Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guide Bearing Lubrication Freq Qty
Guide Bearing Lubrication Freq Qty
Uploaded by
rifal1990Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Math 9 Summative Test Indirect VariationDocument1 pageMath 9 Summative Test Indirect VariationMaricris Dizon-MiguelNo ratings yet
- LG OLED55C7P CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument3 pagesLG OLED55C7P CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- The Key To 5D: A Guide To Spiritual AwakeningDocument129 pagesThe Key To 5D: A Guide To Spiritual AwakeningAndrew Narouz100% (1)
- Planos de Casa Con Estructura MetalicaDocument1 pagePlanos de Casa Con Estructura MetalicagladisNo ratings yet
- Planos de Casa Con Estructura MetalicaDocument1 pagePlanos de Casa Con Estructura MetalicaSamuel GuerraNo ratings yet
- KBU Data Sheet 4921210112 UKDocument9 pagesKBU Data Sheet 4921210112 UKAndy MezetaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Test Chart: Job Activity: DateDocument1 pagePressure Test Chart: Job Activity: DateYongki SuharyaNo ratings yet
- Ev Charging Time Charging SpeedDocument1 pageEv Charging Time Charging SpeedredmsbatteryNo ratings yet
- Wire Size - Area To Diameter ConverterDocument1 pageWire Size - Area To Diameter ConverterrahmatNo ratings yet
- ORacle and MongoDB TCO ComparisonDocument3 pagesORacle and MongoDB TCO ComparisonDuvan MejiaNo ratings yet
- Limit - Switch Test1 Sheet1Document1 pageLimit - Switch Test1 Sheet1Kenneth ChawNo ratings yet
- Tabella Riassuntiva T.A. Di Precisione High Accuracy Cts Selection TableDocument27 pagesTabella Riassuntiva T.A. Di Precisione High Accuracy Cts Selection TableMEINARDONo ratings yet
- Certificate of Verification Vickers: Force CalibrationDocument4 pagesCertificate of Verification Vickers: Force CalibrationNader DallejNo ratings yet
- Precast Beam Detail-1Document1 pagePrecast Beam Detail-1Amin ZuraiqiNo ratings yet
- TCL 55P607 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument3 pagesTCL 55P607 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Vizio E65-E0 CNET Review Calibration ReportDocument3 pagesVizio E65-E0 CNET Review Calibration ReportDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Print Grafik LampiranDocument1 pagePrint Grafik LampiranWahyu Permata LisaNo ratings yet
- Idnev 09.11.2020Document1 pageIdnev 09.11.2020ddgtNo ratings yet
- 24 Factorial DesignDocument47 pages24 Factorial Designrasha assafNo ratings yet
- Parte 3Document1 pageParte 3Ober MacasNo ratings yet
- CatalogDocument22 pagesCatalogmiguel angel vanegas medinaNo ratings yet
- MisureDocument1 pageMisureenricoNo ratings yet
- 1A Tables v2Document1 page1A Tables v2Itss Mee HadiNo ratings yet
- Colour by Number - SpeedDocument2 pagesColour by Number - Speedcristal XuNo ratings yet
- Histograma de Frecuencias: SoluciónDocument2 pagesHistograma de Frecuencias: SoluciónMónica Campuzano ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- AT AzoteaDocument1 pageAT AzoteaFERNANDO ALFONSO SALVADOR MORALESNo ratings yet
- Trazo CuaDocument1 pageTrazo Cuaanalisalazar390No ratings yet
- Biogas Dan Solar CellDocument6 pagesBiogas Dan Solar CellLingga BayuNo ratings yet
- 8' I H G F e 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 4 3A 1' 6A 4': Legenda TavaneDocument1 page8' I H G F e 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 4 3A 1' 6A 4': Legenda TavaneAndraCirtinaNo ratings yet
- GRATINGDocument1 pageGRATINGDoni MuharomNo ratings yet
- Lesion Detection in Mammogram Based On Multiresolution AnalysisDocument17 pagesLesion Detection in Mammogram Based On Multiresolution Analysissujay pujariNo ratings yet
- Week-1 Practice: 21K61A0111 G.Sai DeepikaDocument1 pageWeek-1 Practice: 21K61A0111 G.Sai DeepikajnanendraNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal PeengukuranDocument3 pagesLatihan Soal PeengukuranMEI EDI PRAYITNO, STNo ratings yet
- Overload 5Document1 pageOverload 5elmorseymaNo ratings yet
- Water LayoutDocument1 pageWater LayoutRoseanne CarsolaNo ratings yet
- DiaphragmDocument16 pagesDiaphragmdbhatia8750% (2)
