Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MS Hollowcore Plank Placing Rev A WF
MS Hollowcore Plank Placing Rev A WF
Uploaded by
Choubi ChoubacaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MS Hollowcore Plank Placing Rev A WF
MS Hollowcore Plank Placing Rev A WF
Uploaded by
Choubi ChoubacaCopyright:
Available Formats
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:1/12- 1
-112
- 1 -:
1. Introduction
The particular scope of this Method Statement [M.S] is to provide the user with a solid,
general understanding of the safe standards of work that should be followed and employed
during the construction of:
Slab construction
Hollow Core Planks Installation with use of ERMIB Chains
This Method Statement highlights and explains the various stages of construction, the
various materials and equipment to be used and how they are to be used when carrying out the
above activity, the staff involved and the Health and Safety Requirements. This document
combines the both the Technical and Health and Safety disciplines into one document to
provide a both detailed and well defined document which gives a clear analysis of risks
involved, and methods of risk reduction.
2. Parties Concerned and Addressees
Parties directly concerned by this M.S and their general duties are listed below
Site Manager: is in control of the overall activity of the project including Health and
Safety requirements.
o Decides and appoints competent persons to carry out the different activities
within his organisation.
o Reviews at suitable intervals the competences of staff and supervision to
ensure that the activity is correctly managed and controlled.
o Decides of any modification within his organisation with Project
Management and decides of training requirements for members of his staff.
o Makes sure that enough resources (staff, training, and the like) are in place to
fulfil activity and associated responsibilities.
o Checks and approves the M.S.
Civil Works Manager: is in direct charge of the civil works activity and its specific
Health and Safety requirements.
o Ensures that this Method Statement is drawn up at the start of the project.
o Checks the MS and decides of any amendment, is responsible for ensuring
that the MS is followed.
o Appoints the competent persons to carry out the civil works activity.
o Monitors and reviews appointments regularly, particularly in the event of
changing site conditions, complexity or workload.
Site Health and Safety Manager: ensures that the H&S Regulation and the H&S
Company Policy is applied and followed on site. Also he will organise the Site
Health and Safety Management for the entire project activity.
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:2/12- 2
-212
- 2 -:
o Assists the Site Manager and the Civil Work Manager in the management of
the Health and Safety aspect of the activity on site.
o Trains or organizes trainings with external bodies for members of staff who
may need additional training or refresh on activities involving Health and
Safety requirements or deep knowledge of the Health and Safety regulations.
o Checks and approves the MS.
Project System Manager: reviews the MS under the Quality-Safety-Environmental
[QSE] aspect.
Civil Works Engineer: is in charge of the structural works and its H&S requirements.
o Prepares and amends the MS as necessary. Keeps a record of all relevant
documentation related to the aforementioned activity.
o Must assess Hollow core Planks Installation operations to provide such
planning, selection of materials and equipment, instruction and supervision as
is necessary for the tasks to be undertaken safely.
o Ensures that adequate examination, inspection and maintenance are carried
out and keeps records of examinations, inspections, tests of all cranes, lifting
accessories and equipment.
o Ensures that the certifications for all crane operators, slinger/signaller are
valid.
o Monitors, reviews, reassesses and revises the Method Statement and Risk
Assessment.
Superintendent of Works: supervises either a section of the job or the overall job.
o Checks the MS and proposes of any amendment to site management.
o Makes sure that MS requirements are followed on site.
o Checks competences of supervisor staff, crane coordinator, crane drivers,
banksman, slingers / signallers and skilled workers.
o Assists the Site Engineer in the monitoring and checking of staff
certifications inspection records of equipment and plants.
Site Supervisor: supervises a part of the activity, and also supervises the skilled and
trained workers involved in the activity.
o Reviews the MS with Civil Works engineer and implements the plan on site.
o Is competent, suitably trained and has sufficient experience to carry out these
duties.
o Is fully conversant with the duties of all persons involved in the operation.
o Gives clear, unambiguous instructions to all members of the team under his
control.
o Identifies any danger to the operation from changed circumstances on site.
o Stops operations if he considers them unsafe and reports any problems to the
Site Management.
Banksman, slingers / signallers, who are responsible for the stages of the activity.
They must hold a current CITB Certificate of Training Achievement CPCS or similar
for slinging and signalling, and are responsible for attaching and detaching the load to
and from cranes and for use of the correct lifting accessories in accordance with the
Method Statement.
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:3/12- 3
-312
- 3 -:
The slinger/signaller is also responsible for initiating and directing the safe movement
of the loads and the crane. They are required to wear items of high visibility clothing
that will uniquely identify them to the crane operator.
