Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anto A.au
Anto A.au
Uploaded by
Ethio funCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Histology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For PDFDocument26 pagesHistology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For PDFslinger1482% (96)
- Omaima NotesDocument49 pagesOmaima NotesVictor Fabunmi0% (1)
- An Incident That Changed My LifeDocument4 pagesAn Incident That Changed My Lifesirthana69754775% (4)
- Traumatic Brain Injury: Signs & SymptomsDocument17 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury: Signs & SymptomsGina Gucio100% (2)
- Body Mathching This 1Document6 pagesBody Mathching This 1api-421876727No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument15 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryAbbey Janine Mandapat Passi100% (3)
- Kirkos Biology Model Exame Grade 8 PDFDocument8 pagesKirkos Biology Model Exame Grade 8 PDFEmma Mohamed KhalidNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Part IIIDocument8 pagesDiagnostic Exam Part IIIAkosi AbakadaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Exam IIIDocument8 pagesAnatomy Exam IIIJonathanNo ratings yet
- PC1 ExamsDocument174 pagesPC1 Examsamandagnaw19No ratings yet
- Anaphy Lecture Midterm ExamDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lecture Midterm ExamBulajyo Pangngay JolinaNo ratings yet
- Module IV MCQ Exam (A)Document6 pagesModule IV MCQ Exam (A)Precious JuliusNo ratings yet
- Pre Test - Q2Document9 pagesPre Test - Q2Jon-Jon ManlapasNo ratings yet
- KEY - Q2 - Science - 7 - Michelle Joan Balicao - ASTERIO MADALLADocument5 pagesKEY - Q2 - Science - 7 - Michelle Joan Balicao - ASTERIO MADALLAPrincess AnnNo ratings yet
- LCC Biology (Model Exam)Document6 pagesLCC Biology (Model Exam)Emma Mohamed KhalidNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio FinalsDocument20 pagesAnaphysio FinalsNadiel FerrerNo ratings yet
- Second PT7 For PrintDocument3 pagesSecond PT7 For PrintMarlene Tubieros - InducilNo ratings yet
- Anp 400 P2Document13 pagesAnp 400 P2Safwan_Idham_B_5749No ratings yet
- Lesson1 Week 2Document7 pagesLesson1 Week 2candido evan100% (1)
- Science Grade 8 T3 Revision Mock Ans KeyDocument13 pagesScience Grade 8 T3 Revision Mock Ans Keyahmed5030 ahmed5030No ratings yet
- Biology Unit Test Practice Answers Dec 2014Document4 pagesBiology Unit Test Practice Answers Dec 2014t4jr7g5mjyNo ratings yet
- Science DrillDocument13 pagesScience DrillLovely Demafeliz SulitNo ratings yet
- 500 QuestionsDocument100 pages500 QuestionscentroalemanqroNo ratings yet
- BMA Practice Exam Paper AnswersDocument21 pagesBMA Practice Exam Paper AnswersSiennaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 First Trinal ExaminationDocument7 pagesBio 1 First Trinal ExaminationZERILLE ANNE INSON AGREGADONo ratings yet
- Second Qaurter Exam in Science 7Document5 pagesSecond Qaurter Exam in Science 7sheila mae tadoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology - ExamDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology - ExamQoppppNo ratings yet
- 2nd-Quarter-Exam-in-Science-7 FINALDocument4 pages2nd-Quarter-Exam-in-Science-7 FINALMyth LiliNo ratings yet
- q4 40-Item Final ExamDocument2 pagesq4 40-Item Final ExamMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Q3, G10 Scie Summative TestDocument3 pagesQ3, G10 Scie Summative Testangel pranadaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Practice TestDocument13 pagesCH 1 Practice TestKen DalNo ratings yet
- AnhDocument15 pagesAnhduyanh4583No ratings yet
- 2022 HSF Etest 1 Sample Paper StudentDocument7 pages2022 HSF Etest 1 Sample Paper StudentSamha MahboubNo ratings yet
- Gs Grade 8th-Q&A Wereda 09Document2 pagesGs Grade 8th-Q&A Wereda 09samson amsaluNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ExamDocument4 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Examryan erwin san luisNo ratings yet
- Supp 2017 PDFDocument28 pagesSupp 2017 PDFDesmond BwalyaNo ratings yet
- PRELIMSDocument2 pagesPRELIMSMelinda VillenaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Grade 7Document2 pages2nd Quarter Grade 7Genalyn Cirpo TayoneNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Test-BiologyDocument6 pagesUnit 9 Test-BiologyNicholas PerezNo ratings yet
- Paper-A (Foundation & Blood Module)Document4 pagesPaper-A (Foundation & Blood Module)Sudais KhattakNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY II FBI1224 2022 Question Paper 1Document10 pagesBIOLOGY II FBI1224 2022 Question Paper 1zoulzz0903No ratings yet
- Summative Test 2Document2 pagesSummative Test 2EM GinaNo ratings yet
- T1 Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument2 pagesT1 Introduction To Human AnatomySafaa WaganNo ratings yet
- MC 1 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY MidtermDocument12 pagesMC 1 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY MidtermNicole Sheen EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Exercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsDocument16 pagesExercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsShu85100% (1)
- Grade 7 Final Exam Quarter 2Document4 pagesGrade 7 Final Exam Quarter 2Rizalyn DiazNo ratings yet
- Hes 101 - CfuDocument10 pagesHes 101 - CfuLAGUERTA, JOHN MICHAEL A.No ratings yet