- Financial Reporting and Analysis ReportDocument39 pagesFinancial Reporting and Analysis ReportGamer WorldNo ratings yet
- Epson HC4000 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument3 pagesEpson HC4000 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid Katzmaier0% (1)
- Astm D882Document10 pagesAstm D882AmyNo ratings yet
- Jigs Base: Aliff Asyraf 5/3/2021Document1 pageJigs Base: Aliff Asyraf 5/3/2021Nur SyakilaNo ratings yet
- Permco 257 SERIES BROCHUREDocument2 pagesPermco 257 SERIES BROCHUREJustinNo ratings yet
- Spindo Brochure - Oil & Gas IndustryDocument14 pagesSpindo Brochure - Oil & Gas Industrykiki widyaNo ratings yet
- Ying Hum VA3YH Circular SR-1Document1 pageYing Hum VA3YH Circular SR-1Carlos ToguchiNo ratings yet
- Vivienda Tipo B - ArqDocument1 pageVivienda Tipo B - ArqDaniel PiscoyaNo ratings yet
- PacT Series - ComPacT NSX & NSX'MDocument2 pagesPacT Series - ComPacT NSX & NSX'MvasudevanmohanaveluNo ratings yet
- 8FSPDocument4 pages8FSPUser GoogleNo ratings yet
- Denah Existing (GD PP)Document7 pagesDenah Existing (GD PP)adicondesitNo ratings yet
- Vizio E50-E1 CNET Review Calibration ReportDocument3 pagesVizio E50-E1 CNET Review Calibration ReportDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Hisense 65R8F CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument3 pagesHisense 65R8F CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Rencana Atap: Skala 1: 100 KeteranganDocument1 pageRencana Atap: Skala 1: 100 KeteranganIch BoyNo ratings yet
- Plan Du RDCDocument1 pagePlan Du RDCTaylor Domguia JuniorNo ratings yet
- Papuci Cupru Tip D - Klauke - Gerkon ElectroDocument2 pagesPapuci Cupru Tip D - Klauke - Gerkon ElectroVasilicaNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Fra 740 Catalog 193396 - ADocument4 pagesMitsubishi Fra 740 Catalog 193396 - Ajohn solasNo ratings yet
- MDP 5 - 400 P 405071 en PDFDocument3 pagesMDP 5 - 400 P 405071 en PDFPritesh KoratNo ratings yet
- MDP 5 - 400 P 405071 en PDFDocument3 pagesMDP 5 - 400 P 405071 en PDFPritesh KoratNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering DesignDocument1 pageMechanical Engineering Designhadirul95No ratings yet
- Tubes Inc. CaseDocument20 pagesTubes Inc. CaseKhoi LeNo ratings yet
- Week-1 Practice: 21K61A0117 Sai DeepikaDocument1 pageWeek-1 Practice: 21K61A0117 Sai DeepikajnanendraNo ratings yet
- 650 01 PDFDocument1 page650 01 PDFAnonymous t8U6sKtYSNo ratings yet
- LG OLED65E7P CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument3 pagesLG OLED65E7P CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Plan DemisolDocument1 pagePlan Demisolade vitanNo ratings yet
- Discrete Wavelet Transformations: An Elementary Approach with ApplicationsFrom EverandDiscrete Wavelet Transformations: An Elementary Approach with ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Standard - Amstrong Chemtec - Dry Out Procedure For Electric Heater BundlesDocument3 pagesStandard - Amstrong Chemtec - Dry Out Procedure For Electric Heater Bundlesrifal1990No ratings yet
- Series 8264: Ex D Enclosure System Made of Light Metal or Stainless Steel, "Flameproof Enclosure"Document20 pagesSeries 8264: Ex D Enclosure System Made of Light Metal or Stainless Steel, "Flameproof Enclosure"rifal1990No ratings yet
- Zeal Dial Thermometer ManualDocument1 pageZeal Dial Thermometer Manualrifal1990No ratings yet
- Unistream Hmi Panel: Installation Guide Usp-070-B10, Usp-070-B08 Usp-104-B10, Usp-104-M10 Usp-156-B10Document8 pagesUnistream Hmi Panel: Installation Guide Usp-070-B10, Usp-070-B08 Usp-104-B10, Usp-104-M10 Usp-156-B10rifal1990No ratings yet
- Insulation System Comparison VPI Versus Resin RichDocument9 pagesInsulation System Comparison VPI Versus Resin Richrifal1990No ratings yet
- LAPP - High Temperature CableDocument7 pagesLAPP - High Temperature Cablerifal1990No ratings yet
- Bearing Material LimitsDocument3 pagesBearing Material Limitsrifal1990No ratings yet
- Copper Busbar RatingDocument5 pagesCopper Busbar Ratingrifal1990No ratings yet
- Conventional and Slip Steering For Multi-Wheel Planetary RoversDocument39 pagesConventional and Slip Steering For Multi-Wheel Planetary RoversGreggs ShopukNo ratings yet
