Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Year 9 BUSINESS Unit 1 Knowledge Organiser
Year 9 BUSINESS Unit 1 Knowledge Organiser
Uploaded by
Irenita gacha verseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Year 9 BUSINESS Unit 1 Knowledge Organiser
Year 9 BUSINESS Unit 1 Knowledge Organiser
Uploaded by
Irenita gacha verseCopyright:
Available Formats
AQA GCSE Business Studies. Unit 1: Business In The Real World Knowledge Organiser.
Goods, Services. Needs & Wants Business Ownership Structures Public Limited Companies How can a business measure success?
• Goods – physical (tangible) products such as burgers, cars, laptops. Sole Trader •Profit, number of stores, customer satisfaction, number
Advantages Disadvantages
• Services – non-physical items such as hairdressing, NHS, banks, of customers, reputation, number of items sold, market
insurance. Advantages Disadvantages •Limited liability. •It is expensive to set up a Plc, share.
• Needs – essential for us to live. •You make all the decisions. •Unlimited liability. •Can be easier to raise capital at least £50,000 of share capital
• Wants – things which we desire. (money) as the business can has to be available and legal Factors influencing business location
•You have total control – you •Access to capital (money) – can
decide on the direction of the be harder to get loans as there is release new shares for individu- paperwork needs to be pro- •Proximity to target market, cost, availability of raw
Four Factors Of Production als to purchase – anyone can duced. materials, availability of labour, infrastructure in area,
business. only one person – limits the op-
• Land - A business needs land or a building. purchase shares in a PLC. •The company has to publish its competition.
•You keep all the profits. portunities for growth.
• Labour - A business needs workers. •May not have skills in every •Usually well-known organisa- accounts every year, and these
•Can offer flexibility – e.g. work-
• Capital - A business needs money to start and run. tions with a good reputation, are available for the general Business Plans
ing hours. area to run business as well as it
• Enterprise - An entrepreneur is needed to bring it all together and run that makes it easier for them to public and competitors to see. Main sections: personal details, mission statement, aims
•You can keep your business could.
raise finance. Banks are more •Unwanted takeovers are possi- and objectives, details of product/service, market
the business. affairs private –you don’t need •If you don’t work you don’t
willing to lend to large, estab- ble as shares can be bought by research, production details, expected costs and profit,
to publish the accounts. earn (sickness, holidays etc).
lished companies. anyone; the shareholder who financial documents (break even, cash flow forecast,
Three Business Sectors •Easy to set up – no complicated
• Primary - Extraction of raw materials e.g farmer, coal mining. owns more than half the shares balance sheet, income statement).
• Secondary - Turing the raw materials extracted at the primary stage controls the business.
into finished goods. Partnership Why bother creating a business plan?
• Tertiary - Provide a service and sell the goods and services e.g. NHS, •Forces the owner to think carefully about what the
•Unlimited liability – if the business fails, you not only lose the
shops. Advantages Disadvantages business is going to do and what resources are needed.
money you invested, but your personal possessions can also be
•Extra capital – can invest own savings or if •Unlimited liability •Allows them to calculate how much capital is needed to
taken to repay any debt the business has.
Characteristics of an entrepreneur start the business.
applying for loans enables then to gain a •Disagreements – •Limited liability – you only lose the money that you invested. If
Entrepreneur - someone who takes a risk and starts a business. higher loan - more collateral to offer). may not always want •It is needed to convince banks and investors that the
the business fails and has debts, your personal possessions are
Determination, passion, creative, motivated, takes risk, organised •Different partners can bring different the same thing. business is viable. Without a business plan, banks will not
NOT at risk of being taken.
persistent. invest.
skills. •Profit needs to be
•You can keep your business affairs private shared. •If the idea is a bad idea, planning should help the owner
Aims and Objectives
Objectives of an entrepreneur (reasons for starting a business) –you don’t need to publish the accounts. or financial investors realise this – saves wasting time and
•Aim - An aim is general and is what a business hopes to achieve
• Be their own boss. as a result of its work
money.
• Flexible working hours. e.g. survive, maximize profit, grow, increase market share,
Private Limited Company (LTD) Expanding a business
• Pursue hobby/interest. improve customer satisfaction, be more ethical, increase
• Earn more money. Advantages Disadvantages Organic (internal) growth: franchising, open new stores,
shareholder dividends, break even.
• Identified a gap in the market. embrace e-commerce, outsource, develop new products.
•Limited liability. •More legal for- •Objectives - Objectives state in more detail how an aim will be
• Dissatisfied with current job. •Can be easier to raise capital (money) as the malities than achieved. Objectives should be SMART.
External (inorganic) growth: merger & takeovers.
business can release new shares for individuals sole trader and Specific, Measurable, Achievable Realistic, Time based.
