Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital Adult IV Medication Monograph
Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital Adult IV Medication Monograph
Uploaded by
Rafiq EsufzaeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Upper Face BotoxDocument32 pagesUpper Face Botoxyaseer arafat67% (3)
- Teach ManualDocument78 pagesTeach ManualShouvik DebnathNo ratings yet
- SOP For Administration IV InjectionDocument22 pagesSOP For Administration IV InjectionLimYiNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate 10% Emergency MedicationDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate 10% Emergency MedicationRafiq Esufzae0% (1)
- Pedoman Obat High AlertDocument6 pagesPedoman Obat High AlertErvinaOctavianiNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate 10 Injection B.P DR 1433675212243Document2 pagesCalcium Gluconate 10 Injection B.P DR 1433675212243Ayash Kant HotaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate ANMF2.0 20220311Document6 pagesCalcium Gluconate ANMF2.0 20220311shashiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudyBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Dosage PlusDocument8 pagesCalcium Gluconate Dosage PlusJaved ArifNo ratings yet
- 10% W/V Calcium Gluconate Inj.: B - BraunDocument2 pages10% W/V Calcium Gluconate Inj.: B - BraunFatma HossamNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate 10 PercentDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate 10 PercentEtika Tunjung KencanaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate-Calcium Gluconate Injection, Solution HF Acquisition Co LLC, Dba HealthfirstDocument9 pagesCalcium Gluconate-Calcium Gluconate Injection, Solution HF Acquisition Co LLC, Dba HealthfirstLalrinchhanaNo ratings yet
- Gel A PotDocument3 pagesGel A PotGela PielagoNo ratings yet
- Acute Treatment of Hypocalcaemia (Adults)Document2 pagesAcute Treatment of Hypocalcaemia (Adults)Ahed WarwarNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML SyringeDocument2 pagesSodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML SyringeHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- SyntocinonDocument2 pagesSyntocinonDebarghya MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconat (Ca Gluconas)Document3 pagesCalcium Gluconat (Ca Gluconas)nurchandraNo ratings yet
- Calcium Chloride: Additional InformationDocument4 pagesCalcium Chloride: Additional InformationnurchandraNo ratings yet
- Calcitriol, Calcium Carbonate and Zinc Capsules Calzem CompositionDocument5 pagesCalcitriol, Calcium Carbonate and Zinc Capsules Calzem CompositionAnjali MongaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)Document3 pagesCalcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)govind_soni_15No ratings yet
- Drug Study:: Name: Maria Chrislyn M. Genorga Yr - Sec: BSN 2ADocument2 pagesDrug Study:: Name: Maria Chrislyn M. Genorga Yr - Sec: BSN 2AVic Intia PaaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Complete Drug StudyDocument239 pagesComplete Drug StudyRPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit0% (1)
- TreatmentDocument2 pagesTreatmentJaymark PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Management of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticleDocument4 pagesManagement of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticlealeNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT of DkADocument10 pagesMANAGEMENT of DkAAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Check ListDocument12 pagesChemotherapy Check ListEsraa ShawkyNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument8 pagesSodium BicarbonateRaf AylaniNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Use of Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesGuidelines For The Use of Potassium ChlorideSallie NaomiNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Description: Nutriflex Peri: Each Litre Contains Amino Acids (15 Different Laevorotatory Amino Acids andDocument5 pagesDescription: Nutriflex Peri: Each Litre Contains Amino Acids (15 Different Laevorotatory Amino Acids andgregory johnNo ratings yet
- Ascites, SBP, Encephlopathy 2Document78 pagesAscites, SBP, Encephlopathy 2Rida AkramNo ratings yet
- Renal HaemodialysisDocument7 pagesRenal HaemodialysisRicky HeavenNo ratings yet
