Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pe Day 10
Pe Day 10
Uploaded by
Libin AbrahamCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Machine Tools and Digital Manufacturing (MTDM) : Machining ProcessDocument90 pagesMachine Tools and Digital Manufacturing (MTDM) : Machining ProcessLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Planer MachineDocument46 pagesPlaner Machinepoohru puru100% (15)
- Voltaic Cell Lab ReportDocument5 pagesVoltaic Cell Lab Reporthelia bazarganNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planner Slotter: Reciprocating MachinesDocument75 pagesShaper Planner Slotter: Reciprocating MachinesLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Planer MachineDocument7 pagesPlaner MachineFathy Gamal KhaledNo ratings yet
- Movement Planer Shaper SlotterDocument9 pagesMovement Planer Shaper SlotterDhana MuruganNo ratings yet
- Lecture PPT Planer MachinesDocument26 pagesLecture PPT Planer MachinesS S PatelNo ratings yet
- MC-MT R16 - Unit-3Document63 pagesMC-MT R16 - Unit-3Anonymous GEHeEQlajbNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planner SlotterDocument49 pagesShaper Planner SlotterDeepak RaiNo ratings yet
- (Print 3) Milling MachineDocument32 pages(Print 3) Milling MachineMunem Shahriar100% (1)
- Shaper, Slotter and PlanerDocument9 pagesShaper, Slotter and PlanerRenjith RajendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting Lab ManualDocument54 pagesMetal Cutting Lab ManualAbhay Sharma 2K20PE02No ratings yet
- Planer Machine:: DiagramDocument4 pagesPlaner Machine:: Diagramtanish vermaNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planner SlotterDocument49 pagesShaper Planner SlottershahidNo ratings yet
- Planing and Slotting OperationsDocument4 pagesPlaning and Slotting Operationsmanish kumarNo ratings yet
- Shaper Machine: TH THDocument20 pagesShaper Machine: TH THLokesh LokiNo ratings yet
- Planer Machine 1Document20 pagesPlaner Machine 1Kim Argyle SalinasNo ratings yet
- On Shaper Machine FinalDocument6 pagesOn Shaper Machine FinalSuraj Mukti100% (1)
- On Shaper Machine FinalDocument6 pagesOn Shaper Machine FinalPaida Vishweswar Rao0% (1)
- Name: Hamza Mahmoud Salah ID: 20162750 Supervisor: DR - Nazieh Hasan /eng. Ahmad AL-dalo Class: Workshop 2Document13 pagesName: Hamza Mahmoud Salah ID: 20162750 Supervisor: DR - Nazieh Hasan /eng. Ahmad AL-dalo Class: Workshop 2Hamza MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Planer MachineDocument17 pagesPlaner Machinejasonmani90100% (2)
- Handout131Milling Machines and CuttersDocument23 pagesHandout131Milling Machines and CuttersPamela SidicNo ratings yet
- MTDMDocument14 pagesMTDMsree_guruNo ratings yet
- Milling MachineDocument21 pagesMilling MachineZahra BatoolNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop Theory and Practi Ce: Mechanical EngineeringDocument9 pagesMachine Shop Theory and Practi Ce: Mechanical EngineeringJohn BorjaNo ratings yet
- Prepared by S.sanyasirao, Assistant Professor, VITS College of Engg., Sontyam, VizagDocument14 pagesPrepared by S.sanyasirao, Assistant Professor, VITS College of Engg., Sontyam, Vizagsanyasirao1No ratings yet
- Milling MachineDocument80 pagesMilling Machineravi upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planer and SlotterDocument21 pagesShaper Planer and SlotterBharathiraja MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Planer Machines: A Brief Discussion About Fabrication and Machining ProcessesDocument43 pagesPlaner Machines: A Brief Discussion About Fabrication and Machining ProcessesGautam VatsNo ratings yet
- Milling Machines and CuttersDocument15 pagesMilling Machines and CuttersPamela SidicNo ratings yet
- Planer Machine:: DiagramDocument2 pagesPlaner Machine:: DiagramTanish VermaNo ratings yet
- FFFGFDocument6 pagesFFFGFArthur ShilbyNo ratings yet
- Title: Report On Planing OperationDocument10 pagesTitle: Report On Planing OperationmadNo ratings yet
- Planer MachineDocument37 pagesPlaner Machinemechfame89% (9)
