Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Graduate Attributes and Program Outcomes
Graduate Attributes and Program Outcomes
Uploaded by
BelagaviOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Graduate Attributes and Program Outcomes
Graduate Attributes and Program Outcomes
Uploaded by
BelagaviCopyright:
Available Formats
Program Educational Objectives
PEO 1: To develop successful professionals in
Mechanical Engineering with sound fundamental
knowledge in Mathematics, Science and
Engineering.
PEO 2: To inculcate the students thrust for support higher
studies and research.
PEO 3: To equip students with ability to adopt modern
tools, technology and advanced software’s
leading to lifelong learning.
PEO4: To instill in the students leadership skills with
ethics.
Graduate Attributes and Program Outcomes
Engineering Graduates will be able to:
1. Engineering Knowledge: Apply the knowledge of mathematics, science, engineering
fundamentals, and an engineering specialization to the solution of complex engineering
problems.
2. Problem Analysis: Identify, formulate, review research literature, and analyze complex
engineering problems reaching substantiated conclusions using first principles of
mathematics, natural sciences, and engineering sciences.
3. Design & Development of Solutions: Design solutions for complex engineering problems
and design system components or processes that meet the specified needs with appropriate
consideration for the public health and safety, and the cultural, societal, and environmental
considerations
4. Conduct investigations of complex problems: Use research-based knowledge and
research methods including design of experiments, analysis and interpretation of data, and
synthesis of the information to provide valid conclusions.
5. Modern Tools Usage: Create, select, and apply appropriate techniques, resources, and
modern engineering and IT tools including prediction and modeling to complex
engineering activities with an understanding of the limitations.
6. The engineer and society: Apply reasoning informed by the contextual knowledge to
assess societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues and the consequent responsibilities
relevant to the professional engineering practice
7. Environment & Sustainability: Understand the impact of the professional engineering
solutions in societal and environmental contexts, and demonstrate the knowledge of, and
need for sustainable development.
8. Ethics: Apply ethical principles and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities and
norms of the engineering practice.
9. Individual & Team work: Function effectively as an individual, and as a member or leader
in diverse teams, and in multidisciplinary settings.
10. Communication: Communicate effectively on complex engineering activities with the
engineering community and with society at large, such as, being able to comprehend and
write effective reports and design documentation, make effective presentations, and give
and receive clear instructions.
11. Project management & Finance: Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the
engineering and management principles and apply these to one’s own work, as a member
and leader in a team, to manage projects and in multidisciplinary environments.
12. Lifelong Learning: Recognize the need for, and have the preparation and ability to engage
in independent and life-long learning in the broadest context of technological change.
Course
Outcome Statement
(CO)
CO1 Understand essential factors for product design
CO2 Design product as per customer needs and satisfaction
CO3 Understand Processes and concepts during product development
CO4 Understand methods and processes of Forward and Reverse engineering
CO5 Carry various design processes as DFA, DFMEA, design for safety
CO6 Understand the product life cycle and product data management
Program
Specific
Outcomes Statement
PSO
Design: The ability to provide designs to solve the real life problems in the
PSO1 field of Mechanical Engineering.
Modeling & Analysis: The ability to model and analyze the Mechanical
PSO2 systems/processes using CAE tools.
Society: To strengthen Mechanical Engineering graduates who value
PSO3
professional and ethical responsibilities while solving the societal problems.
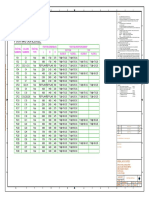
PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PSO PSO PSO
C0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
CO1 3 3 3 3 2 3 2 3 2 ““ 3 ““ 3 ““ 2
CO2 3 3 3 3 2 3 2 3 1 ““ 3 ““ 3 2 2
3
CO3 3 3 3 3 2 3 2 ““ ““ ““ 2 ““ 3 2
CO4 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 ““ 2 3 3 ““ 3 2 3
CO5 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 ““ 3 2 3 3 3 2 3
CO6 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 ““ ““ ““ 1 3 3 2 1
avg 3 3 3 3 2.4 3 2.5 3 2.0 2.5 2.5 3 3 2 2.5
Note: Enter correlation levels 1, 2 or 3 as defined below:
1: Slight (Low) 2: Moderate (Medium) 3: Substantial (High), It there is no correlation,
put “-”
Formation of Topic Level Outcome (TLO)
Topic level outcome
Unit 1: Product Design and development: The Students should able to
Select appropriate advanced design processes.