Crane driver: is responsible for the correct operation of the cranes in accordance with
the manufacturer’s instructions and within the safe system of work.
The operator of the crane on company sites must be competent, and hold a current
CITB Certificate of Training Achievement (CPCS, formally CTA card) for operating
the appropriate category of crane, or similar.
Skilled labourers, who are in charge of all main activities within concrete
construction, especially pouring and vibration.
This M.S has to be issued to all parties prior to the commencement of any works.
3. References to other documents
This current M.S contains reference to other Health and Safety documents which can be
consulted in order to gain more in-depth knowledge on the overall, direct and in-direct issues
covered within Site Health and Safety.
- BYUK Health and Safety Management Plan
- Project Health and Safety Plan
- Project Lifting Management Plan
There are also other documents that will replicate the information supplied in this M.S.
COTYMS 020207: Slab construction –Hollow core slab (with propping) with use of
ERMIB Chains and HC Handrails
4. Management of Resources
4.1 Plant, equipment and materials
Lifting equipment: use of the ERMIB Chains ER-134. The standard “ERMIB”
Equipment ER-134 has got an 8T or a 12T lifting capacity on 4 chains provided that
the angle on top of the sling is not more than 60 degrees. The ERMIB chains are
installed through the Hollow core planks holes.
- Propping system :
Use of single props with tripods and/or shoring towers.
Huge range of manufacturer, dimension, height, capacity, single props, and shoring
towers available.
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:4/12- 4
-412
- 4 -:
The propping system to be used to support the slab has to be designed by the Method
Department or the manufacturer; specific propping drawings have to be prepared and
issued prior to start the activity on site.
For in-depth information regarding the propping systems follow the path below on the BY
Construction Intranet Website.
BY Welcom Page > Services Tab > Materials > [On location map select Quille] > Fiches Techniques
Below are tabulated lists of other equipments, materials and workforce involved in the
activity.
Equipments :
COMPONENT SKILLED OPERATIVE REQUIRED
Single props / shoring towers / Skilled worker / Foreman
universal tripods
Standard small site tools / equipment Skilled labourer; provided with site training on the use of small power
tools
Tower / Mobile crane, ERMIB Crane driver , banksman / slinger / signaller
chains and sling
Tower scaffold / ladders / mobile Skilled and trained worker; provided with a Tool-box talk on the safe use
step ladders of the mobile step ladders, scaffolding
Concrete skip Banks-man / Skilled labourer / Foreman
FULL PERSONAL PROTECTIVE All operatives
EQUIPMENT
Vibrators for concrete Foreman / Skilled labourers
Compressor [If required] Foreman / Skilled labourer
Electrical current converter Foreman / Skilled labourer
Cleaning podium for concrete skip Foreman / Skilled labourer
Power float helicopter for concrete Foreman / Skilled labourer
finish
Safety harness Foreman / Skilled labourers
Typical Materials to be employed:
DESIGNATION TYPE SKILLED OPERATIVE REQUIRED
Concrete to Design Mix Material Foreman / Skilled labourer
Specification
Steel reinforcements / Material Foreman / Skilled labourers
mesh / loose
Hollow core pre-cast Material Foreman / Skilled labourers
planks
Concrete curing product Material Foreman / Skilled labourers
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:5/12- 5
-512
- 5 -:
Workforce :
SKILLED OPERATIVE COMPETENCE LEVEL COMPETENCE PERMIT
REQUIRED REQUIRED
Experienced in working on site, is Is to attend relevant tool-box talk.
aware of all main activities within
concrete construction; inc setting Competence is to be checked by
Skilled labourer out, placing shuttering, steel Supervisor.
reinforcement, pouring, vibration
etc.
Experienced in all types of lifting Is to attend relevant tool-box talk.
operations; inc slinging, Competence is to be checked by
Banks-man / slinger / signaller assembly/de-assembly of lifting Health and Safety Personnel and
beans and all lifting signals. Superintendent
Experienced in concrete works Is to attend relevant tool-box talk.
Steel fixer and aware of specific reinforcing Competence is to be checked by
requirements. Supervisor.
Experienced in concrete works Is to attend relevant tool-box talk.
and is aware of method of pouring Competence is to be checked by
Concrete pourer and checking concrete moisture Supervisor
content.
Experienced in tower crane Tower/Mobile crane driving
driving. Should be responsible for license. Is to attend relevant tool-
the correct operation of the crane box talk. Competence is to be
Crane driver in accordance with the checked by Health and Safety
manufacturer’s instructions and Personnel and superintendent
within the safe system of work.