- Planer MachineDocument37 pagesPlaner MachinejpbhimaniNo ratings yet
- MillingDocument47 pagesMillingAvinash KankipatiNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planner SlotterDocument46 pagesShaper Planner SlotterRam Prasad YadavNo ratings yet
- 3023 Machine Tools M3Document43 pages3023 Machine Tools M3arunsumesh.vfbvmNo ratings yet
- MP GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-6 06042020034404PMDocument24 pagesMP GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-6 06042020034404PMChandresh RanaNo ratings yet
- ShapingDocument17 pagesShapingShardaNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Type Machine ToolsDocument18 pagesReciprocating Type Machine ToolsSpartan 117No ratings yet
- Milling MachineDocument6 pagesMilling MachineAnand BalajiNo ratings yet
- Production Technology Assignment1Document22 pagesProduction Technology Assignment1shah shakeel rssNo ratings yet
- C7 - ShaperDocument11 pagesC7 - ShaperHans PinonNo ratings yet
- Unit III Milling Machine and Slotter 4SEM MP GCOE S N GANDHAREDocument20 pagesUnit III Milling Machine and Slotter 4SEM MP GCOE S N GANDHARE40 siddhesh petkarNo ratings yet
- 003 MillingDocument59 pages003 MillingKalikene MwambeloNo ratings yet
- Lathe-1Document26 pagesLathe-1Meer Umar100% (2)
- Shaper Planer N SlotterDocument23 pagesShaper Planer N SlotterAtif WahidNo ratings yet
- MFT 2 Lab Manual-SasiDocument46 pagesMFT 2 Lab Manual-Sasisikkandar faizNo ratings yet
- Planer Machine: ApplicationsDocument5 pagesPlaner Machine: ApplicationsRey Charvin S. ROCONo ratings yet
- Shaper and Types of Shaper MachinesDocument6 pagesShaper and Types of Shaper MachinesGeraldNo ratings yet
- Finaly Work: Cilco Ii SenatiDocument18 pagesFinaly Work: Cilco Ii Senatiomar daniel gonzales ramosNo ratings yet
- Lathe MachineDocument27 pagesLathe MachineJade IrasgaNo ratings yet
- Shaping Machine Manual FinalDocument4 pagesShaping Machine Manual FinalBarun DeNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document80 pagesUnit 3bmm16957No ratings yet
- MC-MT R16 - Unit-2Document56 pagesMC-MT R16 - Unit-2Anonymous GEHeEQlajbNo ratings yet
- Milling Machines2Document94 pagesMilling Machines2hari_1389100% (1)
- Unit - IIIDocument30 pagesUnit - IIISai RamNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting and Machine Tools Unit - III ObjectiveDocument27 pagesMetal Cutting and Machine Tools Unit - III ObjectivePyla Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Planer Machine and Types of Planer MachineDocument5 pagesPlaner Machine and Types of Planer MachineVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Band Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsFrom EverandBand Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Wood Turning - The Lathe and Its Accessories, Tools, Turning Between Centres Face-Plate Work, Boring, PolishingFrom EverandWood Turning - The Lathe and Its Accessories, Tools, Turning Between Centres Face-Plate Work, Boring, PolishingNo ratings yet
- Production Engineering Day 3 Merchant'S CircleDocument6 pagesProduction Engineering Day 3 Merchant'S CircleLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Conversion CertificateDocument1 pageConversion CertificateLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Thermal Aspects of Machining Module 1Document75 pagesThermal Aspects of Machining Module 1Libin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- s6 Machining Operations-1Document94 pagess6 Machining Operations-1Libin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Microfinishing Machines and OperationsDocument70 pagesMicrofinishing Machines and OperationsLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Attachments For MillingDocument59 pagesAttachments For MillingLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planner Slotter: Reciprocating MachinesDocument75 pagesShaper Planner Slotter: Reciprocating MachinesLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Gravitation PHY 101 U2Document14 pagesGravitation PHY 101 U2Rashmi ParmarNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB 2008 With AnswersDocument33 pagesAP Calculus AB 2008 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- Acm (Folded Plates)Document18 pagesAcm (Folded Plates)mrunalini KolaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Bee NotesDocument47 pagesUnit 4 Bee NotesSagar VatsNo ratings yet