Why do businesses face a constantly changing environment? to purchase – new shareholders usually have to partnership. E.g. To grow by opening 20 new stores within the next two
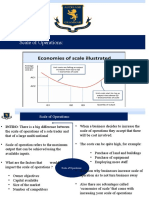
(EXTERNAL INFLUENCES ON A BUSINESS) Economies of scale (the benefits a business gets by
be approved by existing shareholders in a LTD. years.
• Political growing):
•Can’t be taken over (unlike PLC), as sharehold-
• Environmental Purchasing economies of scale, marketing economies of
ers must agree the sale of shares to others.
• Social (trends changing) scale, managerial economies of scale, financial economies
•Different shareholders could bring knowledge
of scale, technical economies of scale.
• Technology Why does a business have aims and objectives?
• Legislation (laws) •To co-ordinate business activity and give a sense of direction –
Diseconomies of scale (the negatives a business can
• Economy (unemployment, interest rates) everyone knows what they should be aiming for.
experience by growing in size):
• Competitors Unit 1 Formulas •Gives a common goal for workforce – can help to motivate and
•Sales Revenue = selling price per item x number sold Poor communication, lack of motivation, loss of direction
make a more efficient and productive workforce.
•Total variable costs = variable cost per item x number sold and co-ordination.
Stakeholders (anyone who is interested or affected by what a business •Helps with decision making – all decisions made by
does). •Total costs = fixed costs + total variable costs departments should help to work towards the business’s aims
• Owners, employees, customers, local community, suppliers, •Profit = sales revenue – total costs and objectives.
government etc. •Cost per unit = total costs ÷ number sold •Act as a yardstick (benchmark) to measure performance –
• Stakeholders sometimes have conflicting views and can influence the •Percentage change = change (difference) ÷ original amount *100 have we done/achieved the objectives. Business can investigate
decisions a business makes. successes or failures and learn from this.
You might also like
- Wells Fargo Everyday Checking: Important Account InformationDocument4 pagesWells Fargo Everyday Checking: Important Account InformationPatricia100% (2)
- Shinola Case Study Questions - Seminar 8 BrandingDocument4 pagesShinola Case Study Questions - Seminar 8 Brandingsilvia100% (1)
- ItcDocument19 pagesItcakshay chothe100% (2)
- Financial Management 1 5Document27 pagesFinancial Management 1 5imrickymaeberdinNo ratings yet
- Financial Management:: Understanding Financial Statements, Taxes, and Cash FlowsDocument102 pagesFinancial Management:: Understanding Financial Statements, Taxes, and Cash FlowsArgem Jay PorioNo ratings yet
- Stakeholders Within Any Business: Stakeholder Group Main Features Most Likely Objectives For The Stakeholder GroupDocument2 pagesStakeholders Within Any Business: Stakeholder Group Main Features Most Likely Objectives For The Stakeholder GroupObert MarongedzaNo ratings yet
- 1.3.3 - Topic 5 - Opportunity Costs and StakeholdersDocument7 pages1.3.3 - Topic 5 - Opportunity Costs and StakeholdersEmperor Saladin100% (1)
- B.arts FridayDocument9 pagesB.arts FridayCatherine Nicole SamsonNo ratings yet
- Nature of BusinessDocument35 pagesNature of Businesssachin rolaNo ratings yet
- Sources of FinanceDocument32 pagesSources of FinanceP RushitaNo ratings yet
- Entrep-Module 2-Part 2Document2 pagesEntrep-Module 2-Part 2Nika MatammuNo ratings yet
- Main Features and Objectives of StakeholdersDocument8 pagesMain Features and Objectives of StakeholdersNha HoangNo ratings yet
- Notebook 1 - Introduction To AccountingDocument4 pagesNotebook 1 - Introduction To AccountingShay MinNo ratings yet
- Business Note 0450Document32 pagesBusiness Note 0450larry wangNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Sources of Finance 2021Document22 pages3.1 Sources of Finance 2021Sahitya AnandNo ratings yet
- Notes in Financial Analysis and ReportingDocument20 pagesNotes in Financial Analysis and ReportingAntonette CallosNo ratings yet
- Business Finance, Needs & Sources.Document23 pagesBusiness Finance, Needs & Sources.Shahannah DOOKHANNo ratings yet
- Business AS NotesDocument114 pagesBusiness AS NotesMohamedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business and Management (IBM) : MC 2019/2020 Week 07bDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Business and Management (IBM) : MC 2019/2020 Week 07b林泳圻No ratings yet
- Environment and MarketDocument39 pagesEnvironment and MarketJoni MurphyNo ratings yet
