Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat Seal Characteristic of Environmental Friendly Films From Thermoplastic Rice Starch Filled Poly (Lactic Acid)
Heat Seal Characteristic of Environmental Friendly Films From Thermoplastic Rice Starch Filled Poly (Lactic Acid)
Uploaded by
TÚ HoàngOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat Seal Characteristic of Environmental Friendly Films From Thermoplastic Rice Starch Filled Poly (Lactic Acid)
Heat Seal Characteristic of Environmental Friendly Films From Thermoplastic Rice Starch Filled Poly (Lactic Acid)
Uploaded by
TÚ HoàngCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/289708248
Heat seal characteristic of environmental friendly films from thermoplastic rice
starch filled poly(lactic acid)
Article · January 2013
CITATION READS
1 2,450
5 authors, including:
Supaphorn Thumsorn Sommai Pivsa-Art
Yamagata University Rajamangala University of Technology Thanyaburi
45 PUBLICATIONS 279 CITATIONS 64 PUBLICATIONS 1,727 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE
Kazushi Yamada Hiroyuki Hamada
Kyoto Institute of Technology Kyoto Institute of Technology
102 PUBLICATIONS 433 CITATIONS 1,043 PUBLICATIONS 7,254 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Crashworthiness of hybrid sandwich composite panels reinforced with braided glass fiber rods for side impact vehicle protection View project
Sunshine Clock View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Supaphorn Thumsorn on 19 January 2017.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
HEAT SEAL CHARACTERISTIC OF ENVIRONMENTAL FRIENDLY FILMS
FROM THERMOPLASTIC RICE STARCH FILLED POLY(LACTIC ACID)
Supaphorn Thumsorn and Sommai Pivsa-Art, Rajamangala University of Technology Thanyaburi,
Pathumthani, Thailand
Ken Miyata, Yamagata University, Yamagata, Japan
Kazushi Yamada and Hiroyuki Hamada, Kyoto Institute of Techmology, Kyoto, Japan
Abstract
Miyata et al [4-5] studied the effect of molecular
An environmental friendly biodegradable polymer weight and cast film conditions on heat seal properties of
film was prepared from poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic high density polyethylene (HDPE) film. They found that
starch (PLA/TPS) blend by cast film process at 0, 5 and the heat seald conditions were important factors to affect
10 wt% of TPS. The PLA/TPS blend films were heat molecular structures, which was also an important for heat
sealed by a heat seal tester at a heat bar temperature of 90 seal properties. Heat seal strength changed depending on
and 100 C. The heat seal time was varied from 0.5 to 2.0 cast film conditions. In low chilled roll speed heat seal
s with a constant seal pressure of 0.2 MPa. The effect of strength was low. The failure mode was peeling. In high
heat seal conditions on heat seal properties of PLA/TPS chilled roll speed heat seal strength was high. The failure
films was investigated. Heat sealed strength was carried mode was changed to tearing. Tetsuya et al [6] focused on
out by peel testing. Differential scanning calorimetry was the effect of heat sealed temperature on properties of
used to analyze thermal properties and crystallinity of the polypropylene (PP) films. Their researchs gave
heat sealed PLA/TPS films. From the results, heat sealed information on the relation between heat seal strength,
strength of PLA/TPS blend films decreased when crystallinity and molecular orientation of PP films. Yuan
increasing the heat sealed times. PLA films was peelable et al [7] investigated heat sealability of laminated films
at the heat sealed temperature of 90 C. PLA/TPS heat with linear lowdensity PE (LLDPE) and low density PE
sealed films exhibited greater crystallinity than the PLA (LDPE) as sealants. This research revealed that heat seal
heat sealed film. strength responsed to laminated film temperature, time
and pressure. However, there are very few researches on
the sealability of biodegradable film materials. Therefore,
Introduction it is important to investigate the heat seal characteristic of
biodegradable plastics and mechanical performance of
The heat sealability of a material is a major property
these materials upon heat sealing.
