Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ISONIAZID
ISONIAZID
Uploaded by
Xerxes Dejito0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
365 views2 pagesThis document summarizes information about the drug Isoniazid (INH) including its classification as an anti-infective and antituberculosis agent. It is usually taken once daily or 2-3 times per week for 6 months to treat tuberculosis by inhibiting mycolic acid synthesis and disrupting the bacterial cell wall. Common side effects include nausea and vomiting while rare but serious adverse effects include neurotoxicity and hepatotoxicity. Nursing responsibilities involve educating patients on monitoring for side effects, avoiding alcohol/certain foods, continuing medical checkups and taking pyridoxine supplements if needed.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes information about the drug Isoniazid (INH) including its classification as an anti-infective and antituberculosis agent. It is usually taken once daily or 2-3 times per week for 6 months to treat tuberculosis by inhibiting mycolic acid synthesis and disrupting the bacterial cell wall. Common side effects include nausea and vomiting while rare but serious adverse effects include neurotoxicity and hepatotoxicity. Nursing responsibilities involve educating patients on monitoring for side effects, avoiding alcohol/certain foods, continuing medical checkups and taking pyridoxine supplements if needed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
365 views2 pagesISONIAZID
ISONIAZID
Uploaded by
Xerxes DejitoThis document summarizes information about the drug Isoniazid (INH) including its classification as an anti-infective and antituberculosis agent. It is usually taken once daily or 2-3 times per week for 6 months to treat tuberculosis by inhibiting mycolic acid synthesis and disrupting the bacterial cell wall. Common side effects include nausea and vomiting while rare but serious adverse effects include neurotoxicity and hepatotoxicity. Nursing responsibilities involve educating patients on monitoring for side effects, avoiding alcohol/certain foods, continuing medical checkups and taking pyridoxine supplements if needed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
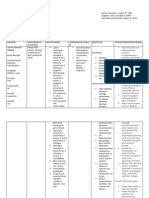
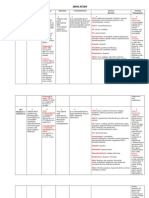
DRUG STUDY
DRUG NAME: Isoniazid (Isonicotinic Acid Hydrazide)
BRAND NAME: Isotamine, Laniazid
Classification: Antiinfective, Antituberculosis agent
Dosage: 5 mg/kg (up to 300 mg) IM or orally once a day,
or 15 mg/kg (up to 900 mg) 2 to 3 times a week for 6
months
Mechanism of Action:
Inhibits mycolic acid synthesis. Causes disruption of bacterial cell wall, loss of acid-fast
properties in susceptible mycobacteria. Active only during bacterial cell division. Therapeutic
Effect: Bactericidal against actively growing intracellular, extracellular susceptible
mycobacteria.
Indications: Treatment of susceptible mycobacterial infection due to Mycobacterium
tuberculosis. Drug of choice in tuberculosis prophylaxis. Used in combination with one or
more other antitubercular agents for treatment of active tuberculosis.
Contraindications:
Contraindications: Acute hepatic disease, history of hypersensitivity reactions, hepatic injury
or severe adverse reactions with previous isoniazid therapy. Cautions: Chronic hepatic disease,
alcoholism, severe renal impairment. May be crosssensitive with nicotinic acid, other
chemically related medications.
Side Effects:
Frequent: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain. Rare: Pain at injection site,
hypersensitivity reaction.
Adverse Effects:
Neurotoxicity (ataxia, paresthesia), optic neuritis, hepatotoxicity occur rarely.
Nursing Responsibilities:
1. Inform to avoid eating tyramine-containing foods (e.g., aged cheeses, smoked fish) as
it may cause palpitation, flushing, and blood pressure elevation.
2. Withhold medication and notify physician if S&S of hepatotoxicity develop (e.g., dark
urine, jaundice, clay-colored stools).
3. Advise to avoid or at least reduce alcohol intake while on isoniazid therapy because of
increased risk of hepatotoxicity.
4. Instruct not to breast feed while taking this drug without consulting physician.
5. Give in an empty stomach 1 hour before or 2 after meals; may be given with food if GI
upset occurs.
6. Educate the patient to have periodic medical check-ups, including an eye examination
and blood test, to evaluate the drug effects.
7. Teach the patient to report for weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite, n/v, yellowing of
skin or eyes, darkening of the urine, numbness or tingling in hands or feet,
8. Evaluate if the patient has had a previous allergic reaction to the drug
9. Inform to have regular consultations with the doctor and arrange for daily pyridoxine
in diabetic, alcoholic or malnourished patient also for patient that develops peripheral
neuritis, and those with HIV.