- Design of Evaporator Cooling Coil For Cooling Load IJERTV10IS110009Document3 pagesDesign of Evaporator Cooling Coil For Cooling Load IJERTV10IS110009Alan syahNo ratings yet
- Hydrotest Method Statement 12th Mar 2012-1Document21 pagesHydrotest Method Statement 12th Mar 2012-1sethu1091100% (21)
- Elastic Potential Energy: English For PhysicsDocument2 pagesElastic Potential Energy: English For Physicshaura 30anNo ratings yet
- Granta EduPack Release NotesDocument8 pagesGranta EduPack Release Notes3220355No ratings yet
- L Shape Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesL Shape Analysis PDFJinesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Care and MaintenanceDocument15 pagesCare and MaintenanceIonut Marian PenciuNo ratings yet
- For Top and Bottom Flange Bolts Group: ForcesDocument86 pagesFor Top and Bottom Flange Bolts Group: ForcesKhaing ThinzarNo ratings yet
- Kollmorgen AKM - ServomotorDocument44 pagesKollmorgen AKM - ServomotorMiguel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- A Solar-PV Integrated Novel Reduced-Switch UPQC Device For Power-Quality ImprovementDocument6 pagesA Solar-PV Integrated Novel Reduced-Switch UPQC Device For Power-Quality ImprovementMuralidhar VermaNo ratings yet
- Eland Cables Power Networks CatalogueDocument68 pagesEland Cables Power Networks CatalogueRyo TevezNo ratings yet
- Momentum Exam Questions Q1Document5 pagesMomentum Exam Questions Q1Sofia YNo ratings yet
- Plate No. 2 Lessons 1 To 5Document3 pagesPlate No. 2 Lessons 1 To 5Sofia Bianca Zerrudo LobosNo ratings yet
- Nord Tanami 12Document5 pagesNord Tanami 12Nagyné ErikaNo ratings yet
- UTV-01/UTV-05: Uhf Panel AntennaDocument4 pagesUTV-01/UTV-05: Uhf Panel AntennaYarinaNo ratings yet
- 160 Grundfos Motor BookDocument16 pages160 Grundfos Motor BookKraponis TylnessNo ratings yet
- Reemplazo de IGBTs PDFDocument13 pagesReemplazo de IGBTs PDFRaul quispe quispeNo ratings yet
- Tesla Sees Evidence Radio and Light Are Sound - N.Y. Times, April 8, 1934Document3 pagesTesla Sees Evidence Radio and Light Are Sound - N.Y. Times, April 8, 1934THE NIKOLA TESLA INSTITUTE100% (1)
- Machine Design REE 302: Tutorial 3 (Ch.2: Materials II)Document19 pagesMachine Design REE 302: Tutorial 3 (Ch.2: Materials II)Dull PersonNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam in Me 313 (Fluid Mechanics)Document2 pagesMidterm Exam in Me 313 (Fluid Mechanics)subyNo ratings yet
- NYJC H2 2021 Prelim P1Document5 pagesNYJC H2 2021 Prelim P1sunguar.sanjayNo ratings yet
- Deutsch-Jozsa Algorithm As A Test of Quantum Computation: David Collins, K. W. Kim and W. C. HoltonDocument10 pagesDeutsch-Jozsa Algorithm As A Test of Quantum Computation: David Collins, K. W. Kim and W. C. HoltonJullyano LinoNo ratings yet
- Cpp-Gaseous State - RGVDocument2 pagesCpp-Gaseous State - RGVGauri KabraNo ratings yet
- Coa PeanutDocument1 pageCoa PeanutAli KhanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Failure of Materials A ReviewDocument42 pagesDynamic Failure of Materials A ReviewÓscar García ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Government of India Ministry of Power Central Electricity Authority New DelhiDocument52 pagesGovernment of India Ministry of Power Central Electricity Authority New DelhiVikrant DeshmukhNo ratings yet
Pe Day 10
Pe Day 10
Uploaded by
Libin AbrahamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pe Day 10
Pe Day 10
Uploaded by
Libin AbrahamCopyright:
Available Formats
PRODUCTION ENGINEERING
DAY 10
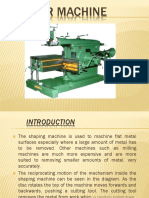
Shaper machine
The shaper machine is a reciprocating type of machine basically used for
producing the horizontal, vertical or flat surfaces.
