Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conjunctions: Conjunctive Adverbs Relative Pronouns Subordinating Conjunctions Coordination Conjunctions
Conjunctions: Conjunctive Adverbs Relative Pronouns Subordinating Conjunctions Coordination Conjunctions
Uploaded by
wjdan asiriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conjunctions: Conjunctive Adverbs Relative Pronouns Subordinating Conjunctions Coordination Conjunctions
Conjunctions: Conjunctive Adverbs Relative Pronouns Subordinating Conjunctions Coordination Conjunctions
Uploaded by
wjdan asiriCopyright:
Available Formats
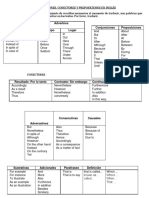
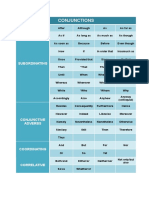
Conjunctions
Coordination Subordinating Relative Pronouns Conjunctive
Conjunctions Conjunctions Adverbs
(FANBOYS)
F: For After That Accordingly
A: And Although Which As a result
N: Nor As Who (ever) Consequently
B: But As if Whom (ever) First
O: Or As long as Whose However
Y: Yet Because Which (ever) Indeed
S: So Before In fact
Even though And sometimes Instead
If when and where Next
Since Otherwise
Than Second
Though Still
Unless For example
Until For instance
When Furthermore
Whenever Hence
Where Likewise
Wherever Meanwhile
While Moreover
So that Nevertheless
Therefore
Thus
Unfortunately
Tips:
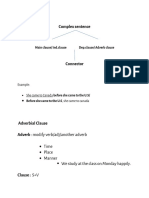
1. Spotting subordinating conjunctions/relative pronouns is the easiest way to identify
a subordinate (dependent) clause.
2. A conjunctive adverb is a word or phrase that serves as a transition, usually between
two main clauses. When a conjunctive adverb joins two main clauses, it is preceded
by a semicolon and followed by a comma. Do not use a semicolon before a
conjunctive adverb that DOES NOT begin with a main clause.
3. Coordinating conjunctions (FANBOYS) connect independent clauses.
You might also like
- Denis Diderot-Jacques The FatalistDocument141 pagesDenis Diderot-Jacques The FatalistGlen Carpenter80% (5)
- Linking Words & Connective PhrasesDocument1 pageLinking Words & Connective Phrasesmiguel angel marin sandovalNo ratings yet
- Bowker Lynne Fisher Des Computer Aided Translation PDFDocument6 pagesBowker Lynne Fisher Des Computer Aided Translation PDFLuis CedricNo ratings yet
- CEG 2136 - Fall 2009 - Final PDFDocument7 pagesCEG 2136 - Fall 2009 - Final PDFAmin DhouibNo ratings yet
- Conjunto de ConectoresDocument1 pageConjunto de ConectoresDiana DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: Coordinating Conjunctive AdverbsDocument1 pageConjunctions: Coordinating Conjunctive AdverbsRiccardo CattaneoNo ratings yet
- Conjunction: at Home" With "We Work in The Office")Document2 pagesConjunction: at Home" With "We Work in The Office")Ehtisham Zafar BhattiNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: A. Coordinating Conjunctions (Fanboys)Document5 pagesConjunctions: A. Coordinating Conjunctions (Fanboys)April Castro Abayo RilloNo ratings yet
- Conjunction WordsDocument1 pageConjunction WordsKIỀU TRINH NGUYỄNNo ratings yet
- Clauses Cheat SheetDocument1 pageClauses Cheat SheetMaryké SteynNo ratings yet
- Cohesive DevicesDocument7 pagesCohesive DevicesDIANA CRISTINA PortoNo ratings yet
- Conjunction ListDocument1 pageConjunction Listreyhanemehrabi63No ratings yet
- ConjunctionsDocument1 pageConjunctionsCeCy GuzmanNo ratings yet
- List of Commonly Used Linking WordsDocument8 pagesList of Commonly Used Linking WordsBlack SmokeNo ratings yet
- Writing - Linking WordsDocument2 pagesWriting - Linking WordsEliseo HENo ratings yet
- Transitions PDFDocument1 pageTransitions PDFMina MinawyNo ratings yet
- Linking WordsDocument8 pagesLinking WordsJosé Ángel GalindoNo ratings yet
- Table of Transitional Words and Phrases: The Academic Resource CenterDocument1 pageTable of Transitional Words and Phrases: The Academic Resource CenterRidha CahyaNo ratings yet
- Connecting WordsDocument7 pagesConnecting WordsBharani ShankarNo ratings yet