- Isomalt FormulationDocument5 pagesIsomalt Formulationanand1540No ratings yet
- Nineveh University - College of Nursing: Intravenous (Solutions) FluidsDocument3 pagesNineveh University - College of Nursing: Intravenous (Solutions) Fluidsyounes.khalafNo ratings yet
- Julius Caesar Francia BS-N4ADocument37 pagesJulius Caesar Francia BS-N4ApauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument5 pagesAcute Renal FailureSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Syok - Anzak Akbar Andin PangeDocument34 pagesSyok - Anzak Akbar Andin PangeannisazakirohNo ratings yet
- 0702-7-45wvpotassiumchlorideinj 2Document2 pages0702-7-45wvpotassiumchlorideinj 2Aleksandar DimovskiNo ratings yet
- 005VIN06EDocument8 pages005VIN06Enavid rostamiNo ratings yet
- Chief Complaint: Body WeaknessDocument13 pagesChief Complaint: Body WeaknessJohn MaglinteNo ratings yet
- HypocalcemiaDocument12 pagesHypocalcemiaKrinessa May100% (1)
- Tavanic 5mgmlsolution SPCDocument16 pagesTavanic 5mgmlsolution SPCanchizNo ratings yet
- HeparinDocument6 pagesHeparinFrank Asiedu AduseiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological SheetDocument22 pagesPharmacological SheetScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument8 pagesGeneric NameRosaree Mae PantojaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous FluidDocument2 pagesIntravenous FluidhanyakleinNo ratings yet
- HyperkalaemiaDocument6 pagesHyperkalaemiaSSNo ratings yet
- HypocalcemiaDocument8 pagesHypocalcemiaTheresa MendoncaNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument1 pageAmlodipineMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Document2 pagesMicro K (Potassium Chloride)ENo ratings yet
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Document4 pagesHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- Endoxan: List of ExcipientsDocument4 pagesEndoxan: List of ExcipientsBashyam RamNo ratings yet
- Iv FluidsDocument2 pagesIv FluidsNaomi VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageCalcium GluconatebacnatjoyNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Hypo and Hypercalcemia FC For StudentsDocument20 pagesTreatment of Hypo and Hypercalcemia FC For Studentsjamil aoudeNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Bullets Part IIDocument11 pagesMedical Surgical Bullets Part IIOmelhayr Serad100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Flucloxacillinaftcapssoln PDFDocument11 pagesFlucloxacillinaftcapssoln PDFLorna TupaeaNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalaemia GuidelinesDocument27 pagesHyperkalaemia GuidelinesJean HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone ResistantDocument5 pagesCeftriaxone ResistantRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Case Report Consent FormDocument2 pagesCase Report Consent FormRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Aynsa 1986Document1 pageAynsa 1986Rafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Clinical/Scientific Notes: The Risk of Abducens Palsy After Diagnostic Lumbar PunctureDocument7 pagesClinical/Scientific Notes: The Risk of Abducens Palsy After Diagnostic Lumbar PunctureRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate 10% Emergency MedicationDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate 10% Emergency MedicationRafiq Esufzae0% (1)
- Atropine Sulphate 1mg/1ml Emergency MedicationDocument2 pagesAtropine Sulphate 1mg/1ml Emergency MedicationRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Intravenous and Intramuscular InjectionsDocument12 pagesIntravenous and Intramuscular Injectionsshubham rathodNo ratings yet
- CPRE Predictor ExamDocument29 pagesCPRE Predictor ExamRommel Bucasas Garcia100% (1)
- Funda Skills ProceduresDocument34 pagesFunda Skills Proceduresjericho obiceNo ratings yet
- Package Insert Fluarix QuadrivalentDocument30 pagesPackage Insert Fluarix QuadrivalentJohn UebersaxNo ratings yet
- Trigger Point InjectionDocument3 pagesTrigger Point Injectionapi-686289317No ratings yet
- Emt HandbookDocument51 pagesEmt HandbookNiki Cheeru100% (1)
- MgSO4 ChecklistDocument2 pagesMgSO4 ChecklistPAOLA LUZ CRUZNo ratings yet
- Valuable CattleDocument2 pagesValuable CattleGurmeet BrarNo ratings yet
- Routes of Drug AdministrationDocument34 pagesRoutes of Drug AdministrationNa SyaNo ratings yet