Should at any time only respond
to the signals from one
slinger/signaller who should be
clearly identified. In an emergency
a commonly recognized stop
signal may be given by any person
observing a situation leading to
danger and the crane operator
should respond to that signal.
Should have sufficient authority to
stop the lifting operation if they
consider it dangerous to proceed.
Experienced in wide range of Is to attend relevant tool-box talk.
Carpenter shutters and formworks. Competence is to be checked by
Supervisor.
Experienced in use of surveying Is to attend relevant tool-box talk.
Surveyor methods of equipment; Theodolite Competence is to be checked by
etc Civil Works Engineer.
4.2 General Safety Recommendations relating to Equipment, Material and Workforce
Lifting equipment and accessories
All lifting equipment and accessories [chains, slings, lifting frames and concrete skips] are to be
thoroughly examined and inspected by a competent person* before use and at 6-monthly
intervals or immediately following any repairs or alterations to the lifting equipment.
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:6/12- 6
-612
- 6 -:
[* A competent individual can be anyone who works with the equipment, has a competent knowledge level
of methods of assembling and de-assembling the equipment, and they must also keep a written record of
these inspections; Proof of training is also required]
Weekly visual inspections of all components are to be made and documented by a
competent individual. [I.e. Use of colour coding checking system]
The equipment supplier must provide a valid certificate of inspection and conformity.
The Engineer in Charge and the H&S Manager are obliged to keep copies of these
inspections and certificates ready for inspection.
Always check the load of equipment to be lifted against the capacity of the crane and
lifting accessories.
Small Power Tools and Electrical Equipment
The use of small power tools and electrical equipment on site is a common
occurrence for skilled operatives. Those who are not skilled in the use of these tools
are to be trained by the use of Tool-box talks to improve and validate their level of
competency.
There is to be a record kept of which individuals are capable of operating this
machinery, and also a record kept of when this equipment is removed from the
equipment store and who is responsible for its return in safe operating conditions.
Tools which will be exposed to the external elements must have water tight industrial
type plugs and sockets must operate on an earth –leakage protection system
Work-force
It is imperative that only competent, skilled individuals are placed in charge of
operations. Superintendent and H&S personal have to check the competence, and
suitability of workforce against the function, mission given.
In addition, ensure that only those operatives who have received adequate training are
given the responsibility of using specific equipment to carry out complex tasks.
Any relevant permits to work are to be submitted by operatives to the
Superintendent, who will give a copy to the H&S Manager and Engineer in Charge.
A record of these permits is to be kept for future reference.
Hazardous Chemicals and Substances
The use of all Hazardous Chemicals and Substances is to be identified by a COSHH
Assessment. Copies of this assessment are to be reviewed and recorded by the Health
and Safety Manager and the Engineer in Charge.
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:7/12- 7
-712
- 7 -:
The Control of Substances Hazardous to Health has to be included in Toolbox talks
and the risk assessed to worker prior to start the activity.
Safety Harness
Always fix the lanyard of a safety harness to a solid anchoring point
Do not fix the lanyard to a weak anchor such as a layer of mesh, single starter bars
rebars diameter 8-10mm, tubes or posts of removable handrails etc…
Fix the lanyard to solid lifting anchors in slabs or beams, to steel rebars big diameter
well anchored in concrete structure, the base of a solid column, any solid point that
might not been bent easily on removed in case of fall.
Always look for the most secure and appropriate anchor point at workplace and check
systematically the solidity and resistance of it before use.
4.3 Implications on QSE
The consideration of Quality, Safety and Environmental consequences of this activity is essential
in the overall deliverance of a ‘Safe and Efficient Method of Work’.
The following points listed are those that give examples of good practice that might contribute to
achieving this status.
As far as possible such initiatives have to be implemented, developed and even improved during
the project.
The use of an electronic converter enables the reduction noise levels, electrical
consumption and subsequently, the size and weight of the machine required to
provide electricity. [For more details contact GIE: Bouygues Materiel]
Employ the use of machines which minimise noise disturbance; i.e. the use of
soundproof compressors, generators, etc.
Minimise the use of chemical based mould oil substance and prefer chemical free oils
as a safer option, for both operatives using the substance and also the surrounding
environment.
Use reasonable means to protect the surrounding environment from harmful hazards
such as spillages and residual waste being left on the ground. [The use of a concrete
residual decanting tank, oil/fuel retention tank, ground sheets when filling and
emptying fuel of plant and machinery, bunded tanks, trip trays etc]
Disposal of inert and non-inert waste using the correct methods and correct channels
of disposal and recycling components wherever possible
When disposing of hazardous waste a record is to be kept of the segregation of waste
disposed of, the quantity and the person charged with its disposal.