The shaper holds the single point cutting tool in ram and workpiece is fixed in the
table.
Clapper mechanism
• Clapper box carries the tool holder. The main function of the clapper box is to provide
clearance for tool in return stroke.
• It prevents the cutting edge dragging the work piece while return stroke and prevent the
tool from wear.
Classifications of Shapers
1. According to the ram driving mechanism
Click here to join our WhatsApp group KPSC TRAILBLAZER ME
(a)Crank shaper: In a crank shaper, a crank and a slotted lever quick return motion
mechanism is used to give reciprocating motion to the ram. The crank arm is adjustable
and is arranged inside the body of a bull gear (also called crank gear).
(b) Geared shaper: In a geared shaper, the ram carries a rack below it, which is driven by
a spur gear. This type of shaper is not widely used.
(c) Hydraulic shaper: In a hydraulic shaper, a hydraulic system is used to drive the ram.
This type of shaper is more efficient than the crank and geared shaper.
2. According to position and travel of ram
(a) Horizontal shaper: In a horizontal shaper, the ram moves or reciprocates in a
horizontal direction. This type of shaper is mainly used for producing flat surfaces.
(b) Vertical shaper: In a vertical shaper, the ram reciprocates vertically in the downward
as well as in upward direction. This type of shaper is very convenient for machining internal
surfaces, keyways, slots or grooves.
3. According to the direction of cutting stroke
(a) Push-Cut shaper: In a push-cut shaper, the ram pushes the tool across the work during
cutting operation. In other words, forward stroke is the cutting stroke and the backward
stroke is an idle stroke. This is the most general type of shaper used in common practice.
(b) Draw-cut shaper: In a draw-cut shaper, the ram draws or pulls the tool across the work
during cutting operation. In other words, the backward stroke is the cutting stroke and
forward stroke is an idle stroke.
4. According to the design of the table
(a)Standard or plain shaper: In a standard or plain shaper, the table has only two
movements i.e., horizontal and vertical, to give the feed. It can not be swiveled or tilted.
(b) Universal shaper: In a universal shaper, in addition to the above two movements, the
table can be swiveled about a horizontal axis parallel to the ram and the upper portion of
the table can be tilted about the other horizontal axis perpendicular to the first axis. This
type of shaper is mostly used in tool room work.
Specifications of a Shaper
1. Maximum length of stroke is millimeters,
2. Size of the table, i.e., length, width and depth of the table,
Click here to join our WhatsApp group KPSC TRAILBLAZER ME
3. Maximum vertical and horizontal travel of the table,
4. Maximum number of strokes per minute,
5. Power of the drive motor,
6. Type of quick return mechanism.
7. Floor space required, and
8. Weight.
Ratchet and Pawl Mechanism
(Automatic Feed Mechanism for the Table)
The table of a shaping machine travels in a cross direction when the crossfeed screw
is rotated.
The cross feed screw is attached to the ratchet wheel.
A spring loaded ‘pawl’ is positioned to be placed between the teeth of the ratchet
wheel.
The pawl is housed within a frame known as rocker arm.
The pawl makes the ratchet to rotate by a small amount in one direction only.
As the cross feed screw is attached to the ratchet wheel, the rotation of the ratchet
wheel will make the table to move in a cross direction.
PLANER
The planer (also called planing machine) is a machine tool used to produce plane and
flat surface by a single point cutting tool.
It is similar to a shaper but its size is very large and is adopted for producing flat
surfaces of much larger work than a shaper.
