Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsDrug Name Drug Interactions Nursing Considerations
Drug Name Drug Interactions Nursing Considerations
Uploaded by
PagodThis document discusses several drug-drug interactions and associated nursing considerations. It provides information on interactions between:
- Celecoxib and ACE inhibitors, noting it may reduce blood pressure and increase risk of heart issues. Nurses should monitor blood pressure closely.
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride and barbiturates, which may increase amitriptyline metabolism. Nurses should monitor patients and consider therapy modifications.
- Acetylcysteine and activated charcoal, noting activated charcoal should not be used before or with oral acetylcysteine as it may decrease effectiveness.
- Budesonide inhalation and ketoconazole, which can increase b
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Shop Manual BF75D - BF90D 2006-2011Document635 pagesShop Manual BF75D - BF90D 2006-2011megclay100% (2)
- Dokumen - Pub Sbas For The Frcstramporth Examination A Companion To Postgraduate Orthopaedics Candidates Guide 1stnbsped 1108789978 9781108789974 1108803644 9781108803649 9781108846790Document646 pagesDokumen - Pub Sbas For The Frcstramporth Examination A Companion To Postgraduate Orthopaedics Candidates Guide 1stnbsped 1108789978 9781108789974 1108803644 9781108803649 9781108846790sharan sambhwani0% (2)
- Vasquez, Julianne Gabrielle G. Pharmacology BSN 2-A-7 Course Task #1Document6 pagesVasquez, Julianne Gabrielle G. Pharmacology BSN 2-A-7 Course Task #1PagodNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Byslate Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Byslate Drug StudyWenalyn Grace Abella Llavan71% (7)
- This Study Resource Was: Session 7: VeritasDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Session 7: VeritasPagod100% (1)
- Practical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersFrom EverandPractical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Inferential Statistics: Positive CorrelationDocument9 pagesInferential Statistics: Positive CorrelationPagodNo ratings yet
- Cosmetology Portfolio: Jaimie R. FortinDocument34 pagesCosmetology Portfolio: Jaimie R. FortinJaimie FantasticNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument10 pagesEmergency DrugsnieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyComia AltheiaNo ratings yet
- Daño Hepatico Manejo DolorDocument6 pagesDaño Hepatico Manejo DolorAngélica Valenzuela AndrighiNo ratings yet
- DS (Ibuprofen)Document6 pagesDS (Ibuprofen)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- DTR PneumoniaDocument16 pagesDTR PneumoniaGUNPLANo ratings yet
- Adverse Effects: Before AdministrationDocument4 pagesAdverse Effects: Before AdministrationMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- Stress-Induced Gastric Ulcer Drug StudyDocument6 pagesStress-Induced Gastric Ulcer Drug StudyBelle LegardeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDrug Study: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesNikki Caryl ZafraNo ratings yet
- Cilostazol (Pletal)Document4 pagesCilostazol (Pletal)Maria Leonie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument1 pageNifedipineMary MannNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - PHARMACOLOGYDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 - PHARMACOLOGYJewel SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMae Navidas DigdiganNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studydana100% (2)
- Medication Route, Dosage & Frequency Mechanism Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: CNS: VertigoDocument4 pagesMedication Route, Dosage & Frequency Mechanism Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: CNS: VertigoLaxy214No ratings yet
- ACARBOSE (Drug Study)Document3 pagesACARBOSE (Drug Study)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Med Ward - Drug Study - LaoDocument3 pagesMed Ward - Drug Study - LaoLady Nadjma M. LaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (CHF)Document9 pagesDrug Study (CHF)Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- DRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDocument1 pageDRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Adverse Effects: Before AdministrationDocument4 pagesAdverse Effects: Before AdministrationMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument3 pagesDrug Study DRGershom Perez AcaboNo ratings yet
- Drug Study1Document3 pagesDrug Study1marieNo ratings yet
- ATORVASTATINDocument1 pageATORVASTATINSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug Study StaDocument3 pagesDrug Study StaarjeighNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Elecoxib BoxDocument4 pagesDrug Study Elecoxib BoxLuffy MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Name OF Drugs Dosage and Route Mechanism and Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesName OF Drugs Dosage and Route Mechanism and Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsAngelyka Abiado AlmodaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJM AcNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Ors 1Document3 pagesParacetamol Ors 1Mini BossNo ratings yet
- Azathioprine - Frequent:: Anti-Inflammatory Immunosuppressive That Can Decrease Joint Damage and DisabilityDocument3 pagesAzathioprine - Frequent:: Anti-Inflammatory Immunosuppressive That Can Decrease Joint Damage and DisabilityJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Vasotec EnalaprilDocument1 pageVasotec EnalaprilCassie100% (1)
- Mfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugsDocument3 pagesName of DrugsMiaLynn PangkuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Duty2)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Duty2)Robert َMirandaNo ratings yet
- مستند بلا عنوان-2Document4 pagesمستند بلا عنوان-2العمري العمريNo ratings yet
- Telmisartan, ISMNDocument8 pagesTelmisartan, ISMNDenise EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IbuprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study IbuprofenblaireNo ratings yet
- It Is A COX-2 Inhibitor. It Is Part of The General Category of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (Nsaids)Document5 pagesIt Is A COX-2 Inhibitor. It Is Part of The General Category of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (Nsaids)Casey WatsonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CVA, DM, CKDDocument11 pagesDrug Study CVA, DM, CKDDylan Angelo AndresNo ratings yet
- Escaran - Drug Study - Set ADocument4 pagesEscaran - Drug Study - Set AFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- D. PharmaDocument45 pagesD. PharmaShivam Das, Tehsil KulpaharNo ratings yet
- Drug Study KetoDocument2 pagesDrug Study KetoRona PieNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing NCLEX Practice Question 700Document75 pagesMental Health and Psychiatric Nursing NCLEX Practice Question 700Jigo ReynaNo ratings yet
- Ascorbic Acid Drug StudyDocument1 pageAscorbic Acid Drug StudyWenalyn Grace Abella Llavan75% (4)
- Drug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDocument10 pagesDrug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- TelmisartanDocument4 pagesTelmisartanHanniel MontecalboNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument27 pagesDrug StudyChan SorianoNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DrugDocument4 pagesPrenatal DrugJorgie Ann ReyNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Mebeverine Hydrochloride Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Mebeverine Hydrochloride Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Assessment & Drug EffectsNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Nebivolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesNebivolol Drug Studyalteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Atorvastatin Brand Name: Lipitor Dosage and RouteDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Atorvastatin Brand Name: Lipitor Dosage and RouteRamsam UayanNo ratings yet
- MEBEVERINE Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMEBEVERINE Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesKat BausaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Drug StudyDocument45 pagesMedical Surgical Drug StudyMichelle Angela AlombroNo ratings yet
- Gloria DS Module 2Document1 pageGloria DS Module 2z6cc9vgg6nNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Edsp For RegionsDocument4 pagesApplication Form For Edsp For RegionsPagodNo ratings yet
- Checklist Open Glove Technique 1Document1 pageChecklist Open Glove Technique 1PagodNo ratings yet
- Roles Functions of Community Health NurseDocument9 pagesRoles Functions of Community Health NursePagodNo ratings yet
- Meds Date Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / SignDocument1 pageMeds Date Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / SignPagodNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (STAS111)Document14 pagesReviewer (STAS111)PagodNo ratings yet
- Smoking Or: The Pill, The Patch, The RingDocument3 pagesSmoking Or: The Pill, The Patch, The RingPagodNo ratings yet