10. Ensure that the drug is taken in a single daily dose.
You might also like
- Set III. Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial Alterations A (Answers)Document9 pagesSet III. Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial Alterations A (Answers)Yaj Cruzada100% (6)
- Mosco's Clerking Guide..Document88 pagesMosco's Clerking Guide..temitopeNo ratings yet
- HydroxyzineDocument3 pagesHydroxyzineapi-3797941100% (2)
- OxacillDocument1 pageOxacillnerissa_villanueva3523No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyKirtia Mae CapuloNo ratings yet
- AmikacinDocument1 pageAmikacinMuhammad Arsalan100% (1)
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study2Document2 pagesDrug Study2Haifi HunNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument4 pagesDrug Study OrthoJhessa Curie Pitagan100% (1)
- Drug Study AmbroxolDocument2 pagesDrug Study AmbroxoledemNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocument4 pagesMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Chloromycetin Generic Name: Chloramphenicol Indication: External Ear CanalDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Chloromycetin Generic Name: Chloramphenicol Indication: External Ear CanalianecunarNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument5 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsYvonne AgathaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument5 pagesDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaNo ratings yet
- XtendaDocument2 pagesXtendaAlexis CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin TrihydrateDocument1 pageAmoxicillin TrihydrateHoney Que BullivantNo ratings yet
- Nursery Drug Study 2 1Document22 pagesNursery Drug Study 2 1Wenalyn Grace Abella LlavanNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin Tri Hydrate Table FormatDocument3 pagesAmoxicillin Tri Hydrate Table FormatNico DonatoNo ratings yet
- Chlorthalidone HygrotonDocument2 pagesChlorthalidone HygrotonLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Pravastatin SodiumDocument3 pagesPravastatin Sodiumapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Cefaclor, Salbutamol, Paracetamol and NCPDocument13 pagesCefaclor, Salbutamol, Paracetamol and NCPAriane Rose Saria CedronNo ratings yet
- CALCITRIOLDocument2 pagesCALCITRIOLdesshe09No ratings yet
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone and MgSO4Document2 pagesDexamethasone and MgSO4Nasriah MacadatoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study #2Document3 pagesDrug Study #2mharjoe pulmanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalsDocument4 pagesDrug Study FinalsKathleen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida InfectionsDocument1 pageGeneric Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida Infectionscen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- TergecefDocument2 pagesTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- Drug Study - OB WardDocument8 pagesDrug Study - OB WardCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Discharge PlanningDocument3 pagesCerebral Palsy Discharge Planningjints poterNo ratings yet
- MoxifloxacinDocument23 pagesMoxifloxacinKaaghu Raghu Micha0% (1)
- Nahco3 Vancomycin AmlodipineDocument3 pagesNahco3 Vancomycin AmlodipineShan Dave TupasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyOlive Keithy Ascaño ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ferrous GluconateDocument2 pagesFerrous GluconateMichael Kuzbyt0% (1)
- TigecyclineDocument2 pagesTigecyclineVanessa Egao100% (1)
- Check The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutDocument2 pagesCheck The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutJust nowNo ratings yet
- LetrozoleDocument2 pagesLetrozoleunkown userNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin, Dinoprostone, Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument3 pagesOxytocin, Dinoprostone, Cefuroxime Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Mupirocin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMupirocin Drug StudymichelleNo ratings yet
- Meclizine Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesMeclizine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Mupirocin DSDocument2 pagesMupirocin DSArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- Pilocarpine (Drug Monograph)Document1 pagePilocarpine (Drug Monograph)Muhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Meclizine Is An Antagonist atDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Meclizine Is An Antagonist atJayson Ray AbellarNo ratings yet
- HNBB Drug StudyDocument4 pagesHNBB Drug StudyYu, Denise Kyla BernadetteNo ratings yet
- Clindamycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesClindamycin Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- DS PiptazDocument1 pageDS PiptazCristel Z. Gabuco100% (1)
- AtroventDocument2 pagesAtroventKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- AldactoneDocument2 pagesAldactoneianecunarNo ratings yet
- INF (Isonicotinic Acid Hydrzide or Isoniazide) : Adult: Patient MonitoringDocument4 pagesINF (Isonicotinic Acid Hydrzide or Isoniazide) : Adult: Patient MonitoringEem Khaye YamsonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJuliana LegarteNo ratings yet
- ETHAMBUTOLDocument2 pagesETHAMBUTOLXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studyjanelee2824No ratings yet