The fundamental difference between a planer and shaper is that in a planer, the tool
remains stationary and the work reciprocates whereas in the shaper, the work remains
stationary and the tool reciprocates.
Types of Planers
1. Standard or double housing planer
2. Open side planer
Click here to join our WhatsApp group KPSC TRAILBLAZER ME
3. Pit planer
4. Edge or plate planer
5. Divided table planer
Standards or double housing planer
The columns are connected at the top by a cast iron support.
The table reciprocates on accurate guide ways provided on a long heavy bed.
The two tool heads which carry the tool are mounted on the cross rails.
These tools may be fed either by hand or by power in crosswise or vertical direction.
Principal Parts of a Planer
1. Bed:
The bed of a planer is a box like casting having cross ribs.
It provides the foundation for the machine and supports the housing and all other
moving parts.
The upper part of the bed is provided with precision V- type guide ways on which the
table slides.
2. Table:
The planer table is a heavy rectangular precision machined casting.
It reciprocates along the ways of the bed and supports the work.
The top face of the table is provided with T-slots and holes uniformly spaced for fixing
the work and work holding devices over the table with the help of T-bolts, clamps etc.
The table may be driven by rack and gear, by rack and double helical gear or by
hydraulic system.
3. Housing (Column)
The housings are rigid column-like castings placed on each side of the bed.
The front face of the housings is accurately machined to provide precision ways.
The housings enclose the cross-rail elevating screws, vertical and cross-feed screws for
the tool heads, counter balancing weights for the cross-rail etc.
4. Cross-rail:
Click here to join our WhatsApp group KPSC TRAILBLAZER ME
The cross-rail is mounted on the precision-machined ways of the two housings.
It may be raised or lowered on the housings to accommodate work of different heights
on the table and to allow for the adjustment of the tools.
5. Tool heads:
The tool heads are mounted on the cross-rail or housings by means of a saddle, which
slides along the rail or housing ways.
The saddle may be made to move transversely on the cross-rail to give cross feed.
Two tool heads are provided on the cross-rail so that the two tools may remove the
material from the work simultaneously.
In addition to these two-tool heads, there are other two-tool heads which are mounted
on each housing.
Size and Specifications of a Planer
1. Width of the table in mm,
2. Maximum distance of the table to the cross-rail in meters,
3. Maximum stroke of the table in mm.
4. Length of bed,
5. Length of the table,
6. Type of drive,
7. Power of the motor, and
8. Number of speed and feed etc.
Planer Tools
The planer tools are mostly made of high speed steel.
The cemented carbide tipped tools are also used on planers for production work.
The planer tools are similar to those used on shaper, but, as the depth of cut are heavier
and cutting strokes are large, the planer tools are large in size.
A planer tool many be classified as roughing or finishing and right hand or left hand
type.
Click here to join our WhatsApp group KPSC TRAILBLAZER ME
Cutting speed
In both shapers and planers, the tool or table starts from rest, picks up speed and then
again slows down to zero speed during the forward or cutting stroke.
It is customary to calculate cutting speed on the basis of average speed during the
forward stroke. Feed and depth of cut are both expressed in mm.
In case of feed, it is the lateral distance moved by the tool (on the cross-rail) per cutting
stroke.
Difference b/w planer and shaper
1. It is a heavy duty machine tool. 1. It is a light duty machine tool.
2. It requires more floor area. 2. It requires less floor area.
3. It is adopted for large works. 3. It is used for small works.
4. More than one cutting tool
can be used at a time. 4. Only one cutting tool is used at a time.
5. Tool is fixed and work moves. 5. Work is fixed and the tool moves.
6. Planer table is either driven
by gears or by hydraulic means. 6. It is normally driven by crank and slotted lever
quick return motion mechanism.
7. Heavier feeds are applied. 7. Lighter feeds are applied.
8. It can take deep cuts. 8. It cannot take deep cuts.
9. Work setting requires much
of skill and takes longer time. 9. Work may be clamped easily and quickly.