- Observations On Centrifugal Operation Part1Document5 pagesObservations On Centrifugal Operation Part1marcio_limaNo ratings yet
- Statics IntroductionDocument19 pagesStatics IntroductionNicoljen MangubatNo ratings yet
- Sikadur 752: Low Viscosity Epoxy Resin InjectionDocument2 pagesSikadur 752: Low Viscosity Epoxy Resin InjectionMike AlarNo ratings yet
- Steel Deck 101Document3 pagesSteel Deck 101arnoldistunoNo ratings yet
- Vapor Power CyclesDocument27 pagesVapor Power Cycleshrithik khannaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Problems Solutions: KJ 51.84 WH 14.4Document8 pagesChapter One Problems Solutions: KJ 51.84 WH 14.4Mohsan HasanNo ratings yet
- Rao Ravula Parsons: Api Standard 650, 10Th Edition, July 1998 Addendum 1, March 2000Document21 pagesRao Ravula Parsons: Api Standard 650, 10Th Edition, July 1998 Addendum 1, March 2000박민규No ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Self Compacting Concrete by Partially Replacing Fine Aggregate With Quartz Sand With Use of Recron FibreDocument6 pagesExperimental Investigation of Self Compacting Concrete by Partially Replacing Fine Aggregate With Quartz Sand With Use of Recron Fibreshivanand hippargaNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument12 pagesProjectile MotionAtharv GoyalNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Text ActivityDocument4 pagesDescriptive Text ActivityDamaiyanti NoveizaNo ratings yet
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 4 - 5Document15 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 4 - 5Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- Theories and Models of The AtomDocument13 pagesTheories and Models of The AtomAlex Omunga100% (2)
- ĐỀ HSG ANH LỚP 9 năm 2021 - 802Document2 pagesĐỀ HSG ANH LỚP 9 năm 2021 - 802Hồ Ngọc TrAnhNo ratings yet
- Comparing Concrete On The Basis of The Bond Developed With Reinforcing SteelDocument4 pagesComparing Concrete On The Basis of The Bond Developed With Reinforcing SteelEvert RiveraNo ratings yet
- K X N X K X N X: 1. PeriodicityDocument13 pagesK X N X K X N X: 1. PeriodicitymakNo ratings yet
- Introduction Electrodynamics Griffiths SolutionsDocument2 pagesIntroduction Electrodynamics Griffiths SolutionsKishore Kumar50% (4)
- Ansys Fluent Simulation Report BatteryDocument13 pagesAnsys Fluent Simulation Report Batterysaitharun reddy.munthaNo ratings yet
- La Concepcion College, Inc.: Evaluation SheetDocument1 pageLa Concepcion College, Inc.: Evaluation SheetMark MarcosNo ratings yet
- HK222 CLC Sample 3 2Document5 pagesHK222 CLC Sample 3 2Tuấn Khang TừNo ratings yet
- 4-Ductor: Insulated Conductor BarDocument13 pages4-Ductor: Insulated Conductor BarMitica TartareanuNo ratings yet
- Pinion Assemblies - AssembleDocument4 pagesPinion Assemblies - Assemblemijael1393No ratings yet
- Hydrology With Schematic Diagram ResearchDocument8 pagesHydrology With Schematic Diagram ResearchGleizel AutorNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) As An Ozone Generator ReactorDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) As An Ozone Generator ReactorFebi Nabila AknurNo ratings yet
- JME 3710 September 3, 2020: L X T TDocument1 pageJME 3710 September 3, 2020: L X T TMichael WendlNo ratings yet
- What IS Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesWhat IS Inorganic ChemistryRoja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Transient Response of A Second-Order SystemDocument12 pagesExperiment 2: Transient Response of A Second-Order SystemReza KühnNo ratings yet
- Spring DesignDocument10 pagesSpring DesignimpetuskolNo ratings yet
Guide Bearing Lubrication Freq Qty
Guide Bearing Lubrication Freq Qty
Uploaded by
rifal1990Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guide Bearing Lubrication Freq Qty
Guide Bearing Lubrication Freq Qty
Uploaded by
rifal1990Copyright:
Available Formats
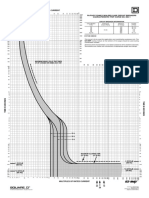
Electric motor bearing lubrication frequency and quantity
Relubrication intervals for rolling element bearings
Grease relubrication intervals for normal operating conditions can be read as a function of bearing speed and bore.