- Small Volume ParenteralsDocument29 pagesSmall Volume ParenteralsHamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- General Pharmacology SendDocument272 pagesGeneral Pharmacology Sendthomasarun2009No ratings yet
- Only For: Final Diagnostic ExamDocument8 pagesOnly For: Final Diagnostic ExamAlfred Benjamin CajitaNo ratings yet
- Birds and Exotics - MCannon PDFDocument42 pagesBirds and Exotics - MCannon PDFAl OyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Sheep and Goat Flock HealthDocument60 pagesChapter 9 - Sheep and Goat Flock Healthayiq_utariNo ratings yet
- NeuroesferasDocument17 pagesNeuroesferasLeilane GlienkeNo ratings yet
- Wilde 2017Document9 pagesWilde 2017sithamastikaNo ratings yet
- The Art of The InjectionDocument87 pagesThe Art of The InjectionAnupamaNo ratings yet
- Checklist For IV Injection - StudentDocument2 pagesChecklist For IV Injection - Studentmaria hmNo ratings yet
- Ozone TherapyDocument15 pagesOzone Therapyebar86100% (5)
- Evaluation Long-Term Safety Biodegradability Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers (YVOIRE®) Correction Nasolabial Folds Two Multicenter, Prospective, Observational Cohort Studies - Xie, 2022Document11 pagesEvaluation Long-Term Safety Biodegradability Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers (YVOIRE®) Correction Nasolabial Folds Two Multicenter, Prospective, Observational Cohort Studies - Xie, 2022Rafael Autran Cavalcante AraújoNo ratings yet
- 6 - USP Packaging Update StultsDocument26 pages6 - USP Packaging Update StultsMohammed HammedNo ratings yet
- Health Management For Fattening PigsDocument24 pagesHealth Management For Fattening PigsMarwin Navarrete100% (1)
- List Harga ALKES AAMDocument41 pagesList Harga ALKES AAMmarsen100% (1)
- Immediate Newborn CareDocument2 pagesImmediate Newborn CareMaurice Ann MarquezNo ratings yet
- Standards of Good Practice For Spinal Interventional ProceduresDocument20 pagesStandards of Good Practice For Spinal Interventional ProceduresMadyline VictoryaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management 109 (Skills) Medication: Drug Type Description ExamplesDocument9 pagesNursing Care Management 109 (Skills) Medication: Drug Type Description ExamplesJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital Adult IV Medication Monograph
Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital Adult IV Medication Monograph
Uploaded by
Rafiq EsufzaeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital Adult IV Medication Monograph
Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital Adult IV Medication Monograph
Uploaded by
Rafiq EsufzaeCopyright:
Available Formats
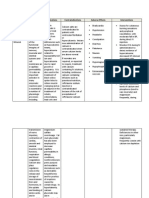
Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital
Adult IV Medication Monograph
Calcium Gluconate 10%
Emergency tray medication – High risk medication
Drug Class Calcium supplement
Available dosage form Injection form - 10ml (Calcium Gluconate – 10%)
Usual Dosing Acute hypocalcaemia: 10-20ml (2.2-4.4mmol)
Fluoride or lead poisoning: 0.3ml/kg (0.07mmol/kg)
Cardiac resuscitation: 7-15ml (1.54-3.3mmol).
Dilution & Preparation Calcium Gluconate Injection can be diluted with glucose 5%
or sodium chloride 0.9%.
It should not be administered at dose more than 2ml/min
(10% calcium gluconate) .
For continuous intravenous infusion, dilute 100 mL of
calcium gluconate 10% in 1 litre of glucose 5% or sodium
chloride 0.9% and give at an initial rate of 50 mL/hour
adjusted according to response.
Administration Intravenous
Dosage adjustment Renal impairement: Use with caution.
Incompatibility Calcium salts can form complexes with many drugs like
amphotericin, ceftriaxone, dobutamine hydrochloride,
prochlorperazine, and tetracyclines.
Dilution into a solution containing bicarbonate, phosphate or
sulfate should be avoided.
Monitoring Monitoring should include heart rate or ECG.
Plasma levels and urinary excretion of calcium should
be monitored when high-dose parenteral calcium is
administered.
Contraindications & Contraindications:
Precautions Hypersensitivity
Patients with severe renal failure;
Patients with hypercalcaemia
Patients with hypercalciuria.
Patients receiving cardiac glycosides.
Co-administration with ceftriaxone.
Repeated or prolonged treatment, including as an
intravenous infusion, in those with impaired renal
function.