10. Tools used are of larger size. 10. Tools used are of smaller size.
Click here to join our WhatsApp group KPSC TRAILBLAZER ME
You might also like
- Machine Tools and Digital Manufacturing (MTDM) : Machining ProcessDocument90 pagesMachine Tools and Digital Manufacturing (MTDM) : Machining ProcessLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Planer MachineDocument46 pagesPlaner Machinepoohru puru100% (15)
- Voltaic Cell Lab ReportDocument5 pagesVoltaic Cell Lab Reporthelia bazarganNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planner Slotter: Reciprocating MachinesDocument75 pagesShaper Planner Slotter: Reciprocating MachinesLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Planer MachineDocument7 pagesPlaner MachineFathy Gamal KhaledNo ratings yet
- Movement Planer Shaper SlotterDocument9 pagesMovement Planer Shaper SlotterDhana MuruganNo ratings yet
- Lecture PPT Planer MachinesDocument26 pagesLecture PPT Planer MachinesS S PatelNo ratings yet
- MC-MT R16 - Unit-3Document63 pagesMC-MT R16 - Unit-3Anonymous GEHeEQlajbNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planner SlotterDocument49 pagesShaper Planner SlotterDeepak RaiNo ratings yet
- (Print 3) Milling MachineDocument32 pages(Print 3) Milling MachineMunem Shahriar100% (1)
- Shaper, Slotter and PlanerDocument9 pagesShaper, Slotter and PlanerRenjith RajendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting Lab ManualDocument54 pagesMetal Cutting Lab ManualAbhay Sharma 2K20PE02No ratings yet
- Planer Machine:: DiagramDocument4 pagesPlaner Machine:: Diagramtanish vermaNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planner SlotterDocument49 pagesShaper Planner SlottershahidNo ratings yet
- Planing and Slotting OperationsDocument4 pagesPlaning and Slotting Operationsmanish kumarNo ratings yet
- Shaper Machine: TH THDocument20 pagesShaper Machine: TH THLokesh LokiNo ratings yet
- Planer Machine 1Document20 pagesPlaner Machine 1Kim Argyle SalinasNo ratings yet
- On Shaper Machine FinalDocument6 pagesOn Shaper Machine FinalSuraj Mukti100% (1)
- On Shaper Machine FinalDocument6 pagesOn Shaper Machine FinalPaida Vishweswar Rao0% (1)
- Name: Hamza Mahmoud Salah ID: 20162750 Supervisor: DR - Nazieh Hasan /eng. Ahmad AL-dalo Class: Workshop 2Document13 pagesName: Hamza Mahmoud Salah ID: 20162750 Supervisor: DR - Nazieh Hasan /eng. Ahmad AL-dalo Class: Workshop 2Hamza MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Planer MachineDocument17 pagesPlaner Machinejasonmani90100% (2)
- Handout131Milling Machines and CuttersDocument23 pagesHandout131Milling Machines and CuttersPamela SidicNo ratings yet
- MTDMDocument14 pagesMTDMsree_guruNo ratings yet
- Milling MachineDocument21 pagesMilling MachineZahra BatoolNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop Theory and Practi Ce: Mechanical EngineeringDocument9 pagesMachine Shop Theory and Practi Ce: Mechanical EngineeringJohn BorjaNo ratings yet
- Prepared by S.sanyasirao, Assistant Professor, VITS College of Engg., Sontyam, VizagDocument14 pagesPrepared by S.sanyasirao, Assistant Professor, VITS College of Engg., Sontyam, Vizagsanyasirao1No ratings yet
- Milling MachineDocument80 pagesMilling Machineravi upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planer and SlotterDocument21 pagesShaper Planer and SlotterBharathiraja MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Planer Machines: A Brief Discussion About Fabrication and Machining ProcessesDocument43 pagesPlaner Machines: A Brief Discussion About Fabrication and Machining ProcessesGautam VatsNo ratings yet
- Milling Machines and CuttersDocument15 pagesMilling Machines and CuttersPamela SidicNo ratings yet
- Planer Machine:: DiagramDocument2 pagesPlaner Machine:: DiagramTanish VermaNo ratings yet
- FFFGFDocument6 pagesFFFGFArthur ShilbyNo ratings yet
- Title: Report On Planing OperationDocument10 pagesTitle: Report On Planing OperationmadNo ratings yet