- Quiz No. 1 Science 6 Second Quarter Name: - Grade: - I. Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answer On The BlankDocument2 pagesQuiz No. 1 Science 6 Second Quarter Name: - Grade: - I. Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answer On The BlankCecilia Guevarra Dumlao100% (4)
- Study Guide - Final ExamDocument7 pagesStudy Guide - Final ExamRichard LaRouechNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Test: Artery in The Latin Language Means What?Document22 pagesAnatomy Test: Artery in The Latin Language Means What?Anonymous MtKJkerbpUNo ratings yet
- 1ST Summative Test in Science 6 Q2Document4 pages1ST Summative Test in Science 6 Q2Liza Mea Guhayon Reblinca0% (1)
- BBS - Finals Compilation - Project Coffee PDFDocument318 pagesBBS - Finals Compilation - Project Coffee PDFNoel JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Biology Worksheet 1Document5 pagesGrade 8 Biology Worksheet 1YonasNo ratings yet
- Ana Physio 1prelims 2021-22 1stsem 1B - ExamDocument5 pagesAna Physio 1prelims 2021-22 1stsem 1B - ExamKwenzie FortalezaNo ratings yet
- Hns 2101 Human Anatomy IDocument5 pagesHns 2101 Human Anatomy IbalancelacktonNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Life Science 2023 For RISODocument5 pagesFinal Exam Life Science 2023 For RISOJoderon NimesNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 (Sum Test)Document2 pagesGrade 11 (Sum Test)Yvuj LagnitabNo ratings yet
- Eart and Life TQ FinalDocument3 pagesEart and Life TQ FinalNel PasaizNo ratings yet
- Biology Form Three Annual 2023Document6 pagesBiology Form Three Annual 2023vecema1296No ratings yet
- Reviewer Science 7Document22 pagesReviewer Science 7Arlynda LampaNo ratings yet
- First Semester Question BankDocument19 pagesFirst Semester Question Banknanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1From EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- NLP Fast PhobiaDocument1 pageNLP Fast PhobiaAnonymous A1LQIfKNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience For Neurosurgeons Feb 29 2024 - 110883146X - Cambridge University Press 1St Edition Farhana Akter Full ChapterDocument68 pagesNeuroscience For Neurosurgeons Feb 29 2024 - 110883146X - Cambridge University Press 1St Edition Farhana Akter Full Chapterdale.freyer940100% (7)
- AOTrauma Course-Basic Principles of Fracture Management April 10-12, 2015 Hefei, ChinaDocument20 pagesAOTrauma Course-Basic Principles of Fracture Management April 10-12, 2015 Hefei, ChinafaluviekadianiNo ratings yet
- GONIOMETRYDocument20 pagesGONIOMETRYkushi98mandyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Lower Limb Assessment Flow SheetDocument2 pagesBasic Lower Limb Assessment Flow Sheetمحمد نعمة جياد100% (1)
- Spinocerebelar Tract-2Document20 pagesSpinocerebelar Tract-2Vijayasekhar VempalliNo ratings yet
- PolyScience 1.5 HP Chiller - 110-392 Durachill 1.5 HP 01-05-2022Document57 pagesPolyScience 1.5 HP Chiller - 110-392 Durachill 1.5 HP 01-05-2022hsghdNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-06-18 at 10.34.34 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-06-18 at 10.34.34 PMNandan BethinaNo ratings yet
- Ortho Rad Sessions FisamDocument20 pagesOrtho Rad Sessions FisamDouglas MutenyoNo ratings yet
- Management of BurnDocument42 pagesManagement of BurnArisa KudidthalertNo ratings yet
- Operating-Manual VSH200 F-011819 19.1Document98 pagesOperating-Manual VSH200 F-011819 19.1Yoyon HaryonoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Neuro Assessment 2021 - 336Document30 pages1 - Neuro Assessment 2021 - 336HADI BADWAN100% (2)
- Rectus Femoris - PhysiopediaDocument5 pagesRectus Femoris - PhysiopediaVahid AtaeiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER3 LAW of TORTS Tresspass To Land and NegligenceDocument36 pagesCHAPTER3 LAW of TORTS Tresspass To Land and NegligenceMuhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- TRACTIONDocument3 pagesTRACTIONCatherineNo ratings yet
- Phases of The PushupDocument2 pagesPhases of The PushupMaryane AngelaNo ratings yet
- Anthropometric MeasurementsDocument17 pagesAnthropometric MeasurementsPunitha PuniNo ratings yet
- Sketetal SystemDocument11 pagesSketetal SystemBryan JagroopNo ratings yet
- DONE Anuat V Pacific Ocean Manning, Inc. G.R. No. 220898, July 23, 2018Document2 pagesDONE Anuat V Pacific Ocean Manning, Inc. G.R. No. 220898, July 23, 2018Kathlene JaoNo ratings yet
- CHESAPEAKE Surgical TechniqueDocument20 pagesCHESAPEAKE Surgical Techniquenvj8wsthdtNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices and Sports Injury Management.Document8 pagesSafety Practices and Sports Injury Management.cejaygecainNo ratings yet
- Reading TestDocument3 pagesReading TestVan NguyenNo ratings yet
- OrthoticsDocument37 pagesOrthoticsergosadia658No ratings yet
- Body MechanicsDocument26 pagesBody MechanicsSandeepNo ratings yet
- Asphyxial Death 160219112440Document22 pagesAsphyxial Death 160219112440Kanokporn PongviratNo ratings yet
- EfaDocument74 pagesEfaKrypton KrNo ratings yet
Anto A.au
Anto A.au
Uploaded by
Ethio funOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anto A.au
Anto A.au
Uploaded by
Ethio funCopyright:
Available Formats
Addis Ababa University
College of Health Sciences
Department of Pharmacy
Human Anatomy and Histology Mid exam-I (30%)
for 1st Year Regular pharmacy students
Date: 30/12 /2017 G.C Time allocated: 1:30hrs.