This diagram is valid for bearings on horizontal shafts in stationary machines under normal conditions.
Bearing Type
C B A
1.5 2.5 3
10,000 2 2.5
6 1.5 2
4 1.5
10,000
2 10,000
8
1000 6 8
8 4
6
HOURS OF OPERATION
3 6
3 2.5
4 2 4
3 1.5 3
2.5 2.5
2 1000 2
40
60
By Tom Bishop, P.E.
80
1.5
100
7.5 1.5
120
180
200
EASA Senior Technical Support Specialist
240
280
100 5 1000
80 4 8
Editor’s Note: PDFs of this article are 60 3 6
50 2.5
available in English and Spanish in the 40 2 4
“Resource Library” of www.easa.com. 30 1.5 3
20 100 2
l l l l l 15 75 1.5
Considerations for lubrication fre- 10 50 100
100 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1000 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10,000
quency and quantity for electric motors Scale A: Radial ball
RPM
(and generators) include the following: Scale B: Cylindrical roller
Scale C: Thrust ball and roller
• Is the lubricant grease or oil?
Figure 1. Relubrication intervals for rolling element bearings.
• Is the bearing type sleeve, ball or
roller?
• If it is a ball bearing, is the enclo-
sure open, shielded or sealed?
In this article we will address the
above by breaking them down into the
following categories:
Figure 2. Formulas to calculate grease relubrication quantities.
• Grease lubrication frequency and
quantity for ball and roller (roll- pending on parameters such as: • Draw a vertical line from the
ing element) bearings. motor rpm to the curve that
Operating temperature
• Oil lubrication frequency and represents the bearing inside
Motor shaft speed
level (relates to quantity) for ball diameter (in millimeters), or the
Bearing size
and roller bearings. next smaller dimension.
Bearing load
• Oil lubrication frequency and • From that point, draw a horizon-
Hours of operation
level (relates to quantity) for tal line to intersect the hours of
sleeve bearings. Environmental conditions/
operation (relubrication interval)
contaminants
Since grease lubrication of sleeve for the applicable bearing type.
Vibration levels
bearings is extremely rare, that topic Example: Determine the lubrication
is not included in this article. Further, If motor manufacturer instructions
frequency of a 6314 bearing operating
since sealed bearings cannot be relu- are not available, determine the appro-
at 1780 rpm in a normal environment.
bricated, that topic also will not be priate grease relubrication intervals for
The inside diameter in millimeters of
included in this article. motors under normal operating condi-
the bearing is 5 times the last 2 digits of
tions using Figure 1. For conditions
Grease lubrication frequency the bearing number. Thus the bearing
such as motors with vertical mounting,
ID is 70 mm (5 x 14). Note that there is
and quantity for ball and roller belt load or used in hostile environ-
no curve for 70 mm, thus use the curve
(rolling element) bearings ments, reduce the interval determined
for the next smaller size, i.e., 60 mm.
from Figure 1 by 50%. To use Figure 1,
The 60 mm curve intersects with the
Relubrication intervals do the following:
1750 rpm value at about 11,000 hours
The frequency of relubrication is • Find the motor rpm on the
application and product specific, de- horizontal axis. Continued on Page 2
Copyright © 2019 • www.easa.com • January 2019 1
Electric motor bearing lubrication frequency and quantity
Continued From Page 1
(using column for type A) for a ball (150 mm) and its width is 1.38” (35 4. If there are no provisions for
bearing. If the motor was operating in mm). The lubricant quantity G is 0.90 grease fittings or pipe plugs, the
a hostile environment, the lubrication fluid ounces (0.11 x 5.91 x 1.38), or 26 bearings are not intended to be
interval would be reduced from 11,000 milliliters (0.005 x 150 x 35). relubricated. Thus, it is not recom-
hours to 5,500 hours (0.5 x 11,000). If mended to remove end brackets
the bearing was a cylindrical roller Lubrication procedure to relubricate bearings.
bearing with the same bore size, such Ball and roller bearings may be 5. Remove relief drain plug or pres-
as an NU214, the lubrication interval lubricated with the motor running sure relief vent fitting.
in a normal environment would be or stationary. However, stationary 6. If grease is caked inside the relief
about 9,000 hours (using column for with the motor at or near operating hole, clean with a wooden stick
type B). temperature is recommended. or suitable tool. If severe caking
Steps: appears at the relief hole, run the
Relubrication quantities 1. If lubrication must be done with motor until the bearing housing
Figure 2 provides a guideline for motor running (not recom- is warm, permitting a free flow of
the grease quantity to be used during mended), make certain to observe grease to exit the housing.
