Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparing Crop Production Methods: Growing A GMO Crop Growing A non-GMO Crop
Comparing Crop Production Methods: Growing A GMO Crop Growing A non-GMO Crop
Uploaded by
Ashley AquinoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Piano Man Lead Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesPiano Man Lead Sheet PDFAnchorage Bike Safety86% (7)
- 05 Activity 1 - ARG-MiceDocument1 page05 Activity 1 - ARG-MiceMark Morales100% (1)
- Typical Properties of Britesorb® L10Document1 pageTypical Properties of Britesorb® L10DhilNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Worksheet 1 ChavezDocument1 page01 Laboratory Worksheet 1 ChavezMaria Cristina ChavezNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Case Analysis: The Kimpton ExperienceDocument2 pagesInstructions: Case Analysis: The Kimpton Experienceliezel pascualNo ratings yet
- Eat Stop Eat Optimized CompressedDocument57 pagesEat Stop Eat Optimized CompressedWayne CaponeNo ratings yet
- CodesDocument3 pagesCodesAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Rovelyn at 18 Emcee Script: Acknowledgement of The ParentsDocument4 pagesRovelyn at 18 Emcee Script: Acknowledgement of The ParentsGWYN KELLY LOBITOSNo ratings yet
- BioethicsCasesEEI 316232215 PDFDocument38 pagesBioethicsCasesEEI 316232215 PDFAman UllahNo ratings yet
- 08 Worksheet 2Document5 pages08 Worksheet 2Ma. Cristina NolloraNo ratings yet
- Golden RiceDocument3 pagesGolden RiceRodel Novesteras ClausNo ratings yet
- JorqueMaclam - 05 Homework 1-ARGDocument2 pagesJorqueMaclam - 05 Homework 1-ARGDeee JorqNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of GMOsDocument1 pageAdvantages and Disadvantages of GMOsSandra Arenas HerreraNo ratings yet
- STS Module 13+finalDocument59 pagesSTS Module 13+finalDesiree GalletoNo ratings yet
- 08-Homework-International CuisinesDocument1 page08-Homework-International CuisinesAngel LiwaNo ratings yet
- Which Culinary Influence in Africa Do You Think Had A Greater Impact On The Cuisines of African Countries? Use The Chart BelowDocument2 pagesWhich Culinary Influence in Africa Do You Think Had A Greater Impact On The Cuisines of African Countries? Use The Chart BelowMary Rose SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Gmo Research ProposalDocument3 pagesGmo Research Proposalapi-3568725770% (2)
- 07 Handout 1Document2 pages07 Handout 1Joana LirioNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument30 pagesFood SecurityLhe NeNo ratings yet
- STS Activity-18 Research-ActivityDocument2 pagesSTS Activity-18 Research-ActivityEvan Caringal SabioNo ratings yet
- 01 Worksheet 1 - Gene TherapyDocument1 page01 Worksheet 1 - Gene TherapyBae MaxZNo ratings yet
- Impact of Genetically-Modified Organisms On The EnvironmentDocument23 pagesImpact of Genetically-Modified Organisms On The Environmentмарина нещеретNo ratings yet
- 06 Video 1 The Price of Sugar ARGDocument1 page06 Video 1 The Price of Sugar ARGRollyAnn BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Why Is It Suddenly Getting So Much AttentionDocument3 pagesWhy Is It Suddenly Getting So Much AttentionZam-zamNo ratings yet
- Greenleaf Hotel: Company HighlightsDocument3 pagesGreenleaf Hotel: Company HighlightsRonald Tres Reyes0% (1)
- Sts Report (That Sugar Film) Part 1Document14 pagesSts Report (That Sugar Film) Part 1Art Nathan OlegarioNo ratings yet
- 07 Journal 1Document3 pages07 Journal 1angelicaNo ratings yet
- Lying A.MDocument2 pagesLying A.MAleksandro MakoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Potential Applications of Nanotechnology in The Philippines?Document2 pagesWhat Are The Potential Applications of Nanotechnology in The Philippines?Sarah GNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 2 - ARG - ENTREPREDocument5 pages01 Activity 2 - ARG - ENTREPREStephanie Kyle ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Ethics Final NotesDocument2 pagesEthics Final NotesBika BikaNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Good Life GargarDocument1 pageAristotle Good Life GargarSarah Jean GargarNo ratings yet
- Group Members: Dimaano, Khyle Ronan MDocument3 pagesGroup Members: Dimaano, Khyle Ronan MKhyle DimaanoNo ratings yet
- To Be Successful in Life and Have A Stable Life, Be Able To Help My Family and Those People Who Need Help and To Have Fun in My Journey Through Life and Learn From My Mistakes.Document2 pagesTo Be Successful in Life and Have A Stable Life, Be Able To Help My Family and Those People Who Need Help and To Have Fun in My Journey Through Life and Learn From My Mistakes.Yanna YapNo ratings yet
- What Are The Advantages of GMOsDocument5 pagesWhat Are The Advantages of GMOsHarsha HinklesNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesQuestionnaireYSA tuttifruttiNo ratings yet
- STS FINAL Module 8 - Biodiversity and Healthy SocietyDocument8 pagesSTS FINAL Module 8 - Biodiversity and Healthy SocietyPrincess BilogNo ratings yet
- Media Review About LastikmanDocument3 pagesMedia Review About LastikmanNin Fernandez0% (1)
- 03 - Activity - 1 (1) SlazarrrjayboDocument2 pages03 - Activity - 1 (1) SlazarrrjayboJaybo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Jorque Christine 05 Homework 1 IC - JPGDocument2 pagesJorque Christine 05 Homework 1 IC - JPGDeee JorqNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Worksheet 1 - ARG Mod. GasDocument1 page01 Laboratory Worksheet 1 - ARG Mod. GasAbegail MaupoyNo ratings yet
- Unmasking Two Decades of Lies About Golden Rice A Critique PaperDocument3 pagesUnmasking Two Decades of Lies About Golden Rice A Critique PaperRodel Novesteras ClausNo ratings yet
- Daguinod Joselle PDFDocument7 pagesDaguinod Joselle PDFJoselle DaguinodNo ratings yet
- Advantages AND Disadvantages of Genetically Modified Foods: Elaborated Mititelu Maia Verified Ciumac Liudmila GR - TPA-181Document7 pagesAdvantages AND Disadvantages of Genetically Modified Foods: Elaborated Mititelu Maia Verified Ciumac Liudmila GR - TPA-181Майя МитителуNo ratings yet
- Reflection On SugarDocument1 pageReflection On SugarLuisa Marie CasasNo ratings yet
- Julius B. Seda BSIT-201 Ethics: AnswerDocument3 pagesJulius B. Seda BSIT-201 Ethics: AnswerJulius SedaNo ratings yet
- 03 Quiz 1-ArgDocument2 pages03 Quiz 1-ArgAileen ComiaNo ratings yet
- 02 Video 1 The History of CorporationDocument1 page02 Video 1 The History of CorporationAbegail Maupoy100% (1)
- The Earth Is Not A Joke": Submitted By: LeaderDocument5 pagesThe Earth Is Not A Joke": Submitted By: LeaderChristian Janary RabenitasNo ratings yet
- 10 The Service of Food and Beverages - MULIDocument6 pages10 The Service of Food and Beverages - MULIEdwin A. Muli Jr.No ratings yet
- ULO 1A-"Let's Check" Activity 1. Now, That You Know The Essential Historical Antecedents of Science andDocument9 pagesULO 1A-"Let's Check" Activity 1. Now, That You Know The Essential Historical Antecedents of Science andRodante P Hernandez Jr.No ratings yet
- 03 Homework 1 - ARGDocument1 page03 Homework 1 - ARGericaNo ratings yet
- Gmo Research Paper Final DraftDocument12 pagesGmo Research Paper Final Draftapi-248187280100% (4)
- Internationaltrade Group7 130702031215 Phpapp01 2Document51 pagesInternationaltrade Group7 130702031215 Phpapp01 2Nagarjuna ReddyNo ratings yet
- 06 Assignment 1-TQM-MACASIRAYDocument2 pages06 Assignment 1-TQM-MACASIRAYNicola Aika MacasirayNo ratings yet
- Do You Believe That Google Makes People StupidDocument1 pageDo You Believe That Google Makes People StupidMelissa Jane MoradoNo ratings yet
- ASSESMENTDocument3 pagesASSESMENTZaraNo ratings yet
- 04 Review 1 - ARGDocument1 page04 Review 1 - ARGDK PanganibanNo ratings yet
- 05 Popular Culture and The MediaDocument2 pages05 Popular Culture and The MediaMark Angelo Valido100% (1)
- 02 Activity 2 CARMENDocument2 pages02 Activity 2 CARMENreighnaNo ratings yet
- Reflective Essay Assignment #5 - Myself As A Responsible Consumer and My Contribution in Sustainable DevelopmentDocument1 pageReflective Essay Assignment #5 - Myself As A Responsible Consumer and My Contribution in Sustainable DevelopmentRej GarbosaNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument3 pagesFinal ExamEunice 04No ratings yet
- Emotion Sensing Facial RecognitionDocument13 pagesEmotion Sensing Facial RecognitionJohn Philip Monera100% (2)
- 02 Exercise Laboratory 1 TOURPLANNINGDocument8 pages02 Exercise Laboratory 1 TOURPLANNINGnicole dordeNo ratings yet
- Genetically Food ResearchDocument8 pagesGenetically Food ResearchVeronica YamatNo ratings yet
- 04 TSK Performance 1 (RPH)Document3 pages04 TSK Performance 1 (RPH)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- 01 Quiz 1B - ARG (RIZALS)Document2 pages01 Quiz 1B - ARG (RIZALS)Ashley Aquino100% (1)
- Cavite MunityDocument1 pageCavite MunityAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise (Programming)Document1 pageLab Exercise (Programming)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
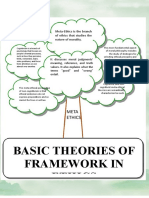
- Tree Analysis For Ethical Theories (ETHICS)Document1 pageTree Analysis For Ethical Theories (ETHICS)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- 01 Quiz 1B - ARG (RIZALS)Document2 pages01 Quiz 1B - ARG (RIZALS)Ashley Aquino100% (1)
- 5 Activity 2 (RPH Slogan)Document2 pages5 Activity 2 (RPH Slogan)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Week13 Paraphrasing (PC)Document2 pagesWeek13 Paraphrasing (PC)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper Sa Ngalan NG Karapatan (ETHICS)Document5 pagesReflection Paper Sa Ngalan NG Karapatan (ETHICS)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Smart Car: Research By: Ashley Aquino 2021Document8 pagesSmart Car: Research By: Ashley Aquino 2021Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Aesthetics A Branch Of: Philosophy Concerned With The Study of Art and BeautyDocument10 pagesAesthetics A Branch Of: Philosophy Concerned With The Study of Art and BeautyAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Art and ScienceDocument1 pageArt and ScienceAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- What Is Your First Impression Regarding The Market's Owner, Boss Da? Is Your First Impression Correct?Document1 pageWhat Is Your First Impression Regarding The Market's Owner, Boss Da? Is Your First Impression Correct?Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARG (HCI)Document3 pages01 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARG (HCI)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- 01 Worksheet 1A: Title of The Reading: Reading BreakdownDocument3 pages01 Worksheet 1A: Title of The Reading: Reading BreakdownAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Workflow Template Task 5Document4 pagesWorkflow Template Task 5nirajan parajuli100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson PlanitsmeJelly RoseNo ratings yet
- Sudan Return Index Beta (Final)Document21 pagesSudan Return Index Beta (Final)Social InquiryNo ratings yet
- Calculus Newton Law of Cooling SolutionsDocument4 pagesCalculus Newton Law of Cooling SolutionsCristopher JhanrieNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For HypertensionDocument21 pagesNutrition For HypertensionMina Magdy FahmyNo ratings yet
- Mini Case Burger King Group 1Document5 pagesMini Case Burger King Group 1nino laoshviliNo ratings yet
- Octopus CultureDocument33 pagesOctopus CultureAtul SinghNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/61Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/61afy100% (1)
- Nasreddin Goes Shopping: Grade 10: Reading Passage 1Document8 pagesNasreddin Goes Shopping: Grade 10: Reading Passage 1Al Lhea Bandayanon MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cenovnik 2022 NAJNOVIJI 09.12.2022Document7 pagesCenovnik 2022 NAJNOVIJI 09.12.2022Dragoljub MilinovićNo ratings yet
- Fortified Refined Rapeseed OilDocument5 pagesFortified Refined Rapeseed Oilkadma13No ratings yet
- ALICE in WONDERLAND Analyse and PlanningDocument4 pagesALICE in WONDERLAND Analyse and PlanningAulia MaghfirahNo ratings yet
- MP Cola War - Group 1Document15 pagesMP Cola War - Group 1Shivani GuptaNo ratings yet
- Microsart Manifold SartoriusDocument8 pagesMicrosart Manifold SartoriusPutri Tania ArianaNo ratings yet
- Fabricantes Estandarizados Feb 2023Document223 pagesFabricantes Estandarizados Feb 2023Diana Melo QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Planning of Irrigation ProjectDocument18 pagesPlanning of Irrigation Projectaamir raza100% (1)
- He Lavor PprenticeDocument2 pagesHe Lavor PprenticeRafli MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PharmaceuticalDocument44 pagesChapter 6 PharmaceuticalAsmaa HanafiahNo ratings yet
- Crown Paladin - Complete Spell ListDocument1 pageCrown Paladin - Complete Spell ListDObatakeNo ratings yet
- Kuat Tarik PatentDocument8 pagesKuat Tarik Patentannisa latifaNo ratings yet
- Baked Oatmeal RecipesDocument9 pagesBaked Oatmeal RecipesYuznia PutriNo ratings yet
- Agro 1Document3 pagesAgro 1Sugie BarreraNo ratings yet
- TD2213 ThermodynamicsDocument81 pagesTD2213 Thermodynamicsb.nithinNo ratings yet
- Stok 17 April 2024Document286 pagesStok 17 April 2024rettaagnasia00No ratings yet
- Good Topics For A Cause and Effect EssayDocument6 pagesGood Topics For A Cause and Effect Essaylmfbcmaeg100% (3)
- Tenses of The VerbDocument96 pagesTenses of The VerbFroilan TinduganNo ratings yet
Comparing Crop Production Methods: Growing A GMO Crop Growing A non-GMO Crop
Comparing Crop Production Methods: Growing A GMO Crop Growing A non-GMO Crop
Uploaded by
Ashley AquinoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparing Crop Production Methods: Growing A GMO Crop Growing A non-GMO Crop
Comparing Crop Production Methods: Growing A GMO Crop Growing A non-GMO Crop
Uploaded by
Ashley AquinoCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPARING CROP PRODUCTION METHODS
Growing a GMO crop Growing a non-GMO crop
Food that has been
genetically engineered in Food that hasn't been
some way, usually in a genetically modified, or
laboratory, is known as non-GMO food, hasn't
GMO food. They are both been altered or
GM is a technique that conventionally engineered in any
includes introducing produced foods manner.
DNA into an organism's that provide Food that isn't genetically
genome. New DNA is put important modified (non-GMO)
into plant cells to create a components to doesn't always follow the
GM plant. Typically, the our diets, same rules as organic
cells are cultivated in especially in food.
tissue culture and terms of our
subsequently transformed health.
into plants.
BENEFITS OF GMO RISKS OF GMO CROPS
CROPS
Food that is more nutritious. GMOs have the potential to induce
allergic responses. Because GMO
Food that is more delicious. foods contain DNA from other
organisms, it's possible that the new
Plants that are disease- and DNA will cause allergies in people
drought-resistant and use fewer who aren't sensitive to the food in
resources in the environment (such the first place.
as water and fertilizer).
Antibiotic resistance may be
Pesticides are used less frequently. exacerbated by GMOs. When GMO
scientists insert new DNA into plant
Increased food supply at a lower cells, they frequently include an
cost and with a longer shelf life. additional gene that confers
antibiotic resistance to the modified
Plants and animals that grow faster. cells. They can then kill any plant
cells that didn't effectively take in
Food with better qualities, such as the new DNA with an antibiotic.
fried potatoes that release less of a
cancer-causing chemical. Genetic changes that are
unexpected or negative.
Medicinal foods with the potential to
be utilized as vaccinations or other Foods that aren't as healthful as
medications. others.
CRITICALLY THINKING IN PAIRS
STEP 1: After being grouped into pairs, you will be assigned in a position on
the use of GMOs in our food supply. Mark it below:
I am in favor of GMOs. I am against GMOs.
STEP 2: Find evidence to support your assigned position. List three (3)
pieces of evidence below in order, form highest to lowest quality. Your notes
on the two (2) pages of this worksheet will serve as your reference.
1st evidence: Every year, billions of edible animals are raised in the United
States on GMO-containing feed, with no indication of harm. According to a
2014 assessment published in the Journal of Animal Science, the genetically
altered feed actually improved animal health and growth efficiency.
2nd evidence: Farmers have been able to use less pesticides while boosting
yields by engineering insect resistance, which improves farmer and
environmental safety while cutting food costs and improving availability. Corn,
cotton, and soybean yields are estimated to have increased by 20% to 30%
as a result of genetic engineering.
3rd Evidence: A number of noteworthy advantages have been found. For
example, researchers in Pisa, Italy, found that genetically altered corn had a
much better yield than non-genetically modified cultivars and contains lower
levels of fungi-produced toxins in a review of 76 papers published in February
in Scientific Reports.
STEP 3: Formulate your argument to support the position you have been
assigned. Summarize it below in 1-2 paragraphs.
Wider acceptance of genetic engineering, particularly in African and Asian
countries that have yet to embrace the technique, could significantly
enhance food supply in locations where climate change will increasingly
necessitate crops that can grow in dry, saline soils and withstand
temperature extremes. Despite the negative effects, GMOs do have some
beneficial effects. These unfavorable consequences may improve with
additional research, indicating that they can be avoided. Also, if you list
the beneficial benefits, there are several favorable consequences on our
bodies, particularly in our health. There are also some indications that it is
a great help to many countries, particularly in terms of food supply and
production.
STEP 4: With your partner, discuss your final positions on the use of GMOs
and the evidence for each position. Identify which portions of the position are
based on scientific research and which portions are based more on social
issues. List them below:
SCIENTIFIC ISSUES SOCIAL ISSUES
Interbreeding/Genetic
Impacts on the Ecosystem.
Contamination. GMOs that
Changes in a single species
have been introduced may
can have far-reaching
interbreed with wild-type or
consequences for the
sexually compatible relatives.
ecosystem. The risk of
Unless the unique trait gives a
ecosystem damage and
selection advantage to the
destruction is always present
recipient, it may be lost in wild
in single impacts.
kinds. However, wild types'
tolerance abilities may
develop, changing the native
species' ecological relationship
and behavior.
SCIENTIFIC ISSUES SOCIAL ISSUES
Augmented Selection Pressure People's or the environment's
on Both Target and Nontarget health is adversely affected.
Organisms. Target and nontarget Increased disease burden if the
species may face increased recipient organism is a pathogenic
pressure to adapt to the microorganism or virus, increased
introduced changes, similar to a weed or pest burden if the recipient
geological change or natural organism is a plant or invertebrate,
selection pressure, resulting in and adverse effects on species,
the evolution of distinct resistant communities, or ecosystems are
populations. among these.
STEP 5: Reach a consensus. The use of GMOs is a topic that combines
both social and scientific issues. Your consensus will be a combination of the
two (2) opposing views based on multiple lines of evidence. Below, formulate
a NEW position, which addresses the needs and wants of both sides of the
issue. (Note: The consensus could include multiple solutions. )
For both concerns, my solution is to research it again and test it. It will be
a waste if we completely disregard or eliminate it. GMOs have a favorable
impact on many countries and people, and they also help with food
production. The negative impacts of GMOs must be addressed in some
way, such as conducting additional study and compiling a list of negative
impacts that can be eliminated if the negative impacts are resolved. Then,
after some investigation and testing, they can give to the people or society
if all of the negatives have been resolved. If this occurs, people will be
relieved of their worries and will have a sufficient quantity of food to assist
them in their daily lives.
You might also like
- Piano Man Lead Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesPiano Man Lead Sheet PDFAnchorage Bike Safety86% (7)
- 05 Activity 1 - ARG-MiceDocument1 page05 Activity 1 - ARG-MiceMark Morales100% (1)
- Typical Properties of Britesorb® L10Document1 pageTypical Properties of Britesorb® L10DhilNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Worksheet 1 ChavezDocument1 page01 Laboratory Worksheet 1 ChavezMaria Cristina ChavezNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Case Analysis: The Kimpton ExperienceDocument2 pagesInstructions: Case Analysis: The Kimpton Experienceliezel pascualNo ratings yet
- Eat Stop Eat Optimized CompressedDocument57 pagesEat Stop Eat Optimized CompressedWayne CaponeNo ratings yet
- CodesDocument3 pagesCodesAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Rovelyn at 18 Emcee Script: Acknowledgement of The ParentsDocument4 pagesRovelyn at 18 Emcee Script: Acknowledgement of The ParentsGWYN KELLY LOBITOSNo ratings yet
- BioethicsCasesEEI 316232215 PDFDocument38 pagesBioethicsCasesEEI 316232215 PDFAman UllahNo ratings yet
- 08 Worksheet 2Document5 pages08 Worksheet 2Ma. Cristina NolloraNo ratings yet
- Golden RiceDocument3 pagesGolden RiceRodel Novesteras ClausNo ratings yet
- JorqueMaclam - 05 Homework 1-ARGDocument2 pagesJorqueMaclam - 05 Homework 1-ARGDeee JorqNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of GMOsDocument1 pageAdvantages and Disadvantages of GMOsSandra Arenas HerreraNo ratings yet
- STS Module 13+finalDocument59 pagesSTS Module 13+finalDesiree GalletoNo ratings yet
- 08-Homework-International CuisinesDocument1 page08-Homework-International CuisinesAngel LiwaNo ratings yet
- Which Culinary Influence in Africa Do You Think Had A Greater Impact On The Cuisines of African Countries? Use The Chart BelowDocument2 pagesWhich Culinary Influence in Africa Do You Think Had A Greater Impact On The Cuisines of African Countries? Use The Chart BelowMary Rose SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Gmo Research ProposalDocument3 pagesGmo Research Proposalapi-3568725770% (2)
- 07 Handout 1Document2 pages07 Handout 1Joana LirioNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument30 pagesFood SecurityLhe NeNo ratings yet
- STS Activity-18 Research-ActivityDocument2 pagesSTS Activity-18 Research-ActivityEvan Caringal SabioNo ratings yet
- 01 Worksheet 1 - Gene TherapyDocument1 page01 Worksheet 1 - Gene TherapyBae MaxZNo ratings yet
- Impact of Genetically-Modified Organisms On The EnvironmentDocument23 pagesImpact of Genetically-Modified Organisms On The Environmentмарина нещеретNo ratings yet
- 06 Video 1 The Price of Sugar ARGDocument1 page06 Video 1 The Price of Sugar ARGRollyAnn BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Why Is It Suddenly Getting So Much AttentionDocument3 pagesWhy Is It Suddenly Getting So Much AttentionZam-zamNo ratings yet
- Greenleaf Hotel: Company HighlightsDocument3 pagesGreenleaf Hotel: Company HighlightsRonald Tres Reyes0% (1)
- Sts Report (That Sugar Film) Part 1Document14 pagesSts Report (That Sugar Film) Part 1Art Nathan OlegarioNo ratings yet
- 07 Journal 1Document3 pages07 Journal 1angelicaNo ratings yet
- Lying A.MDocument2 pagesLying A.MAleksandro MakoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Potential Applications of Nanotechnology in The Philippines?Document2 pagesWhat Are The Potential Applications of Nanotechnology in The Philippines?Sarah GNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 2 - ARG - ENTREPREDocument5 pages01 Activity 2 - ARG - ENTREPREStephanie Kyle ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Ethics Final NotesDocument2 pagesEthics Final NotesBika BikaNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Good Life GargarDocument1 pageAristotle Good Life GargarSarah Jean GargarNo ratings yet
- Group Members: Dimaano, Khyle Ronan MDocument3 pagesGroup Members: Dimaano, Khyle Ronan MKhyle DimaanoNo ratings yet
- To Be Successful in Life and Have A Stable Life, Be Able To Help My Family and Those People Who Need Help and To Have Fun in My Journey Through Life and Learn From My Mistakes.Document2 pagesTo Be Successful in Life and Have A Stable Life, Be Able To Help My Family and Those People Who Need Help and To Have Fun in My Journey Through Life and Learn From My Mistakes.Yanna YapNo ratings yet
- What Are The Advantages of GMOsDocument5 pagesWhat Are The Advantages of GMOsHarsha HinklesNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesQuestionnaireYSA tuttifruttiNo ratings yet
- STS FINAL Module 8 - Biodiversity and Healthy SocietyDocument8 pagesSTS FINAL Module 8 - Biodiversity and Healthy SocietyPrincess BilogNo ratings yet
- Media Review About LastikmanDocument3 pagesMedia Review About LastikmanNin Fernandez0% (1)
- 03 - Activity - 1 (1) SlazarrrjayboDocument2 pages03 - Activity - 1 (1) SlazarrrjayboJaybo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Jorque Christine 05 Homework 1 IC - JPGDocument2 pagesJorque Christine 05 Homework 1 IC - JPGDeee JorqNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Worksheet 1 - ARG Mod. GasDocument1 page01 Laboratory Worksheet 1 - ARG Mod. GasAbegail MaupoyNo ratings yet
- Unmasking Two Decades of Lies About Golden Rice A Critique PaperDocument3 pagesUnmasking Two Decades of Lies About Golden Rice A Critique PaperRodel Novesteras ClausNo ratings yet
- Daguinod Joselle PDFDocument7 pagesDaguinod Joselle PDFJoselle DaguinodNo ratings yet
- Advantages AND Disadvantages of Genetically Modified Foods: Elaborated Mititelu Maia Verified Ciumac Liudmila GR - TPA-181Document7 pagesAdvantages AND Disadvantages of Genetically Modified Foods: Elaborated Mititelu Maia Verified Ciumac Liudmila GR - TPA-181Майя МитителуNo ratings yet
- Reflection On SugarDocument1 pageReflection On SugarLuisa Marie CasasNo ratings yet
- Julius B. Seda BSIT-201 Ethics: AnswerDocument3 pagesJulius B. Seda BSIT-201 Ethics: AnswerJulius SedaNo ratings yet
- 03 Quiz 1-ArgDocument2 pages03 Quiz 1-ArgAileen ComiaNo ratings yet
- 02 Video 1 The History of CorporationDocument1 page02 Video 1 The History of CorporationAbegail Maupoy100% (1)
- The Earth Is Not A Joke": Submitted By: LeaderDocument5 pagesThe Earth Is Not A Joke": Submitted By: LeaderChristian Janary RabenitasNo ratings yet
- 10 The Service of Food and Beverages - MULIDocument6 pages10 The Service of Food and Beverages - MULIEdwin A. Muli Jr.No ratings yet
- ULO 1A-"Let's Check" Activity 1. Now, That You Know The Essential Historical Antecedents of Science andDocument9 pagesULO 1A-"Let's Check" Activity 1. Now, That You Know The Essential Historical Antecedents of Science andRodante P Hernandez Jr.No ratings yet
- 03 Homework 1 - ARGDocument1 page03 Homework 1 - ARGericaNo ratings yet
- Gmo Research Paper Final DraftDocument12 pagesGmo Research Paper Final Draftapi-248187280100% (4)
- Internationaltrade Group7 130702031215 Phpapp01 2Document51 pagesInternationaltrade Group7 130702031215 Phpapp01 2Nagarjuna ReddyNo ratings yet
- 06 Assignment 1-TQM-MACASIRAYDocument2 pages06 Assignment 1-TQM-MACASIRAYNicola Aika MacasirayNo ratings yet
- Do You Believe That Google Makes People StupidDocument1 pageDo You Believe That Google Makes People StupidMelissa Jane MoradoNo ratings yet
- ASSESMENTDocument3 pagesASSESMENTZaraNo ratings yet
- 04 Review 1 - ARGDocument1 page04 Review 1 - ARGDK PanganibanNo ratings yet
- 05 Popular Culture and The MediaDocument2 pages05 Popular Culture and The MediaMark Angelo Valido100% (1)
- 02 Activity 2 CARMENDocument2 pages02 Activity 2 CARMENreighnaNo ratings yet
- Reflective Essay Assignment #5 - Myself As A Responsible Consumer and My Contribution in Sustainable DevelopmentDocument1 pageReflective Essay Assignment #5 - Myself As A Responsible Consumer and My Contribution in Sustainable DevelopmentRej GarbosaNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument3 pagesFinal ExamEunice 04No ratings yet
- Emotion Sensing Facial RecognitionDocument13 pagesEmotion Sensing Facial RecognitionJohn Philip Monera100% (2)
- 02 Exercise Laboratory 1 TOURPLANNINGDocument8 pages02 Exercise Laboratory 1 TOURPLANNINGnicole dordeNo ratings yet
- Genetically Food ResearchDocument8 pagesGenetically Food ResearchVeronica YamatNo ratings yet
- 04 TSK Performance 1 (RPH)Document3 pages04 TSK Performance 1 (RPH)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- 01 Quiz 1B - ARG (RIZALS)Document2 pages01 Quiz 1B - ARG (RIZALS)Ashley Aquino100% (1)
- Cavite MunityDocument1 pageCavite MunityAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise (Programming)Document1 pageLab Exercise (Programming)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Tree Analysis For Ethical Theories (ETHICS)Document1 pageTree Analysis For Ethical Theories (ETHICS)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- 01 Quiz 1B - ARG (RIZALS)Document2 pages01 Quiz 1B - ARG (RIZALS)Ashley Aquino100% (1)