- Planer MachineDocument37 pagesPlaner Machinemechfame89% (9)
- Planer MachineDocument37 pagesPlaner MachinejpbhimaniNo ratings yet
- MillingDocument47 pagesMillingAvinash KankipatiNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planner SlotterDocument46 pagesShaper Planner SlotterRam Prasad YadavNo ratings yet
- 3023 Machine Tools M3Document43 pages3023 Machine Tools M3arunsumesh.vfbvmNo ratings yet
- MP GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-6 06042020034404PMDocument24 pagesMP GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-6 06042020034404PMChandresh RanaNo ratings yet
- ShapingDocument17 pagesShapingShardaNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Type Machine ToolsDocument18 pagesReciprocating Type Machine ToolsSpartan 117No ratings yet
- Milling MachineDocument6 pagesMilling MachineAnand BalajiNo ratings yet
- Production Technology Assignment1Document22 pagesProduction Technology Assignment1shah shakeel rssNo ratings yet
- C7 - ShaperDocument11 pagesC7 - ShaperHans PinonNo ratings yet
- Unit III Milling Machine and Slotter 4SEM MP GCOE S N GANDHAREDocument20 pagesUnit III Milling Machine and Slotter 4SEM MP GCOE S N GANDHARE40 siddhesh petkarNo ratings yet
- 003 MillingDocument59 pages003 MillingKalikene MwambeloNo ratings yet
- Lathe-1Document26 pagesLathe-1Meer Umar100% (2)
- Shaper Planer N SlotterDocument23 pagesShaper Planer N SlotterAtif WahidNo ratings yet
- MFT 2 Lab Manual-SasiDocument46 pagesMFT 2 Lab Manual-Sasisikkandar faizNo ratings yet
- Planer Machine: ApplicationsDocument5 pagesPlaner Machine: ApplicationsRey Charvin S. ROCONo ratings yet
- Shaper and Types of Shaper MachinesDocument6 pagesShaper and Types of Shaper MachinesGeraldNo ratings yet
- Finaly Work: Cilco Ii SenatiDocument18 pagesFinaly Work: Cilco Ii Senatiomar daniel gonzales ramosNo ratings yet
- Lathe MachineDocument27 pagesLathe MachineJade IrasgaNo ratings yet
- Shaping Machine Manual FinalDocument4 pagesShaping Machine Manual FinalBarun DeNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document80 pagesUnit 3bmm16957No ratings yet
- MC-MT R16 - Unit-2Document56 pagesMC-MT R16 - Unit-2Anonymous GEHeEQlajbNo ratings yet
- Milling Machines2Document94 pagesMilling Machines2hari_1389100% (1)
- Unit - IIIDocument30 pagesUnit - IIISai RamNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting and Machine Tools Unit - III ObjectiveDocument27 pagesMetal Cutting and Machine Tools Unit - III ObjectivePyla Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Planer Machine and Types of Planer MachineDocument5 pagesPlaner Machine and Types of Planer MachineVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Band Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsFrom EverandBand Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Wood Turning - The Lathe and Its Accessories, Tools, Turning Between Centres Face-Plate Work, Boring, PolishingFrom EverandWood Turning - The Lathe and Its Accessories, Tools, Turning Between Centres Face-Plate Work, Boring, PolishingNo ratings yet
- Production Engineering Day 3 Merchant'S CircleDocument6 pagesProduction Engineering Day 3 Merchant'S CircleLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Conversion CertificateDocument1 pageConversion CertificateLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Thermal Aspects of Machining Module 1Document75 pagesThermal Aspects of Machining Module 1Libin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- s6 Machining Operations-1Document94 pagess6 Machining Operations-1Libin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Microfinishing Machines and OperationsDocument70 pagesMicrofinishing Machines and OperationsLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Attachments For MillingDocument59 pagesAttachments For MillingLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Shaper