relubrication. all safety precautions. 7. Add the recommended volume of
Example: The relubrication quantity
2. Locate and clean the grease inlet the recommended lubricant using
for the 6314 ball bearing will be cal-
area. a hand operated grease gun.
culated. The outside diameter is 5.91”
3. If equipped 8. Run the motor for one-half hour
with a pipe with relief drain plug removed
Automatic plug, replace it before replacing plug. For
Rolling element bearing with a grease increased reliability, replace drain
oiler
fitting. For plug with pressure relief vent
increased reli- fitting rated 1 to 5 psi (7 to 35
ability, replace kPA) to continually purge excess
grease (Zerk) grease, and eliminate the one-half
fitting with a hour waiting period for lubricant
Oil shutoff style purge.
level fitting hav- 9. Replace the pipe plugs, if appli-
ing a release cable, and wipe off excess grease.
pressure limit Note: Shielded bearings allow for a
of 5 to 20 psi “small” amount of relubrication but
(35 to 140 kPA) with little effect, depending upon the
to help prevent clearance between the inner race and
damage to the
Figure 3. Oil level for rolling element bearings in horizontal motor. bearing when Continued on Page 3
adding grease.
Running level
inside oil Running
reservoir level inside
Sight glass oil reservoir
Standstill level
Standstill level
Running Running
oil level oil level
inside inside
bearing bearing
chamber chamber
A: Ball bearings B: Roller bearings
Figure 4. Oil level for rolling element bearings in vertical motor.
2 Copyright © 2019 • www.easa.com • January 2019
Electric motor bearing lubrication frequency and quantity
Continued From Page 2
the shield. This clearance varies among Table 1. Sleeve bearing oil viscosity and lubrication intervals.
manufacturers from 0.003” to 0.015”
(0.08 to 0.38 mm). Empirical evidence
shows a certain amount of oil from the Ambient starting and
Shaft speeds ISO Viscosity Lubrication
lubricant will “find its way” into the operating temperature
(rpm) range interval
ball area, but the shield will limit the range °C (°F)
amount of foreign material that can
enter and cause damage. All Consult ---
Below 10° C (50° F)
manufacturer
Oil lubrication frequency and
level (relates to quantity) for ball Above 1800 32 to 68 5000 operat-
and roller bearings ing hours or 1
10° C to 32° C year, whichever
For horizontal shaft applications,
(50° F to 90° F) comes first
the oil level should be maintained
at approximately the center of the Up to 1800 68 to 100 1 year
lowest rolling element (see Figure 3),
according to the oil gauge, when the All Consult ---
Above 32° C (90° F)
motor is not operating. For vertical manufacturer
shafts, the standstill oil level should
be maintained at approximately 50%
submergence of the uppermost row three months to determine when oil When replacing the oil, fill the reservoir
of the rolling elements (see Figure 4). replacement is necessary. to the level that’s normally shown on
The interval at which lubricating the sight glass.
oil should be changed varies depend- Oil lubrication frequency and
ing upon operating conditions, oil level (relates to quantity) for Sleeve bearing oil level
quantity, and type of oil used. In gen- sleeve bearings If oil level information is available
eral, for oil bath lubrication where the from the motor manufacturer, fol-
The clearance between the shaft
operating temperature is 50° C (120° low it. If not, as a general guideline,
journal and the bearing bore is critical
F) or less, oil should be replaced once the oil rings should be immersed to
with sleeve bearings. Any short-term,
a year. When the operating tempera- approximately one-quarter of their
metal-to-metal contact can increase
ture is between 80° C – 100° C (176° circumference or 20% of the diameter
the bearing temperature, and the
F – 212° F), oil should be replaced at of the rings (see Figure 5).
associated “wiping” can quickly de-
least every three months. For critical Too low a stationary level means
grade the bearing, possibly causing
equipment, it is advisable that lubri- the oil level is dangerously low when
catastrophic failure. To maintain sleeve
cating oil be analyzed at least every some of the oil is in play (in the bear-
bearing clearances, follow the lubrica-
ing, dripping down the inside of the
tion guidelines in Table 1.
chamber, etc.). Too high an oil level
Select relubrication intervals based
means increased friction between oil
on the motor manufacturer's instruc-
and rings. The rings will turn slower,
tions (if available). Otherwise, use the
supplying less oil to the bearing.
intervals provided in Table 1. Frequent
Adding oil with the machine at rest
starting and stopping, damp or dusty
is preferable to when the machine is
environments, extreme temperatures
operating. Overfilling when running
and other severe service conditions
can initiate a siphoning effect of oil
warrant more frequent oil changes than
through the labyrinth passages, thus
shown in Table 1. Contact the motor
leading to chronic oil leakage.
manufacturer regarding oil change
A note about temperature limits
About 1/4 of circumference intervals for specific situations, or reg-
or 20% of diameter that is applicable to ball, roller and
of oil ring ularly check the oil for contaminants or
sleeve bearings. The suggested bearing
Oil Oil discoloration and replace it as needed.
temperature limit for normal operation
level level Another way to determine oil replace-
is 80° C (176° F), alarm at 90° C (194° F)
ment intervals is to have a laboratory
and trip at 100° C (212° F). l
analyze oil samples periodically. Tip:
Take oil samples with the motor shut
Figure 5. Oil level for sleeve bearings. down to avoid removing too much.