to maintain the integrity of a package, especially in
medical, food packaging, pharmaceutical applications,
In this study, the biodegradable plastic films of PLA
and so on. To obtain a proper heat seal is of paramount
filled with rice starch were prepared. The heat sealed of
importance in packaging because heat seal failure is a
the biodegradable plastic films was performed by thermal
more frequent cause of product deterioration than the
heat sealed method. In order to evaluate the effects of heat
failure of the package itself. Selecting the right material
sealed parameters on the quality of the seal, heat-sealing
that will perform under the right conditions requires
was performed at several temperatures and the strength of
careful consideration of the functional requirements of the
heat sealed part was evaluated. This research will perform
package and the method of packaging.
the heat seal characteristic of rice starch filled
biodegradable plastic films for utilization in packaging
In the present day, biodegradable plastics have been
applications
introduced for packaging industries due to the emphasis
on the environmental consideration. The biodegradability
of biodegradable plastics would overcome for less Experimental
garbage, reducing energy for incineration and lack of land
fill space. The various kinds of biodegradable plastics Poly(lactic acid) (Grade 2002D) was supplier by
packaging are available. Nevertheless, the drawbacks of NatureWorks LLC, USA. The melt fow rate was 5 g/10
biodegradable plastics are still high cost and low thermal min. Thermoplastic starch (TPS) was prepared from
resistance. Therefore, biodegradable fillers such as starch mixing rice starch with 30 wt% glycerol in a twin screw
and clay are adding for obtaining low cost plastic film extruder (Lab Tech Engineering, Thailand). The bareel
packaging and enhancing their thermal resistance [1-2]. temperature was set at 100-120 C with a screw apeed of
Moreover, heat seal technology is an essential technique 80 rpm. After pelletized, TPS was dried at 60 C for 12
for intermediate packaging industries. hours. PLA and TPS films were fabricated by a twin
ANTEC® 2013 / 1331
screw extruder (KZW-30; Technovel Co., Ltd., Japan) films at sealing temperature of 100 C decreased with
equipped with T die. The ratio of length and diameter, increasing heat sealed times. At this heat sealed
L/D, of the screw was 45. The extruder barrel temperature temperature, all films were pulled out such a suddenly
was set at 150-190 ºC. The T-die temperature was set at tearing. It can be note that the temperature higher than 100
190 ºC. The thickness of extruded film was controlled to C was not suitable for peelable PLA and PLA/TPS films.
around 50 μm by chilled roll and screw rotating speed.
The PLA/TPS films were done with varied contents of Table 1. Heat seal strength of PLA and PLA/TPS films.
TPS from 5 and 10 wt%. The films were then referred as
PLA/TPS-5 and PLA/TPS-10 for the films of adding TPS Heat sealed strength
5 wt% and 10 wt%, respectively. PLA films were also Temperature (N/15 mm)
Samples
prepared as controlled. (C)
0.5 s 1.0 s 2.0 s
Extruded PLA/TPS films were heat sealed by using a PLA 22.33 22.16 26.31
heat seal tester (TP-701-B; Tester Sangyo Co., Ltd.). Two 90 PLA/TPS-5 23.38 20.65 18.72
pieces of the film were thermally sealed near their melting PLA/TPS-10 22.37 20.20 11.25
temperature. The heat bar temperature was varied at 90 ºC
and 100 ºC. The seal pressure was kept constantly at 0.2 PLA 26.51 19.40 18.23
MPa. The heat seal time was varied from 0.2 to 2.0 100 PLA/TPS-5 20.98 17.91 9.22
seconds. PLA/TPS heat sealed films were cut to 100 mm PLA/TPS-10 18.25 7.20 5.87
long and 15 mm wide for peel testing.