- TransitionsDocument1 pageTransitionsnourinzidan71No ratings yet
- Adjective Clause Noun Clauses Adverbial ClausesDocument2 pagesAdjective Clause Noun Clauses Adverbial ClausesKarol GuerronNo ratings yet
- Transitional WordsDocument2 pagesTransitional Wordsabdollahi20No ratings yet
- Linking Words: 1. Position in The TextDocument19 pagesLinking Words: 1. Position in The TextBoumata Badda Mbark100% (1)
- Transition Words PDFDocument1 pageTransition Words PDFHîsökå WMNo ratings yet
- IELTS Band 9 Vocab SecretsDocument3 pagesIELTS Band 9 Vocab SecretsShoxruxNo ratings yet
- Independent ClauseDocument2 pagesIndependent ClauseMax FloresNo ratings yet
- 06.05 MadziaDocument2 pages06.05 MadziaOla BaczNo ratings yet
- ConjunctionsDocument2 pagesConjunctionsCarolynn Louisa GohNo ratings yet
- Notable Idioms in English & Conjunction WordsDocument35 pagesNotable Idioms in English & Conjunction WordsJYang Kek100% (1)
- Grammar - ConjunctionsDocument3 pagesGrammar - Conjunctionswyl lavacdNo ratings yet
- Speaking/ Writing Writing Speaking-Confidence Answer Reading /listening/ Writing (Argue)Document1 pageSpeaking/ Writing Writing Speaking-Confidence Answer Reading /listening/ Writing (Argue)Asad Ali0% (1)
- Advanced Linking Words: Adding and Contrasting Expressing Cause / ReasonDocument5 pagesAdvanced Linking Words: Adding and Contrasting Expressing Cause / ReasonThuyển ThuyểnNo ratings yet
- Linking Words. Connectors. Prepositions: ListingDocument2 pagesLinking Words. Connectors. Prepositions: ListingYvonne CarlileNo ratings yet
- Linking WordsDocument2 pagesLinking WordsJuan Jesús Pesado del RíoNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: A. Coordinating Conjunctions (Fanboys)Document6 pagesConjunctions: A. Coordinating Conjunctions (Fanboys)Mana GargiNo ratings yet
- Linking WordsDocument5 pagesLinking WordsdanielitoNo ratings yet
- Transition ChartDocument1 pageTransition ChartFrancesco CroccoNo ratings yet
- ConnectorsDocument2 pagesConnectorsrioNo ratings yet
- Documents - Pub Linking Words by Viv Quarry Extended VersionDocument6 pagesDocuments - Pub Linking Words by Viv Quarry Extended VersionMNo ratings yet
- LISTA DE CONECTORES InglesDocument2 pagesLISTA DE CONECTORES InglesFranco MalcorraNo ratings yet
- Emphasizing Reformulating Summing Up Concluding Introducing Ideas and Facts ConditionDocument1 pageEmphasizing Reformulating Summing Up Concluding Introducing Ideas and Facts ConditionAhmed FaidNo ratings yet
- Transition Words and PhrasesDocument2 pagesTransition Words and Phrasesapi-252894921No ratings yet
- ConnectorsDocument1 pageConnectorsrebolloalejandro23No ratings yet
- Adverbial ClauseDocument11 pagesAdverbial ClauseWahyuni OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Writing - Linking WordsDocument3 pagesWriting - Linking WordsPanayota LioupiNo ratings yet
- Compound and Simple SentencesDocument1 pageCompound and Simple SentencesLuis ArangoNo ratings yet
- Transition Words and Phrases - ListDocument1 pageTransition Words and Phrases - ListCristian RosalesNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: A. Coordinating Conjunctions (Fanboys)Document7 pagesConjunctions: A. Coordinating Conjunctions (Fanboys)dicky ardiasyahNo ratings yet
- Linking WordsDocument7 pagesLinking WordsRubén García FigueroaNo ratings yet
- CJC Lesson6 PerpconjinterjectionDocument7 pagesCJC Lesson6 PerpconjinterjectionRose Marie Florencio EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Course: English Ii Code: IN302 Cycle: Iv Professor: Mg. Graciela Britto Gutiérrez Subject: ConjunctionsDocument8 pagesCourse: English Ii Code: IN302 Cycle: Iv Professor: Mg. Graciela Britto Gutiérrez Subject: ConjunctionsTatiana AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Linking Words Write The Sentence AgainDocument20 pagesLinking Words Write The Sentence AgainTharGyi N MieNgeNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument2 pagesBusiness Communicationabdul wajidNo ratings yet