Copyright © 2019 • www.easa.com • January 2019 3
You might also like
- Math 9 Summative Test Indirect VariationDocument1 pageMath 9 Summative Test Indirect VariationMaricris Dizon-MiguelNo ratings yet
- LG OLED55C7P CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument3 pagesLG OLED55C7P CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- The Key To 5D: A Guide To Spiritual AwakeningDocument129 pagesThe Key To 5D: A Guide To Spiritual AwakeningAndrew Narouz100% (1)
- Planos de Casa Con Estructura MetalicaDocument1 pagePlanos de Casa Con Estructura MetalicagladisNo ratings yet
- Planos de Casa Con Estructura MetalicaDocument1 pagePlanos de Casa Con Estructura MetalicaSamuel GuerraNo ratings yet
- KBU Data Sheet 4921210112 UKDocument9 pagesKBU Data Sheet 4921210112 UKAndy MezetaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Test Chart: Job Activity: DateDocument1 pagePressure Test Chart: Job Activity: DateYongki SuharyaNo ratings yet
- Ev Charging Time Charging SpeedDocument1 pageEv Charging Time Charging SpeedredmsbatteryNo ratings yet
- Wire Size - Area To Diameter ConverterDocument1 pageWire Size - Area To Diameter ConverterrahmatNo ratings yet
- ORacle and MongoDB TCO ComparisonDocument3 pagesORacle and MongoDB TCO ComparisonDuvan MejiaNo ratings yet
- Limit - Switch Test1 Sheet1Document1 pageLimit - Switch Test1 Sheet1Kenneth ChawNo ratings yet
- Tabella Riassuntiva T.A. Di Precisione High Accuracy Cts Selection TableDocument27 pagesTabella Riassuntiva T.A. Di Precisione High Accuracy Cts Selection TableMEINARDONo ratings yet
- Certificate of Verification Vickers: Force CalibrationDocument4 pagesCertificate of Verification Vickers: Force CalibrationNader DallejNo ratings yet
- Precast Beam Detail-1Document1 pagePrecast Beam Detail-1Amin ZuraiqiNo ratings yet
- TCL 55P607 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument3 pagesTCL 55P607 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Vizio E65-E0 CNET Review Calibration ReportDocument3 pagesVizio E65-E0 CNET Review Calibration ReportDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Print Grafik LampiranDocument1 pagePrint Grafik LampiranWahyu Permata LisaNo ratings yet
- Idnev 09.11.2020Document1 pageIdnev 09.11.2020ddgtNo ratings yet
- 24 Factorial DesignDocument47 pages24 Factorial Designrasha assafNo ratings yet
- Parte 3Document1 pageParte 3Ober MacasNo ratings yet
- CatalogDocument22 pagesCatalogmiguel angel vanegas medinaNo ratings yet
- MisureDocument1 pageMisureenricoNo ratings yet
- 1A Tables v2Document1 page1A Tables v2Itss Mee HadiNo ratings yet
- Colour by Number - SpeedDocument2 pagesColour by Number - Speedcristal XuNo ratings yet
- Histograma de Frecuencias: SoluciónDocument2 pagesHistograma de Frecuencias: SoluciónMónica Campuzano ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- AT AzoteaDocument1 pageAT AzoteaFERNANDO ALFONSO SALVADOR MORALESNo ratings yet
- Trazo CuaDocument1 pageTrazo Cuaanalisalazar390No ratings yet
- Biogas Dan Solar CellDocument6 pagesBiogas Dan Solar CellLingga BayuNo ratings yet
- 8' I H G F e 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 4 3A 1' 6A 4': Legenda TavaneDocument1 page8' I H G F e 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 4 3A 1' 6A 4': Legenda TavaneAndraCirtinaNo ratings yet
- GRATINGDocument1 pageGRATINGDoni MuharomNo ratings yet
- Lesion Detection in Mammogram Based On Multiresolution AnalysisDocument17 pagesLesion Detection in Mammogram Based On Multiresolution Analysissujay pujariNo ratings yet
- Week-1 Practice: 21K61A0111 G.Sai DeepikaDocument1 pageWeek-1 Practice: 21K61A0111 G.Sai DeepikajnanendraNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal PeengukuranDocument3 pagesLatihan Soal PeengukuranMEI EDI PRAYITNO, STNo ratings yet
- Overload 5Document1 pageOverload 5elmorseymaNo ratings yet
- Water LayoutDocument1 pageWater LayoutRoseanne CarsolaNo ratings yet
