Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impaired Urinary Elimination
Impaired Urinary Elimination
Uploaded by
Agcopra MtchOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impaired Urinary Elimination
Impaired Urinary Elimination
Uploaded by
Agcopra MtchCopyright:
Available Formats
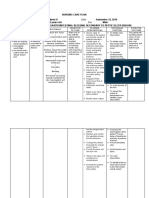
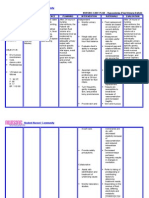
Name of Patient: Patient P.N.
Age/Sex: 19 / Female__________ Room/Bed no.: Room 123 Bed no. 3
Chief Complaint: Hallucinations___________________ Attending Physician: Dr. Perez
Diagnosis: Guillain Barre Syndrome
Date Cues Nee Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Nursing Interventions IMPLIMEN
/Ti d TATION
me
S: E Impaired urinary elimination r/t Within 8 hours of 1. Assess progressive degree 1
O L neuromuscular impairment as nursing care, the of paralysis and effect on
C O: I evidenced by urinary retention patient will be able urinary elimination.
T M and paralysis. to establish routine R: To establish data on the
O I urinary elimination effect of motor dysfunction
B Urinary N Rationale: patterns. that travels upward from
E retention A Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) extremities.
R Paralysis T is a dangerous health condition 2
Muscle I that develops when the body's 2. Monitor the intake and output
2 weakness O defense (immune) system attacks of the patient every 4 to 8
Oligoria N a section of the peripheral hours and assess for the
0 Urine nervous system by accident. The color(appearance) of urine if
ouput of 24 P peripheral nervous system allows its cloudy and check for foul
2 A the brain and spinal cord to smelling urine.
cc/hr
T communicate with various parts
1 of the body. If the PNS fails or is
T R: Monitoring the I&o helps
E damaged, nerve inflammation to determine if there is any
R occurs, resulting in numbness, changes in the I&O ratio of
N muscle weakness, or the inability the patient. Checking the
to move a part or all of one side appearance and the smell of
of the body (paralysis), which urine helps to identify
includes the loss of bladder presence of infection or 3
control. further type of elimination
(Martin, P., 2019) problem.
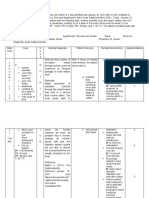
Martin, P., (2019). 6th 3. Palpate the bladder every 2
Guillain-Barre Syndrome hours. 4
Nursing Care Plans. R: To determine presence of
Retrieved on September 29, urinary retention as paralysis
2021 from progresses.
https://nurseslabs.com/guilla
in-barre-syndrome-nursing- 5
care-plans/ 4. Monitor BUN, creatinine,
white blood cell (WBC)
count.
R: These reflect renal
function and identify
complications.
5. Catheterize patient for 6
residual urine, as indicated.
Insert an indwelling urinary
catheter.
R: To maintain elimination
and this helps to relieve
bladder distention and urinary
retention of the patient.
7
6. Assist client in urinary
elimination rehabilitation
program; perform Crede’s
maneuver in a gentle manner
if indicated.
R: Promotes urine elimination
and return to a normal pattern 8
as soon as possible.
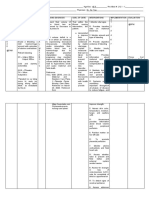
7. Instruct the patient to increase
Fluid intake up to 1,500-2,000
ml daily.
R: Sufficient hydration 9
promotes urinary output and
aids in preventing infection.
8. Encourage Client to limit
intake of coffee and alcohol.
R: Coffee and Alcohol are
chemicals known to be
bladder irritants.
10
9. Instruct patient to avoid
constipation or fecal
impaction by eating well
balanced diet with plenty of
fiber (fruits, vegetables and
whole grains).
R: Impacted stool may place
pressure on the bladder
outlet, causing urinary
retention.
10. Instruct the patient to report Mitchie E.
any reduction or absence of Agcopra St. N
urinary elimination.
R: Avoids complication
of neuromuscular impairment
of disease and effect on
urinary bladder function.
References:
Doenges, M., Moorhouse, M.,
& Murr, A., (2016). Nurse’s
Pocket Guide.14th Edition.
F.A. Davis Company
Martin, P., (2019). 6th
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Nursing Care Plans.
Retrieved on September 29,
2021 from
https://nurseslabs.com/guillai
n-barre-syndrome-nursing-
care-plans/
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2No ratings yet
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocument2 pagesRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On CystoceleDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan On Cystoceleleo100% (1)
- Avulsed Wound Left FootDocument6 pagesAvulsed Wound Left FootClaire Nimor VentulanNo ratings yet
- Buteyko Meets DR MewDocument176 pagesButeyko Meets DR MewAnonymous hndaj8zCA100% (1)
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Volume DeficitNecheal BaayNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 Elevated Boy TempDocument2 pagesNCP 1 Elevated Boy TempDudong SasakiNo ratings yet
- NCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeryanNo ratings yet
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan For AppendectomyDocument1 pageDischarge Plan For AppendectomyMyra AtuleNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusNo ratings yet
- Betty Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesBetty Impaired Skin IntegrityBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanAldrein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Aminogen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAminogen Drug Studymilesmin100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNo ratings yet
- NCP FVDDocument2 pagesNCP FVDMarlon AnryNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDocument2 pagesDisturbed Sleep PatternROxanne S. RendonNo ratings yet
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument2 pages"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Document1 pageNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDocument13 pagesNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- NCP For Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNCP For Impaired Skin IntegrityAemz Alacasnap Ainegud100% (1)
- NCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNCP Cva Ineffective Tissue Perfusionexcel21121No ratings yet
- D.A. DolcetDocument2 pagesD.A. DolcetSasha FongNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Therabloc DrugDocument2 pagesTherabloc DrugMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- NCP Altered Thermoregulation HypothermiaDocument2 pagesNCP Altered Thermoregulation HypothermiaJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- DolcetDocument2 pagesDolcetmarc_hansen_1312No ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrosisDocument2 pagesNCP Liver CirrosisRosebud RoseNo ratings yet
- Or NCP (Impaired Elimination)Document1 pageOr NCP (Impaired Elimination)Nikki M. ArapolNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitiesangel cenaNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument2 pagesConcept Mapjunifer laynoNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide: Ngeles Niversity OundationDocument9 pagesLearning Guide: Ngeles Niversity OundationNYCA GRACIA TUAZONNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP Activity Intolerancerobbiematro100% (1)
- Focus Diagnosis Action ResponseDocument2 pagesFocus Diagnosis Action ResponseGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPeun kyung shinNo ratings yet
- Assessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationkyaw100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- PDF NCP Electrolyte Imbalance - CompressDocument3 pagesPDF NCP Electrolyte Imbalance - Compressclaire yows100% (1)
- Deficit)Document2 pagesDeficit)Lee DeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationeihjay-bravo-8041No ratings yet
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Hip Fracture Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For Hip Fracture Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntolerancedohbleNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1Rommelie CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Cad NCPDocument1 pageCad NCPKrizzia Mae F. MayoresNo ratings yet