- Franchise Reviewer 1Document3 pagesFranchise Reviewer 1roselyn cortezNo ratings yet
- Equity PartnershipsDocument3 pagesEquity Partnershipssami ullahNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Cycles and Analysis - Course PresentationDocument53 pagesCash Flow Cycles and Analysis - Course PresentationKoko BarakhianNo ratings yet
- Producer Agent Distributer Wholesale Retail ConsumerDocument3 pagesProducer Agent Distributer Wholesale Retail ConsumerDeon LatchmanNo ratings yet
- 0450 - 1.5 Business Objectives and Stakeholder ObjectivesDocument11 pages0450 - 1.5 Business Objectives and Stakeholder ObjectivesCherylNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document42 pagesLecture 02CaraboNo ratings yet
- Vce PresentationDocument42 pagesVce PresentationWawa RusliNo ratings yet
- EEE 509 L6 EntrepreneushipDocument12 pagesEEE 509 L6 EntrepreneushipAbdulraheem KabaraNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship NotesDocument11 pagesEntrepreneurship NotesKeren Margarette AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Bus PlanDocument4 pagesBus PlanMohamed BanounNo ratings yet
- RVD Business Consultancy IncDocument8 pagesRVD Business Consultancy IncReimon DoblonNo ratings yet
- Writing A Business Plan: Start-Up BriefingDocument4 pagesWriting A Business Plan: Start-Up BriefingTarun MoteeNo ratings yet
- 34.scale of OperationsDocument5 pages34.scale of OperationsAndrei PrunilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Enterprise - The Nature of Business ActivityDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - Enterprise - The Nature of Business ActivityAmour PartekaNo ratings yet
- Opsimise: Augment Operational Efficiency: Round 2: Case StudyDocument6 pagesOpsimise: Augment Operational Efficiency: Round 2: Case StudySIDDHARTH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Yona 1Document25 pagesFinal Exam Yona 1HazemNo ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument48 pagesWorking Capital Managementreal history and series real history and seriesNo ratings yet
- Group 06Document24 pagesGroup 06hathu.newindNo ratings yet
- Opsimise: Augment Operational Efficiency: Team TrifectoDocument6 pagesOpsimise: Augment Operational Efficiency: Team TrifectoSIDDHARTH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Commercial Studies 7101 SPN 21 Year 9 Normal Track - 3 YearsDocument37 pagesCommercial Studies 7101 SPN 21 Year 9 Normal Track - 3 YearsYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Business NotesDocument45 pagesIGCSE Business NotesLin Nandar AungNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument4 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIPYsa belNo ratings yet
- Business Plan ImplementationDocument52 pagesBusiness Plan ImplementationVICENTA SAN FELIPENo ratings yet
- Entrep ReviewerDocument7 pagesEntrep ReviewerJustin JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Powerpuff 1 1Document13 pagesPowerpuff 1 1Karl TristanNo ratings yet
- Dp1 Unit1 StakeholdersDocument13 pagesDp1 Unit1 StakeholdersananditaNo ratings yet
- Internal Scanning: Ag Decision MakerDocument5 pagesInternal Scanning: Ag Decision MakerKhurram Ali SyedNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument161 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIPcremelita malacasNo ratings yet
- Sec Quarter Entrep ReviewerDocument14 pagesSec Quarter Entrep ReviewerSherie Hazzell BasaNo ratings yet
- BM Study Guide HLDocument70 pagesBM Study Guide HLKirsten Dell GayataoNo ratings yet
- MBA 533 Lecture 4 Introduction To Financial AccountingDocument41 pagesMBA 533 Lecture 4 Introduction To Financial AccountingGlentonNo ratings yet
- Organization Management Module 15Document12 pagesOrganization Management Module 15Michelle AJCNNo ratings yet
- Lecturer IntroductoryDocument22 pagesLecturer IntroductoryKo Nay Min AyeNo ratings yet
- Business Management: Chapter 9Document2 pagesBusiness Management: Chapter 9Javier BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Chinhsua 2Document14 pagesChinhsua 20012Nguyễn Văn CôngNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Entrepreneurial MindDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 4 Entrepreneurial MindXOLCHITNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Course OverviewDocument13 pagesEntrepreneurship Course OverviewMarcelo RzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Challenges in The Internal EnvironmentDocument29 pagesLesson 4 - Challenges in The Internal EnvironmentLoslyn LumacangNo ratings yet