Compare different advanced designs of competitors
Unit 2: Product Development –Technical and Business Concerns: The Students should able to
Select appropriate forecasting for developing a new product
Combine different forecasts of competitors for best design considerations.
Unit 3: Product Development from Concept to Product Function: The Students should able to
To apply the knowledge of Product Design and Development in business, industry as well as
in management
Compare different advanced techniques.
Unit 4: Reverse Engineering: The Students should able to
Applying the mathematical skills for dealing real life problems.
Unit 5: Design for X: The Students should able to
Select appropriate additive Processes, material, and process parameters.
Unit 6: Product Life Cycle Management and Product Data Management: The Students should
able to
To continue to learn and adapt to the growing needs of the society to meet the future real life
challenges.
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Engineering Design Graphics Sketching Modeling and Visualization Leake 2nd EditionDocument3 pagesSolution Manual For Engineering Design Graphics Sketching Modeling and Visualization Leake 2nd EditionCory Smith100% (37)
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successFrom EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Curriculum Map (EAPP 1st Sem)Document11 pagesCurriculum Map (EAPP 1st Sem)Rodrick RamosNo ratings yet
- Faculty Python Lab ManualDocument33 pagesFaculty Python Lab ManualJitendra Kumar Chauhan100% (1)
- Chapter 12 - Structural RobustnessDocument22 pagesChapter 12 - Structural RobustnessErnie ErnieNo ratings yet
- MEC3416 Semester2 2016Document28 pagesMEC3416 Semester2 2016Aloysi DelouizaNo ratings yet
- CCS356 Oose Lab ManualDocument16 pagesCCS356 Oose Lab ManualMakendran CSENo ratings yet
- KHALIk FirstDocument10 pagesKHALIk FirstNikhil BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Anushka Final ReportDocument38 pagesAnushka Final ReportAnjaliNo ratings yet
- BTY350 Zero LectureDocument20 pagesBTY350 Zero Lecturevivekanand879355443612No ratings yet
- Co Po Mapping IEMDocument7 pagesCo Po Mapping IEMram prasadNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Human Being (Ask)Document13 pagesUnderstanding The Human Being (Ask)Nikhil BaliyanNo ratings yet
- CS3491AI & ML Lab ManualDocument105 pagesCS3491AI & ML Lab Manualsspradeepa44No ratings yet
- Po - Pso - CoDocument3 pagesPo - Pso - CoBalakarthikeyan MNo ratings yet
- QB Third YearDocument199 pagesQB Third YearPericherla Rakesh varmaNo ratings yet
- Project Report Final Updated'Document37 pagesProject Report Final Updated'SAKSHAM PRATAP RANANo ratings yet
- It WorkshopDocument51 pagesIt WorkshopSarthak DugarNo ratings yet
- Machine Design - I COPODocument5 pagesMachine Design - I COPOrajdecoratorsNo ratings yet
- Mec481 PDFDocument9 pagesMec481 PDFpoomarimuthukumarNo ratings yet
- BE - Civil - Padeepz AppDocument362 pagesBE - Civil - Padeepz AppsujithrathiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- CN Lab Front PageDocument5 pagesCN Lab Front PageSarang HaeNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems - Final MaterialsDocument181 pagesDistributed Systems - Final MaterialsGaneshNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science and Engineering: Code Name of The Course OutcomeDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineering: Code Name of The Course OutcomeVikram AnandNo ratings yet
- B E MechDocument363 pagesB E MechAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- 20AIL58A (Lab Manual Final) - 1Document47 pages20AIL58A (Lab Manual Final) - 1adarshramesh2002No ratings yet
- SRM TRP Engineering College TrichyDocument13 pagesSRM TRP Engineering College TrichyMANI KANDANNo ratings yet
- Uid LabDocument2 pagesUid Labsrustishree sahuNo ratings yet
- DWM Lab CopomappingDocument7 pagesDWM Lab CopomappingRajesh KannaNo ratings yet
- ESIOT Lab Manual - 240503 - 132515Document125 pagesESIOT Lab Manual - 240503 - 132515rolexman398No ratings yet
- Record Final 123 - Merged PDFDocument118 pagesRecord Final 123 - Merged PDFZenofer NishaNo ratings yet
- MTech SMFE Rev12032019Document78 pagesMTech SMFE Rev12032019Mr.Bhaskar WabhitkarNo ratings yet
- Internship Manual and DiaryDocument73 pagesInternship Manual and DiaryYash TipsNo ratings yet
- Ppsuc Manual r20Document98 pagesPpsuc Manual r20202 SAI KRISHNANo ratings yet
- COMPUTER-NETWORKS-CourseFile 28 11 2022Document10 pagesCOMPUTER-NETWORKS-CourseFile 28 11 2022pvssivaprasadcseNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Innovaton and Design ThinkingDocument2 pagesSyllabus - Innovaton and Design Thinkinglikithaswath2No ratings yet
- B.Tech Chemical EngineeringDocument166 pagesB.Tech Chemical EngineeringkrishnaNo ratings yet
- B.tech It Syllabus Reg 2017Document138 pagesB.tech It Syllabus Reg 2017Infi Coaching CenterNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Andhra PradeshDocument197 pagesNational Institute of Technology Andhra PradeshrakikiraNo ratings yet
- Modified DSP Course File (2018-19)Document30 pagesModified DSP Course File (2018-19)annam karthikNo ratings yet
- BE CivilDocument362 pagesBE CivilVVCET - CSE DEPARTMENTNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Lab 313Document46 pagesMicroprocessor Lab 313krishnverma2006No ratings yet
- 6 (L: 0 T: 0 P:6) - Sem 6: 90 (Sem 6)Document2 pages6 (L: 0 T: 0 P:6) - Sem 6: 90 (Sem 6)adomax2003No ratings yet
- B.Tech ChemicalDocument183 pagesB.Tech ChemicalKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Report Formation TemplateDocument10 pagesSummer Internship Report Formation TemplateHarshit RaoNo ratings yet
- DTPIDocument96 pagesDTPITurpati HarshithNo ratings yet
- R 19 B.tech ChemicalDocument189 pagesR 19 B.tech ChemicalBeril NavinNo ratings yet
- NBA Meeting PresentationDocument10 pagesNBA Meeting PresentationlokgenieNo ratings yet
- Production Technology Lab ManualDocument59 pagesProduction Technology Lab Manualuma deviNo ratings yet
- Part ADocument7 pagesPart AValerius HellNo ratings yet
- CD Lab ManualDocument20 pagesCD Lab ManualSuneeta KintaliNo ratings yet
- PYTHON PROGRAMMING-CourseFile 05 09 2022Document11 pagesPYTHON PROGRAMMING-CourseFile 05 09 2022pvssivaprasadcseNo ratings yet
- File 1681230537 0008406 DCLDocument15 pagesFile 1681230537 0008406 DCLAditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- SWPD - 4311603 - CO-PO-PSO Mapping With Justification Format For ComplianceDocument7 pagesSWPD - 4311603 - CO-PO-PSO Mapping With Justification Format For ComplianceNilay PatelNo ratings yet
- Cs431 Compiler Design LabDocument95 pagesCs431 Compiler Design LabANITHARANI KNo ratings yet
- 21CS52Document42 pages21CS52Sidharth PremdasNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lab Manual - 21cs52Document56 pagesComputer Networks Lab Manual - 21cs52NIKHIL N KUMARNo ratings yet
- Summer Training ReportDocument34 pagesSummer Training ReportPråshãnt ShärmãNo ratings yet
- CN Manual 2022Document80 pagesCN Manual 2022Harris AhmedNo ratings yet
- BE CivilDocument82 pagesBE CivilAshwin DeepakNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document36 pagesDocument 5agarwalakshat924No ratings yet
- CAD-CAM Handout 2023 - 24 (1)Document28 pagesCAD-CAM Handout 2023 - 24 (1)kk11091079No ratings yet
- DBMS LabDocument58 pagesDBMS Labmahedi.hassanNo ratings yet
- 19BT50109 RT SVEC2019 III I OE 1 ArticulationDocument53 pages19BT50109 RT SVEC2019 III I OE 1 ArticulationChithambar Ganesh ANo ratings yet
- Internship Manual and DiaryDocument55 pagesInternship Manual and DiarySaurabh AsnareNo ratings yet
- Why ? PLM: (Product Lifecycle Management)Document22 pagesWhy ? PLM: (Product Lifecycle Management)BelagaviNo ratings yet
- A General Procedure For Finite Element AnalysisDocument11 pagesA General Procedure For Finite Element AnalysisBelagaviNo ratings yet
- MCQ Books List 1Document1 pageMCQ Books List 1BelagaviNo ratings yet
- PDD - Unit - 3 MCQ'sDocument9 pagesPDD - Unit - 3 MCQ'sBelagaviNo ratings yet
