 6 Positive Youth DevelopmentDocument14 pagesChapter 6 Positive Youth DevelopmentDon JuanNo ratings yet
- Community Education - : Lesson 2: Concepts and Theoretical Foundations of Community EducationDocument2 pagesCommunity Education - : Lesson 2: Concepts and Theoretical Foundations of Community EducationMaria GieNo ratings yet
- Module 2 in Foundation of Social StudiesDocument17 pagesModule 2 in Foundation of Social StudiesRomar M. DavidNo ratings yet
- Nature Hand-Drawing Fresh Pink Card Letter-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesNature Hand-Drawing Fresh Pink Card Letter-WPS OfficeLeslie mae GioNo ratings yet
- Social Responsibility - Executive Summary For EducatorsDocument3 pagesSocial Responsibility - Executive Summary For EducatorsDelia CristeaNo ratings yet
- The Education, Religion, Institution and Health: Understanding Culture, Society, and PoliticsDocument5 pagesThe Education, Religion, Institution and Health: Understanding Culture, Society, and PoliticsJhon Keneth NamiasNo ratings yet
- Educ 5Document3 pagesEduc 5jamesmatthew.maderazoNo ratings yet
- NSTP Week 5 7Document9 pagesNSTP Week 5 7Val PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Abueva - Lesson 1-2 Concept MapsDocument2 pagesAbueva - Lesson 1-2 Concept MapsJaye LenizoNo ratings yet
- PROF ED 7: The Teacher and The Community, School Culture and Organizational LeadershipDocument2 pagesPROF ED 7: The Teacher and The Community, School Culture and Organizational LeadershipSison, Mikyle M.No ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Overview of Popular EducationDocument2 pagesLesson 4: Overview of Popular EducationMaria GieNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The Community, School Culture and Organizational Leadership - ReviwerDocument4 pagesThe Teacher and The Community, School Culture and Organizational Leadership - ReviwerAnnika Rose PereyraNo ratings yet
- Dr. LaudDocument106 pagesDr. LaudRogelio LadieroNo ratings yet
- Arellano University: Mas 106: Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumDocument2 pagesArellano University: Mas 106: Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumCarl LewisNo ratings yet
- Social Responsibilities: Cambridge Life Competencies FrameworkDocument8 pagesSocial Responsibilities: Cambridge Life Competencies FrameworkGalina BazhuraNo ratings yet
- EDUCATION ActivitiesDocument3 pagesEDUCATION ActivitiesShiera Mae PuguonNo ratings yet
- Written Report in Functions of Educational SociologyDocument3 pagesWritten Report in Functions of Educational SociologyNathan100% (2)
- Unit-10 School - Industry InterfaceDocument11 pagesUnit-10 School - Industry InterfaceCarlMasstownNo ratings yet
- Social Responsibilities: Cambridge Life Competencies FrameworkDocument11 pagesSocial Responsibilities: Cambridge Life Competencies FrameworkJairo JuniorNo ratings yet
- Bte2601 Assignment 04Document14 pagesBte2601 Assignment 04Vincentius KrigeNo ratings yet
- Akhuwat Internship Program ProfileDocument13 pagesAkhuwat Internship Program ProfileSawaiz RiazNo ratings yet
- NSTP Mid-Community-ImmersionDocument4 pagesNSTP Mid-Community-ImmersionMarianneNo ratings yet
- Importance of Community ParticipationDocument8 pagesImportance of Community ParticipationLikassa LemessaNo ratings yet
- Social Dimensions in EducationDocument23 pagesSocial Dimensions in EducationRyan Cornista100% (1)
- UNESCOs Five Pillars of EducationDocument10 pagesUNESCOs Five Pillars of EducationIvy GonzagaNo ratings yet
- NSTP Community Immersion As Foundation of National DevelopmentDocument3 pagesNSTP Community Immersion As Foundation of National DevelopmentULTRAK NROLLNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Bureau of Learning Delivery Teaching and Learning DivisionDocument7 pagesDepartment of Education Bureau of Learning Delivery Teaching and Learning DivisionShein Gonzales50% (2)