- Human Space Time TheoryDocument1 pageHuman Space Time TheoryPagodNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan TentativeDocument2 pagesTeaching Plan TentativePagodNo ratings yet
- Reason For Home Health Care VisitDocument4 pagesReason For Home Health Care VisitPagodNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint OutlineDocument5 pagesPowerpoint OutlinePagodNo ratings yet
- The OvariesDocument2 pagesThe OvariesPagodNo ratings yet
- Approach To Neonatal HyperbilirubinemiaDocument34 pagesApproach To Neonatal HyperbilirubinemiaNilesh HatzadeNo ratings yet
- Food & Beverage Controls - Solved Papers - 2016-2017 - 3rd Sem B.SC HHA - Hmhub - Perfect ? Hub For 120k+ ? Hospitality ?? ? StudentsDocument23 pagesFood & Beverage Controls - Solved Papers - 2016-2017 - 3rd Sem B.SC HHA - Hmhub - Perfect ? Hub For 120k+ ? Hospitality ?? ? StudentsTharun SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment!: 6 Young Filipinos Making A Difference in Their CommunitiesDocument6 pagesPre-Assessment!: 6 Young Filipinos Making A Difference in Their Communitieseulegio dela peñaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Financial PositionDocument28 pagesStatement of Financial Positionsammie helsonNo ratings yet
- Artikel Desi AriantiDocument9 pagesArtikel Desi AriantiJefrioSuyantoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On MotivationDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On MotivationAshma SthaNo ratings yet
- CH 18Document51 pagesCH 18NghiaBuiQuang100% (4)
- Hormonal CoordinationDocument4 pagesHormonal Coordinationtalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- Answersheet Week8Document2 pagesAnswersheet Week8Daniel AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- What Is The Role of Literature Review in Research ProcessDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Role of Literature Review in Research Processc5qz47smNo ratings yet
- Manual Lab Anatomy of Breast - LA RPS2 W3Document6 pagesManual Lab Anatomy of Breast - LA RPS2 W3Maharani KartikaNo ratings yet
- Small Bore Fitting (SBF) Vibration Fatigue CalculationDocument26 pagesSmall Bore Fitting (SBF) Vibration Fatigue CalculationgopaltryNo ratings yet
- Unique and Common Traits in Mycorrhizal SymbiosesDocument12 pagesUnique and Common Traits in Mycorrhizal SymbiosesThắng Trần BảoNo ratings yet
- Bantinaki The Paradox of HorrorDocument11 pagesBantinaki The Paradox of HorrorbrianNo ratings yet
- Barang Bebas Buat PKPADocument152 pagesBarang Bebas Buat PKPABrian FoxNo ratings yet
- Euromedica MhsDocument374 pagesEuromedica MhsLuther BlissettNo ratings yet
- H&C Analysis Unit 3 09Document22 pagesH&C Analysis Unit 3 09Seenu PusuluruNo ratings yet
- NEW LTC - Price Update 2020Document13 pagesNEW LTC - Price Update 2020dwi prasetyo wibowoNo ratings yet
- Convum Vacuum Filters OnlyDocument2 pagesConvum Vacuum Filters OnlyDeprina Aprilia SembodoNo ratings yet
- ECLOS-Difference Course OutlineDocument3 pagesECLOS-Difference Course OutlineJosé Manuel Valdez RevillaNo ratings yet
- FMCG Industry Review of Bangladesh PDFDocument33 pagesFMCG Industry Review of Bangladesh PDFShoaib HussainNo ratings yet
- ABG QuizDocument3 pagesABG QuizMelchor Felipe SalvosaNo ratings yet
- Cable CatalogDocument44 pagesCable CatalogRahmat Izaizi100% (3)
- Leijssen Mia. (Manuscript MOOC) .: The Existential Approach: An IntroductionDocument6 pagesLeijssen Mia. (Manuscript MOOC) .: The Existential Approach: An IntroductionSofiaLimaNo ratings yet
- The Excretory/ Urinary System: Lecture By: Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, MSCDocument29 pagesThe Excretory/ Urinary System: Lecture By: Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, MSCHeaven SolNo ratings yet
- Steve F. Carlisle,: Professional SummaryDocument5 pagesSteve F. Carlisle,: Professional SummaryRickey StokesNo ratings yet
- Previous HSE Questions From The Chapter "ELECTROCHEMISTRY": E E - 2.303RT Log (M) NF (M)Document2 pagesPrevious HSE Questions From The Chapter "ELECTROCHEMISTRY": E E - 2.303RT Log (M) NF (M)Chemistry MESNo ratings yet
Drug Name Drug Interactions Nursing Considerations
Drug Name Drug Interactions Nursing Considerations
Uploaded by
Pagod0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesThis document discusses several drug-drug interactions and associated nursing considerations. It provides information on interactions between:
- Celecoxib and ACE inhibitors, noting it may reduce blood pressure and increase risk of heart issues. Nurses should monitor blood pressure closely.