- 5 Activity 2 (RPH Slogan)Document2 pages5 Activity 2 (RPH Slogan)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Week13 Paraphrasing (PC)Document2 pagesWeek13 Paraphrasing (PC)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper Sa Ngalan NG Karapatan (ETHICS)Document5 pagesReflection Paper Sa Ngalan NG Karapatan (ETHICS)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Smart Car: Research By: Ashley Aquino 2021Document8 pagesSmart Car: Research By: Ashley Aquino 2021Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Aesthetics A Branch Of: Philosophy Concerned With The Study of Art and BeautyDocument10 pagesAesthetics A Branch Of: Philosophy Concerned With The Study of Art and BeautyAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Art and ScienceDocument1 pageArt and ScienceAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- What Is Your First Impression Regarding The Market's Owner, Boss Da? Is Your First Impression Correct?Document1 pageWhat Is Your First Impression Regarding The Market's Owner, Boss Da? Is Your First Impression Correct?Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARG (HCI)Document3 pages01 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARG (HCI)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- 01 Worksheet 1A: Title of The Reading: Reading BreakdownDocument3 pages01 Worksheet 1A: Title of The Reading: Reading BreakdownAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Workflow Template Task 5Document4 pagesWorkflow Template Task 5nirajan parajuli100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson PlanitsmeJelly RoseNo ratings yet
- Sudan Return Index Beta (Final)Document21 pagesSudan Return Index Beta (Final)Social InquiryNo ratings yet
- Calculus Newton Law of Cooling SolutionsDocument4 pagesCalculus Newton Law of Cooling SolutionsCristopher JhanrieNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For HypertensionDocument21 pagesNutrition For HypertensionMina Magdy FahmyNo ratings yet
- Mini Case Burger King Group 1Document5 pagesMini Case Burger King Group 1nino laoshviliNo ratings yet
- Octopus CultureDocument33 pagesOctopus CultureAtul SinghNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/61Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/61afy100% (1)
- Nasreddin Goes Shopping: Grade 10: Reading Passage 1Document8 pagesNasreddin Goes Shopping: Grade 10: Reading Passage 1Al Lhea Bandayanon MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cenovnik 2022 NAJNOVIJI 09.12.2022Document7 pagesCenovnik 2022 NAJNOVIJI 09.12.2022Dragoljub MilinovićNo ratings yet
- Fortified Refined Rapeseed OilDocument5 pagesFortified Refined Rapeseed Oilkadma13No ratings yet
- ALICE in WONDERLAND Analyse and PlanningDocument4 pagesALICE in WONDERLAND Analyse and PlanningAulia MaghfirahNo ratings yet
- MP Cola War - Group 1Document15 pagesMP Cola War - Group 1Shivani GuptaNo ratings yet
- Microsart Manifold SartoriusDocument8 pagesMicrosart Manifold SartoriusPutri Tania ArianaNo ratings yet
- Fabricantes Estandarizados Feb 2023Document223 pagesFabricantes Estandarizados Feb 2023Diana Melo QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Planning of Irrigation ProjectDocument18 pagesPlanning of Irrigation Projectaamir raza100% (1)
- He Lavor PprenticeDocument2 pagesHe Lavor PprenticeRafli MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PharmaceuticalDocument44 pagesChapter 6 PharmaceuticalAsmaa HanafiahNo ratings yet
- Crown Paladin - Complete Spell ListDocument1 pageCrown Paladin - Complete Spell ListDObatakeNo ratings yet
- Kuat Tarik PatentDocument8 pagesKuat Tarik Patentannisa latifaNo ratings yet
- Baked Oatmeal RecipesDocument9 pagesBaked Oatmeal RecipesYuznia PutriNo ratings yet
- Agro 1Document3 pagesAgro 1Sugie BarreraNo ratings yet
- TD2213 ThermodynamicsDocument81 pagesTD2213 Thermodynamicsb.nithinNo ratings yet
- Stok 17 April 2024Document286 pagesStok 17 April 2024rettaagnasia00No ratings yet
- Good Topics For A Cause and Effect EssayDocument6 pagesGood Topics For A Cause and Effect Essaylmfbcmaeg100% (3)
- Tenses of The VerbDocument96 pagesTenses of The VerbFroilan TinduganNo ratings yet