Planner Slotter: Reciprocating MachinesDocument75 pagesShaper Planner Slotter: Reciprocating MachinesLibin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Gravitation PHY 101 U2Document14 pagesGravitation PHY 101 U2Rashmi ParmarNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB 2008 With AnswersDocument33 pagesAP Calculus AB 2008 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- Acm (Folded Plates)Document18 pagesAcm (Folded Plates)mrunalini KolaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Bee NotesDocument47 pagesUnit 4 Bee NotesSagar VatsNo ratings yet
- Design of Evaporator Cooling Coil For Cooling Load IJERTV10IS110009Document3 pagesDesign of Evaporator Cooling Coil For Cooling Load IJERTV10IS110009Alan syahNo ratings yet
- Hydrotest Method Statement 12th Mar 2012-1Document21 pagesHydrotest Method Statement 12th Mar 2012-1sethu1091100% (21)
- Elastic Potential Energy: English For PhysicsDocument2 pagesElastic Potential Energy: English For Physicshaura 30anNo ratings yet
- Granta EduPack Release NotesDocument8 pagesGranta EduPack Release Notes3220355No ratings yet
- L Shape Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesL Shape Analysis PDFJinesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Care and MaintenanceDocument15 pagesCare and MaintenanceIonut Marian PenciuNo ratings yet
- For Top and Bottom Flange Bolts Group: ForcesDocument86 pagesFor Top and Bottom Flange Bolts Group: ForcesKhaing ThinzarNo ratings yet
- Kollmorgen AKM - ServomotorDocument44 pagesKollmorgen AKM - ServomotorMiguel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- A Solar-PV Integrated Novel Reduced-Switch UPQC Device For Power-Quality ImprovementDocument6 pagesA Solar-PV Integrated Novel Reduced-Switch UPQC Device For Power-Quality ImprovementMuralidhar VermaNo ratings yet
- Eland Cables Power Networks CatalogueDocument68 pagesEland Cables Power Networks CatalogueRyo TevezNo ratings yet
- Momentum Exam Questions Q1Document5 pagesMomentum Exam Questions Q1Sofia YNo ratings yet
- Plate No. 2 Lessons 1 To 5Document3 pagesPlate No. 2 Lessons 1 To 5Sofia Bianca Zerrudo LobosNo ratings yet
- Nord Tanami 12Document5 pagesNord Tanami 12Nagyné ErikaNo ratings yet
- UTV-01/UTV-05: Uhf Panel AntennaDocument4 pagesUTV-01/UTV-05: Uhf Panel AntennaYarinaNo ratings yet
- 160 Grundfos Motor BookDocument16 pages160 Grundfos Motor BookKraponis TylnessNo ratings yet
- Reemplazo de IGBTs PDFDocument13 pagesReemplazo de IGBTs PDFRaul quispe quispeNo ratings yet
- Tesla Sees Evidence Radio and Light Are Sound - N.Y. Times, April 8, 1934Document3 pagesTesla Sees Evidence Radio and Light Are Sound - N.Y. Times, April 8, 1934THE NIKOLA TESLA INSTITUTE100% (1)
- Machine Design REE 302: Tutorial 3 (Ch.2: Materials II)Document19 pagesMachine Design REE 302: Tutorial 3 (Ch.2: Materials II)Dull PersonNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam in Me 313 (Fluid Mechanics)Document2 pagesMidterm Exam in Me 313 (Fluid Mechanics)subyNo ratings yet
- NYJC H2 2021 Prelim P1Document5 pagesNYJC H2 2021 Prelim P1sunguar.sanjayNo ratings yet
- Deutsch-Jozsa Algorithm As A Test of Quantum Computation: David Collins, K. W. Kim and W. C. HoltonDocument10 pagesDeutsch-Jozsa Algorithm As A Test of Quantum Computation: David Collins, K. W. Kim and W. C. HoltonJullyano LinoNo ratings yet
- Cpp-Gaseous State - RGVDocument2 pagesCpp-Gaseous State - RGVGauri KabraNo ratings yet
- Coa PeanutDocument1 pageCoa PeanutAli KhanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Failure of Materials A ReviewDocument42 pagesDynamic Failure of Materials A ReviewÓscar García ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Government of India Ministry of Power Central Electricity Authority New DelhiDocument52 pagesGovernment of India Ministry of Power Central Electricity Authority New DelhiVikrant DeshmukhNo ratings yet