Peel testing of PLA/TPS heat sealed films specimens 30
Heat sealed 90 C
was carried out by universal tensile testing machine Heat seal strenght (N/15 mm)
(Hounsfield) with the extension rate of 300 mm/min. 25
Thermal properties and crystallinity of the films 20
before and after heat sealed were analyzed by differential
scanning calorimetry (NETZSCH, DSC 200 F3) at 30- 15
200 C at heating and cooling rate of 10 C/min.
10
Results and Discussion
5
Heat seal strength of PLA and PLA/TPS films PLA PLA/TPS-5 PLA/TPS-10
0
The effect of heat sealed temperature and time on 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
heat seal strength of PLA and PLA/TPS films is tabulated Heat seal time (s)
in Table 1 and depicted in Figures 1 and 2. Table 1
Figure 1. Heat seal strength of the films at heat sealed
summarizes the heat seal strength of PLA and PLA/TPS
temperature 90 C.
films. Healt seal strength of the films exhibited
declination when increasing heat sealed temperatures and 30
times. Heat sealed 100 C
Heat seal strenght (N/15 mm)
25
Figure 1 presents the heat seal strength of films at
heat sealed temperature of 90 C. The heat seal strength
20
was approximately 22 N/15 mm. However, heat seal
strength of the PLA/TPS films decreased with increasing
15
heat sealed time. The films were torn and separated
without peeling at the heat sealed part. The failure mode
of these films was tearing failure [4]. The results indicated 10
that this heat sealed temperature was too high for
fabricating PLA/TPS heat sealed films. On the other hand, 5
the heat sealed strength of the PLA films increased when PLA PLA/TPS-5 PLA/TPS-10
heat sealed time increased. The PLA films were well 0
adhered at this temperature and peelable at the 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
temperature lower than 2.0 s. The failure mechanism of Heat seal time (s)
PLA heat sealed films was peeling and adhesive failure Figure 2. Heat seal strength of the films at heat sealed
[4]. On the contrary, the heat sealed strength of the all temperature 100 C.
ANTEC® 2013 / 1332
Thermal properties of PLA and PLA/TPS films temperature 90 C for 0.5-2.0 s. The thermograms
exhibited the faster of cold crystallization in the films that
Thermal properties and crystallization of PLA and heat sealed for 0.5 s, which this point the films could be
PLA/TPS films before and after heat sealed were carried obtain higher crystallinity than the others. Therefore, the
out by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The increment in heat sealed time in PLA/TPS films would not
results are illustrated in Figures 3-7. Figure 3 shows yield in an enhancement of heat seal strength as can be
thermograms of neat PLA and PLA/TPS films before heat seen in the heat sealed strength results.
sealing. These thermograms exhibited endothermic and
exothermic peaks during the melting. The slope at around Figure 6 exhibits the effect of heat sealed temperature
60 C indicated glass transition temperature of PLA on thermal properties and crytallization of PLA and
followed by the exothermic peak of precrystallization PLA/TPS films. The results showed the thermograms
(cold crystallization) of PLA at about 120 C. It can be comparison between PLA and PLA/TPS films at heat
seen that the addition of TPS in the PLA improved PLA sealed temperature of 90 and 100 C. From the results,
crystallization by presented the lower in cold higher heat sealed temperature affected on the shift of the
crystallization temperature as compared to the PLA film cold crystallization temperature of PLA in the films. The
[8]. lower heat sealed temperature of 90 C was better in
crystallization.
2.0
2.0
PLA PLA/TPS-5 PLA/TPS-10 Heat sealed 90 C 1.0 s
1.6
Heat flow endo up (W/g)
1.6 PLA PLA/TPS-5 PLA/TPS-10
1.2 Heat flow endo up (W/g)
1.2
0.8
0.8
0.4
0.4
0.0
30 60 90 120 150 180 0.0
Temperature (C) 30 60 90 120 150 180
Temperature (C)
Figure 3. DSC thermograms of the films before heat
Figure 4. DSC thermograms of heat sealed films at heat
sealed.
sealed temperature 90 C for 1.0 s.
The endothermic peaks around 154 C indicated melting
2.0
temperature of PLA. TPS influenced on PLA PLA/TPS-5
crystallization by presented a small peak in the melting
endothermic peak, which resulting from the melting of 1.6 0.5 s 1.0 s 2.0 s
Heat flow endo up (W/g)
difference PLA crystal sizes in these PLA/TPS films [9].