- DiaphragmDocument16 pagesDiaphragmdbhatia8750% (2)
- Financial Reporting and Analysis ReportDocument39 pagesFinancial Reporting and Analysis ReportGamer WorldNo ratings yet
- Epson HC4000 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument3 pagesEpson HC4000 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid Katzmaier0% (1)
- Astm D882Document10 pagesAstm D882AmyNo ratings yet
- Jigs Base: Aliff Asyraf 5/3/2021Document1 pageJigs Base: Aliff Asyraf 5/3/2021Nur SyakilaNo ratings yet
- Permco 257 SERIES BROCHUREDocument2 pagesPermco 257 SERIES BROCHUREJustinNo ratings yet
- Spindo Brochure - Oil & Gas IndustryDocument14 pagesSpindo Brochure - Oil & Gas Industrykiki widyaNo ratings yet
- Ying Hum VA3YH Circular SR-1Document1 pageYing Hum VA3YH Circular SR-1Carlos ToguchiNo ratings yet
- Vivienda Tipo B - ArqDocument1 pageVivienda Tipo B - ArqDaniel PiscoyaNo ratings yet
- PacT Series - ComPacT NSX & NSX'MDocument2 pagesPacT Series - ComPacT NSX & NSX'MvasudevanmohanaveluNo ratings yet
- 8FSPDocument4 pages8FSPUser GoogleNo ratings yet
- Denah Existing (GD PP)Document7 pagesDenah Existing (GD PP)adicondesitNo ratings yet
- Vizio E50-E1 CNET Review Calibration ReportDocument3 pagesVizio E50-E1 CNET Review Calibration ReportDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Hisense 65R8F CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument3 pagesHisense 65R8F CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Rencana Atap: Skala 1: 100 KeteranganDocument1 pageRencana Atap: Skala 1: 100 KeteranganIch BoyNo ratings yet
- Plan Du RDCDocument1 pagePlan Du RDCTaylor Domguia JuniorNo ratings yet
- Papuci Cupru Tip D - Klauke - Gerkon ElectroDocument2 pagesPapuci Cupru Tip D - Klauke - Gerkon ElectroVasilicaNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Fra 740 Catalog 193396 - ADocument4 pagesMitsubishi Fra 740 Catalog 193396 - Ajohn solasNo ratings yet
- MDP 5 - 400 P 405071 en PDFDocument3 pagesMDP 5 - 400 P 405071 en PDFPritesh KoratNo ratings yet
- MDP 5 - 400 P 405071 en PDFDocument3 pagesMDP 5 - 400 P 405071 en PDFPritesh KoratNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering DesignDocument1 pageMechanical Engineering Designhadirul95No ratings yet
- Tubes Inc. CaseDocument20 pagesTubes Inc. CaseKhoi LeNo ratings yet
- Week-1 Practice: 21K61A0117 Sai DeepikaDocument1 pageWeek-1 Practice: 21K61A0117 Sai DeepikajnanendraNo ratings yet
- 650 01 PDFDocument1 page650 01 PDFAnonymous t8U6sKtYSNo ratings yet
- LG OLED65E7P CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument3 pagesLG OLED65E7P CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Plan DemisolDocument1 pagePlan Demisolade vitanNo ratings yet
- Discrete Wavelet Transformations: An Elementary Approach with ApplicationsFrom EverandDiscrete Wavelet Transformations: An Elementary Approach with ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Standard - Amstrong Chemtec - Dry Out Procedure For Electric Heater BundlesDocument3 pagesStandard - Amstrong Chemtec - Dry Out Procedure For Electric Heater Bundlesrifal1990No ratings yet
- Series 8264: Ex D Enclosure System Made of Light Metal or Stainless Steel, "Flameproof Enclosure"Document20 pagesSeries 8264: Ex D Enclosure System Made of Light Metal or Stainless Steel, "Flameproof Enclosure"rifal1990No ratings yet
- Zeal Dial Thermometer ManualDocument1 pageZeal Dial Thermometer Manualrifal1990No ratings yet
- Unistream Hmi Panel: Installation Guide Usp-070-B10, Usp-070-B08 Usp-104-B10, Usp-104-M10 Usp-156-B10Document8 pagesUnistream Hmi Panel: Installation Guide Usp-070-B10, Usp-070-B08 Usp-104-B10, Usp-104-M10 Usp-156-B10rifal1990No ratings yet
- Insulation System Comparison VPI Versus Resin RichDocument9 pagesInsulation System Comparison VPI Versus Resin Richrifal1990No ratings yet
- LAPP - High Temperature CableDocument7 pagesLAPP - High Temperature Cablerifal1990No ratings yet
