Professional Documents
Culture Documents
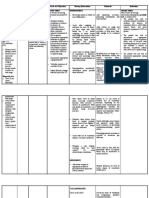
Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Bianca Mikaela DosdosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
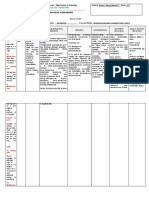
Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Bianca Mikaela DosdosCopyright:
Available Formats
NURSING CARE PLAN
Identified Problem: Dyspnea
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Gas Exchange r/t removal of lung tissue evidenced by dyspnea
CUES OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Short term objectives: Independent Short term:
Had a surgery in the After 4 hours of Note respiratory rate, depth, and ease of Respirations may be increased After 4 hours of comprehensive
past to remove the comprehensive nursing respiration. Observe for use of accessory as a result of pain or as an nursing intervention, the patient
lower lobe (left) of his intervention, the patient will be muscles, pursed-lip breathing, changes in initial compensatory was able to:
lung. able to: skin or mucous membrane color, pallor, mechanism to accommodate
cyanosis. for the loss of lung tissue Goal partially met: demonstrated
Objective: 1. Demonstrate appropriate Auscultate lungs for air movement and Consolidation and lack of air appropriate coping behaviors
Shortness of breathing coping behaviors abnormal breath sounds. movement on the operative
Productive cough side are normal in the
(green) pneumonectomy patient
Fever – 380C Long term objectives: Evaluate cough Indicates possible obstruction
85%, SaO2 (room air) After 8 hours of Investigate restlessness and changes in May indicate increased hypoxia Long term:
comprehensive nursing mentation or level of consciousness or complications such as a After 8 hours of comprehensive
intervention, the patient will be mediastinal shift in nursing intervention, the patient
able to: pneumonectomy patient when was able to:
accompanied by tachypnea,
1. Establish a normal, effective tachycardia, and tracheal Goal met:
respiratory pattern as deviation. 1. Established a normal, effective
evidenced by absence of Review laboratory data such as ABGs Determines degree of respiratory pattern as evidenced
cyanosis and other oxygenation and carbon dioxide by absence of cyanosis and other
signs/symptoms of hypoxia, retention signs/symptoms of hypoxia, with
with arterial blood gasses Review drug screens and pulmonary function Determines vital capacity/tidal arterial blood gasses (ABGs)
(ABGs) within client’s normal studies volume within client’s normal or
or acceptable range acceptable range
Assess for concomitant pain/discomfort This may restrict respiratory
2. Verbalize awareness of 2. Verbalized awareness of
effort
causative factors causative factors
Suction airway as needed To clear secretions
Elevate the head of bed and/or have the To promote physiological and
client sit up in a chair, as appropriate psychological ease of maximal
inspiration
Encourage slower/deeper respirations, use To assist the client in “taking
of pursed-lip technique, and so on control” of the situation
Monitor pulse oximetry, as indicated To verify
maintenance/improvement in
O2 saturation
Note development of fever Fever within the first 24 hr after
surgery is frequently due to
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 1
atelectasis. Temperature
elevation within the 5th or 10th
postoperative day usually
indicates a wound or systemic.
Maintain patent airway by positioning, Airway obstruction impedes
suctioning, use of airway adjuncts ventilation impairing gas
exchange.
Administer supplemental oxygen nasal Maximizes available oxygen,
cannula, partial rebreathing mask, or high- especially while ventilation is
humidity face mask, as indicated. reduced because of anesthetic,
depression, or pain, and during
period of compensatory
physiological shift of circulation
to remaining functional alveolar
Collaboration units.