- Education in EmergenciesDocument7 pagesEducation in EmergenciesDianne AldovinoNo ratings yet
- Social Responsibility of Educators: Original ArticleDocument6 pagesSocial Responsibility of Educators: Original ArticleEmmalyn PatindolNo ratings yet
- SW Community Education and TrainingDocument13 pagesSW Community Education and Trainingrobelyn gayagay100% (1)
- 2 Community Engagement in Education ProgramsDocument12 pages2 Community Engagement in Education Programssharmakhan433No ratings yet
- UNESCO's Five Pillars of Education in The 21st Century Teaching and LearningDocument5 pagesUNESCO's Five Pillars of Education in The 21st Century Teaching and LearningAlthea SombilonNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Principles of Immersion Lesson 6Document2 pagesConcepts and Principles of Immersion Lesson 6Gringgo PanesNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Learning-SrnDocument46 pagesCollaborative Learning-SrnMelly ChaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 in Foundation of Social StudiesDocument11 pagesModule 2 in Foundation of Social Studiesjesan villaceranNo ratings yet
- Cesc G12Q4W6Document12 pagesCesc G12Q4W6jiremesamsondamianjiremeNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Self EfficacyDocument24 pagesThe Effect of Self EfficacyDikky JulistianNo ratings yet
- B.Ed 101Document45 pagesB.Ed 101vogedi5897No ratings yet
- NSTP NotesDocument15 pagesNSTP Notesrheena espirituNo ratings yet
- GR 12. HUMSS (Module 3 Week 4) 4th QDocument3 pagesGR 12. HUMSS (Module 3 Week 4) 4th QAcilla Mae BongoNo ratings yet
- Essence of and A Model For Reflective Practice in Development CommuniationDocument21 pagesEssence of and A Model For Reflective Practice in Development CommuniationJeannie Rose M. Sarabia IIINo ratings yet
- LCN Module 1 OverviewDocument19 pagesLCN Module 1 OverviewSalisa100% (1)
- 1 Class and EducationDocument1 page1 Class and EducationValeria OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Socio CulturalDocument5 pagesSocio CulturalFretche MiñozaNo ratings yet
- A Thesis Chapters Draft 1Document29 pagesA Thesis Chapters Draft 1Rogelio SorianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Latest) - Socialization School CultureDocument20 pagesChapter 4 (Latest) - Socialization School CultureNur Khairunnisa Nezam II0% (1)
- The Role of Teachers in Nation's Building - LinkedInDocument4 pagesThe Role of Teachers in Nation's Building - LinkedInMirza Zia HussainNo ratings yet
- Teori Dan Aplikasi Pendidikan MasyarakatDocument20 pagesTeori Dan Aplikasi Pendidikan MasyarakatyulitaramadantiNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 312Document3 pagesProf Ed 312Stephanie Cruz100% (1)
- SSC Act Lesson 3 6 1Document8 pagesSSC Act Lesson 3 6 1Ana Marie NasoleNo ratings yet
- University of Cagayan Valley College of HealthDocument2 pagesUniversity of Cagayan Valley College of HealthMac Paul V AlariaoNo ratings yet
- CESC12 Q1 M6 Forms of Community EngagementDocument16 pagesCESC12 Q1 M6 Forms of Community EngagementJeffrey LozadaNo ratings yet
- Social Entrepreneurship Andragogy-Based For Community EmpowermentDocument6 pagesSocial Entrepreneurship Andragogy-Based For Community EmpowermentHalim Pandu LatifahNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The School and The CommunityDocument8 pagesThe Teacher and The School and The CommunityKaren Palasigue Felipe100% (1)
- Module 8 Ucsp EducationDocument4 pagesModule 8 Ucsp EducationAnatta AttanaNo ratings yet