Name____________________________________
ID NO____________________
Instructions:
1. Check your questions booklet has 22 matching, 78 MCQ,
9 short answers and 12 pages including both the cover
page and answer sheet
2. Please, Switch off your mobile phone
3. Trying of cheating and any misconduct will disqualify your
result
4. Only write your answers in Block letter on the last page
of the answer sheet. Not allowed exaggerated tick/circle
on the question booklet
5. Don’t turn this page until you are told to do so!
1|Page By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
Part-I: Match the various types of epithelial tissues given under column „A‟
with their site of locations listed under column „B‟ (worth 0.5 point each).
Column „A‟ Column „B‟
1. Simple squamous epithelium A. skin, oral surface of hard palate
2. Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium B. stomach, gall bladder, small intestine
3. Transitional epithelium C. uterus, uterine tubes
4. Pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium D. proximal convoluted tubule of kidney
5. Simple cuboidal epithelium E. nasopharynx, trachea, bronchi
6. Simple ciliated columnar epithelium F. renal pelvis, ureters, urinary bladder
7. Simple non-ciliated columnar epithelium G. oropharynx, esophagus, anal canal
H. heart, blood vessels, serous membranes
Part II: Match from column “B” that fits the column “A” (0.5 pt. each).
A B
1. ___Bone forming cells A. Chondroblasts
2. ___Mature bone cells B. Osteoblasts
3. ___Bone breaking cells C. Chondrocytes
4. ___Cartilage forming cells D. Osteocytes
5. ___Mature cartilage cells E. Osteoclasts
F. Osteogenic cells
Part III: match the following anatomical terminologies given under column
„A‟ with their meaning described under column „B‟.
1. ___Extension A. increasing the angle between the bones joint
2. ___Flexion B. Moving the body part away from the midline
3. ___Adduction C. Parts of the body found above the horizontal plane
4. ___Abduction D. The palms face downward
5. ___Superior E. decreasing the angle between the bones joint
6. ___Inferior F. Parts of the body found below horizontal plane
7. ___Superficial G. The palms face upward
8. ___Supination H. Moving the parts of body toward the midline
9. ___Pronation I. Moving the sole of foot towards the midline
10. ___Eversion J. Structures of body found externally
K. Moving the sole of foot away from the midline
2|Page By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
Part III: Choose and write the best answer from the given alternatives (0.5 pt. each).
1. The study of anatomy by our naked eye is said to be:
A. Gross anatomy C. Macroanatomy E. A & C
B. Microanatomy D. Cytology
2. A person who is standing in the anatomical position is:
A. Facing laterally
B. Have the palms of the hands directed medially
C. Is standing on his/her toes
D. Have the upper limbs by the sides of the trunk
E. None of the above
3. Your nose is_____________to your eyes.
A. Superiolateral C. Inferoateral E. None of the above
B. Inferiormedial D. Superomedial
4. Which subdivision of anatomy uses imaging techniques to study the normal and diseased
internal structures of the human body?
A. Surface anatomy D. Radiological anatomy
B. Clinical anatomy E. Gross anatomy
C. Surgical anatomy
5. Which body plane divides the body into anterior and posterior parts?
A. Sagittal plane C. Oblique plane E. None of the above
B. Median plane D. Coronal plane
6. Anatomical term used for a patient lying on back is:
A. Supine position C. Lateral position E. All of the above
B. Prone position D. Medial position
7. Which one of the following is angular movement?
A. The movement of thigh towards the midline of the body
B. The movement of index finger away from the middle finger
C. The movement of trunk towards the thigh
D. The movement of forearm away from the arm
E. The movement of head towards the side of shoulder
8. All are belongs to special movement except:
A. Elevation of shoulder D. Protrusion of tongue
B. Eversion of foot E. None of the above
C. Depression of mandible
9. Which body cavities protect the central nervous system?
A. Cranial cavity C. Anterior cavity E. All of the above
B. Spinal cavity D. A and B
3|Page By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
10. All of the following body membranes are made from epithelial tissue except:
A. Serous membrane D. Synovial membrane
B. Mucus membrane E. All of the above
C. Cutaneous membrane
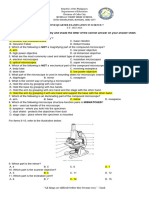
11. What is the total magnification achieved with a compound light microscope?
A. Magnification of ocular lens added to the magnification of the objective lens
B. Magnification of ocular lens multiplied by the magnification of the objective lens
C. Magnification of condenser lens multiplied by the magnification of the objective lens
D. Magnification of objective lens
E. Magnification of ocular lens
12. ___________is a group of structurally and functionally similar cells.