1.2
Figure 4 depicts DSC thermograms of the heat sealed
films at 90 C for 1.0 s. From the results, glass transition
temperature and melting temperature of PLA in the films 0.8
were unchanged after heat sealing. However, the cold
crystallization temperature of PLA heat sealed films was
0.4
lower than in the PLA/TPS films. Therefore, crystallinity
of PLA film was higher than the PLA/TPS one. It can be
seen that the heat seal strength of the PLA film was also 0.0
higher than that of PLA/TPS films. Therefore, 30 60 90 120 150 180
crystallinity influenced on enhanced the heat seal stregth. Temperature (C)
Figure 5. DSC thermograms of heat sealed PLA/TPS-5
The effect of heat sealed time on thermal properties films films at heat sealed temperature 90 C with varied
of the films was presented in Figure 5. Figure 5 shows the heat sealed times.
thermograms of PLA/TPS-5 films at heat sealed
ANTEC® 2013 / 1333
2.0 2.5
PLA-90 C PLA-100 C Heat sealed 100 C
PLA/TPS-10-90 C PLA/TPS-10-100 C
Endothermic enthalpy (J/g)
1.6 2.0
Heat flow endo up (W/g)
1.2 1.5
0.8 1.0
0.4 0.5
PLA PLA/TPS-5 PLA/TPS-10
0.0 0.0
30 60 90 120 150 180 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0
Temperature (C) Heat seal time (s)
Figure 6. DSC thermograms of heat sealed films at heat Figure 8. Effect of heat sealed time on endothermi
sealed temperature 90 C and 100 C for 2.0 s. enthalpy of heat sealed films at 100 C.
Figures 7 and 8 illustrate endothermic enthalpies of PLA heat selaed films, which exhibited peeling
the heat sealed films at heat sealed temperature of 90 and characteristic in failure mode. On the other hand, these
100 C, respectively. The enthalpy of PLA heat sealed heat sealed temperatures and times were not suitable for
film exhibited higer than the PLA/TPS films. It indicated improved the heat seal strength of PLA/TPS films, which
that the crystallinity of PLA films was better than the the PLA/TPS heat sealed film presented tearing in failure
others. The DSC results could be considered that the mode. The improvement of heat seal strength and
crystallinity of the films depended on heat sealed peelability of PLA/TPS films might be obtain when using
temperature, time and the composition of the films. It is the heat sealed temperature lower than 90 C.
intersting to note that the heat sealed films with higher
crystallinity would be resulting in better heat seal strength.
Acknowledgment
2.5 The authors greatfully acknowledge Thailand
Heat sealed 90 C
Research Fund (TRF) for supporting a research grant for
Endothermic enthalpy (J/g)
2.0 new scholar (MRG2555) contact no. MRG5580020.
1.5
References
1. L.-T. Lim, R. Auras and M. Rubino, Prog. Polym.
1.0 Sci., 33, 820 (2008).
2. R.N. Tharanathan, Trends Food Sci. Tech., 14, 71
(2003).
0.5
3. M. Avella, J.J. De Vlieger, M.E. Errico, S. Fischer, P.
PLA PLA/TPS-5 PLA/TPS-10 Vacca and M.G. Volpe, Food Chem., 93, 467 (2005).
0.0 4. K. Miyata, T. Ozama, A. Nishioka, T. Koda and G.
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 Murasawa, SPE-ANTEC Tech. Papers, 399 (2010).
Heat seal time (s) 5. K. Miyata, T. Ozama, A. Nishioka, T. Koda and G.
Murasawa, SPE-ANTEC Tech. Papers, 406 (2010)
Figure 7. Effect of heat sealed time on endothermi 6. T. Tetsuya, U.S. Ishiaku, M. Mizuguchi and H.
enthalpy of heat sealed films at 90 C. Hamada, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 97, 753 (2005)..
7. C.S. Yuan and A. Hassan, eXPress Polym. Lett., 11,
Conclusions 773 (2007).