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:8/12- 8
-812
- 8 -:
When disposing of hazardous waste, the person charged with its disposal is required
to supply transfer notes or consignment notes
ALWAYS RESEARCHING WAYS TO SAFELY CONSERVE MATERIAL,
INCLUDING PURCHASING, AND REDUCE THE EFFECTS OF THE
CONSTRUCTION PROCESS ON OUR SURROUNDINGS
5. Description of the process
For the full breakdown of the construction process of
HOLLOWCORE PLANKS Installation (with propping) with use of ERMIB Chains
Refer directly to COTYMS 02027
Main sequences of work :
a. Install the ERMIB chains through the Hollow core planks holes and secure the
lifting chains underneath the planks with the getting back cable fitted to the ERMIB
chains. The angle on top of the sling has not to be more than 60 degrees, use chains
with adequate length to respect this rule. Lift and move the precast floor element.
b. Prior to installation of hollow core planks, slab edge safety (handrails on top of
walls) has to be installed from mobile step ladders and propping has to be installed in
accordance with the propping drawings provided by the Methods or Manufacturer
and approved For Construction. Make sure that propping system is well stabilized and
will not collapse while installing the plank (use of tripods + tie the props to the
concrete walls if necessary).
c. The first hollow core planks are installed by making use of mobile steps ladders
erected below and at the side of the slab that is going to be constructed.
d. Further the first plank being installed the subsequent planks are installed from the
level being constructed by use of a life line attached to the existing structure and use
of harness by the operatives hooked onto the life line.
e. Once the installation of an area is completed a line of barrier is installed, 1 meter
from the edge of the planks while safety at the façade edge is provided by either post
and barrier tube and toe board or the installation of external platforms.
f. Install reinforcement and make sure that plastic caps obstruct the open cores in
hollow core planks
g. Clean thoroughly the planks and key with compressor air, wet the plank prior to
cast the concrete topping.
h. Cast the topping and key with approved concrete mixture.
i. Vibrate the concrete and regulate the surface level of topping
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:9/12- 9
-912
- 9 -:
j. Check the level of top of slab
k. Use of helicopters to power float the surface of concrete slab
l. Use curing product if needed on finish slab.
m. Remove the propping system once the concrete has sufficient strength to support
the slab dead load + additional working loads on the upper levels. Use of back-
propping if necessary. Check the time scale to remove propping with the Method
Department or Structural consultant.
6. Identification of Direct and Indirect Hazards
The following non-exhaustive list is of the main potential hazards identified within the
aforementioned activity. All of the potential hazards involved in this activity cannot be fully
listed; instead the focus is placed on the major, more frequent hazards or those which can create
a high / medium level of risk. It remains the responsibility of competent and skilled
superintendents to assess the other risks to their workforce.
The identification and classification of hazards listed below makes easier the assessment of
risks in section 7:
6.1 General and Physical Site Layout, Storage Hazards
Storage area for Equipment and Material
- Bad surface conditions, slippery or obstructed ground slab causing hazards to
operatives and poor safety.
Weather conditions
- High speed wind
- Rain, frost and subsequent ground freeze, which can cause slippery ground
conditions
6.2 Chemical and Substance Hazards
- Cement based products, Concrete and cement in powder / liquid form posing
health risk through inhalation or contact with skin
- Curing product causing posing health risk by splashing operatives and accidental
ingestion, inhalation, or risk of ground / top-soil contamination when being
applied
- Petrol or diesel spillages from the compressor, generators causing flammable risk
and contamination of the soil.
6.3 Machinery and Equipment Hazards
- Use of inadequate or incorrect use of lifting equipment (i.e. ERMIB chains,
slings)
- Use of inadequate or unsafe small tools and equipment (i.e. small power tools and
larger site equipment );
- Unsafe / untrained usage of power tools by operatives
- Incorrect erection of propping system and tower scaffolds
- Use of inadequate propping system ( overloading of props, poor stability )
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:10/12
-1012
- 10 -:
6.4 Work Activity Hazards
Crane operations
- Incorrect use of crane or poor standard of operation
- Overloading of crane and lifting equipment
- Loose tools / equipment / material left on formworks, and falling off after being
hoisted by crane, also loads falling due to inadequate use of lifting equipment
- Poor lifting instructions
- High wind causing loss of control of the load, injury to workforce and damage to
building
Installation of steel reinforcements
- Risk of lacerations to operatives from cut and exposed reinforcement steel
Working at height
- Leaving unprotected opening in slabs or handrails not installed at edge causing
potential fall from height
Erecting / dismantle of propping system:
- Fall of a piece of equipment whilst installed by operatives
- Fall of propping due to lack of stability
Pre-cast plank installation:
- Fall or collapse of hollow core plank due to lack of stability or incorrect location
of propping system
- Crushing of operatives whilst installing planks
Concrete pouring / vibration
- Concrete splashing causing injury to operatives.