A. Organ C. System E. All of the above
B. Tissue D. Organelle
13. The membrane stability can be maintained by which one of the membrane structure?
A. Phospholipid C. Integral protein E. All of the above
B. Cholesterol D. Glycolipid
14. All of the following are true regarding the cytoplasmic organelles EXCEPT:
A. Perform life sustaining activities
B. Are metabolically active
C. Are lifeless and non-membrane bounded
D. Perform specific activities
E. None of the above
15. Mitochondria are the power house of the cell, this most important structure is belongs to
which level of organization?
A. Cellular level C. Organelle level E. Organ system
B. Organ level D. Tissue level
16. All are exoskeleton of a cell EXCEPT:
A. Intermediate filament D. Microtubule
B. Microfilament E. None of the above
C. Lipofuscin
17. One is FALSE regarding the nucleus?
A. Has a double membrane
B. Has a nuclear pore at regular interval
C. Contains none membrane bounded nuclear inclusions (nucleolus)
D. Has euchromatin which is transcriptionally inactive
E. None of the above
4|Page By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
18. Which one of the following is FALSE regarding the epithelial tissues?
A. Avascular except glands
B. Have little or no intercellular space
C. Are derived from three germ layers
D. Have an apical surface exposed to the environment
E. They have high capacity of regeneration
19. The connective tissue type that is characterized by loosely arranged extracellular matrix
fibers and relative abundance of cells is:
A. Loose connective tissue D. Stratified squamous connective
B. Dense regular connective tissue tissue
C. Dense irregular connective tissue E. None of the above
20. Undifferentiated tissue found in the embryo. What type of connective tissue is:
A. Reticular connective tissue D. Dense connective tissue
B. Mesenchyme E. Areolar connective tissue
C. Loose irregular connective tissue
21. Antibody producing cells within connective tissue are termed as:
A. Mast cells C. Plasma cells E. Adipocytes
B. Fibroblasts D. Macrophages
22. Which connective tissue cell produces natural anticoagulant (heparin)?
A. Plasma cell C. Mast cells E. Fibroblast
B. Macrophage D. Adipocyte
23. Which one of the following is NOT considered as inclusion?
A. Pigment C. Lipid E. Lysosome
B. Glycogen D. Lipofuscin
24. Which one of the following exocrine gland discharges its secretion by pinching off the apical
parts of its secretory cell?
A. Merocrine gland C. Apocrine gland E. None of the above
B. Eccrine gland D. Holocrine gland
25. Simple squamous epithelium that lines the lumen of blood vessels is said to be:
A. Mesothelium C. Transitional E. All of the above
B. Epitheloid D. Endothelium
26. Which of the following is a circulating blood cell that is capable of differentiating into a
plasma cell?
A. Neutrophil C. B lymphocyte E. Monocyte
B. Basophil D. T lymphocyte
27. Which one of the following types of tissue has large amounts of extracellular matrix and
relatively large space between cells?
A. Epithelial tissue C. Muscular tissue E. None of the above
B. Connective tissue D. Nervous tissue
5|Page By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
28. Which one of the following organelles has double membrane?
A. Nucleus C. Lysosome E. A and B
B. Mitochondria D. Peroxisome
29. Which one of the following organelles is used to digest foreign substances and aged
organelles?
A. Nucleus C. Lysosome E. A and B
B. Mitochondrion D. Ribosome
30. Which molecule largely contributes for cell membrane structure?
A. Cholesterol C. Peripheral protein E. None of the above
B. Phospholipid D. Glycolipid
31. Which of the following mucopolysaccharide ECM is non-sulfated and most abundant in
tissues and used as beauty treatment on wrinkle skin?
A. Heparin C. Keratan sulfate E. Hyaluronic acid
B. Dermatan sulfate D. Chondroitin sulfate
32. In embryo, the skeleton is primarily made of _______, but in the adult, most of the skeletons
are _______.