8. D. battegazzore, S. Bocchini and A. Frache, eXPress
Biodegradable polymer films were successfully Polym. Lett., 10, 849 (2011).
prepared from PLA incorporated with thermoplastic rice 9. H. Xiao, L. Yang, X. Ren, T. Jiang and J.-T. Yeh,
starch. Heat seal strength of PLA and PLA/TPS films are Polym. Comp., 31, 2057 (2010).
significantly improved by the crystallinity of the films.
The heat sealed temperature of 90 C provided peelable of
ANTEC® 2013 / 1334
View publication stats
You might also like
- AQA 8464 C 1H Final MS Jun23 v1.0Document20 pagesAQA 8464 C 1H Final MS Jun23 v1.0meherun.hamzaNo ratings yet
- BOQ CulvertDocument38 pagesBOQ CulvertDeepak_pethkar100% (1)
- IseceDocument16 pagesIseceManoj PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Thermal Insulation Handbook for the Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical IndustriesFrom EverandThermal Insulation Handbook for the Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical IndustriesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Sandblasting - Application TrainingDocument44 pagesSandblasting - Application TrainingNurul Alam100% (2)
- Thesis Proposal: Compressive Strength of Fiber Reinforced Concrete Hollow Blocks (CHB) Using Plastic Bags As Fibers and Palm Oil Fuel Ash (Pofa) As Partial Replacement For CementDocument21 pagesThesis Proposal: Compressive Strength of Fiber Reinforced Concrete Hollow Blocks (CHB) Using Plastic Bags As Fibers and Palm Oil Fuel Ash (Pofa) As Partial Replacement For CementJerrick Wayne VertudazoNo ratings yet
- 15 pts.2562Document11 pages15 pts.2562Bram BampsNo ratings yet
- Tetsuya 2005Document8 pagesTetsuya 2005Vasanth KolurNo ratings yet
- EXO-EnDO CFA Effect Exo and Endothermic Blowing and Wetting Agent On Morphology Density and Hardness of Thermoplastic Pu FoamDocument17 pagesEXO-EnDO CFA Effect Exo and Endothermic Blowing and Wetting Agent On Morphology Density and Hardness of Thermoplastic Pu FoamProton HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Contrast Joints of Glass-Fibre With Carbon-Fibre Reinforced Polystyrene Composite Bonded by Microwave IrradiationDocument33 pagesContrast Joints of Glass-Fibre With Carbon-Fibre Reinforced Polystyrene Composite Bonded by Microwave IrradiationBuyandalai KhuurchNo ratings yet
- Crystallinity and Dimensional Stability of Biaxial Oriented Poly (Lactic Acid) FilmsDocument7 pagesCrystallinity and Dimensional Stability of Biaxial Oriented Poly (Lactic Acid) FilmsLong LeNo ratings yet
- Influence of Film Preparation Procedures On The Crystanllinity Morphology and Mechanical Properties of LLDPE FilmsDocument9 pagesInfluence of Film Preparation Procedures On The Crystanllinity Morphology and Mechanical Properties of LLDPE FilmsTrần ĐạtNo ratings yet
- San Thermal PropertiespdfDocument7 pagesSan Thermal Propertiespdfsukhabhukha987No ratings yet
- Indones. J. Chem., 2019, 19 (3), 545 - 555: AbstractDocument11 pagesIndones. J. Chem., 2019, 19 (3), 545 - 555: Abstractt3guhku2hNo ratings yet
- Polymer Testing: Fernanda C. Soares, Fabio Yamashita, Carmen M.O. Müller, Alfredo T.N. PiresDocument5 pagesPolymer Testing: Fernanda C. Soares, Fabio Yamashita, Carmen M.O. Müller, Alfredo T.N. PiresSiddharthBhasneyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Drilling Mud Waste-Filled Low Density Polyethylene CompositesDocument9 pagesMechanical Properties of Drilling Mud Waste-Filled Low Density Polyethylene Compositesgplese0No ratings yet