- Sewing MachineDocument1 pageSewing MachineBelagaviNo ratings yet
- SL No. Dept. H.O.D Contact Details 1 2 CS Dept 3 E&C Dept 4 Mech DeptDocument6 pagesSL No. Dept. H.O.D Contact Details 1 2 CS Dept 3 E&C Dept 4 Mech DeptBelagaviNo ratings yet
- Mediclaim 2019Document7 pagesMediclaim 2019BelagaviNo ratings yet
- 2015 - 2016 CHARIS Washington DC Bible Reading PlanDocument3 pages2015 - 2016 CHARIS Washington DC Bible Reading PlanBelagaviNo ratings yet
- FEM Analysis of Ring Type Compressor Valve SeatDocument6 pagesFEM Analysis of Ring Type Compressor Valve SeatBelagaviNo ratings yet
- Firms List IndiaDocument4 pagesFirms List Indiakarthika PNo ratings yet
- Product and Service DesignDocument46 pagesProduct and Service DesignKim TaengoossNo ratings yet
- LIS 2022 New 1-145-153Document9 pagesLIS 2022 New 1-145-153Lppm Politeknik JambiNo ratings yet
- Cane Collection 2018 Web CatalogDocument46 pagesCane Collection 2018 Web CatalogSteviro Dany TendeanNo ratings yet
- 3DS 2020 Academia Brochure A5 FINAL WEBDocument20 pages3DS 2020 Academia Brochure A5 FINAL WEBcarlosNo ratings yet
- UI UX Designer BootcampDocument21 pagesUI UX Designer BootcampSam AryanNo ratings yet
- BIM PresentationDocument73 pagesBIM PresentationAnonymous mFO3zAqC100% (1)
- Arts 6 - Q4 - Module 1 - Design-Principles-and-ElementsDocument21 pagesArts 6 - Q4 - Module 1 - Design-Principles-and-ElementsKirstin LogronioNo ratings yet
- Final Year Projects - Class of 2012Document108 pagesFinal Year Projects - Class of 2012Mahmoud DoughanNo ratings yet
- (2016) Angarita - Beneficios Económicos de La Certificación LEED Edificio Centro Atico - Caso de Estudio ENGLISH Version PDFDocument8 pages(2016) Angarita - Beneficios Económicos de La Certificación LEED Edificio Centro Atico - Caso de Estudio ENGLISH Version PDFDnukumNo ratings yet
- Steamed Books - The Cow Tripped Over The MoonDocument2 pagesSteamed Books - The Cow Tripped Over The Moonapi-358459648No ratings yet
- Structural Morphology PDFDocument211 pagesStructural Morphology PDFKoilgoodyNo ratings yet
- Cable Routing Management: An AVEVA Business PaperDocument8 pagesCable Routing Management: An AVEVA Business PaperBakri IsmailNo ratings yet
- UX Design ProcessDocument27 pagesUX Design Processcj100% (2)
- UX Guide To Uxdesign Process and Documentation PDFDocument104 pagesUX Guide To Uxdesign Process and Documentation PDFArthur AefNo ratings yet
- Future City Outline For StudentsDocument7 pagesFuture City Outline For Studentsapi-237272805No ratings yet
- SCHEDULESDocument1 pageSCHEDULESpankaj kushwahNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Traffic Controller Using VHDL: Interim Project ReportDocument21 pagesDesign and Implementation of Traffic Controller Using VHDL: Interim Project ReportAugusto Germano da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Hexagon Smart P-IDDocument4 pagesHexagon Smart P-IDRaja0% (1)
- ImaginXP UX Integrated Program 2020 SPIT BTech Revised 08oct20Document3 pagesImaginXP UX Integrated Program 2020 SPIT BTech Revised 08oct20TPO SPCENo ratings yet
- Design & Cinema: A Timeline of Graphic Design in Film: Helena Tude ESAD Matosinhos, PortugalDocument10 pagesDesign & Cinema: A Timeline of Graphic Design in Film: Helena Tude ESAD Matosinhos, PortugalRui Bastos GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Improvement of The Particle Size Analyzer PSI® 300I: SubtitleDocument37 pagesImprovement of The Particle Size Analyzer PSI® 300I: SubtitleEkri BilalNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Strategic Management of Technological Innovation 6th Edition Melissa Schilling PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Strategic Management of Technological Innovation 6th Edition Melissa Schilling PDF Full Chapterrosarymollyvbdu796% (23)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To VLSI TestingDocument67 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To VLSI TestingSiva SreeramdasNo ratings yet
- 2 IDTheoriesDocument340 pages2 IDTheoriesCarlos Felipe UrquizarNo ratings yet