- Vibration of concrete causing ‘White Finger Syndrome’.
- Collapse of plank due to excessive weight of concrete stored onto it
6.5 Interfaces with other trades and sub-contractors & public safety
- Security of the site, storage areas and current areas of work; obstruction of these
areas is a hazard to all operatives
- Crane lifting materials over other working areas
6.6 Waste and Environmental Risks
- Air pollution from petrol/diesel powered machinery (I.e. compressor)
- Noise pollution from heavy plant/machinery
- Ground contamination by products used on the site
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
08/05/2007
METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOW CORE PLANKS INSTALLATION WITH USE OF ERMIB CHAINS Page:11/12
-1112
- 11 -:
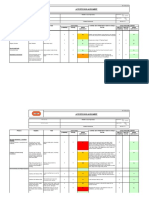
7. Activity Risk Assessment :
7.1 Level of Risk assessment:
severity
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
1
probability of occurrence
2 4 6 8 10
2
3 6 9 12 15
3
4 8 12 16 20
4
5 10 15 20 25
5
"low" risk
"Medium" Risk
"High" Risk
7.2 Risk assessment for lifting operations and use of tower crane:
Refer to Risk Assessment matrix.
Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
12/11/2005
GENERIC METHOD STATEMENT
SLAB CONSTRUCTION
HOLLOWCORE PLANKS INSTALLATION PAGE : 12 / 12
8. Example of relevant Tool-Box Talks to be carried out :
Use of regular Tool-Box Talks to clearly explain to the operatives the operational procedure
and the safest method of working are to be held regularly by either the Engineer in Charge,
Superintendent of Works, or the H&S Manager.
Each Tool-Box Talk should last between 15 min – 30 min, and should follow the typical
content.
- Purpose of the Tool-Box Talk
- Description of the work activity to be carried out
- H&S Risk Assessment
- Questions, observations and comments from the attendees.
Specific Tool-Box Talks in relation to the aforementioned activity :
- Correct erection and dismantle of propping system.
- Use of ERMIB chains system for hollow core planks
- Safe installation of hollow core planks onto props & walls
- Concrete slab surface power floating and curing
Generic Tool-box Talks applicable ;
- Working at height & correct use of safety harness and line life
- Crane lifting operations / Hoist and lift instructions and signals
- Manual Handling
- Safe use of ladders / step ladders / assembly and de-assembly of Step ladders, Mobile
Towers and Working Platforms
- PPE
Each Tool-Box Talk includes a list of people who have attended training sessions and they are
asked to verify their understanding of the content, to agree to update these methods on site
when necessary and endorse their compliance to this method of work with their signature.