- BO - Process of Setting Up A Business enterprise-UNIT 3Document13 pagesBO - Process of Setting Up A Business enterprise-UNIT 3Shiwangi Alind TiwaryNo ratings yet
- Icaew, Valutaion of BusinessDocument4 pagesIcaew, Valutaion of BusinessMujahid ImtiazNo ratings yet
- BCK CH 1Document4 pagesBCK CH 1NOOB GAMER RELOADEDNo ratings yet
- VC Evaluating BusinessDocument14 pagesVC Evaluating BusinessAvanish Nagar 23No ratings yet
- Careers in Finance and Finance Interview PrepDocument14 pagesCareers in Finance and Finance Interview PrepAlyssa HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Start & Run an Internet Research BusinessFrom EverandStart & Run an Internet Research BusinessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Welcome: Vocabulary: StructuresDocument3 pagesWelcome: Vocabulary: StructuresIrenita gacha verseNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. The Variety of Life PDFDocument7 pagesUnit 2. The Variety of Life PDFIrenita gacha verseNo ratings yet
- Guia Pag70 Ud01Document71 pagesGuia Pag70 Ud01Irenita gacha verseNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement 1 U 1Document1 pageReinforcement 1 U 1Irenita gacha verseNo ratings yet
- Islands Contents 5Document4 pagesIslands Contents 5Irenita gacha verseNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. The Organisation of Living ThingsDocument9 pagesUnit 1. The Organisation of Living ThingsIrenita gacha verseNo ratings yet
- BAB 6 Efficient Capital MarketDocument61 pagesBAB 6 Efficient Capital MarketGirl HyukNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Project Synopsis On "Future of India-China Bilateral Trade Relations"Document8 pagesDissertation Project Synopsis On "Future of India-China Bilateral Trade Relations"rohanNo ratings yet
- ABMFABM2 q2 Mod2 FundOfAcctng Taxation-Corrected2Document45 pagesABMFABM2 q2 Mod2 FundOfAcctng Taxation-Corrected2Willie Montes Poblacion Jr.No ratings yet
- Instructions ITR2 AY2021 22Document125 pagesInstructions ITR2 AY2021 22Help Tubestar CrewNo ratings yet
- Inspection Rubber BoatDocument1 pageInspection Rubber Boatyusro romadhoniNo ratings yet
- StatementOfAccount 9Document4 pagesStatementOfAccount 9brapayne4No ratings yet
- Green Marketing - NotesDocument4 pagesGreen Marketing - NotesAyush Mittal100% (1)
- Social Return On Investment Study in ESAF Microfinance, Kerala, IndiaDocument78 pagesSocial Return On Investment Study in ESAF Microfinance, Kerala, IndiaJaimoenNo ratings yet
- 2016 - Tang - Self-Esteem, Financial Knowledge and Financial Behavior - RecursoDocument13 pages2016 - Tang - Self-Esteem, Financial Knowledge and Financial Behavior - RecursoZilma DalaNo ratings yet
- Sample-Global-Plywood Manufacturing Plant Project Report-SyndicatedDocument75 pagesSample-Global-Plywood Manufacturing Plant Project Report-SyndicatedSajal AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Credit Blueprint 1Document12 pagesCredit Blueprint 1Geo Staffan100% (3)
- Terms of EngagementDocument8 pagesTerms of EngagementSuresh RajputNo ratings yet
- Warehousing Management Using 5S Methodology 555Document50 pagesWarehousing Management Using 5S Methodology 555Nirmal ThapaNo ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoiceRythmn MagnaniNo ratings yet
- Strategic Supply Chain Management Case Study Analysis: AssignmentDocument8 pagesStrategic Supply Chain Management Case Study Analysis: Assignmentsushil messiNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Lesson 2Document48 pagesApplied Economics - Lesson 2Ma Nicole Ann ManteleNo ratings yet
- Background Check Authorization FormDocument7 pagesBackground Check Authorization FormShabNo ratings yet
- Data Mahasiswa Briefing Softcover Thesis Paper Semester Ganjil 2023 P2Document14 pagesData Mahasiswa Briefing Softcover Thesis Paper Semester Ganjil 2023 P2adityashaldy53No ratings yet
- To View KFC Associate Members - Kenya Flower CouncilDocument4 pagesTo View KFC Associate Members - Kenya Flower CouncilLily Li100% (1)
- Lecture 2 Monopoly Power-1Document40 pagesLecture 2 Monopoly Power-1Yaasiin Muxyadiin CiidNo ratings yet
- 2020-20211003 LLB TycDocument94 pages2020-20211003 LLB TycGeeta GuptaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER FOUR Financial Forcasting and PlanningDocument15 pagesCHAPTER FOUR Financial Forcasting and PlanningSoftware Lab MISKERNo ratings yet
- Finance ProjectDocument80 pagesFinance ProjectDinoop Devaraj0% (1)
- Corporate Board ResolutionDocument2 pagesCorporate Board ResolutionkimitiNo ratings yet
- Udyam MsmeDocument3 pagesUdyam MsmemmindustriesbbsrNo ratings yet
- Niti AayogDocument4 pagesNiti AayogPalak JioNo ratings yet