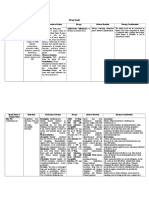
Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital
Adult IV Medication Monograph
Precautions:
In patients receiving ceftriaxone, it can be administered
sequentially one after another if infusion lines at
different sites are used to avoid precipitation.
Solutions containing calcium should be administered
slowly to minimise peripheral vasodilation and cardiac
depression.
Calcium salts are irritant. The infusion site must be
monitored regularly to ensure extravasation injury has
not occurred.
Patients receiving calcium salts should be monitored
carefully to ensure maintenance of correct calcium
balance without tissue deposition.
High Vitamin D intake should be avoided.
Combination with thiazide diuretics may induce
hypercalcaemia as these medicinal products reduce renal
calcium excretion.
Calcium may antagonise the effect of calcium
antagonists (calcium channel blockers).
Clinical considerations Hypocalcemic tetany
Cardiac resuscitation
Acute colic of lead poisoning
Acute fluoride poisoning
Prevention of hypocalcemia after mass transfusion/exchange
transfusion.
Adverse Effects Cardiovascular and other systemic undesirable effects are
likely to occur from intravenous overdose or too rapid
intravenous injection.
Cardiac disorders
Bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmia.
Hypotension, vasodilatation, circulatory collapse (possibly
fatal), flushing, mainly after too rapid injection.
Nausea, vomiting.
Heat sensations, sweating.
Calcinosis cutis, possibly followed by skin ablation and
necrosis. Reddening of skin, burning sensation or pain
during intravenous injection may indicate accidental
perivascular injection, which may lead to tissue necrosis.
Pregnancy Pregnancy
Department of Medicine, MTI, Khyber Teaching Hospital
Adult IV Medication Monograph
Calcium Gluconate Injection BP should not be used during
pregnancy unless clearly indicated.
The administered dose should be carefully calculated, and
the serum calcium level regularly evaluated in order to avoid
hypercalcaemia, which may be deleterious for the foetus.
Calcium is excreted in breast milk. A decision must be made
whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to
discontinue/abstain from Calcium Gluconate Injection BP
therapy taking into account the benefit of breast feeding for
the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman.
You might also like
- Upper Face BotoxDocument32 pagesUpper Face Botoxyaseer arafat67% (3)
- Teach ManualDocument78 pagesTeach ManualShouvik DebnathNo ratings yet
- SOP For Administration IV InjectionDocument22 pagesSOP For Administration IV InjectionLimYiNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate 10% Emergency MedicationDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate 10% Emergency MedicationRafiq Esufzae0% (1)
- Pedoman Obat High AlertDocument6 pagesPedoman Obat High AlertErvinaOctavianiNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate 10 Injection B.P DR 1433675212243Document2 pagesCalcium Gluconate 10 Injection B.P DR 1433675212243Ayash Kant HotaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate ANMF2.0 20220311Document6 pagesCalcium Gluconate ANMF2.0 20220311shashiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudyBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Dosage PlusDocument8 pagesCalcium Gluconate Dosage PlusJaved ArifNo ratings yet
- 10% W/V Calcium Gluconate Inj.: B - BraunDocument2 pages10% W/V Calcium Gluconate Inj.: B - BraunFatma HossamNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate 10 PercentDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate 10 PercentEtika Tunjung KencanaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate-Calcium Gluconate Injection, Solution HF Acquisition Co LLC, Dba HealthfirstDocument9 pagesCalcium Gluconate-Calcium Gluconate Injection, Solution HF Acquisition Co LLC, Dba HealthfirstLalrinchhanaNo ratings yet
- Gel A PotDocument3 pagesGel A PotGela PielagoNo ratings yet
- Acute Treatment of Hypocalcaemia (Adults)Document2 pagesAcute Treatment of Hypocalcaemia (Adults)Ahed WarwarNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML SyringeDocument2 pagesSodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML SyringeHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- SyntocinonDocument2 pagesSyntocinonDebarghya MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconat (Ca Gluconas)Document3 pagesCalcium Gluconat (Ca Gluconas)nurchandraNo ratings yet
