Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prelab: EXPERIMENT 2: Protein Quantification Applying Hartree-Lowry Assay
Prelab: EXPERIMENT 2: Protein Quantification Applying Hartree-Lowry Assay
Uploaded by
Lan Anh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views3 pagesThis document provides information about an experiment involving the quantification of the protein bromelain using the Hartree-Lowry assay. Bromelain is an enzyme extracted from pineapple that is used for meat tenderizing. The experiment involves using tyrosine as a standard and measuring the amount of tyrosine released from casein through bromelain's proteolytic activity to determine the activity of bromelain in Units/mL. Several students' statements about the experimental procedure are evaluated in the document as well.
Original Description:
Original Title
Prelab Biochem 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about an experiment involving the quantification of the protein bromelain using the Hartree-Lowry assay. Bromelain is an enzyme extracted from pineapple that is used for meat tenderizing. The experiment involves using tyrosine as a standard and measuring the amount of tyrosine released from casein through bromelain's proteolytic activity to determine the activity of bromelain in Units/mL. Several students' statements about the experimental procedure are evaluated in the document as well.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views3 pagesPrelab: EXPERIMENT 2: Protein Quantification Applying Hartree-Lowry Assay
Prelab: EXPERIMENT 2: Protein Quantification Applying Hartree-Lowry Assay
Uploaded by
Lan AnhThis document provides information about an experiment involving the quantification of the protein bromelain using the Hartree-Lowry assay. Bromelain is an enzyme extracted from pineapple that is used for meat tenderizing. The experiment involves using tyrosine as a standard and measuring the amount of tyrosine released from casein through bromelain's proteolytic activity to determine the activity of bromelain in Units/mL. Several students' statements about the experimental procedure are evaluated in the document as well.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
International University, Vietnam National University – HCMC
Biochemistry
Prelab: EXPERIMENT 2
PROTEIN QUANTIFICATION APPLYING
HARTREE-LOWRY ASSAY
Full name: Nguyen Thi Lan Anh
Student ID: BTFTIU19041
Group: Durian
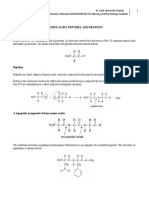
1. What fruit was bromelain extracted from? What is the main function
of bromelain?
Bromelain is extracted from pineapple.
Bromelain is one of the most popular proteases to use for meat tenderizing.
While there have been studies into the medical use of bromelain, "the
majority of them have methodological issues that make it difficult to draw
definite conclusions", as none definitively established efficacy,
recommended dosage, long term safety, or adverse interaction with other
medications.
2. What are crucial factors that can have effects on enzymatic activity?
Enzyme activity can be affected by a variety of factors, such as
temperature, pH, and concentration.
3. Are fixed times important for exploring/studying the enzymatic
activity? Explain why.
Yes, the study of enzyme activity should be performed within a fixed time.
The fixed-time assay measures enzyme concentration in fixed periods of
time.
4. Why is trichloroacetic acid added into tube of Tyrosine and tube of
water immediately right after putting casein solution into the test
tubes while with respect to tube of sample, trichloroacetic acid is
added at the end of the process?
Trichloroacetic acid is added to inhibit the degradation of casein in the tubes
of Tyrosine and water while in the tube of the sample, we want to measure
the enzymatic activity -> adding the trichloroacetic to stop the reaction.
5. Why shouldn’t we add Tyrosine into tube of sample?
Bromelain was extracted and the activity of the enzyme was measured using
tyrosine as standard and expressed in Units/mL of the enzyme. The amount of
tyrosine released is quantifiable. The more tyrosine that is released from
casein, the stronger the activity of the protease. Therefore, if Tyrosine is added
to the test tube of the sample, it is not possible to accurately determine the
activity of the enzyme
6. How can the activity of enzyme be determined in this experiment?
The activity of bromelain enzyme is determined depending on quantity (μg)
of tyrosine produced from casein degradation under catalysis of enzyme in
1mL of solution or 1mg of bromelain mixture for 1 minute.
7. Student A says that when doing this practical, he can prepare the
tubes of tyrosine and tubes of water first and then measure the
optical density in order to save time. Does he says it right or wrong?
Explain why.
He says it wrong because the test tubes need to be prepared at the same time
so that when measuring the optical density, we can compare their differences
8. Student B says that the more he add bromelain, the faster the
catalytic reaction occurs. Does he says it right or wrong? Explain
why.