- Conjunction SummaryDocument4 pagesConjunction SummarytbykslNo ratings yet
- Linking WordsDocument1 pageLinking WordsMateus SousaNo ratings yet
- Dependent ClausesDocument2 pagesDependent ClausesMahmood HamidiNo ratings yet
- Subordinate ConjunctionsDocument1 pageSubordinate ConjunctionsFares Bassel HosneyNo ratings yet
- Transition Words and PhrasesDocument2 pagesTransition Words and PhrasesJayvee DividinaNo ratings yet
- Linking Words PDFDocument2 pagesLinking Words PDFMorgen SFNo ratings yet
- Linking and Connecting Words List: Result Emphasis AdditionDocument4 pagesLinking and Connecting Words List: Result Emphasis AdditionAlice RamosNo ratings yet
- Section 11: Final Exam Semester 1Document17 pagesSection 11: Final Exam Semester 1Jorge OrozcoNo ratings yet
- High Level ChecklistDocument2 pagesHigh Level Checklistshuruq aliNo ratings yet
- Onwuka Fredrick Original Gauge Proof For Reimenn HypothesisDocument14 pagesOnwuka Fredrick Original Gauge Proof For Reimenn HypothesisLeojlevamor D. AgumbayNo ratings yet
- Improve Your Reading Skills For 3rd B.tech CecDocument6 pagesImprove Your Reading Skills For 3rd B.tech CeckbaluenglishNo ratings yet
- Inanna and The Sacred Marriage The KingDocument10 pagesInanna and The Sacred Marriage The KingÖzcanNo ratings yet
- CM 2022 Grade 7Document11 pagesCM 2022 Grade 7Marjorie100% (1)
- WRITING and SPEECHDocument25 pagesWRITING and SPEECHRenalyn Rose MandiqueNo ratings yet
- ES1103 Tutorial 8Document19 pagesES1103 Tutorial 8dessohNo ratings yet
- Basics of Pauline EthicsDocument25 pagesBasics of Pauline EthicsRh2223dbNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature SyllabusDocument44 pagesPhilippine Literature SyllabusFroscheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsDocument15 pagesChapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsBearish PaleroNo ratings yet
- Actix One ReportDocument10 pagesActix One ReportSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism and ApproachesDocument12 pagesLiterary Criticism and ApproachesAnne Nicole CruzNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Charmed The Enchanted Kingdom Chronicles Book 2 Camille Peters Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pages(Download PDF) Charmed The Enchanted Kingdom Chronicles Book 2 Camille Peters Full Chapter PDFsekotoartai100% (7)
- Comparing The Effectiveness of CLT With ALMDocument20 pagesComparing The Effectiveness of CLT With ALMAndrianNo ratings yet
- ServiceDocument2 pagesServiceMohamed AwadNo ratings yet
- 16 Paper - Guidelines For Effective Bible Study ComDocument18 pages16 Paper - Guidelines For Effective Bible Study ComMazlow Jonah MorainNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice 5Document5 pagesPassive Voice 5LalitheNo ratings yet
- Becoming A Holy People Student Course GuideDocument83 pagesBecoming A Holy People Student Course GuideApril ShowersNo ratings yet
- Rephrasing Exercises 11th FormDocument2 pagesRephrasing Exercises 11th FormLeandro BarrosNo ratings yet
- Early Christianity To AD 313Document13 pagesEarly Christianity To AD 313Jozsef MokulaNo ratings yet
- Indian Vendors List 1Document34 pagesIndian Vendors List 1samarth.neotericNo ratings yet
- Iep Mickey Mouse Docx FluencyDocument9 pagesIep Mickey Mouse Docx Fluencyapi-304732665No ratings yet
- 1 - SPS Mapping Unidrive M DE PDFDocument12 pages1 - SPS Mapping Unidrive M DE PDFJosé Titla CosmeNo ratings yet
- Massively Multiplayer Online Gaming and English Language LearningDocument12 pagesMassively Multiplayer Online Gaming and English Language LearningSie VelanciaNo ratings yet
- Task-3 - NAT Failover With Two ISPDocument10 pagesTask-3 - NAT Failover With Two ISPNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Poetics PDFDocument93 pagesPoetics PDFCristina IonescuNo ratings yet