- Calcium Chloride: Additional InformationDocument4 pagesCalcium Chloride: Additional InformationnurchandraNo ratings yet
- Calcitriol, Calcium Carbonate and Zinc Capsules Calzem CompositionDocument5 pagesCalcitriol, Calcium Carbonate and Zinc Capsules Calzem CompositionAnjali MongaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)Document3 pagesCalcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)govind_soni_15No ratings yet
- Drug Study:: Name: Maria Chrislyn M. Genorga Yr - Sec: BSN 2ADocument2 pagesDrug Study:: Name: Maria Chrislyn M. Genorga Yr - Sec: BSN 2AVic Intia PaaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Complete Drug StudyDocument239 pagesComplete Drug StudyRPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit0% (1)
- TreatmentDocument2 pagesTreatmentJaymark PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Management of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticleDocument4 pagesManagement of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticlealeNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT of DkADocument10 pagesMANAGEMENT of DkAAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Check ListDocument12 pagesChemotherapy Check ListEsraa ShawkyNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument8 pagesSodium BicarbonateRaf AylaniNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Use of Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesGuidelines For The Use of Potassium ChlorideSallie NaomiNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Description: Nutriflex Peri: Each Litre Contains Amino Acids (15 Different Laevorotatory Amino Acids andDocument5 pagesDescription: Nutriflex Peri: Each Litre Contains Amino Acids (15 Different Laevorotatory Amino Acids andgregory johnNo ratings yet
- Ascites, SBP, Encephlopathy 2Document78 pagesAscites, SBP, Encephlopathy 2Rida AkramNo ratings yet
- Renal HaemodialysisDocument7 pagesRenal HaemodialysisRicky HeavenNo ratings yet
- Isomalt FormulationDocument5 pagesIsomalt Formulationanand1540No ratings yet
- Nineveh University - College of Nursing: Intravenous (Solutions) FluidsDocument3 pagesNineveh University - College of Nursing: Intravenous (Solutions) Fluidsyounes.khalafNo ratings yet
- Julius Caesar Francia BS-N4ADocument37 pagesJulius Caesar Francia BS-N4ApauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument5 pagesAcute Renal FailureSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Syok - Anzak Akbar Andin PangeDocument34 pagesSyok - Anzak Akbar Andin PangeannisazakirohNo ratings yet
- 0702-7-45wvpotassiumchlorideinj 2Document2 pages0702-7-45wvpotassiumchlorideinj 2Aleksandar DimovskiNo ratings yet
- 005VIN06EDocument8 pages005VIN06Enavid rostamiNo ratings yet
- Chief Complaint: Body WeaknessDocument13 pagesChief Complaint: Body WeaknessJohn MaglinteNo ratings yet
- HypocalcemiaDocument12 pagesHypocalcemiaKrinessa May100% (1)
- Tavanic 5mgmlsolution SPCDocument16 pagesTavanic 5mgmlsolution SPCanchizNo ratings yet
- HeparinDocument6 pagesHeparinFrank Asiedu AduseiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological SheetDocument22 pagesPharmacological SheetScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument8 pagesGeneric NameRosaree Mae PantojaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous FluidDocument2 pagesIntravenous FluidhanyakleinNo ratings yet
- HyperkalaemiaDocument6 pagesHyperkalaemiaSSNo ratings yet
- HypocalcemiaDocument8 pagesHypocalcemiaTheresa MendoncaNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument1 pageAmlodipineMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Document2 pagesMicro K (Potassium Chloride)ENo ratings yet
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Document4 pagesHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- Endoxan: List of ExcipientsDocument4 pagesEndoxan: List of ExcipientsBashyam RamNo ratings yet