It is right because the more bromelain in the solution, more chance for
enzyme bound to substrate lead to the faster of catalytic reaction.
9. Student C says that if he can purify and recover the bromelain used
in this practical, he can continue to use it for the catalytic reaction next
time in order to save the enzyme. Does he says it right or wrong?
Explain why.
It is wrong because after the reaction, some bromelain molecules are
inactive so it will affect to next result leading to having the wrong result in
the next experiment.
10. Student D says that there is a paradox in enzymatic activity. He
supposes that protease can degrade itself because it is also a protein.
Does he says it right or wrong? Explain why.
The enzyme works on specific substrates that mostly are simpler chemical
compounds, less complicated than enzyme-type protein complex. So, unless
the enzymatic protein is degraded first and or becoming a less simple
protein that protease will recognize, protease will not do its job to destroy
its own kind.
You might also like
- Enzymes Report Biology AS Core Practical Write Up EdexcelDocument7 pagesEnzymes Report Biology AS Core Practical Write Up EdexcelthariniNo ratings yet
- IB 1108 L08 EnzymesDocument5 pagesIB 1108 L08 EnzymesT CaffeeNo ratings yet
- Biology IADocument16 pagesBiology IAAngelina TomacNo ratings yet
- Lab09 Catechol OxidaseDocument9 pagesLab09 Catechol Oxidaseastromaze10No ratings yet
- Lab04 AnswerkeyDocument5 pagesLab04 AnswerkeyAnonymous VSDYrQ83% (12)
- Purposive Communication - Ep4Document16 pagesPurposive Communication - Ep4John Christian James Arellano100% (2)
- Prelab 1Document4 pagesPrelab 1Huyen Tram NguyenNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.11 Trypsin Report of Core Practical Edexcel AsDocument5 pagesActivity 2.11 Trypsin Report of Core Practical Edexcel AsJesse EnglandNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Concentration and Rate of ReactionDocument5 pagesEnzyme Concentration and Rate of ReactionherederaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan March 29, 2019 Biochemistry Chapter 5 Topic: Enzymes Pp. 43-47Document3 pagesLesson Plan March 29, 2019 Biochemistry Chapter 5 Topic: Enzymes Pp. 43-47enilegnavemartinezNo ratings yet
- Biology Coursework Enzymes ConclusionDocument4 pagesBiology Coursework Enzymes Conclusionafaydebwo100% (2)
- AFL 2 10th - Enzymes LaboratoryDocument3 pagesAFL 2 10th - Enzymes LaboratoryCAMILO GUZMAN DORADONo ratings yet
- O Level BiologyDocument2 pagesO Level Biology⟬⟭ ⟭⟬No ratings yet
- BIO50 Lab Report: Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesBIO50 Lab Report: Cellular RespirationSarah Carat17No ratings yet
- Total Protein Determination: Unit Intended Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesTotal Protein Determination: Unit Intended Learning OutcomesMaria ClaraNo ratings yet
- Biology Enzymes CourseworkDocument4 pagesBiology Enzymes Courseworkkqosmkjbf100% (2)
- Biochemistry Laboratory Review Questions For The Final Exam: Instructor: Msc. Nguyen Tuong LinhDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Laboratory Review Questions For The Final Exam: Instructor: Msc. Nguyen Tuong LinhAyase YukiNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document4 pagesActivity 2german guazaNo ratings yet
- Labjournal1 For NursingDocument2 pagesLabjournal1 For NursingDanielle MatelNo ratings yet
- Biology Coursework Enzyme ActivityDocument4 pagesBiology Coursework Enzyme Activityfzdpofajd100% (2)
- Enzymes ReportDocument7 pagesEnzymes ReportthariniNo ratings yet
- Report 3 OfficiallyDocument7 pagesReport 3 OfficiallyLinhNguyeNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Lactase Enzyme Activity Kanika KumarDocument4 pages2.5 Lactase Enzyme Activity Kanika KumarKanika KumarNo ratings yet
- I. Title of Experiment: Determining The Value of Protein in ADocument29 pagesI. Title of Experiment: Determining The Value of Protein in AAnggraini Nugroho PNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Metabolism and Enzymes: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 - Metabolism and Enzymes: Learning Objectivesthanks btNo ratings yet
- Biology Coursework EnzymesDocument7 pagesBiology Coursework Enzymesmhzkehajd100% (2)
- Virtual Lab About The Factors That Influence Enzyme Activity Página 1 de 10 Virtual Lab About The Factors That Influence Enzyme ActivityDocument6 pagesVirtual Lab About The Factors That Influence Enzyme Activity Página 1 de 10 Virtual Lab About The Factors That Influence Enzyme ActivitySanty M . E . :vNo ratings yet
- Pex 08 01 PDFDocument4 pagesPex 08 01 PDFSyarifah KhaerunnisaNo ratings yet
- Pex 08 03Document4 pagesPex 08 03Froi Jovanni Perez89% (9)
- Lab 3 - Biology 1003A (Joseph)Document8 pagesLab 3 - Biology 1003A (Joseph)JosephDionNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Properties of β-glucosidase/ Cellobiase from Aspergillus NigerDocument20 pagesKinetic Properties of β-glucosidase/ Cellobiase from Aspergillus Nigerapi-340517298No ratings yet
- Jurnal Biokimia Hidrolisis Enzim SistematisDocument7 pagesJurnal Biokimia Hidrolisis Enzim SistematisFajar Nurul ArifahNo ratings yet
- Tugas PubMed Diyan PDFDocument10 pagesTugas PubMed Diyan PDFdiyanNo ratings yet
- Exp 8 Amino Acids, PeptidesDocument14 pagesExp 8 Amino Acids, PeptidesAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- Investigating Effect of Concentration On The Activity of TrypsinDocument4 pagesInvestigating Effect of Concentration On The Activity of Trypsinrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- LAB - Food Chemistry 1Document6 pagesLAB - Food Chemistry 1nur hanisahNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 PDFDocument15 pagesLab 3 PDFGift BandaNo ratings yet
- Development of Ethosomes Containing Mycophenolic Acid: T. Limsuwan, T. AmnuaikitDocument8 pagesDevelopment of Ethosomes Containing Mycophenolic Acid: T. Limsuwan, T. AmnuaikitDenize JozzNo ratings yet
- 6 EnzymesDocument6 pages6 EnzymesAntonio CharismaNo ratings yet
- PAG4.2 Student The Effect of Enzyme Conc On The Rate of A Reaction - v0.1Document2 pagesPAG4.2 Student The Effect of Enzyme Conc On The Rate of A Reaction - v0.1Zeeshan FarooqNo ratings yet
- Pex 08 01Document4 pagesPex 08 01Adriana Anaya GaribaldiNo ratings yet
- AkkermanciaDocument21 pagesAkkermanciaEvangelina RivarolaNo ratings yet
- Ezyme and Its Activity - Lab ReportDocument17 pagesEzyme and Its Activity - Lab ReportRibka Kristania HadhiwaluyoNo ratings yet
- Webinar On Osteoarthritis - With Answers To Questions: Barbara MellenDocument6 pagesWebinar On Osteoarthritis - With Answers To Questions: Barbara Mellengeta_dan_846701717No ratings yet
- A Level Biology Coursework EnzymesDocument8 pagesA Level Biology Coursework Enzymesf5d7ejd0100% (2)
- Cinética Da Papaína - Um Experimento Laboratorial de Bioquímica IntrodutóriaDocument2 pagesCinética Da Papaína - Um Experimento Laboratorial de Bioquímica IntrodutóriaRenan OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Biology Coursework Enzymes PHDocument5 pagesBiology Coursework Enzymes PHkllnmfajd100% (2)
- Chapter C Enzymes PART 2Document3 pagesChapter C Enzymes PART 2Gilbert HTNo ratings yet
- PAG4.2 Student The Effect of Enzyme ConcDocument2 pagesPAG4.2 Student The Effect of Enzyme ConcAmaniNo ratings yet
- Enm 32 18 PDFDocument5 pagesEnm 32 18 PDFSofia andrea MezaNo ratings yet
- PDF 0235Document18 pagesPDF 0235NirmaLa SariNo ratings yet
- Lab ReflectionDocument2 pagesLab Reflectionapi-384057570No ratings yet
- Lab Activity 6 Denaturation of ProteinsDocument2 pagesLab Activity 6 Denaturation of ProteinsAkira Poscablo PiranteNo ratings yet
- Bio 150-Experiment 1Document8 pagesBio 150-Experiment 1Aina MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Virtual LabDocument4 pagesEnzymes Virtual Labapi-34000547527% (11)
- Exp 6 Formal Lab Report 113BDocument14 pagesExp 6 Formal Lab Report 113BAlaina Weinheimer100% (3)
- Vlachou Et Al., 2016Document5 pagesVlachou Et Al., 2016manoscharNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Catalysis LabDocument8 pagesEnzyme Catalysis LabAzra RamicNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in General Biology Week 9 Activity 1: The Catalyst ADocument6 pagesAnswer Sheet in General Biology Week 9 Activity 1: The Catalyst AMark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Ppt-NandanaDocument26 pagesEnzymes Ppt-NandanaLingaraj Kumar100% (1)
- Methods for Analysis of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Photosynthetic Organisms: Plants, Green Algae and CyanobacteriaFrom EverandMethods for Analysis of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Photosynthetic Organisms: Plants, Green Algae and CyanobacteriaNo ratings yet
- Professional ResumeDocument4 pagesProfessional Resumeapi-396410708No ratings yet
- HieroglyphicsDocument3 pagesHieroglyphicsgraceNo ratings yet
- Weight Loss Tracker Template 04Document5 pagesWeight Loss Tracker Template 04Youssef N1No ratings yet
- Sectional Title Ownership Podcast SummaryDocument4 pagesSectional Title Ownership Podcast SummaryannNo ratings yet
- DSM IIIDocument2 pagesDSM IIIapi-281903183No ratings yet
- Mexican MariachiDocument2 pagesMexican MariachiAgusteenNo ratings yet
- Reyes, E. - Performance Task 2 PDFDocument4 pagesReyes, E. - Performance Task 2 PDFEzechael ReyesNo ratings yet
- Truex2019 Tell Asmar EshnunnaDocument23 pagesTruex2019 Tell Asmar EshnunnaRaphael OrgeoletNo ratings yet
- 20bal146 Case Analysis PDFDocument15 pages20bal146 Case Analysis PDFTris EatonNo ratings yet
- A Culture of AccountabilityDocument8 pagesA Culture of Accountabilitymaheshwari janiNo ratings yet
- Number Series 5Document22 pagesNumber Series 5Sowmiyia100% (3)
- Tao Te ChingDocument26 pagesTao Te ChingdrevenackNo ratings yet
- FIN630 Final Term 6 PapersDocument66 pagesFIN630 Final Term 6 PapersKamran HaiderNo ratings yet
- Yamuna Biodiversity Park Yamuna Biodiversity ParkDocument37 pagesYamuna Biodiversity Park Yamuna Biodiversity ParkAnsh SagrohaNo ratings yet
- Di Compilation PDFDocument844 pagesDi Compilation PDFbhavnesh firkeNo ratings yet
- The Fontan Circulation Contin EducDocument5 pagesThe Fontan Circulation Contin EducAishu BNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 9-A - Module 2 - Tumacder, DHMLDocument5 pagesProf Ed 9-A - Module 2 - Tumacder, DHMLDanica Hannah Mae TumacderNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FictionDocument7 pagesIntroduction To FictionParlin PardedeNo ratings yet
- JIS College of Engineering: Vision and Mission of The DepartmentDocument4 pagesJIS College of Engineering: Vision and Mission of The DepartmentAnushka SikdarNo ratings yet
- Soal Latihan Recount Untuk Siswa 2Document2 pagesSoal Latihan Recount Untuk Siswa 2YANTI MOELNo ratings yet
- ICA Notes For Telegram 1646048676072Document18 pagesICA Notes For Telegram 1646048676072Aditi JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Moral ActionsDocument33 pagesLesson 3 Moral Actionsjeruel luminariasNo ratings yet
- Vaccine ExemptionDocument1 pageVaccine ExemptionEnlou FrereNo ratings yet
- Understanding Emotions From An Indian PerspectiveDocument29 pagesUnderstanding Emotions From An Indian PerspectiveRatan SikderNo ratings yet
- HRM 4410 - Human Resources Management - PostingDocument7 pagesHRM 4410 - Human Resources Management - PostingThomas YousifNo ratings yet
- The Third Philippine RepublicDocument24 pagesThe Third Philippine RepublicDelfin DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Using Deep Learning To Recognize Therapeutic Effects of Music Based On EmotionsDocument13 pagesUsing Deep Learning To Recognize Therapeutic Effects of Music Based On EmotionsJan LAWNo ratings yet
- Peace Psychology PPT Sadia's GroupDocument49 pagesPeace Psychology PPT Sadia's GroupSadia khanNo ratings yet
- Scrim Sessions (Full PDF)Document27 pagesScrim Sessions (Full PDF)Alex PaimNo ratings yet