- LOGICofTasks Format SampleDocument4 pagesLOGICofTasks Format SampleXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Form Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations/ Patient and Family TeachingDocument2 pagesDrug Study Form Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations/ Patient and Family TeachingXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Family Health, Maternal and Child Health, Procreative Health, Responsible Parenthood and Personal Value On LifeDocument5 pagesFamily Health, Maternal and Child Health, Procreative Health, Responsible Parenthood and Personal Value On LifeXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Own Definition in Nursing AssignmentDocument2 pagesOwn Definition in Nursing AssignmentXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Name: Age: Sex: Date Admitted: Admitted Via: Physician: Admitting DiagnosisDocument3 pagesName: Age: Sex: Date Admitted: Admitted Via: Physician: Admitting DiagnosisXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug StudyXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- ENDORSEMENTDocument3 pagesENDORSEMENTXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Funda RleDocument4 pagesFunda RleXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- ETHAMBUTOLDocument2 pagesETHAMBUTOLXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- NCM 1234 - AbdomenDocument67 pagesNCM 1234 - AbdomenXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- NCM 1234 - Thorax and LungsDocument150 pagesNCM 1234 - Thorax and LungsXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Form Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations/ Patient and Family TeachingDocument2 pagesDrug Study Form Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations/ Patient and Family TeachingXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Form Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations/ Patient and Family TeachingDocument2 pagesDrug Study Form Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations/ Patient and Family TeachingXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanXerxes Dejito0% (1)
- GREAT SupremeHealth and GREAT TotalCare Brochure (Full)Document22 pagesGREAT SupremeHealth and GREAT TotalCare Brochure (Full)jingzhitanNo ratings yet
- Proofed Nurs 2020 LearnDocument5 pagesProofed Nurs 2020 Learnapi-313199824No ratings yet
- ASI 10003B 7 Steps To Ensure Safe Water in HydrotherapyDocument9 pagesASI 10003B 7 Steps To Ensure Safe Water in HydrotherapyAbdullah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- ALLEVYN GENTLE BORDER LITE Location GuideDocument2 pagesALLEVYN GENTLE BORDER LITE Location GuideKmj AvotriniainaNo ratings yet
- Nosocomial: Infections in The Neonatal Intensive Care UnitDocument9 pagesNosocomial: Infections in The Neonatal Intensive Care UnitCleoanne Gallegos100% (1)
- GRP 3 - Galatians - Borgia Et1Document3 pagesGRP 3 - Galatians - Borgia Et1Kyle BARRIOSNo ratings yet
- Sampalok/Tamarind: Scientific Name: Tamarindus IndicaDocument8 pagesSampalok/Tamarind: Scientific Name: Tamarindus IndicaJudel GuiraldoNo ratings yet
- Depresia PostpartumDocument18 pagesDepresia PostpartumIonela BogdanNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Epulis GranulomatosaDocument7 pagesRecurrent Epulis GranulomatosaAnnisa ghina imaniarNo ratings yet
- FeverDocument29 pagesFeverYogesh KharcheNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: La Consolacion University Philippines Malolos City, BulacanDocument6 pagesCase Presentation: La Consolacion University Philippines Malolos City, BulacanElijah MancoNo ratings yet
- Wound CleansingDocument5 pagesWound CleansingPrince Maynerd SaguidNo ratings yet
- 2017 Certificate of Health 1Document2 pages2017 Certificate of Health 1herman syahNo ratings yet
- 1-Liver Function Test - PO4201376835-816 PDFDocument6 pages1-Liver Function Test - PO4201376835-816 PDFkhooniNo ratings yet
- GI PhysiologyDocument3 pagesGI PhysiologyAkhil MogalapalliNo ratings yet
- The Effect of WarDocument16 pagesThe Effect of Warapi-251665102No ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument10 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisdhanasundariNo ratings yet
- Scientific PaperDocument7 pagesScientific PaperLaura AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Ckhs Empiric Antibiotic Guidance For Adult Pneumonia.2016Document3 pagesCkhs Empiric Antibiotic Guidance For Adult Pneumonia.2016surenvishvaNo ratings yet
- Purdy Andrew Curriculum VitaeDocument8 pagesPurdy Andrew Curriculum Vitaeapi-614156568No ratings yet
- Sample Charting (Fdar)Document3 pagesSample Charting (Fdar)Mary Beth AbelidoNo ratings yet
- Bio Project AnshikaDocument16 pagesBio Project AnshikaAnshika AroraNo ratings yet
- Sarojini Devi Eye Hospital Hyderabad (OP Timings and Address)Document1 pageSarojini Devi Eye Hospital Hyderabad (OP Timings and Address)mrs.shweta4444No ratings yet
- S6.ICSH Guidelines For The Evaluation Blood Cell AnalysersDocument15 pagesS6.ICSH Guidelines For The Evaluation Blood Cell AnalysersKenneth Valverde CalderonNo ratings yet
- Clindamycin, Chloramphenicol, Streptogramin, Oxazolidinones IDK2014Document4 pagesClindamycin, Chloramphenicol, Streptogramin, Oxazolidinones IDK2014Frankie LiuNo ratings yet
- 2022 Article 775Document17 pages2022 Article 775Felipe CortesNo ratings yet
- Burning Mouth SyndromeDocument40 pagesBurning Mouth SyndromeSuci Sylvana HrpNo ratings yet
- Hearing Screening Protocols - Decision-MakingDocument4 pagesHearing Screening Protocols - Decision-Makingapi-523392209No ratings yet