- Bearing Material LimitsDocument3 pagesBearing Material Limitsrifal1990No ratings yet
- Copper Busbar RatingDocument5 pagesCopper Busbar Ratingrifal1990No ratings yet
- Conventional and Slip Steering For Multi-Wheel Planetary RoversDocument39 pagesConventional and Slip Steering For Multi-Wheel Planetary RoversGreggs ShopukNo ratings yet
- Observations On Centrifugal Operation Part1Document5 pagesObservations On Centrifugal Operation Part1marcio_limaNo ratings yet
- Statics IntroductionDocument19 pagesStatics IntroductionNicoljen MangubatNo ratings yet
- Sikadur 752: Low Viscosity Epoxy Resin InjectionDocument2 pagesSikadur 752: Low Viscosity Epoxy Resin InjectionMike AlarNo ratings yet
- Steel Deck 101Document3 pagesSteel Deck 101arnoldistunoNo ratings yet
- Vapor Power CyclesDocument27 pagesVapor Power Cycleshrithik khannaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Problems Solutions: KJ 51.84 WH 14.4Document8 pagesChapter One Problems Solutions: KJ 51.84 WH 14.4Mohsan HasanNo ratings yet
- Rao Ravula Parsons: Api Standard 650, 10Th Edition, July 1998 Addendum 1, March 2000Document21 pagesRao Ravula Parsons: Api Standard 650, 10Th Edition, July 1998 Addendum 1, March 2000박민규No ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Self Compacting Concrete by Partially Replacing Fine Aggregate With Quartz Sand With Use of Recron FibreDocument6 pagesExperimental Investigation of Self Compacting Concrete by Partially Replacing Fine Aggregate With Quartz Sand With Use of Recron Fibreshivanand hippargaNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument12 pagesProjectile MotionAtharv GoyalNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Text ActivityDocument4 pagesDescriptive Text ActivityDamaiyanti NoveizaNo ratings yet
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 4 - 5Document15 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 4 - 5Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- Theories and Models of The AtomDocument13 pagesTheories and Models of The AtomAlex Omunga100% (2)
- ĐỀ HSG ANH LỚP 9 năm 2021 - 802Document2 pagesĐỀ HSG ANH LỚP 9 năm 2021 - 802Hồ Ngọc TrAnhNo ratings yet
- Comparing Concrete On The Basis of The Bond Developed With Reinforcing SteelDocument4 pagesComparing Concrete On The Basis of The Bond Developed With Reinforcing SteelEvert RiveraNo ratings yet
- K X N X K X N X: 1. PeriodicityDocument13 pagesK X N X K X N X: 1. PeriodicitymakNo ratings yet
- Introduction Electrodynamics Griffiths SolutionsDocument2 pagesIntroduction Electrodynamics Griffiths SolutionsKishore Kumar50% (4)
- Ansys Fluent Simulation Report BatteryDocument13 pagesAnsys Fluent Simulation Report Batterysaitharun reddy.munthaNo ratings yet
- La Concepcion College, Inc.: Evaluation SheetDocument1 pageLa Concepcion College, Inc.: Evaluation SheetMark MarcosNo ratings yet
- HK222 CLC Sample 3 2Document5 pagesHK222 CLC Sample 3 2Tuấn Khang TừNo ratings yet
- 4-Ductor: Insulated Conductor BarDocument13 pages4-Ductor: Insulated Conductor BarMitica TartareanuNo ratings yet
- Pinion Assemblies - AssembleDocument4 pagesPinion Assemblies - Assemblemijael1393No ratings yet
- Hydrology With Schematic Diagram ResearchDocument8 pagesHydrology With Schematic Diagram ResearchGleizel AutorNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) As An Ozone Generator ReactorDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) As An Ozone Generator ReactorFebi Nabila AknurNo ratings yet
- JME 3710 September 3, 2020: L X T TDocument1 pageJME 3710 September 3, 2020: L X T TMichael WendlNo ratings yet
- What IS Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesWhat IS Inorganic ChemistryRoja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Transient Response of A Second-Order SystemDocument12 pagesExperiment 2: Transient Response of A Second-Order SystemReza KühnNo ratings yet
- Spring DesignDocument10 pagesSpring DesignimpetuskolNo ratings yet