- NSTP 2 - Social Preparation (Optional Module) : All CoursesDocument11 pagesNSTP 2 - Social Preparation (Optional Module) : All CoursesMarylene Conge AbantaoNo ratings yet
- (Final) Academic Calendar 2022-2023Document3 pages(Final) Academic Calendar 2022-2023Haseeba KhanNo ratings yet
- V3i710 1 1Document13 pagesV3i710 1 1Aikin AmorinNo ratings yet
- Think Paper (Rizal's Brindis Speech)Document2 pagesThink Paper (Rizal's Brindis Speech)KIMVERLIE PASCUANo ratings yet
- 2017-2018 1st Sem PGDE Exams Time-TableDocument2 pages2017-2018 1st Sem PGDE Exams Time-Tablesodunke omolaraNo ratings yet
- Book of Abstracts 7-06-18Document220 pagesBook of Abstracts 7-06-18克麦No ratings yet
- Delights and Difficulties Multi-Grade Teachers in Rural Schools, PhilippinesDocument6 pagesDelights and Difficulties Multi-Grade Teachers in Rural Schools, PhilippinesJhessmarck PalmaresNo ratings yet
- Brigada Pagbasa ImplementationDocument5 pagesBrigada Pagbasa Implementationarbert lanchitaNo ratings yet
- Research Broken Family-1 0Document34 pagesResearch Broken Family-1 0Mary Cess Unido87% (15)
- Mains Question Paper 5 (Hindi) - 2013Document6 pagesMains Question Paper 5 (Hindi) - 2013abhimanyuNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Davao University: Graduate SchoolDocument1 pageAteneo de Davao University: Graduate Schoolkfbrand71No ratings yet
- Edci 569 - Final Project - Comp 7Document7 pagesEdci 569 - Final Project - Comp 7api-245517809No ratings yet
- Molloy Lesson Plan Rev August 19 2013-2Document14 pagesMolloy Lesson Plan Rev August 19 2013-2api-287651509No ratings yet
- Orientation: 2. Student HandbookDocument3 pagesOrientation: 2. Student HandbookRonalyn ManzanoNo ratings yet
- EDU301 General Methods of Teaching (Current Solved Paper Final Term 2021)Document17 pagesEDU301 General Methods of Teaching (Current Solved Paper Final Term 2021)Misbah HanifNo ratings yet
- Ks 5Document17 pagesKs 5api-265219702No ratings yet
- Open High School FormsDocument8 pagesOpen High School FormsAlicia EspirituNo ratings yet
- Becoming A Cambridge International School PDFDocument9 pagesBecoming A Cambridge International School PDFAnis AtmjNo ratings yet
- Discussion TextDocument20 pagesDiscussion TextPutri Nur AidaNo ratings yet
- Compulsory MiseducationDocument65 pagesCompulsory Miseducationapi-3705112No ratings yet
- Language Learning Material DevelopmentDocument20 pagesLanguage Learning Material DevelopmentEllen Grace Baguilat Putac100% (2)
- Confidential Internship Acceptance LetterDocument3 pagesConfidential Internship Acceptance Lettermohamedamine.hajjiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Common TerminologiesDocument48 pagesLesson 2 - Common TerminologiesSydNo ratings yet
- Emplyoment and Vocational Skills Development Myanmar - Praesentation DEZA PDFDocument12 pagesEmplyoment and Vocational Skills Development Myanmar - Praesentation DEZA PDFDi VineNo ratings yet
- 1644911083ielts Writing Task 2 (Essays)Document30 pages1644911083ielts Writing Task 2 (Essays)oshadhee ImeshaNo ratings yet
- English 2 Activity Sheet: Quarter 2 - MELC No. 3Document9 pagesEnglish 2 Activity Sheet: Quarter 2 - MELC No. 3Brittaney BatoNo ratings yet
- Article 1Document16 pagesArticle 1Eman SwaidanNo ratings yet
- Carlos Tünnermann Bernheim La Educación Permanente y Su Impacto en La Educación SuperiorDocument47 pagesCarlos Tünnermann Bernheim La Educación Permanente y Su Impacto en La Educación SuperiorÁngel García AbreuNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes: by The End of The Lesson You Will Be Able ToDocument11 pagesLearning Objectives Learning Outcomes: by The End of The Lesson You Will Be Able ToChristian Dave TasicNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument3 pagesSpeechxhNo ratings yet