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride and barbiturates, which may increase amitriptyline metabolism. Nurses should monitor patients and consider therapy modifications.
- Acetylcysteine and activated charcoal, noting activated charcoal should not be used before or with oral acetylcysteine as it may decrease effectiveness.
- Budesonide inhalation and ketoconazole, which can increase b
Original Description:
Original Title
COURSE TASK 2 PHARMA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses several drug-drug interactions and associated nursing considerations. It provides information on interactions between:
- Celecoxib and ACE inhibitors, noting it may reduce blood pressure and increase risk of heart issues. Nurses should monitor blood pressure closely.
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride and barbiturates, which may increase amitriptyline metabolism. Nurses should monitor patients and consider therapy modifications.
- Acetylcysteine and activated charcoal, noting activated charcoal should not be used before or with oral acetylcysteine as it may decrease effectiveness.
- Budesonide inhalation and ketoconazole, which can increase b
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesDrug Name Drug Interactions Nursing Considerations
Drug Name Drug Interactions Nursing Considerations
Uploaded by
PagodThis document discusses several drug-drug interactions and associated nursing considerations. It provides information on interactions between:
- Celecoxib and ACE inhibitors, noting it may reduce blood pressure and increase risk of heart issues. Nurses should monitor blood pressure closely.
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride and barbiturates, which may increase amitriptyline metabolism. Nurses should monitor patients and consider therapy modifications.
- Acetylcysteine and activated charcoal, noting activated charcoal should not be used before or with oral acetylcysteine as it may decrease effectiveness.
- Budesonide inhalation and ketoconazole, which can increase b
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
VASQUEZ, JULIANNE GABRIELLE G.
PHARMACOLOGY
BSN 2-A-7 COURSE TASK 2
Using your drug handbook, answer the following questions:
Look for the drug-drug interaction of the following drugs given and give nursing considerations
as you give the drugs together:
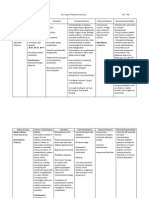
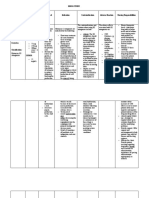
DRUG NAME DRUG INTERACTIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
Celecoxib with ACE inhibitors May reduce the Use celecoxib cautiously in
antihypertensive patients with hypertension,
effects and monitor blood pressure
closely throughout therapy
because drug can start or
worsen hypertension
Dosage should start at half
the lowest recommended
amount. For patients with
juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
who are also poor CYP2C9
metabolizers, alternative
management should be
considered.
Should be avoided in
patients with a recent MI
because risk of reinfarction
increases with NSAID
therapy. If therapy is
unavoidable, monitor patient
closely for signs of cardiac
ischemia.
Should not be given to
patients with severe heart
failure because risk of heart
failure increases with NSAID
use. If use is unavoidable,
monitor patient for
worsening of heart failure
Amitriptyline hydrochloride May increase Monitor patients during
with barbiturates amitriptyline concurrent use.
metabolism. Consider therapy
modification
Use caution if patient has a
history of seizures, urine
retention, or angle-closure
glaucoma
Acetylcysteine with activated Possibly adsorption Avoid using activated
charcoal and decreased charcoal before or with oral
effectiveness of oral acetylcysteine
acetylcysteine
May limit
acetylcysteine’s
effectiveness.
VASQUEZ, JULIANNE GABRIELLE G. PHARMACOLOGY
BSN 2-A-7 COURSE TASK 2
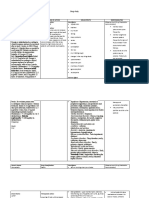
Budesonide inhalation with Increased systemic Monitor patient for adverse
katoconazole exposure and side reactions and adjust dosage
effects with CYP3A4 as needed
inhibitors Assess patient who switches
May inhibit from a systemic
metabolism and corticosteroid to inhaled
increase level of budesonide for adrenal
budesonide. insufficiency (fatigue,
hypotension, lassitude,
nausea, vomiting,
weakness), which may be
life-threatening
Closely monitor a child’s
growth pattern – once
administered; budesonide
may stunt growth
Monitor patients with
conditions such as diabetes
mellitus, glaucoma or
cataracts, hypertension,
osteoporosis, or peptic ulcer,
as glucocorticosteroid
therapy may increase
adverse effects. Also
monitor patients with a
family history of diabetes or
glaucoma.
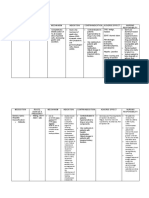
Clobazam with hormonal Decreased serum Patient should use
contraceptives concentration nonhormonal contraceptives
May diminish as needed.
contraceptive Counsel women to also use
effectiveness. non-hormonal methods of
contraception when
clobazam is used with
hormonal contraceptives
and to continue these
alternative methods for 28
days after discontinuing
clobazam to ensure
contraceptive reliability.
Esmolol hydrochloride with May increase blood Closely monitor blood
antidiabetic agents glucose-lowering glucose concentration
effect of antidiabetic Monitor ECG and BP
agent continuously during infusion.
Nearly half of patients will
develop hypotension.
Diaphoresis and dizziness
may accompany
hypotension. Monitor patient
closely, especially if he had
VASQUEZ, JULIANNE GABRIELLE G. PHARMACOLOGY
BSN 2-A-7 COURSE TASK 2
low BP before treatment.
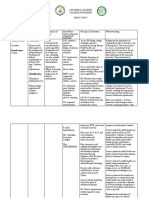
Indomethacin with May enhance toxicity Avoid using drugs together
aminoglycosides of these drugs May cause kidney damage
and increase that risk,
particularly if the latter is
used chronically for
prolonged periods.
During coadministration,
plasma antibiotic
concentrations and renal
function should be closely
monitored, and the antibiotic
dosage further adjusted as
necessary
Isoniazid with May inhibit Monitor patient closely for
acetaminophen acetaminophen hepatotoxicity
metabolism Close attention should be
Increased risk of paid to clinical and
hepatotoxicity laboratory evidence of
hepatotoxicity. Both drugs
should be discontinued if
evidence of hepatoxicity is
observed. Aspirin or
nonsteroidal inflammatory
agents may be safer
alternatives
Mesalamine with warfarin May decrease Monitor effectiveness of
anticoagulation effect therapy closely.
Patients should be advised
to promptly report any signs
of bleeding (e.g., headache,
dizziness, weakness,
prolonged bleeding from
cuts, increased menstrual
flow, vaginal bleeding,
nosebleeds, bleeding of
gums from brushing,
unusual bleeding or bruising,
red or brown urine, or red or
black stools) or blood clots
(e.g., chest pain, shortness
of breath, sudden loss of
vision, or pain, redness or
swelling in an extremity)
Rifampicin with probenecid May increase rifampin Use together cautiously.
levels Monitor hepatic function,
hematopoietic studies, and
uric acid levels. Drug’s
systemic effects may
asymptomatically raise LFT
VASQUEZ, JULIANNE GABRIELLE G. PHARMACOLOGY
BSN 2-A-7 COURSE TASK 2
results and uric acid level.
May increase uric levels
Give the adverse reactions of the following drugs on the systems indicated:
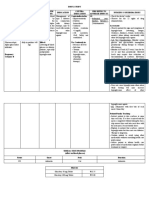
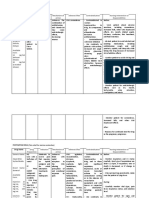
DRUG NAME BODY SYSTEM ADVERSE REACTIONS
Cimetidine GI mild and transient
diarrhea.
Esterified estrogen CNS headache, dizziness,
chorea, depression,
stroke, seizures
Gentamicin sulfate RESPIRATORY apnea
Iloperidone EENT blurred vision,
conjunctivitis, dry mouth,
nasal congestion,
nasopharyngitis
Meropenem CNS seizures, headache
Simvastatin RESPIRATORY URI (Upper Respiratory
Infection)
Tropism chloride EENT dry eyes and nose
Desmopressin acetate GI nausea, abdominal
cramps
Ethambutol hydrochloride MUSCULOSKELETAL joint pain
Promethazine hydrochloride METABOLIC hyperglycemia
References:
Jones & Bartlett Learning., & Jones & Bartlett Publishers. (2021). Nurse's drug handbook.
Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
Wolters Kluwer (Firm),. (2018). Nursing 2019 Drug Handbook.
You might also like
- Shop Manual BF75D - BF90D 2006-2011Document635 pagesShop Manual BF75D - BF90D 2006-2011megclay100% (2)
- Dokumen - Pub Sbas For The Frcstramporth Examination A Companion To Postgraduate Orthopaedics Candidates Guide 1stnbsped 1108789978 9781108789974 1108803644 9781108803649 9781108846790Document646 pagesDokumen - Pub Sbas For The Frcstramporth Examination A Companion To Postgraduate Orthopaedics Candidates Guide 1stnbsped 1108789978 9781108789974 1108803644 9781108803649 9781108846790sharan sambhwani0% (2)
- Vasquez, Julianne Gabrielle G. Pharmacology BSN 2-A-7 Course Task #1Document6 pagesVasquez, Julianne Gabrielle G. Pharmacology BSN 2-A-7 Course Task #1PagodNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Byslate Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Byslate Drug StudyWenalyn Grace Abella Llavan71% (7)
- This Study Resource Was: Session 7: VeritasDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Session 7: VeritasPagod100% (1)
- Practical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersFrom EverandPractical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Inferential Statistics: Positive CorrelationDocument9 pagesInferential Statistics: Positive CorrelationPagodNo ratings yet
- Cosmetology Portfolio: Jaimie R. FortinDocument34 pagesCosmetology Portfolio: Jaimie R. FortinJaimie FantasticNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument10 pagesEmergency DrugsnieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyComia AltheiaNo ratings yet
- Daño Hepatico Manejo DolorDocument6 pagesDaño Hepatico Manejo DolorAngélica Valenzuela AndrighiNo ratings yet
- DS (Ibuprofen)Document6 pagesDS (Ibuprofen)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- DTR PneumoniaDocument16 pagesDTR PneumoniaGUNPLANo ratings yet
- Adverse Effects: Before AdministrationDocument4 pagesAdverse Effects: Before AdministrationMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- Stress-Induced Gastric Ulcer Drug StudyDocument6 pagesStress-Induced Gastric Ulcer Drug StudyBelle LegardeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDrug Study: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesNikki Caryl ZafraNo ratings yet
- Cilostazol (Pletal)Document4 pagesCilostazol (Pletal)Maria Leonie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument1 pageNifedipineMary MannNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - PHARMACOLOGYDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 - PHARMACOLOGYJewel SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMae Navidas DigdiganNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studydana100% (2)
- Medication Route, Dosage & Frequency Mechanism Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: CNS: VertigoDocument4 pagesMedication Route, Dosage & Frequency Mechanism Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: CNS: VertigoLaxy214No ratings yet
- ACARBOSE (Drug Study)Document3 pagesACARBOSE (Drug Study)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Med Ward - Drug Study - LaoDocument3 pagesMed Ward - Drug Study - LaoLady Nadjma M. LaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (CHF)Document9 pagesDrug Study (CHF)Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- DRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDocument1 pageDRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Adverse Effects: Before AdministrationDocument4 pagesAdverse Effects: Before AdministrationMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument3 pagesDrug Study DRGershom Perez AcaboNo ratings yet
- Drug Study1Document3 pagesDrug Study1marieNo ratings yet
- ATORVASTATINDocument1 pageATORVASTATINSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug Study StaDocument3 pagesDrug Study StaarjeighNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Elecoxib BoxDocument4 pagesDrug Study Elecoxib BoxLuffy MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Name OF Drugs Dosage and Route Mechanism and Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesName OF Drugs Dosage and Route Mechanism and Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsAngelyka Abiado AlmodaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJM AcNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Ors 1Document3 pagesParacetamol Ors 1Mini BossNo ratings yet
- Azathioprine - Frequent:: Anti-Inflammatory Immunosuppressive That Can Decrease Joint Damage and DisabilityDocument3 pagesAzathioprine - Frequent:: Anti-Inflammatory Immunosuppressive That Can Decrease Joint Damage and DisabilityJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Vasotec EnalaprilDocument1 pageVasotec EnalaprilCassie100% (1)
- Mfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugsDocument3 pagesName of DrugsMiaLynn PangkuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Duty2)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Duty2)Robert َMirandaNo ratings yet
- مستند بلا عنوان-2Document4 pagesمستند بلا عنوان-2العمري العمريNo ratings yet
- Telmisartan, ISMNDocument8 pagesTelmisartan, ISMNDenise EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IbuprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study IbuprofenblaireNo ratings yet
- It Is A COX-2 Inhibitor. It Is Part of The General Category of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (Nsaids)Document5 pagesIt Is A COX-2 Inhibitor. It Is Part of The General Category of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (Nsaids)Casey WatsonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CVA, DM, CKDDocument11 pagesDrug Study CVA, DM, CKDDylan Angelo AndresNo ratings yet
- Escaran - Drug Study - Set ADocument4 pagesEscaran - Drug Study - Set AFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- D. PharmaDocument45 pagesD. PharmaShivam Das, Tehsil KulpaharNo ratings yet
- Drug Study KetoDocument2 pagesDrug Study KetoRona PieNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing NCLEX Practice Question 700Document75 pagesMental Health and Psychiatric Nursing NCLEX Practice Question 700Jigo ReynaNo ratings yet
- Ascorbic Acid Drug StudyDocument1 pageAscorbic Acid Drug StudyWenalyn Grace Abella Llavan75% (4)
- Drug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDocument10 pagesDrug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- TelmisartanDocument4 pagesTelmisartanHanniel MontecalboNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument27 pagesDrug StudyChan SorianoNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DrugDocument4 pagesPrenatal DrugJorgie Ann ReyNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Mebeverine Hydrochloride Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Mebeverine Hydrochloride Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Assessment & Drug EffectsNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Nebivolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesNebivolol Drug Studyalteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Atorvastatin Brand Name: Lipitor Dosage and RouteDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Atorvastatin Brand Name: Lipitor Dosage and RouteRamsam UayanNo ratings yet
- MEBEVERINE Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMEBEVERINE Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesKat BausaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Drug StudyDocument45 pagesMedical Surgical Drug StudyMichelle Angela AlombroNo ratings yet
- Gloria DS Module 2Document1 pageGloria DS Module 2z6cc9vgg6nNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Edsp For RegionsDocument4 pagesApplication Form For Edsp For RegionsPagodNo ratings yet
- Checklist Open Glove Technique 1Document1 pageChecklist Open Glove Technique 1PagodNo ratings yet
- Roles Functions of Community Health NurseDocument9 pagesRoles Functions of Community Health NursePagodNo ratings yet
- Meds Date Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / SignDocument1 pageMeds Date Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / Sign Time / SignPagodNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (STAS111)Document14 pagesReviewer (STAS111)PagodNo ratings yet
- Smoking Or: The Pill, The Patch, The RingDocument3 pagesSmoking Or: The Pill, The Patch, The RingPagodNo ratings yet
- Human Space Time TheoryDocument1 pageHuman Space Time TheoryPagodNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan TentativeDocument2 pagesTeaching Plan TentativePagodNo ratings yet
- Reason For Home Health Care VisitDocument4 pagesReason For Home Health Care VisitPagodNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint OutlineDocument5 pagesPowerpoint OutlinePagodNo ratings yet
- The OvariesDocument2 pagesThe OvariesPagodNo ratings yet
- Approach To Neonatal HyperbilirubinemiaDocument34 pagesApproach To Neonatal HyperbilirubinemiaNilesh HatzadeNo ratings yet
- Food & Beverage Controls - Solved Papers - 2016-2017 - 3rd Sem B.SC HHA - Hmhub - Perfect ? Hub For 120k+ ? Hospitality ?? ? StudentsDocument23 pagesFood & Beverage Controls - Solved Papers - 2016-2017 - 3rd Sem B.SC HHA - Hmhub - Perfect ? Hub For 120k+ ? Hospitality ?? ? StudentsTharun SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment!: 6 Young Filipinos Making A Difference in Their CommunitiesDocument6 pagesPre-Assessment!: 6 Young Filipinos Making A Difference in Their Communitieseulegio dela peñaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Financial PositionDocument28 pagesStatement of Financial Positionsammie helsonNo ratings yet
- Artikel Desi AriantiDocument9 pagesArtikel Desi AriantiJefrioSuyantoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On MotivationDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On MotivationAshma SthaNo ratings yet
- CH 18Document51 pagesCH 18NghiaBuiQuang100% (4)
- Hormonal CoordinationDocument4 pagesHormonal Coordinationtalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- Answersheet Week8Document2 pagesAnswersheet Week8Daniel AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- What Is The Role of Literature Review in Research ProcessDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Role of Literature Review in Research Processc5qz47smNo ratings yet
- Manual Lab Anatomy of Breast - LA RPS2 W3Document6 pagesManual Lab Anatomy of Breast - LA RPS2 W3Maharani KartikaNo ratings yet
- Small Bore Fitting (SBF) Vibration Fatigue CalculationDocument26 pagesSmall Bore Fitting (SBF) Vibration Fatigue CalculationgopaltryNo ratings yet
- Unique and Common Traits in Mycorrhizal SymbiosesDocument12 pagesUnique and Common Traits in Mycorrhizal SymbiosesThắng Trần BảoNo ratings yet
- Bantinaki The Paradox of HorrorDocument11 pagesBantinaki The Paradox of HorrorbrianNo ratings yet
- Barang Bebas Buat PKPADocument152 pagesBarang Bebas Buat PKPABrian FoxNo ratings yet
- Euromedica MhsDocument374 pagesEuromedica MhsLuther BlissettNo ratings yet
- H&C Analysis Unit 3 09Document22 pagesH&C Analysis Unit 3 09Seenu PusuluruNo ratings yet
- NEW LTC - Price Update 2020Document13 pagesNEW LTC - Price Update 2020dwi prasetyo wibowoNo ratings yet
- Convum Vacuum Filters OnlyDocument2 pagesConvum Vacuum Filters OnlyDeprina Aprilia SembodoNo ratings yet
- ECLOS-Difference Course OutlineDocument3 pagesECLOS-Difference Course OutlineJosé Manuel Valdez RevillaNo ratings yet
- FMCG Industry Review of Bangladesh PDFDocument33 pagesFMCG Industry Review of Bangladesh PDFShoaib HussainNo ratings yet
- ABG QuizDocument3 pagesABG QuizMelchor Felipe SalvosaNo ratings yet
- Cable CatalogDocument44 pagesCable CatalogRahmat Izaizi100% (3)
- Leijssen Mia. (Manuscript MOOC) .: The Existential Approach: An IntroductionDocument6 pagesLeijssen Mia. (Manuscript MOOC) .: The Existential Approach: An IntroductionSofiaLimaNo ratings yet
- The Excretory/ Urinary System: Lecture By: Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, MSCDocument29 pagesThe Excretory/ Urinary System: Lecture By: Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, MSCHeaven SolNo ratings yet
- Steve F. Carlisle,: Professional SummaryDocument5 pagesSteve F. Carlisle,: Professional SummaryRickey StokesNo ratings yet
- Previous HSE Questions From The Chapter "ELECTROCHEMISTRY": E E - 2.303RT Log (M) NF (M)Document2 pagesPrevious HSE Questions From The Chapter "ELECTROCHEMISTRY": E E - 2.303RT Log (M) NF (M)Chemistry MESNo ratings yet