- Sin 2023 J. Phys. - Conf. Ser. 2523 012023Document15 pagesSin 2023 J. Phys. - Conf. Ser. 2523 012023Junaid AliNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of Chemical Crosslinking Effect On Properties of High-Density PolyethyleneDocument9 pagesAn Investigation of Chemical Crosslinking Effect On Properties of High-Density PolyethyleneAmirhosein FazilatiNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastic - Composite MaterialsDocument156 pagesThermoplastic - Composite MaterialsJosé Ramírez100% (1)
- Hassan 2019Document6 pagesHassan 2019phillynovitaNo ratings yet
- Zuo 2015Document6 pagesZuo 2015dannykusuma28No ratings yet
- Polymer: Mohit Gupta, Yijian Lin, Taneisha Deans, Alexis Crosby, Eric Baer, Anne Hiltner, David A. SchiraldiDocument7 pagesPolymer: Mohit Gupta, Yijian Lin, Taneisha Deans, Alexis Crosby, Eric Baer, Anne Hiltner, David A. Schiraldilylya_bejenaruNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Starch/poly (Vinyl Alcohol) /clay Nanocomposite Films Prepared in Twin-Screw Extruder For Food Packaging ApplicationDocument29 pagesCharacterization of Starch/poly (Vinyl Alcohol) /clay Nanocomposite Films Prepared in Twin-Screw Extruder For Food Packaging ApplicationfadilaNo ratings yet
- TheeffectofhightemperatureannealingprocessoncrystallizationprocessDocument13 pagesTheeffectofhightemperatureannealingprocessoncrystallizationprocessIshah ahamed KaziNo ratings yet
- Fulltext ID114202290PLACEBOIE PDFDocument11 pagesFulltext ID114202290PLACEBOIE PDFLaury Suarez BayonaNo ratings yet
- Feldmann 2016Document7 pagesFeldmann 2016MOSTAFA MOHSENNo ratings yet
- Fulltext ID114202290PLACEBOIE PDFDocument11 pagesFulltext ID114202290PLACEBOIE PDFLaury Suarez BayonaNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastics and Thermosetting PlasticDocument24 pagesThermoplastics and Thermosetting PlasticKAPIL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Materials Science For Energy Technologies: Masoud Habibi Zare, Nasibeh Hajilary, Mashallah RezakazemiDocument7 pagesMaterials Science For Energy Technologies: Masoud Habibi Zare, Nasibeh Hajilary, Mashallah RezakazemiOnime No IchinoseNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Physical Properties of PP and HDPE: Engineering ScienceDocument9 pagesMechanical and Physical Properties of PP and HDPE: Engineering ScienceVisaya L. ClaudineNo ratings yet
- Consumer Goods - Low Cost and Easy Processability Make HDPE A Material of Choice inDocument5 pagesConsumer Goods - Low Cost and Easy Processability Make HDPE A Material of Choice inDwi YuliantoNo ratings yet
- Alternate Material For Pressure Cooker Gasket Zalaki - 2020 - J. - Phys. - Conf. - Ser. - 1706 - 012181Document13 pagesAlternate Material For Pressure Cooker Gasket Zalaki - 2020 - J. - Phys. - Conf. - Ser. - 1706 - 012181viscairsyad96No ratings yet
- Dupont Compounds UL 1446Document20 pagesDupont Compounds UL 1446alex696No ratings yet
- Charpy Test ArticleDocument8 pagesCharpy Test Articlehabiba jamilNo ratings yet
- Tributyl Citrate Oligomers As Plasticizers For PLA 2003Document10 pagesTributyl Citrate Oligomers As Plasticizers For PLA 2003TOUFIKNo ratings yet
- MSRI Vol 16 No 1 P 70-75Document6 pagesMSRI Vol 16 No 1 P 70-75Cyrilia K.No ratings yet
- 10 I January 2022Document10 pages10 I January 2022Shreyas BiswasNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastic Film From Superfine Wool Powder: Xin Wang, Weilin Xu, Wenbin Li, Xungai WangDocument5 pagesThermoplastic Film From Superfine Wool Powder: Xin Wang, Weilin Xu, Wenbin Li, Xungai WangHector ParamoNo ratings yet
- TMA of Packaging Materials: Thermal AnalysisDocument4 pagesTMA of Packaging Materials: Thermal AnalysisHarold MangaNo ratings yet
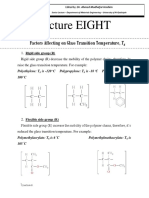
- Lecture EIGHT: Factors Affecting On Glass Transition Temperature, TDocument7 pagesLecture EIGHT: Factors Affecting On Glass Transition Temperature, TSadiq SalamNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastic Composites - Best Practice GuideDocument49 pagesThermoplastic Composites - Best Practice GuidemanikandapriyaNo ratings yet
- Study The Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Biodegradable Polylactic Acid/poly Ethylene Glycol NanocompositesDocument6 pagesStudy The Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Biodegradable Polylactic Acid/poly Ethylene Glycol NanocompositesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- 2010 FortunatiDocument7 pages2010 Fortunatijoan manuel MolinaNo ratings yet
- Use of Waste Plastic in Road ConstructionDocument6 pagesUse of Waste Plastic in Road ConstructionPranay ManwarNo ratings yet
- Studies On Modifications of PLA Films With Nanographene Clay and Silane Treated Hydrous ClayDocument8 pagesStudies On Modifications of PLA Films With Nanographene Clay and Silane Treated Hydrous ClayIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine BladesDocument6 pagesWind Turbine BladesSudhanwa KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Hdpe Plastic FilDocument7 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Hdpe Plastic FilshafiraNo ratings yet
- Mechanicaland Physical Propertiesof PPand HDPEDocument10 pagesMechanicaland Physical Propertiesof PPand HDPEVisaya L. ClaudineNo ratings yet
- Gasket Application and Material Selection GuideDocument10 pagesGasket Application and Material Selection GuideTieu KakaNo ratings yet
- 2008, Salomi, Potter, Spring-In Angle As Molding Distortion For Thermoplastic Matrix CompositeDocument8 pages2008, Salomi, Potter, Spring-In Angle As Molding Distortion For Thermoplastic Matrix Compositehalil yıldırımNo ratings yet
- Matecconf Iceim2015 02001Document4 pagesMatecconf Iceim2015 02001Abraham Adera BezabihNo ratings yet
- Inoue Iyota 19 17507 JSFEDocument8 pagesInoue Iyota 19 17507 JSFETarek Radwan BayramNo ratings yet
- Memon 2013Document9 pagesMemon 2013Likith Kumar B GNo ratings yet
- Suaduang 2019Document7 pagesSuaduang 2019Feyza Igra Harda PutraNo ratings yet
- PP Foams Nanofibrillar CompositesDocument11 pagesPP Foams Nanofibrillar CompositesPrashant Mani ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- 2003 Potting Hillman-BaylakogluDocument9 pages2003 Potting Hillman-BaylakogluVansala GanesanNo ratings yet
- Very ImportantDocument13 pagesVery ImportantadiNo ratings yet
- Ajassp 2017 878 885Document8 pagesAjassp 2017 878 885vijayNo ratings yet
- A. El-Sonbati - Thermoplastic Elastomers-Intech (2012) PDFDocument428 pagesA. El-Sonbati - Thermoplastic Elastomers-Intech (2012) PDFXuan Phuong HuynhNo ratings yet
- Preparing Flame-Retardant Polymer CompositesDocument6 pagesPreparing Flame-Retardant Polymer CompositesvNo ratings yet
- Ijaerv10n11spl 13Document6 pagesIjaerv10n11spl 13khm792352No ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of Polymers: A ReviewDocument9 pagesHeat Treatment of Polymers: A ReviewApurv PaulNo ratings yet
- Thermoforming of Single and Multilayer Laminates: Plastic Films Technologies, Testing, and ApplicationsFrom EverandThermoforming of Single and Multilayer Laminates: Plastic Films Technologies, Testing, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 2007 Strenx 700 CR 2017-04-20 52 371857150 enDocument2 pagesData Sheet 2007 Strenx 700 CR 2017-04-20 52 371857150 enThainã NavarroNo ratings yet