Assist with/review results of necessary To diagnose the
testing presence/severity of lung
diseases
For management of underlying
Administer oxygen at lowest concentration pulmonary condition,
indicated and prescribed respiratory respiratory distress, or cyanosis
medications
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 2
You might also like
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument8 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care Plansmonisha100% (2)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansjamieboyRN87% (62)
- WizardryDocument20 pagesWizardryey100% (3)
- Clinical Case Scenario 6Document17 pagesClinical Case Scenario 6Sean Menard Flores100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternReichelle Perlas62% (13)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Clinical OphthalmologyDocument357 pagesClinical OphthalmologyAnonymous 0WDdDLGg100% (3)
- SPARQ Info For ClubsDocument5 pagesSPARQ Info For Clubsdnutter012576No ratings yet
- Elementary Present Simple ExercisesDocument7 pagesElementary Present Simple ExercisesMaria Jesus Martinez MorenoNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Ncps FinalDocument13 pagesCase Pres Ncps FinalMariejoy YadaoNo ratings yet
- Viray, Messiah Jezreel: NCP #3 For RHDDocument3 pagesViray, Messiah Jezreel: NCP #3 For RHDJezzy VeeNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationDocument4 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationVanessa Charlotte LagunayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- NCP Copd FinalDocument3 pagesNCP Copd FinalGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP For Scenario BreathingDocument4 pagesNCP For Scenario Breathingmy moznNo ratings yet
- NCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceDocument8 pagesNCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceWyen Cabatbat100% (2)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPErica Denice CastilloNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Taken As FollowsDocument10 pagesVital Signs Taken As FollowsKyle AndrewNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternPaolo Anthony GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Actual - NCP. PT AgnoDocument2 pagesActual - NCP. PT AgnoKate WeyganNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnossis Scientific Basis Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnossis Scientific Basis Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentPamela laquindanumNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug StudyDocument7 pagesNCP and Drug StudyKirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Short TermDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Short TermKristine Young100% (1)
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Requirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaDocument7 pagesRequirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- PNNCPDocument2 pagesPNNCPJacky BrightNo ratings yet
- NCP PcapDocument2 pagesNCP PcapKenj Pereña100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument19 pagesNursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationZIANAH JOY FAMYNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT NCPDocument4 pagesASSESSMENT NCPjana manaloNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Plan of Care/Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvlatuationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Plan of Care/Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvlatuationgoyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Pedia)Document5 pagesNursing Care Plan (Pedia)JA BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElla EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Bautista - 3 Way Bottle SystemDocument4 pagesBautista - 3 Way Bottle SystemKatherine BautistaNo ratings yet
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessement Diagnosis Goals and Desired Outcomes Nursing Intervention Implementation EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessement Diagnosis Goals and Desired Outcomes Nursing Intervention Implementation EvaluationJoshua Selwyn SalazarNo ratings yet
- Vii. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Prioritization SignificanceDocument7 pagesVii. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Prioritization SignificanceMarichu Bajado0% (1)
- NCP For BronchitisDocument2 pagesNCP For BronchitisJefherrson Nericua Jemilo50% (2)
- Name: Mr. M AGE: 62 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Persistent Cough Admitting/Working Diagnosis: PnuemoniaDocument3 pagesName: Mr. M AGE: 62 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Persistent Cough Admitting/Working Diagnosis: PnuemoniaMae Therese B. MAGNONo ratings yet
- "She Can't Breathe Well Especially During Episodes of Spasms" As Verbalized byDocument2 pages"She Can't Breathe Well Especially During Episodes of Spasms" As Verbalized byCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis PneumoniaDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis PneumoniaPasa ShresthaNo ratings yet
- NUR 103A RLE Learning Activity - PneumothoraxDocument8 pagesNUR 103A RLE Learning Activity - PneumothoraxLaica & AivanNo ratings yet
- Cap Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesCap Nursing Care PlanCharlene Grace ReginoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute BronchitisDocument9 pagesNCP Acute BronchitisCarl Simon CalingacionNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short TermDocument7 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short TermOUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Actaul Drug StudyDocument2 pagesActaul Drug Studyjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Pulmo Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesPulmo Nursing Care PlanVincent RoyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledPie CanapiNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embol-WPS OfficeDocument49 pagesPulmonary Embol-WPS OfficeBryan BuendiaNo ratings yet
- NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP For PneumoniaLeogalvez BedanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- 2 Assisting Clients To Use Incentive Spirometer DosdosDocument3 pages2 Assisting Clients To Use Incentive Spirometer DosdosBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- 1-Deep Breathing and Cough Exercises - DosdosDocument6 pages1-Deep Breathing and Cough Exercises - DosdosBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- 1ST SceneSpanish Tried To Get St. Michael To OzamisDocument2 pages1ST SceneSpanish Tried To Get St. Michael To OzamisBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- 1 Quarter Reflection and 2 Quarter GoalsDocument2 pages1 Quarter Reflection and 2 Quarter GoalsBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Endorsement NotesDocument2 pagesEndorsement NotesBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Summative Assessment Answer SheetDocument1 page1st Quarter Summative Assessment Answer SheetBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Wound Irrigation DefinitionDocument3 pagesWound Irrigation DefinitionBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology: Nursing Health Assessment IDocument2 pagesMSU-Iligan Institute of Technology: Nursing Health Assessment IBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- 2nd Appraisal Exam DosdosDocument5 pages2nd Appraisal Exam DosdosBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of Systems: Patient's Name / Room No. - 1Document3 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of Systems: Patient's Name / Room No. - 1Bianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Evaluator/Signature: - GradeDocument3 pagesName: - Date: - Evaluator/Signature: - GradeBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Evaluator/Signature: - GradeDocument7 pagesName: - Date: - Evaluator/Signature: - GradeBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Changing A Dry Sterile DressingDocument6 pagesChanging A Dry Sterile DressingBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Module 3: The Web and The Internet: College of Computer and Information SciencesDocument9 pagesModule 3: The Web and The Internet: College of Computer and Information SciencesBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Applying A Wet-To-dry DressingDocument4 pagesApplying A Wet-To-dry DressingBianca Mikaela Dosdos0% (1)
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- WSC - BSBFIA401 SD Asset Register Worksheet V 1.0Document6 pagesWSC - BSBFIA401 SD Asset Register Worksheet V 1.0Gursheen KaurNo ratings yet
- We Will Rock YouDocument1 pageWe Will Rock YouMontseNANo ratings yet
- How To Introduce Yourself ProfessionallyDocument22 pagesHow To Introduce Yourself ProfessionallyAufar yodha kazhimiNo ratings yet
- Is Yom Haatzmaut Worth A Hallel?: Rabbi Yitzchak TwerskyDocument4 pagesIs Yom Haatzmaut Worth A Hallel?: Rabbi Yitzchak Twerskyoutdash2No ratings yet
- Top 5 Customer ComplaintsDocument2 pagesTop 5 Customer ComplaintsNasir BukhariNo ratings yet
- Chapter I: Executive SummaryDocument12 pagesChapter I: Executive SummaryEllaiza Lopez100% (1)
- Agra Case DigestDocument18 pagesAgra Case DigestCarla Virtucio50% (2)
- UMT TriboLab Mechanical Tester and Tribometer-B1002 RevA2-Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesUMT TriboLab Mechanical Tester and Tribometer-B1002 RevA2-Brochure PDFcatalineuuNo ratings yet
- Francesco Petrarch 1304-1374: To Be Able To Say How Much You Love Is To Love But Little."Document1 pageFrancesco Petrarch 1304-1374: To Be Able To Say How Much You Love Is To Love But Little."JongJin ParkNo ratings yet
- Applied For The Post Of: PGT/TGT English Curriculum Vitae Roopali AroraDocument6 pagesApplied For The Post Of: PGT/TGT English Curriculum Vitae Roopali AroraRahul SaraswatNo ratings yet
- 1) Politics - Gilles Deleuze & Claire ParnetDocument2 pages1) Politics - Gilles Deleuze & Claire Parnetrayrod614No ratings yet
- Contoh Retaining WallDocument19 pagesContoh Retaining WallAndre SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Oracle Financial Services Software: Management Strategy and Key Highlights of FY20Document13 pagesOracle Financial Services Software: Management Strategy and Key Highlights of FY20Jeet SinghNo ratings yet
- TRB Answer KeyDocument70 pagesTRB Answer KeyVskm Nagarajan MuthuragavanNo ratings yet
- IITE Affiliated Colleges 2021Document24 pagesIITE Affiliated Colleges 2021riju nairNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Role of Imagination in Narrative Construction-2Document21 pages1.1 The Role of Imagination in Narrative Construction-2RainforestLeadership MccaNo ratings yet
- Familylifeeducation CEJERDocument8 pagesFamilylifeeducation CEJERSHABRINA WIDAD NAZIHAH 2021No ratings yet
- Meaning and Evolution of EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesMeaning and Evolution of EntrepreneurshipAnurag AllaNo ratings yet
- Vintage Material 1Document85 pagesVintage Material 1api-19940859No ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN IN General Physics 1 CO1Document8 pagesLESSON PLAN IN General Physics 1 CO1jmym0902No ratings yet
- FMEA10 Sample PagesDocument24 pagesFMEA10 Sample Pageswy1suwirjaNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus - Q2 - Week 1 - 4Document65 pagesBasic Calculus - Q2 - Week 1 - 4Venice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet
- Godel Escher Bach Ebook ItaDocument4 pagesGodel Escher Bach Ebook ItaJulie0% (1)
- APA Jamii Plus Family Medical Cover BrochureDocument8 pagesAPA Jamii Plus Family Medical Cover BrochureADANARABOW100% (1)
- Implicit DifferentiationDocument12 pagesImplicit DifferentiationNaitsirc UluputipanNo ratings yet
- The Gratitude That Endears Us To God: Indigenous Peoples' SundayDocument4 pagesThe Gratitude That Endears Us To God: Indigenous Peoples' SundaycharissamacNo ratings yet