- Iv FluidsDocument2 pagesIv FluidsNaomi VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageCalcium GluconatebacnatjoyNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Hypo and Hypercalcemia FC For StudentsDocument20 pagesTreatment of Hypo and Hypercalcemia FC For Studentsjamil aoudeNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Bullets Part IIDocument11 pagesMedical Surgical Bullets Part IIOmelhayr Serad100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Flucloxacillinaftcapssoln PDFDocument11 pagesFlucloxacillinaftcapssoln PDFLorna TupaeaNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalaemia GuidelinesDocument27 pagesHyperkalaemia GuidelinesJean HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone ResistantDocument5 pagesCeftriaxone ResistantRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Case Report Consent FormDocument2 pagesCase Report Consent FormRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Aynsa 1986Document1 pageAynsa 1986Rafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Clinical/Scientific Notes: The Risk of Abducens Palsy After Diagnostic Lumbar PunctureDocument7 pagesClinical/Scientific Notes: The Risk of Abducens Palsy After Diagnostic Lumbar PunctureRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate 10% Emergency MedicationDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate 10% Emergency MedicationRafiq Esufzae0% (1)
- Atropine Sulphate 1mg/1ml Emergency MedicationDocument2 pagesAtropine Sulphate 1mg/1ml Emergency MedicationRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- Intravenous and Intramuscular InjectionsDocument12 pagesIntravenous and Intramuscular Injectionsshubham rathodNo ratings yet
- CPRE Predictor ExamDocument29 pagesCPRE Predictor ExamRommel Bucasas Garcia100% (1)
- Funda Skills ProceduresDocument34 pagesFunda Skills Proceduresjericho obiceNo ratings yet
- Package Insert Fluarix QuadrivalentDocument30 pagesPackage Insert Fluarix QuadrivalentJohn UebersaxNo ratings yet
- Trigger Point InjectionDocument3 pagesTrigger Point Injectionapi-686289317No ratings yet
- Emt HandbookDocument51 pagesEmt HandbookNiki Cheeru100% (1)
- MgSO4 ChecklistDocument2 pagesMgSO4 ChecklistPAOLA LUZ CRUZNo ratings yet
- Valuable CattleDocument2 pagesValuable CattleGurmeet BrarNo ratings yet
- Routes of Drug AdministrationDocument34 pagesRoutes of Drug AdministrationNa SyaNo ratings yet
- Small Volume ParenteralsDocument29 pagesSmall Volume ParenteralsHamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- General Pharmacology SendDocument272 pagesGeneral Pharmacology Sendthomasarun2009No ratings yet
- Only For: Final Diagnostic ExamDocument8 pagesOnly For: Final Diagnostic ExamAlfred Benjamin CajitaNo ratings yet
- Birds and Exotics - MCannon PDFDocument42 pagesBirds and Exotics - MCannon PDFAl OyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Sheep and Goat Flock HealthDocument60 pagesChapter 9 - Sheep and Goat Flock Healthayiq_utariNo ratings yet
- NeuroesferasDocument17 pagesNeuroesferasLeilane GlienkeNo ratings yet
- Wilde 2017Document9 pagesWilde 2017sithamastikaNo ratings yet
- The Art of The InjectionDocument87 pagesThe Art of The InjectionAnupamaNo ratings yet
- Checklist For IV Injection - StudentDocument2 pagesChecklist For IV Injection - Studentmaria hmNo ratings yet
- Ozone TherapyDocument15 pagesOzone Therapyebar86100% (5)
- Evaluation Long-Term Safety Biodegradability Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers (YVOIRE®) Correction Nasolabial Folds Two Multicenter, Prospective, Observational Cohort Studies - Xie, 2022Document11 pagesEvaluation Long-Term Safety Biodegradability Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers (YVOIRE®) Correction Nasolabial Folds Two Multicenter, Prospective, Observational Cohort Studies - Xie, 2022Rafael Autran Cavalcante AraújoNo ratings yet
- 6 - USP Packaging Update StultsDocument26 pages6 - USP Packaging Update StultsMohammed HammedNo ratings yet
- Health Management For Fattening PigsDocument24 pagesHealth Management For Fattening PigsMarwin Navarrete100% (1)
- List Harga ALKES AAMDocument41 pagesList Harga ALKES AAMmarsen100% (1)
- Immediate Newborn CareDocument2 pagesImmediate Newborn CareMaurice Ann MarquezNo ratings yet
- Standards of Good Practice For Spinal Interventional ProceduresDocument20 pagesStandards of Good Practice For Spinal Interventional ProceduresMadyline VictoryaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management 109 (Skills) Medication: Drug Type Description ExamplesDocument9 pagesNursing Care Management 109 (Skills) Medication: Drug Type Description ExamplesJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet