Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Drug Name: Ceftriaxone A. Classification
Drug Study Drug Name: Ceftriaxone A. Classification
Uploaded by
Mark BarengCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Assessment, Nursing Interventions GuideFrom EverandNursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Assessment, Nursing Interventions GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Cefixime Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCefixime Drug StudyJonalin Magbanua100% (12)
- CefoxitinDocument3 pagesCefoxitinAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug: Ceftriaxone 2g/IVDocument3 pagesName of Drug: Ceftriaxone 2g/IVAllan DiazNo ratings yet
- Cholera Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCholera Drug StudyImongheartNo ratings yet
- Gamutin Drug Study-PediatricsDocument6 pagesGamutin Drug Study-PediatricsJhulia GamutinNo ratings yet
- Hernia Medical ManagementDocument5 pagesHernia Medical ManagementCherilyn MedalleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Hiv AidsDocument7 pagesHiv AidsPrecious UncianoNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument4 pagesReportKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- 9) Medical Complications of Drug TakingDocument44 pages9) Medical Complications of Drug TakingDr. Zirwa AsimNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDocument6 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- V. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationDocument23 pagesV. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationAvigael Gabriel AvilesNo ratings yet
- CefazolinDocument3 pagesCefazolinDanielle Marie SamblacenoNo ratings yet
- Suppurative AppendicitisDocument2 pagesSuppurative Appendicitisreanne_davidNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsElisa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCiprofloxacin Drug StudyRosalie Delfin89% (9)
- Week 5 LecturesDocument18 pagesWeek 5 LecturesJana-Tae KerrNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRyan BancoloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studym100% (1)
- CefazolinDocument2 pagesCefazolinConn_Casipe_8158100% (1)
- Invanz (Ertapenem)Document2 pagesInvanz (Ertapenem)E100% (1)
- CEFRADINEDocument2 pagesCEFRADINEAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument7 pagesScriptcyrilperry1No ratings yet
- Drug Study: Cavite State University (Cvsu)Document2 pagesDrug Study: Cavite State University (Cvsu)Angelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Ther. Class: Antiulcer Pharm. Class: Proton Indications: CNS: DizzinessDocument5 pagesTher. Class: Antiulcer Pharm. Class: Proton Indications: CNS: DizzinessLorenzo Daniel AntonioNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Action Indication Side Effect Nsg. ManagementDocument5 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Action Indication Side Effect Nsg. ManagementGreg DustNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument2 pagesGeneric NamePei BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Enoxirt CeftraxioneDocument10 pagesEnoxirt CeftraxioneAhmed DawodNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRowland PascuaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Reporting Ii - AntibioticsDocument9 pagesPharma Reporting Ii - AntibioticsD A M N E R ANo ratings yet
- Class 05 (Autosaved)Document75 pagesClass 05 (Autosaved)Paolo MendozaNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument3 pagesCeftriaxoneMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- Botulism: Physical ExamDocument13 pagesBotulism: Physical ExamAlexandria P. OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- Cleocin: Clindamycin 300 Mg/cap TID X 7 Days, Per OremDocument3 pagesCleocin: Clindamycin 300 Mg/cap TID X 7 Days, Per OremMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Management and Nursing Care PlanDocument37 pagesAppendicitis Management and Nursing Care PlanAlva AlfaNo ratings yet
- GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesGastroenteritisNicoleNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument5 pagesCeftriaxoneCastillo MikaellaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CloxacillinDocument2 pagesDrug Study CloxacillinKen Ancheta Lagayada33% (3)
- Group-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Document31 pagesGroup-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Hanna CarsanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis: Diseases and Conditions: GastroenteritisDocument6 pagesGastroenteritis: Diseases and Conditions: GastroenteritisWen RodsaNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument20 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDeniela Jamaicy Herbert100% (1)
- Silgram Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSilgram Drug StudyJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- ZegenDocument9 pagesZegenJefferson ManasanNo ratings yet
- Erythromycin & Pneumococcal VaccineDocument6 pagesErythromycin & Pneumococcal VaccineNikki Joy NavarroNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument17 pagesName of DrugAllan DiazNo ratings yet
- Practical Nursing Diploma Program Pre-Clinical Nursing Care Research Assignment "Prep and Plan"Document7 pagesPractical Nursing Diploma Program Pre-Clinical Nursing Care Research Assignment "Prep and Plan"Jeremy ThomasNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICABLE DISEASES - Power Point PDFDocument143 pagesCOMMUNICABLE DISEASES - Power Point PDFGel Marie LobatonNo ratings yet
- NCP: Puerperal InfectionDocument8 pagesNCP: Puerperal InfectionJavie83% (12)
- Generic NameDocument8 pagesGeneric Namemel aquinoNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximeRox SanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMaAngelica Tresha RaonNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNCP Drug StudyArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- NCP Neonatal SepsisDocument1 pageNCP Neonatal SepsisGen-GenMedranoGirayNo ratings yet
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- A Practical Guide to Common Presenting Complaints in Primary CareFrom EverandA Practical Guide to Common Presenting Complaints in Primary CareNo ratings yet
- Diverticulitis Diet: A 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide for Women, With Curated Recipes and a Sample Meal PlanFrom EverandDiverticulitis Diet: A 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide for Women, With Curated Recipes and a Sample Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeFrom EverandFemale Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeBob YangNo ratings yet
- Lab 2,3Document18 pagesLab 2,3Nosheela KhalidNo ratings yet
- Tdiagnostics - Telangana.gov - in ViewFiles - Aspx ReportId p1s0K7qAzHwmL8S2z98THgDocument3 pagesTdiagnostics - Telangana.gov - in ViewFiles - Aspx ReportId p1s0K7qAzHwmL8S2z98THgyesawovNo ratings yet
- Synopsis SsDocument14 pagesSynopsis SsJYOTI KATIYAR SVUNo ratings yet
- ICMR Revised SRF For Covid TestDocument2 pagesICMR Revised SRF For Covid TestDEVIKA PHULENo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections StisDocument2 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections Stisapi-646865632No ratings yet
- Abnormal Psych CiaDocument7 pagesAbnormal Psych CiaN SINDHU 2237406No ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Pathology, and Etiology in Adults - UpToDateDocument32 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Pathology, and Etiology in Adults - UpToDatecuentaparatrabajosdelau10No ratings yet
- Churg-Strauss SyndromeDocument17 pagesChurg-Strauss SyndromeLia GNo ratings yet
- Immune DisorderDocument37 pagesImmune DisorderJessica TieuNo ratings yet
- +lymphoedema 150118110815 Conversion Gate02Document24 pages+lymphoedema 150118110815 Conversion Gate02Oussama ANo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVD InfarctDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CVD InfarctIris Caberte86% (7)
- Teste de Proficiência Da Cultura Inglesa-SPDocument9 pagesTeste de Proficiência Da Cultura Inglesa-SPLarissa AzevedoNo ratings yet
- LEPTOSPIROSISDocument74 pagesLEPTOSPIROSIStummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- NeuroQuantology Publication June 2022 Vol 20 Issue 6 AU Category B JournalDocument7 pagesNeuroQuantology Publication June 2022 Vol 20 Issue 6 AU Category B JournalNARESHNo ratings yet
- COVID Vaccine FAQ_18 April 2021Document8 pagesCOVID Vaccine FAQ_18 April 2021Humam AltabibNo ratings yet
- Presentasi DR Baskoro Stroke Day Door To NeedleDocument30 pagesPresentasi DR Baskoro Stroke Day Door To NeedleagengNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 5 Nutritional Status AssessmentDocument5 pagesACTIVITY 5 Nutritional Status AssessmentNicole BeronioNo ratings yet
- Oropharyngeal Cancer: Current Understanding and ManagementDocument7 pagesOropharyngeal Cancer: Current Understanding and ManagementbgdNo ratings yet
- Malaria Research in South East AsiaDocument186 pagesMalaria Research in South East AsiaRizal QowiNo ratings yet
- Tongue DisordersDocument10 pagesTongue DisordersMohan VeerabomalaNo ratings yet
- "Ni-Raspa Ako Dahil Nalalag Yung Baby Ko." As Verbalized byDocument1 page"Ni-Raspa Ako Dahil Nalalag Yung Baby Ko." As Verbalized byMary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam On Community Health Nursing (Communicable Diseases)Document3 pagesSample Exam On Community Health Nursing (Communicable Diseases)John Eldrin LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Neurodegenerative Disorders: - DR - Dharmishta PatelDocument44 pagesNeurodegenerative Disorders: - DR - Dharmishta PatelHumanNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Studies On Black Quarter in Cattle: The Indian Veterinary Journal March 2018Document4 pagesEpidemiological Studies On Black Quarter in Cattle: The Indian Veterinary Journal March 2018Uttiya MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Medbio Krok 1 Lab Exam 4 2019-2020Document9 pagesMedbio Krok 1 Lab Exam 4 2019-2020stojan.vlad-iptNo ratings yet
- Path Lung McqsDocument24 pagesPath Lung McqsShafaque IrfanNo ratings yet
- Thesis TopicDocument17 pagesThesis Topicreamer27100% (1)
- Study Notes Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesStudy Notes Respiratory SystemAnde Mangkuluhur Azhari ThalibbanNo ratings yet
- English Test: Dash-A-Thon 2020 'The Novel Coronavirus Pandemic'Document5 pagesEnglish Test: Dash-A-Thon 2020 'The Novel Coronavirus Pandemic'William Phoenix75% (4)
- Zarina Infection Control WorkshopDocument52 pagesZarina Infection Control WorkshopEggy ZarinaNo ratings yet
Drug Study Drug Name: Ceftriaxone A. Classification
Drug Study Drug Name: Ceftriaxone A. Classification
Uploaded by
Mark BarengOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Drug Name: Ceftriaxone A. Classification
Drug Study Drug Name: Ceftriaxone A. Classification
Uploaded by
Mark BarengCopyright:
Available Formats
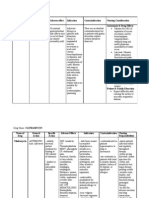
Drug Study
Drug name: Ceftriaxone
A. Classification:
General Classification – Antibiotic
Specific Classification – Cephalosporin (third generation)
B. Why the drug is given:
This drug is given to treat susceptible infections that are caused by bacteria like infection of
the intestinal tract.
C. Mechanism of action:
Ceftriaxone binds to bacterial cell membranes to inhibit cell wall synthesis. This cause
disruption of the bacterial cell wall and leads to bacterial cell death.
D. Desired effect:
This drug is given to the patient to prevent the growth of bacterial infections that may
develop.
This drug is given to the patient to kill the bacterial infection that resides in its body.
E. Nursing Responsibilities:
Independent
Inspect injection sites for induration and inflammation.
To note IV injection sites for signs of phlebitis.
Patient/Family-Related Instruction
Continue to administer this medication until the full-prescribed amount is finished
even if symptoms disappear after a few days.
Stopping the medication too early may allow bacteria to continue to grow,
which may result in a relapse of the infection and develop resistance to
antibiotic.
Instruct the patient to drink a lots of fluids and to maintain nutrition even though
nausea and vomiting may occur.
To keep the kidneys working properly while using it.
Instruct the family to always wash hands thoroughly and disinfect equipment Use
universal precautions or isolation procedures as indicated for specific patients.
To help prevent the spread of infection.
Dependent
Monitor signs of pseudomembranous colitis, including diarrhea, abdominal pain,
fever, pus or mucus in stools, and other severe or prolonged GI problems (nausea,
vomiting, heartburn).
Notify physician if these reactions occur to prevent untoward complications.
Monitor signs of petechiae, ecchymotic areas, epistaxis, or any unexplained bleeding.
Notify physician immediately if these reactions occur. Ceftriaxone appears to
alter vitamin K–producing gut bacteria therefore, hypoprothrombinemic
bleeding may occur.
Monitor signs of blood dyscrasias, including eosinophilia (fatigue, weakness,
myalgia), hemolytic anemia (malaise, dizziness, jaundice,), leukopenia (fever, sore
throat, mucosal lesions, signs of infection), or thrombocytosis (headache, dizziness,
chest pain, fainting, visual disturbances, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet).
Report this signs to the physician.
Most patients with typhoid fever are moderately anemic.
Monitor signs of allergic reactions and anaphylaxis, including pulmonary symptoms
(tightness in the throat and chest, wheezing, cough dyspnea) or skin reactions (rash,
pruritus, urticaria). Report this signs to the physician.
This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic
reactions or other problems.
Monitor injection site for pain, swelling, and irritation. Report prolonged or excessive
injection site reactions to the physician.
To avoid the risk of having skin problems.
Interdependent
Perform culture and sensitivity tests before initiation of therapy and periodically
before therapy.
To find the most effective antibiotic to kill an infecting microorganism.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Assessment, Nursing Interventions GuideFrom EverandNursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Assessment, Nursing Interventions GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Cefixime Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCefixime Drug StudyJonalin Magbanua100% (12)
- CefoxitinDocument3 pagesCefoxitinAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug: Ceftriaxone 2g/IVDocument3 pagesName of Drug: Ceftriaxone 2g/IVAllan DiazNo ratings yet
- Cholera Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCholera Drug StudyImongheartNo ratings yet
- Gamutin Drug Study-PediatricsDocument6 pagesGamutin Drug Study-PediatricsJhulia GamutinNo ratings yet
- Hernia Medical ManagementDocument5 pagesHernia Medical ManagementCherilyn MedalleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Hiv AidsDocument7 pagesHiv AidsPrecious UncianoNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument4 pagesReportKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- 9) Medical Complications of Drug TakingDocument44 pages9) Medical Complications of Drug TakingDr. Zirwa AsimNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDocument6 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- V. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationDocument23 pagesV. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationAvigael Gabriel AvilesNo ratings yet
- CefazolinDocument3 pagesCefazolinDanielle Marie SamblacenoNo ratings yet
- Suppurative AppendicitisDocument2 pagesSuppurative Appendicitisreanne_davidNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsElisa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCiprofloxacin Drug StudyRosalie Delfin89% (9)
- Week 5 LecturesDocument18 pagesWeek 5 LecturesJana-Tae KerrNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRyan BancoloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studym100% (1)
- CefazolinDocument2 pagesCefazolinConn_Casipe_8158100% (1)
- Invanz (Ertapenem)Document2 pagesInvanz (Ertapenem)E100% (1)
- CEFRADINEDocument2 pagesCEFRADINEAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument7 pagesScriptcyrilperry1No ratings yet
- Drug Study: Cavite State University (Cvsu)Document2 pagesDrug Study: Cavite State University (Cvsu)Angelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Ther. Class: Antiulcer Pharm. Class: Proton Indications: CNS: DizzinessDocument5 pagesTher. Class: Antiulcer Pharm. Class: Proton Indications: CNS: DizzinessLorenzo Daniel AntonioNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Action Indication Side Effect Nsg. ManagementDocument5 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Action Indication Side Effect Nsg. ManagementGreg DustNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument2 pagesGeneric NamePei BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Enoxirt CeftraxioneDocument10 pagesEnoxirt CeftraxioneAhmed DawodNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRowland PascuaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Reporting Ii - AntibioticsDocument9 pagesPharma Reporting Ii - AntibioticsD A M N E R ANo ratings yet
- Class 05 (Autosaved)Document75 pagesClass 05 (Autosaved)Paolo MendozaNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument3 pagesCeftriaxoneMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- Botulism: Physical ExamDocument13 pagesBotulism: Physical ExamAlexandria P. OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- Cleocin: Clindamycin 300 Mg/cap TID X 7 Days, Per OremDocument3 pagesCleocin: Clindamycin 300 Mg/cap TID X 7 Days, Per OremMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Management and Nursing Care PlanDocument37 pagesAppendicitis Management and Nursing Care PlanAlva AlfaNo ratings yet
- GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesGastroenteritisNicoleNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument5 pagesCeftriaxoneCastillo MikaellaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CloxacillinDocument2 pagesDrug Study CloxacillinKen Ancheta Lagayada33% (3)
- Group-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Document31 pagesGroup-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Hanna CarsanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis: Diseases and Conditions: GastroenteritisDocument6 pagesGastroenteritis: Diseases and Conditions: GastroenteritisWen RodsaNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument20 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDeniela Jamaicy Herbert100% (1)
- Silgram Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSilgram Drug StudyJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- ZegenDocument9 pagesZegenJefferson ManasanNo ratings yet
- Erythromycin & Pneumococcal VaccineDocument6 pagesErythromycin & Pneumococcal VaccineNikki Joy NavarroNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument17 pagesName of DrugAllan DiazNo ratings yet
- Practical Nursing Diploma Program Pre-Clinical Nursing Care Research Assignment "Prep and Plan"Document7 pagesPractical Nursing Diploma Program Pre-Clinical Nursing Care Research Assignment "Prep and Plan"Jeremy ThomasNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICABLE DISEASES - Power Point PDFDocument143 pagesCOMMUNICABLE DISEASES - Power Point PDFGel Marie LobatonNo ratings yet
- NCP: Puerperal InfectionDocument8 pagesNCP: Puerperal InfectionJavie83% (12)
- Generic NameDocument8 pagesGeneric Namemel aquinoNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximeRox SanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMaAngelica Tresha RaonNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNCP Drug StudyArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- NCP Neonatal SepsisDocument1 pageNCP Neonatal SepsisGen-GenMedranoGirayNo ratings yet
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- A Practical Guide to Common Presenting Complaints in Primary CareFrom EverandA Practical Guide to Common Presenting Complaints in Primary CareNo ratings yet
- Diverticulitis Diet: A 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide for Women, With Curated Recipes and a Sample Meal PlanFrom EverandDiverticulitis Diet: A 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide for Women, With Curated Recipes and a Sample Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeFrom EverandFemale Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeBob YangNo ratings yet
- Lab 2,3Document18 pagesLab 2,3Nosheela KhalidNo ratings yet
- Tdiagnostics - Telangana.gov - in ViewFiles - Aspx ReportId p1s0K7qAzHwmL8S2z98THgDocument3 pagesTdiagnostics - Telangana.gov - in ViewFiles - Aspx ReportId p1s0K7qAzHwmL8S2z98THgyesawovNo ratings yet
- Synopsis SsDocument14 pagesSynopsis SsJYOTI KATIYAR SVUNo ratings yet
- ICMR Revised SRF For Covid TestDocument2 pagesICMR Revised SRF For Covid TestDEVIKA PHULENo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections StisDocument2 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections Stisapi-646865632No ratings yet
- Abnormal Psych CiaDocument7 pagesAbnormal Psych CiaN SINDHU 2237406No ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Pathology, and Etiology in Adults - UpToDateDocument32 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Pathology, and Etiology in Adults - UpToDatecuentaparatrabajosdelau10No ratings yet
- Churg-Strauss SyndromeDocument17 pagesChurg-Strauss SyndromeLia GNo ratings yet
- Immune DisorderDocument37 pagesImmune DisorderJessica TieuNo ratings yet
- +lymphoedema 150118110815 Conversion Gate02Document24 pages+lymphoedema 150118110815 Conversion Gate02Oussama ANo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVD InfarctDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CVD InfarctIris Caberte86% (7)
- Teste de Proficiência Da Cultura Inglesa-SPDocument9 pagesTeste de Proficiência Da Cultura Inglesa-SPLarissa AzevedoNo ratings yet
- LEPTOSPIROSISDocument74 pagesLEPTOSPIROSIStummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- NeuroQuantology Publication June 2022 Vol 20 Issue 6 AU Category B JournalDocument7 pagesNeuroQuantology Publication June 2022 Vol 20 Issue 6 AU Category B JournalNARESHNo ratings yet
- COVID Vaccine FAQ_18 April 2021Document8 pagesCOVID Vaccine FAQ_18 April 2021Humam AltabibNo ratings yet
- Presentasi DR Baskoro Stroke Day Door To NeedleDocument30 pagesPresentasi DR Baskoro Stroke Day Door To NeedleagengNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 5 Nutritional Status AssessmentDocument5 pagesACTIVITY 5 Nutritional Status AssessmentNicole BeronioNo ratings yet
- Oropharyngeal Cancer: Current Understanding and ManagementDocument7 pagesOropharyngeal Cancer: Current Understanding and ManagementbgdNo ratings yet
- Malaria Research in South East AsiaDocument186 pagesMalaria Research in South East AsiaRizal QowiNo ratings yet
- Tongue DisordersDocument10 pagesTongue DisordersMohan VeerabomalaNo ratings yet
- "Ni-Raspa Ako Dahil Nalalag Yung Baby Ko." As Verbalized byDocument1 page"Ni-Raspa Ako Dahil Nalalag Yung Baby Ko." As Verbalized byMary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam On Community Health Nursing (Communicable Diseases)Document3 pagesSample Exam On Community Health Nursing (Communicable Diseases)John Eldrin LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Neurodegenerative Disorders: - DR - Dharmishta PatelDocument44 pagesNeurodegenerative Disorders: - DR - Dharmishta PatelHumanNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Studies On Black Quarter in Cattle: The Indian Veterinary Journal March 2018Document4 pagesEpidemiological Studies On Black Quarter in Cattle: The Indian Veterinary Journal March 2018Uttiya MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Medbio Krok 1 Lab Exam 4 2019-2020Document9 pagesMedbio Krok 1 Lab Exam 4 2019-2020stojan.vlad-iptNo ratings yet
- Path Lung McqsDocument24 pagesPath Lung McqsShafaque IrfanNo ratings yet
- Thesis TopicDocument17 pagesThesis Topicreamer27100% (1)
- Study Notes Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesStudy Notes Respiratory SystemAnde Mangkuluhur Azhari ThalibbanNo ratings yet
- English Test: Dash-A-Thon 2020 'The Novel Coronavirus Pandemic'Document5 pagesEnglish Test: Dash-A-Thon 2020 'The Novel Coronavirus Pandemic'William Phoenix75% (4)
- Zarina Infection Control WorkshopDocument52 pagesZarina Infection Control WorkshopEggy ZarinaNo ratings yet