A. Elastic cartilage and bone D. Hyaline cartilage and bone
B. Hyaline cartilage and fibrocartilage E. None of the above
C. Fibrocartilage and bone
33. Which of the following bone does not articulate with another bone?
A. Scapula C. Frontal E. Hyoid
B. Sternum D. Occipital
34. Which statement is INCORRECT about fertilization?
A. It restores the normal number of chromosomes
B. It stimulates the penetrated oocytes to complete the first meiotic division
C. It causes the metabolic activation of the ovum and initiate cleavage of the zygote
D. It results the variation of the human species
E. It determines the chromosomal sex of the embryo
35. With regard to spermatogenesis, which statement is NOT CORRECT?
A. Spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa by spermatogenesis
B. The entire process of spermatogenesis takes approximately 72 hours
C. The primary spermatocytes are the largest cells in the seminiferous tubules
D. Spermatogenesis begins at puberty
E. Spermatogonia begin to increase in number at puberty
36. How many somatic chromosomes are in a normal human karyotype?
A. 22 C. 26 E. 46
B. 23 D. 44
37. Which part of the fallopian tube fertilization takes place?
A. Ampulla C. Intramural E. None of the above
B. Infundibulum D. Isthmus
6|Page By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
38. When does the second meiotic division completed in oogenesis process?
A. Before birth C. During fertilization E. None of the above
B. At ovulation D. Before ovulation
39. The matured form of sperm is called:
A. Spermatogonia D. Spermatozoa
B. Spermatids E. Secondary spermatocytes
C. Primary spermatocytes
40. To what does the term cleavage refer?
A. A series of cellular expansions D. A series of cellular specializations
B. A series of cellular divisions E. All of the above
C. A series of cellular extensions
41. Which of the following has stages of human development arranged in the sequence in which
they occur?
A. Zygoteblastulamorulaembryofetus
B. Zygotemorulablastulaembryofetus
C. Zygoteembryomorulafetusblastula
D. Morulablastulazygoteembryofetus
E. Blastulafetusembryoembryozygote
42. The HCG is a marker for pregnancy test by day 8 in mother serum and by day 10 in mother’s
urine produced by what cells?
A. Cytotrophoblast D. Epiblast
B. Syncytiotrophoblast E. Hypoblast
C. Aminoblast
43. When implantation of embryo completed?
A. First week C. Third week E. None of the above
B. Second week D. Fourth week
44. Which one of the following is not a derivative of ectoderm
A. Central nervous system D. Connective tissue and cartilage
B. Peripheral nervous system E. Adrenal medulla
C. Epidermis and its appendages
45. One of the following organs is derived from endoderm germ layer?
A. Adrenal cortex D. Parenchyma of thyroid gland
B. Adrenal medulla E. Stroma of thyroid gland
C. Pituitary gland
46. The embryonic period which is critical and susceptible for teratogen agents?
A. is between 1st and 2nd week of development
B. is between 3rd and 4th week of development
C. is between 3rd to 8th week of development
D. is a period of organogenesis
E. C and D
7|Page By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
47. A type of zygote developed when an ovum is fertilized by a single spermatozoon is:
A. Monozygotic twin C. Fraternal twin E. A and D
B. Dizygotic twin D. Identical twin
48. Which of the following is the longest and most variable cell-cycle phase in continuously
dividing cells?
A. G0 phase C. G2 phase E. S phase
B. G1 phase D. M phase
49. The most abounding cartilage in the body?
A. Hyaline B. Fibrocartilage C. Elastic D. Spongy E. None
50. The most abundant connective tissue cells that synthesis fibers and maintain ECM is:
A. Chondrocytes B. Fibroblasts C. Osteocytes D. Plasma cells E. None
51. The modified unicellular glands composed of columnar cells that secrete mucous are known
as:
A. Cilia C. Goblet cells E. Basal cells
B. Microvilli D. Endocrine glands
52. Which of the following is involuntary and striated?
A. Skeletal muscle tissue D. Visceral muscle tissue
B. Cardiac muscle tissue E. Neural tissue
C. Smooth muscle tissue
53. Which tissue is characterized by the presence of cell body, dendrites and axon?
A. Muscle C. Nervous E. Osseous
B. Vascular D. Epithelial
54. The system that controls smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and gland activity is the:
A. Somatic nervous system D. Sensory nervous system
B. Autonomic nervous system E. None of the above
C. Skeletal division
55. The most abundant which account 90% of the total epidermal cells are:
A. Merkel cells C. Melanocytes E. None of the above
B. Langerha cells D. Keratinocytes
56. Which one of the epidermal cells has a role in ultraviolet light protection released from sun?
A. Merkel cells C. Keratinocytes E. Fibrocytes
B. Melanocytes D. Langerhan cells
57. All are the appendages of skin except:
A. Hair C. Sebaceous gland E. None of the above
B. Nail D. Sweat gland
58. Which layer of the epidermis absent in thin skin?
A. Stratum spinosum D. Stratum basale
B. Stratum granulosum E. None of the above
C. Stratum corneum
8|Page By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
59. In which degree burn that the burn involves the entire loss of skin and underlying structures?
A. First C. Third E. None of the above
B. Second D. A & B
60. Which one is belongs to skin disorder because of localized loss of melanin?
A. Psoriasis C. Acne E. All of the above
B. Vitiligo D. Albino
61. Growth in length of long bone takes place at:
A. Epiphyseal line C. Epiphysis E. None of the above
B. Diaphysis D. All of the above
62. No or Nodding of the head occurs at which of the following joint?
A. Atlantoccipital joint D. All of the above
B. Atlantoaxial joint E. None of the above
C. TMJ
63. The outer fibrous membrane that covers the surface of the bone is:
A. Perimysium C. Periosteum E. Perimysium
B. Endosteum D. Perichondrium
64. Which bones form acetabulum?
A. Ischium C. Pubis E. None of the above
B. Ilium D. All
65. The type of joint commonly found between the skull bones is/are:
A. Syndesmoses C. Sutures E. Sympysis
B. Synchondroses D. Gomphoses
66. One of the following bones is not found in axial skeleton.
A. Scapula C. Sternum E. Atlas
B. Mandible D. Sacrum
67. All carpal bones are found in the proximal row except:
A. Hamate C. Lunate E. Triqutreum
B. Scaphoid D. Pisiform
68. Which structure of connective tissue those connect bone to bone?
A. Aponeurosis C. Fascia E. Epimysium
B. Tendon D. Ligament
69. A constricted region between the head and body of bone is:
A. Neck C. Condyle E. Cleft
B. Facet D. Tubercle
70. Which one of the following bone surface markings forms articulation?
A. Condyle C. Head E. All except B
B. Epicondyle D. Facet
9|Page By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
71. The following statements are true regarding the ribs:
A. The 1-7th ribs have direct connection with the sternum, hence true ribs
B. 8-10th ribs have no direct attachment with the sternum, hence false ribs
C. 11th and 12th ribs do not have any attachment with the sternum, hence floating ribs
D. All
E. None of the above
72. All are belongs to cranial bone except:
A. Occipital bone C. Temporal bone E. Sphenoid bone
B. Parietal bone D. Zygomatic bone
73. The followings are bone of forearm except:
A. Humerus C. Ulna E. None of the above
B. Radius D. All of the above
74. Which type of fracture one end of fractured bone is forcefully derived into the interior of the
other?
A. Capillary fracture D. Greenstick fracture
B. Displaced fracture E. Impacted fracture
C. Comminuted fracture
75. A partial fracture in which one side of the bone is broken and the other side bends and
common in children’s called:
A. Impacted fracture D. Capillary fracture
B. Comminuted fracture E. None of the above
C. Greenstick fracture
76. The only moveable skull bone is:
A. Frontal bone C. Maxillae E. All of the above
B. Parietal bone D. Mandible
77. The cartilage that we found in the pubic symphysis and intervertebral disc called:
A. Fibrocartilage C. Hyaline cartilage E. None of the above
B. Elastic cartilage D. All of the above
78. Which one of the following statement is False?
A. Ulna is medial to radius bone
B. Tibia is lateral to fibula bone
C. Patella is the largest sesamoid bone
D. Femur is the largest and strongest bone
E. Femur is proximal to tibia bone
10 | P a g e By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
Part IV: Give short answers with neat and correct spellings.
1. Write the following opposites (0.5 point each).
A. inversion ________________
B. posterior ________________
C. contralateral_______________
E. adduction_________________
2. Trace out the biological organization of human being? (2 point)
3. Explain the two types of skin? (2 points)
4. Distinguish the difference between embryology and teratology? (2 point)
5. Where the sperm and ovum produced? (2 points)
6. Explain the compact and spongy bone tissues? (2 points)
7. Discuss in detail the three types of joints structurally and functionally? (3 points)
8. What are the four types of tissues and give examples for each? (2 points)
9. What are the three types of cartilage and give examples of location for each? (3 points)
11 | P a g e By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
Answer sheet
Name____________________________________ID NO___________Score: ___/30%
1. 4. 9. 9. 19. 29. 39. 49. 59. 69.
2. 5. 10. 10. 20. 30. 40. 50. 60. 70.
3. 1. 1. 11. 21. 31. 41. 51. 61. 71.
4. 2. 2. 12. 22. 32. 42. 52. 62. 72.
5. 3. 3. 13 23. 33. 43. 53. 63. 73.
6. 4. 4. 14. 24. 34. 44. 54. 64. 74.
7. 5. 5. 15. 25. 35. 45. 55. 65. 75.
1. 6. 6. 16. 26. 36. 46. 56. 66. 76.
2. 7. 7. 17. 27. 37. 47. 57. 67. 77.
3. 8. 8. 18. 28. 38. 48. 58. 68. 78.
12 | P a g e By: Fikre B. AAU, 2017
You might also like
- Histology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For PDFDocument26 pagesHistology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For PDFslinger1482% (96)
- Omaima NotesDocument49 pagesOmaima NotesVictor Fabunmi0% (1)
- An Incident That Changed My LifeDocument4 pagesAn Incident That Changed My Lifesirthana69754775% (4)
- Traumatic Brain Injury: Signs & SymptomsDocument17 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury: Signs & SymptomsGina Gucio100% (2)
- Body Mathching This 1Document6 pagesBody Mathching This 1api-421876727No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument15 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryAbbey Janine Mandapat Passi100% (3)
- Kirkos Biology Model Exame Grade 8 PDFDocument8 pagesKirkos Biology Model Exame Grade 8 PDFEmma Mohamed KhalidNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Part IIIDocument8 pagesDiagnostic Exam Part IIIAkosi AbakadaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Exam IIIDocument8 pagesAnatomy Exam IIIJonathanNo ratings yet
- PC1 ExamsDocument174 pagesPC1 Examsamandagnaw19No ratings yet
- Anaphy Lecture Midterm ExamDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lecture Midterm ExamBulajyo Pangngay JolinaNo ratings yet
- Module IV MCQ Exam (A)Document6 pagesModule IV MCQ Exam (A)Precious JuliusNo ratings yet
- Pre Test - Q2Document9 pagesPre Test - Q2Jon-Jon ManlapasNo ratings yet
- KEY - Q2 - Science - 7 - Michelle Joan Balicao - ASTERIO MADALLADocument5 pagesKEY - Q2 - Science - 7 - Michelle Joan Balicao - ASTERIO MADALLAPrincess AnnNo ratings yet
- LCC Biology (Model Exam)Document6 pagesLCC Biology (Model Exam)Emma Mohamed KhalidNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio FinalsDocument20 pagesAnaphysio FinalsNadiel FerrerNo ratings yet
- Second PT7 For PrintDocument3 pagesSecond PT7 For PrintMarlene Tubieros - InducilNo ratings yet
- Anp 400 P2Document13 pagesAnp 400 P2Safwan_Idham_B_5749No ratings yet
- Lesson1 Week 2Document7 pagesLesson1 Week 2candido evan100% (1)
- Science Grade 8 T3 Revision Mock Ans KeyDocument13 pagesScience Grade 8 T3 Revision Mock Ans Keyahmed5030 ahmed5030No ratings yet
- Biology Unit Test Practice Answers Dec 2014Document4 pagesBiology Unit Test Practice Answers Dec 2014t4jr7g5mjyNo ratings yet
- Science DrillDocument13 pagesScience DrillLovely Demafeliz SulitNo ratings yet
- 500 QuestionsDocument100 pages500 QuestionscentroalemanqroNo ratings yet
- BMA Practice Exam Paper AnswersDocument21 pagesBMA Practice Exam Paper AnswersSiennaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 First Trinal ExaminationDocument7 pagesBio 1 First Trinal ExaminationZERILLE ANNE INSON AGREGADONo ratings yet
- Second Qaurter Exam in Science 7Document5 pagesSecond Qaurter Exam in Science 7sheila mae tadoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology - ExamDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology - ExamQoppppNo ratings yet
- 2nd-Quarter-Exam-in-Science-7 FINALDocument4 pages2nd-Quarter-Exam-in-Science-7 FINALMyth LiliNo ratings yet
- q4 40-Item Final ExamDocument2 pagesq4 40-Item Final ExamMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Q3, G10 Scie Summative TestDocument3 pagesQ3, G10 Scie Summative Testangel pranadaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Practice TestDocument13 pagesCH 1 Practice TestKen DalNo ratings yet
- AnhDocument15 pagesAnhduyanh4583No ratings yet
- 2022 HSF Etest 1 Sample Paper StudentDocument7 pages2022 HSF Etest 1 Sample Paper StudentSamha MahboubNo ratings yet
- Gs Grade 8th-Q&A Wereda 09Document2 pagesGs Grade 8th-Q&A Wereda 09samson amsaluNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ExamDocument4 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Examryan erwin san luisNo ratings yet
- Supp 2017 PDFDocument28 pagesSupp 2017 PDFDesmond BwalyaNo ratings yet
- PRELIMSDocument2 pagesPRELIMSMelinda VillenaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Grade 7Document2 pages2nd Quarter Grade 7Genalyn Cirpo TayoneNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Test-BiologyDocument6 pagesUnit 9 Test-BiologyNicholas PerezNo ratings yet
- Paper-A (Foundation & Blood Module)Document4 pagesPaper-A (Foundation & Blood Module)Sudais KhattakNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY II FBI1224 2022 Question Paper 1Document10 pagesBIOLOGY II FBI1224 2022 Question Paper 1zoulzz0903No ratings yet
- Summative Test 2Document2 pagesSummative Test 2EM GinaNo ratings yet
- T1 Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument2 pagesT1 Introduction To Human AnatomySafaa WaganNo ratings yet
- MC 1 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY MidtermDocument12 pagesMC 1 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY MidtermNicole Sheen EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Exercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsDocument16 pagesExercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsShu85100% (1)
- Grade 7 Final Exam Quarter 2Document4 pagesGrade 7 Final Exam Quarter 2Rizalyn DiazNo ratings yet
- Hes 101 - CfuDocument10 pagesHes 101 - CfuLAGUERTA, JOHN MICHAEL A.No ratings yet
- Quiz No. 1 Science 6 Second Quarter Name: - Grade: - I. Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answer On The BlankDocument2 pagesQuiz No. 1 Science 6 Second Quarter Name: - Grade: - I. Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answer On The BlankCecilia Guevarra Dumlao100% (4)
- Study Guide - Final ExamDocument7 pagesStudy Guide - Final ExamRichard LaRouechNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Test: Artery in The Latin Language Means What?Document22 pagesAnatomy Test: Artery in The Latin Language Means What?Anonymous MtKJkerbpUNo ratings yet
- 1ST Summative Test in Science 6 Q2Document4 pages1ST Summative Test in Science 6 Q2Liza Mea Guhayon Reblinca0% (1)
- BBS - Finals Compilation - Project Coffee PDFDocument318 pagesBBS - Finals Compilation - Project Coffee PDFNoel JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Biology Worksheet 1Document5 pagesGrade 8 Biology Worksheet 1YonasNo ratings yet
- Ana Physio 1prelims 2021-22 1stsem 1B - ExamDocument5 pagesAna Physio 1prelims 2021-22 1stsem 1B - ExamKwenzie FortalezaNo ratings yet
- Hns 2101 Human Anatomy IDocument5 pagesHns 2101 Human Anatomy IbalancelacktonNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Life Science 2023 For RISODocument5 pagesFinal Exam Life Science 2023 For RISOJoderon NimesNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 (Sum Test)Document2 pagesGrade 11 (Sum Test)Yvuj LagnitabNo ratings yet
- Eart and Life TQ FinalDocument3 pagesEart and Life TQ FinalNel PasaizNo ratings yet
- Biology Form Three Annual 2023Document6 pagesBiology Form Three Annual 2023vecema1296No ratings yet
- Reviewer Science 7Document22 pagesReviewer Science 7Arlynda LampaNo ratings yet
- First Semester Question BankDocument19 pagesFirst Semester Question Banknanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1From EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- NLP Fast PhobiaDocument1 pageNLP Fast PhobiaAnonymous A1LQIfKNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience For Neurosurgeons Feb 29 2024 - 110883146X - Cambridge University Press 1St Edition Farhana Akter Full ChapterDocument68 pagesNeuroscience For Neurosurgeons Feb 29 2024 - 110883146X - Cambridge University Press 1St Edition Farhana Akter Full Chapterdale.freyer940100% (7)
- AOTrauma Course-Basic Principles of Fracture Management April 10-12, 2015 Hefei, ChinaDocument20 pagesAOTrauma Course-Basic Principles of Fracture Management April 10-12, 2015 Hefei, ChinafaluviekadianiNo ratings yet
- GONIOMETRYDocument20 pagesGONIOMETRYkushi98mandyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Lower Limb Assessment Flow SheetDocument2 pagesBasic Lower Limb Assessment Flow Sheetمحمد نعمة جياد100% (1)
- Spinocerebelar Tract-2Document20 pagesSpinocerebelar Tract-2Vijayasekhar VempalliNo ratings yet
- PolyScience 1.5 HP Chiller - 110-392 Durachill 1.5 HP 01-05-2022Document57 pagesPolyScience 1.5 HP Chiller - 110-392 Durachill 1.5 HP 01-05-2022hsghdNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-06-18 at 10.34.34 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-06-18 at 10.34.34 PMNandan BethinaNo ratings yet
- Ortho Rad Sessions FisamDocument20 pagesOrtho Rad Sessions FisamDouglas MutenyoNo ratings yet
- Management of BurnDocument42 pagesManagement of BurnArisa KudidthalertNo ratings yet
- Operating-Manual VSH200 F-011819 19.1Document98 pagesOperating-Manual VSH200 F-011819 19.1Yoyon HaryonoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Neuro Assessment 2021 - 336Document30 pages1 - Neuro Assessment 2021 - 336HADI BADWAN100% (2)
- Rectus Femoris - PhysiopediaDocument5 pagesRectus Femoris - PhysiopediaVahid AtaeiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER3 LAW of TORTS Tresspass To Land and NegligenceDocument36 pagesCHAPTER3 LAW of TORTS Tresspass To Land and NegligenceMuhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- TRACTIONDocument3 pagesTRACTIONCatherineNo ratings yet
- Phases of The PushupDocument2 pagesPhases of The PushupMaryane AngelaNo ratings yet
- Anthropometric MeasurementsDocument17 pagesAnthropometric MeasurementsPunitha PuniNo ratings yet
- Sketetal SystemDocument11 pagesSketetal SystemBryan JagroopNo ratings yet
- DONE Anuat V Pacific Ocean Manning, Inc. G.R. No. 220898, July 23, 2018Document2 pagesDONE Anuat V Pacific Ocean Manning, Inc. G.R. No. 220898, July 23, 2018Kathlene JaoNo ratings yet
- CHESAPEAKE Surgical TechniqueDocument20 pagesCHESAPEAKE Surgical Techniquenvj8wsthdtNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices and Sports Injury Management.Document8 pagesSafety Practices and Sports Injury Management.cejaygecainNo ratings yet
- Reading TestDocument3 pagesReading TestVan NguyenNo ratings yet
- OrthoticsDocument37 pagesOrthoticsergosadia658No ratings yet
- Body MechanicsDocument26 pagesBody MechanicsSandeepNo ratings yet
- Asphyxial Death 160219112440Document22 pagesAsphyxial Death 160219112440Kanokporn PongviratNo ratings yet
- EfaDocument74 pagesEfaKrypton KrNo ratings yet