Generic Method Statement – Slab construction – Hollow core planks installation
You might also like
- SS 497 - Code of Practice For Design, Safe Use and Maintenance of Gantry CranesDocument20 pagesSS 497 - Code of Practice For Design, Safe Use and Maintenance of Gantry CranesTest75% (4)
- Fall Protection Plan PDFDocument11 pagesFall Protection Plan PDFMohd Zulhaidy100% (2)
- Method Statement For Cable Tray and Truncking InstallationDocument9 pagesMethod Statement For Cable Tray and Truncking InstallationAnandu AshokanNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Port of SoharDocument3 pagesMethod Statement Port of SoharEldho George100% (1)
- Tenant Protection Plan Notes Per 2014 Code 28-104.8.4 As Modified by Nyc Ll154 of 2017Document8 pagesTenant Protection Plan Notes Per 2014 Code 28-104.8.4 As Modified by Nyc Ll154 of 2017Leonardo Jr. SasingNo ratings yet
- Ms For Tele Tower ErectionDocument12 pagesMs For Tele Tower ErectionSahabzada AamirNo ratings yet
- Method Statement - SCSDocument9 pagesMethod Statement - SCSYazan ZahalqaNo ratings yet
- Rigging and Lifting ProcedureDocument16 pagesRigging and Lifting ProcedureGhazi Kallel67% (3)
- Heavy LiftingDocument8 pagesHeavy LiftingEncik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For LV Cables, Wiring For Lighting and Power InstallationDocument11 pagesMethod Statement For LV Cables, Wiring For Lighting and Power InstallationAnandu Ashokan67% (3)
- MEGA Attendee Roster - Alpha Company FinalDocument150 pagesMEGA Attendee Roster - Alpha Company FinalCole BeneNo ratings yet
- MS Undercroft Hollowcore Plank Placing Rev A WFDocument12 pagesMS Undercroft Hollowcore Plank Placing Rev A WFChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MS Precast Beams WF Rev ADocument11 pagesMS Precast Beams WF Rev AChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MS Insitu Slab RevA WFDocument12 pagesMS Insitu Slab RevA WFChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MS Concrete Columns With Cardboard Formworks WF - Rev ADocument11 pagesMS Concrete Columns With Cardboard Formworks WF - Rev AChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- GMS Precast Stairs Rev CDocument11 pagesGMS Precast Stairs Rev CChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MS Mobile Crane Rev A WFDocument10 pagesMS Mobile Crane Rev A WFChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MS Facade Walls Proby & Compass WF - Rev ADocument12 pagesMS Facade Walls Proby & Compass WF - Rev AChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MS WF Safety Platforms Installation - Rev ADocument9 pagesMS WF Safety Platforms Installation - Rev AChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- ADICC-OSHMS-SoP-26 ScaffoldingDocument18 pagesADICC-OSHMS-SoP-26 ScaffoldingZahid ImamNo ratings yet
- Erection Method Statement - Birla White (Gotan)Document15 pagesErection Method Statement - Birla White (Gotan)SEPL SEPLNo ratings yet
- Demolition Using Plant PDFDocument8 pagesDemolition Using Plant PDFianllagasNo ratings yet
- MOS Structure Lifting PlanDocument15 pagesMOS Structure Lifting Planmuiqbal.workNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Scaffolding Erection & DismantlingDocument6 pagesMethod Statement For Scaffolding Erection & DismantlingAamir Khan100% (1)
- LMP Frederick Bremer - Rev BDocument20 pagesLMP Frederick Bremer - Rev BChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- 10.0 Ms For Scaffolding WorksDocument7 pages10.0 Ms For Scaffolding WorksilliasuddinNo ratings yet
- Neom Occupational Safety and Health Governance FrameworkDocument29 pagesNeom Occupational Safety and Health Governance Frameworkmohamed.elsawafNo ratings yet
- Cranes and DerricksDocument15 pagesCranes and DerricksAl Hamra AyashofiyaNo ratings yet
- Method of Statement For Bus DuctDocument11 pagesMethod of Statement For Bus DuctTalha AltafNo ratings yet
- ABC Guidelines V6-1Document27 pagesABC Guidelines V6-1Ryler VinNo ratings yet
- Method Statement - Installation of Sewerage Piles in Live LineDocument9 pagesMethod Statement - Installation of Sewerage Piles in Live LineaceNo ratings yet
- Work InstructionsDocument32 pagesWork InstructionshainguyenbkvhvNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Welding Works - Welding TechniquesDocument15 pagesMethod Statement For Welding Works - Welding TechniquesNaing Win TunNo ratings yet
- 2 - REV Method Statement For Electrical Installations of CableDocument10 pages2 - REV Method Statement For Electrical Installations of CableAyda JohariNo ratings yet
- Scaffold Safe Work Method Statement: Project TitleDocument11 pagesScaffold Safe Work Method Statement: Project TitleGirish R RaoNo ratings yet
- Tower Crane ChecklistDocument10 pagesTower Crane ChecklistumamNo ratings yet
- Steeplejack Competency RequirementsDocument3 pagesSteeplejack Competency RequirementsPaulSwinbankNo ratings yet
- 7.method Statement BlockworkDocument3 pages7.method Statement Blockworkشاز إياسNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Scaffolding Works and Installation of Acoustic PanelsDocument8 pagesMethod Statement For Scaffolding Works and Installation of Acoustic PanelsSujan AugustinNo ratings yet
- METHOD OF WORK - ELEVATION WORK PROCEDURE WITH CHAIN BLOCK Pump GFDocument5 pagesMETHOD OF WORK - ELEVATION WORK PROCEDURE WITH CHAIN BLOCK Pump GFCarlos ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Lifting Plan HVACDocument10 pagesLifting Plan HVACFMU KSA100% (1)
- TATA Power Scaffold Safety StandardDocument7 pagesTATA Power Scaffold Safety StandardDSG100% (1)
- Scaffolds StadiumDocument12 pagesScaffolds Stadiumnazulailawitra95No ratings yet
- METHOD OF STATEMENT - ALKHOMRA PROJECT - CarbstoneDocument7 pagesMETHOD OF STATEMENT - ALKHOMRA PROJECT - Carbstoneahmed samirNo ratings yet
- Method Statement - Installation of Sewerage Piles in Live LineDocument9 pagesMethod Statement - Installation of Sewerage Piles in Live LineaceNo ratings yet
- Safe Use of Cranes: Site Lifting PlanDocument26 pagesSafe Use of Cranes: Site Lifting PlanMuhammad BabarNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Welding Works - Welding TechniquesDocument15 pagesMethod Statement For Welding Works - Welding TechniquesLokesh SahuNo ratings yet
- MAC SEC FINAL - MergedDocument12 pagesMAC SEC FINAL - Mergedhanafi7180No ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.3: Erection III: Steel Construction: Fabrication and ErectionDocument4 pagesLecture 3.2.3: Erection III: Steel Construction: Fabrication and ErectionMihajloDjurdjevicNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For BACKFILLING WORKSDocument12 pagesMethod Statement For BACKFILLING WORKSYash Sharma50% (2)
- Cs S 15ingaa CSCG Pipeloading Unloading During Construction PDFDocument10 pagesCs S 15ingaa CSCG Pipeloading Unloading During Construction PDFSham AranNo ratings yet
- Instruction - Transport, Assembly and Disassembly of Terex Demag 400 Ton Crane CC 2400-1Document129 pagesInstruction - Transport, Assembly and Disassembly of Terex Demag 400 Ton Crane CC 2400-1Mariela Fernández Morey100% (1)
- MS For Surface Rock Bolts and Dowels (Rev-2)Document23 pagesMS For Surface Rock Bolts and Dowels (Rev-2)shahzadNo ratings yet
- Lifting Plan FF - Sprinkler ActivitiesDocument9 pagesLifting Plan FF - Sprinkler ActivitiesFMU KSANo ratings yet
- Erecting Altering Dismantling Scaffolding Prefabricated Steel Modular Scaffolding Industry Safety Standard 2373Document32 pagesErecting Altering Dismantling Scaffolding Prefabricated Steel Modular Scaffolding Industry Safety Standard 2373madhav0303No ratings yet
- Lifting Code of PracticeDocument34 pagesLifting Code of Practiceakubestlah67% (3)
- Crane Hoist Safety ProgramDocument11 pagesCrane Hoist Safety ProgramAssawin AnonuNo ratings yet
- Rigging CourseDocument16 pagesRigging Coursemianba17100% (1)
- Construction Supervision Qc + Hse Management in Practice: Quality Control, Ohs, and Environmental Performance Reference GuideFrom EverandConstruction Supervision Qc + Hse Management in Practice: Quality Control, Ohs, and Environmental Performance Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Engineering Critical Assessment (ECA) for Offshore Pipeline SystemsFrom EverandEngineering Critical Assessment (ECA) for Offshore Pipeline SystemsNo ratings yet
- Prem UrsDocument4 pagesPrem UrsChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- Mose 030 ADocument2 pagesMose 030 AChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- Mose 110 ADocument4 pagesMose 110 AChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- Balcon GC HautDocument1 pageBalcon GC HautChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- 200 Cover PageDocument1 page200 Cover PageChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MTH 015 Cotyms ListDocument2 pagesMTH 015 Cotyms ListChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- Sabot 00Document1 pageSabot 00Choubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MTH 015 Cotyms ManagementDocument3 pagesMTH 015 Cotyms ManagementChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- Work Order Cube Tests WFDocument6 pagesWork Order Cube Tests WFChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- WMP Steel Reinforcement WF Cover Page RevADocument1 pageWMP Steel Reinforcement WF Cover Page RevAChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- WF Steel Order Testing WMPDocument7 pagesWF Steel Order Testing WMPChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- WF Concrete Order Testing WMPDocument16 pagesWF Concrete Order Testing WMPChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MS Mobile Crane Rev A WFDocument10 pagesMS Mobile Crane Rev A WFChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- GMS Precast Stairs Rev CDocument11 pagesGMS Precast Stairs Rev CChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- Activity Risk Assessment - Mobile Crane WFDocument3 pagesActivity Risk Assessment - Mobile Crane WFChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- WF Steel Order Testing WMPDocument7 pagesWF Steel Order Testing WMPChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MS Undercroft Hollowcore Plank Placing Rev A WFDocument12 pagesMS Undercroft Hollowcore Plank Placing Rev A WFChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- MS WF Safety Platforms Installation - Rev ADocument9 pagesMS WF Safety Platforms Installation - Rev AChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- Standard Activity Risk Assessment Precast StairsaDocument6 pagesStandard Activity Risk Assessment Precast StairsaChoubi ChoubacaNo ratings yet
- Clipper Installation DetailsDocument1 pageClipper Installation DetailsMahmoud Al HomranNo ratings yet
- UBBGDocument13 pagesUBBGheyydeko100% (2)
- Gypsum Drywall Wastes Reuse As Subgrade Road StabilizerDocument52 pagesGypsum Drywall Wastes Reuse As Subgrade Road StabilizertiteNo ratings yet
- Quotation For Example Bathroom RenovationDocument6 pagesQuotation For Example Bathroom RenovationFadi HouraniNo ratings yet
- Modularization - The Key To Success in Today's MarketDocument5 pagesModularization - The Key To Success in Today's MarketrajeshbharatNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design Awards 2018Document32 pagesStructural Steel Design Awards 2018bachNo ratings yet
- Text Books For Reference: TH NDDocument14 pagesText Books For Reference: TH NDajeng.saraswatiNo ratings yet
- STEEL REQUIREMENT & BOQ 18m CG (SSM-MOHANNIA)Document29 pagesSTEEL REQUIREMENT & BOQ 18m CG (SSM-MOHANNIA)AKHILESHNo ratings yet
- Linear Guideways: 2-4 MG Series - Miniature Linear GuidewayDocument10 pagesLinear Guideways: 2-4 MG Series - Miniature Linear GuidewayVũ Minh TuấnNo ratings yet
- DS - en 1992-1-1 DK Na - 2011 eDocument33 pagesDS - en 1992-1-1 DK Na - 2011 ep_meulendijks108No ratings yet
- 0 0 101121121012161Volume-IIA DesignReportHighwayDocument74 pages0 0 101121121012161Volume-IIA DesignReportHighwayAmul KotharkarNo ratings yet
- About UsDocument3 pagesAbout UsShahid Rizwan KhokharNo ratings yet
- Contact List of Patna BuildersDocument2 pagesContact List of Patna Builderschetangrv41No ratings yet
- Cfi Building Construction Project: Preliminary Progress ReportDocument10 pagesCfi Building Construction Project: Preliminary Progress ReportKarthick NandakumarNo ratings yet
- Trenching Safety Tailgate TopicsDocument1 pageTrenching Safety Tailgate TopicsAldrien CabinteNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship @essar Projects (I) Ltd.Document44 pagesSummer Internship @essar Projects (I) Ltd.ROHAN CHOPDENo ratings yet
- 8351 - L&T Arch CommentsDocument1 page8351 - L&T Arch CommentsVarunn VelNo ratings yet
- Vacation HouseDocument10 pagesVacation HouseLight VaemerNo ratings yet
- Census of India 2011 Houses, Household Amenities and Assets Figures at A GlanceDocument12 pagesCensus of India 2011 Houses, Household Amenities and Assets Figures at A GlanceHashirKhanNo ratings yet
- Induction Sheet A (002) (23163)Document1 pageInduction Sheet A (002) (23163)Vladut FaneaNo ratings yet
- 03 ConcreteDocument72 pages03 ConcreteAlyanna Pauline GomezNo ratings yet
- Davenport Building InvestigationDocument113 pagesDavenport Building InvestigationNewsNation DigitalNo ratings yet
- Steelsmart: Mystic Marriott Hotel & Spa Groton, ConnecticutDocument4 pagesSteelsmart: Mystic Marriott Hotel & Spa Groton, ConnecticutsamehNo ratings yet
- 9 Method Statement For Floor TilesDocument10 pages9 Method Statement For Floor Tilesirfan khanNo ratings yet
- 3 Mget SP MKT Get and Buckets Surface Mining EnglishDocument15 pages3 Mget SP MKT Get and Buckets Surface Mining EnglishMarcoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1,008 pagesUntitledRodriguez, Avy Danielle G.No ratings yet
- Docks: Open Berths: Where Tidal Ranges Are Very Marked and Large, Docks Are Formed by EnclosuresDocument15 pagesDocks: Open Berths: Where Tidal Ranges Are Very Marked and Large, Docks Are Formed by EnclosuresathiraNo ratings yet