- NCP Pedia RotDocument5 pagesNCP Pedia RotGian kyle AradillosNo ratings yet
- NCP FluidDocument4 pagesNCP FluidSofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP Format LatestDocument5 pagesNCP Format LatestPrinceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing RotationDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan: Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing RotationMary Justine Nuyad-AfricaNo ratings yet
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- NCP - Mod9Document3 pagesNCP - Mod9designericlelynsoronioNo ratings yet
- NCP - Villahermosa - Risk For InfectionDocument5 pagesNCP - Villahermosa - Risk For InfectionJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- CONSTIPATIONDocument4 pagesCONSTIPATIONKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- Risk For Falls Aeb Loss of BalanceDocument4 pagesRisk For Falls Aeb Loss of BalanceAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Helicobacter Pylori, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument7 pagesHelicobacter Pylori, Diagnosis and TreatmentTrifan_DumitruNo ratings yet
- Avoid Spot Treat HeatDocument1 pageAvoid Spot Treat HeatMichael CooperNo ratings yet
- Tropical Diseases An Unsolved ChallengeDocument9 pagesTropical Diseases An Unsolved ChallengeYet Barreda BasbasNo ratings yet
- Alvise Sforza Tarabochia-Psychiatry, Subjectivity, Community - Franco Basaglia and Biopolitics-Peter Lang AG, Internationaler Verlag Der Wissenschaften (2013)Document231 pagesAlvise Sforza Tarabochia-Psychiatry, Subjectivity, Community - Franco Basaglia and Biopolitics-Peter Lang AG, Internationaler Verlag Der Wissenschaften (2013)Eddy VicenteNo ratings yet
- Ranolazine and Hallucinations: Case ReportDocument3 pagesRanolazine and Hallucinations: Case ReportKenny KenNo ratings yet
- Quiz 5 Test BankDocument37 pagesQuiz 5 Test BankOnyeka O AniyedeNo ratings yet
- Nasal Lacrimal Duct ObstructionDocument2 pagesNasal Lacrimal Duct ObstructionAgitha Melita PutriNo ratings yet
- Common Neonatal ProblemsDocument32 pagesCommon Neonatal ProblemsbrhomzalatNo ratings yet
- Vol 19.2 Dementia.2013Document208 pagesVol 19.2 Dementia.2013Martoiu MariaNo ratings yet
- Contoh Naskah Presentasi KD 26Document3 pagesContoh Naskah Presentasi KD 26Kharisma Nur FajriyahNo ratings yet
- PACS QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesPACS QuestionnaireakashniranjaneNo ratings yet
- Advanced Life Support AssessmentDocument1 pageAdvanced Life Support AssessmentbbyesNo ratings yet
- Pertanyaan JurnalDocument2 pagesPertanyaan JurnalodivarNo ratings yet
- Know Your Superannuation BenefitsDocument20 pagesKnow Your Superannuation BenefitsSanketNo ratings yet
- Inflammation in AgingDocument14 pagesInflammation in AgingmonitamiftahNo ratings yet
- Pooja Gangwar:::: Patient Age / Sex 23 Y / Female BranchDocument1 pagePooja Gangwar:::: Patient Age / Sex 23 Y / Female BranchSnehal GholapNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Reaction PDFDocument1 pageTransfusion Reaction PDFKah Man GohNo ratings yet
- Foundations - 2 (Part 2)Document54 pagesFoundations - 2 (Part 2)Minatulahamida Al-fitra KadayunanNo ratings yet
- Answers of 2012Document60 pagesAnswers of 2012MohsenNo ratings yet
- Hipertiroidism - EnglezaDocument13 pagesHipertiroidism - Englezaalexya2008No ratings yet
- 1 Typhoid FeverDocument14 pages1 Typhoid FeverWildan YogaNo ratings yet
- Daniela GarciaDocument8 pagesDaniela GarciaSagar ShahNo ratings yet
- White Lesions On The Hands and Lower ExtremitiesDocument2 pagesWhite Lesions On The Hands and Lower Extremitieshossein kasiriNo ratings yet
- CV KPM Jan 2020Document13 pagesCV KPM Jan 2020Prof. Dr. Kamlesh MehtaNo ratings yet
- CHN CH 4 Maternal and Child Care Including Bemonc and CemoncDocument5 pagesCHN CH 4 Maternal and Child Care Including Bemonc and CemoncElaiza RiegoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Occupational Therapy in OncologyDocument2 pagesThe Role of Occupational Therapy in OncologyThe American Occupational Therapy Association100% (1)
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument84 pagesNephrotic SyndromeRahul DhakerNo ratings yet
- Bettencourt Et Al - 2017Document5 pagesBettencourt Et Al - 2017Andreia BettencourtNo ratings yet