- Surface & Coatings Technology: Sudarshan Devaraj, Bobby Anand, Michael Gibbons, André Mcdonald, Sanjeev Chandra TDocument15 pagesSurface & Coatings Technology: Sudarshan Devaraj, Bobby Anand, Michael Gibbons, André Mcdonald, Sanjeev Chandra TMazurchevici Andrei DănuţNo ratings yet
- Salt Preparation - Bonding - Moles Revision Past PapersDocument6 pagesSalt Preparation - Bonding - Moles Revision Past PapersAnasha Éttienne-TaylorNo ratings yet
- Weld Test Checklist: Welder (S) DetailsDocument2 pagesWeld Test Checklist: Welder (S) DetailsScott Trainor100% (1)
- Poster 22216 PDFDocument1 pagePoster 22216 PDFHaneen AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Ceramics For Medical Applications A Picture For The Next 20 YearsDocument11 pagesCeramics For Medical Applications A Picture For The Next 20 YearsNícolas LaraNo ratings yet
- Set-On and Set-Through Nozzle InstallationDocument3 pagesSet-On and Set-Through Nozzle InstallationLiu Yangtze100% (1)
- Making Carbon Black: Presented by Sid Richardson Carbon CoDocument37 pagesMaking Carbon Black: Presented by Sid Richardson Carbon ColatshareNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Specification For Coarse Aggregate For Water Bound Macadam (Document8 pagesIndian Standard: Specification For Coarse Aggregate For Water Bound Macadam (ar TaNo ratings yet
- Sintering and Related Phenomena - Proceedings of The Third International Conference On Sintering and Related Phenomena, Held at The University of Notre Dame, June 5-7, 1972 PDFDocument450 pagesSintering and Related Phenomena - Proceedings of The Third International Conference On Sintering and Related Phenomena, Held at The University of Notre Dame, June 5-7, 1972 PDFbicky180No ratings yet
- Calcium Silicate Block and Pipe Thermal Insulation: Standard Specification ForDocument4 pagesCalcium Silicate Block and Pipe Thermal Insulation: Standard Specification ForRizal Mohamad Al-AyyubiNo ratings yet
- Monoliths - A Review of The Basics, Preparation Methods and Their Relevance To OxidationDocument29 pagesMonoliths - A Review of The Basics, Preparation Methods and Their Relevance To OxidationAnoopNo ratings yet
- TDS Disperbyk-108 en PDFDocument2 pagesTDS Disperbyk-108 en PDFpattycastillojNo ratings yet
- Avesta Finishing Solutions For Petrochemicals IndustryDocument92 pagesAvesta Finishing Solutions For Petrochemicals IndustryHAKANNo ratings yet
- Henco Multilayer Pipe: GAS Heating Sanitary Underfloor HeatingDocument4 pagesHenco Multilayer Pipe: GAS Heating Sanitary Underfloor HeatingSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit Weight of Materials Used at Construction Site PDFDocument2 pagesUnit Weight of Materials Used at Construction Site PDFDaryl J. S. BadajosNo ratings yet
- Specifications: Ruanta C12Document1 pageSpecifications: Ruanta C12Fransiscus Xaverius Patrick RustanNo ratings yet
- Cpe 601 Mini ProjectDocument9 pagesCpe 601 Mini ProjectSchaieraNo ratings yet
- Welding ProblemsDocument11 pagesWelding ProblemsJohn BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Pistoale de Vopsit AirProDocument12 pagesPistoale de Vopsit AirProDanaNo ratings yet
- Tacas (Brgy Hall)Document5 pagesTacas (Brgy Hall)Bob ShadowNo ratings yet
- BOQ FormatDocument5 pagesBOQ FormatRam Samujh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Corner FootingDocument19 pagesCorner Footingvenkatesh19701100% (1)
- Project Profiles 3Document2 pagesProject Profiles 3pradip_kumarNo ratings yet
- EDUS391100 F6 FXAQ PVJU Wall Mounted Engineering DataDocument42 pagesEDUS391100 F6 FXAQ PVJU Wall Mounted Engineering DataIbnuyusoff77No ratings yet