Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study: Cotrimoxazole: Cotrimoxazole 500mg Tab PO TID X 7 Days
Drug Study: Cotrimoxazole: Cotrimoxazole 500mg Tab PO TID X 7 Days
Uploaded by
bobo gamingOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study: Cotrimoxazole: Cotrimoxazole 500mg Tab PO TID X 7 Days
Drug Study: Cotrimoxazole: Cotrimoxazole 500mg Tab PO TID X 7 Days
Uploaded by
bobo gamingCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study: COTRIMOXAZOLE
Complete the drug study of the ordered drug below. You may use a drug handbook such as Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide as your reference.
Dr. Postrano ordered the drug: Cotrimoxazole 500mg tab PO TID x 7 days
Patient HRN: 1234567 Age/Gender: 30/F Rm: 102
Admitting Diagnosis: Urinary Tract Infection Birthday: 10/24/1990
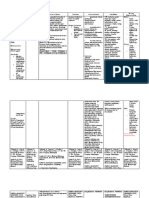
Drug Mechanism of Action Indications or Purpose Contraindications Side Effects Adverse Reactions Nursing Responsibilities
Uncomplicated UTIs Dermatologic: Rash, Inform patient of potential
Generic Name: caused by pruritus, exfoliative adverse reactions.
susceptible strains of dermatitis
Eschirichia coli, Contraindicated Tell patient to take drug as
Proteus mirabilis, with allergy to prescribed, even if he feels
Inhibits folic acid Klebsiella trimethoprim, GI: Epigastric distress,
nausea, vomiting, better.
Trimethoprim reduction to pneumoniae, pregnancy
tetrahydrofolate in Enterobacter species, (teratogenic in glossitis
Instruct patient to take oral
Sulfamethoxazo susceptible bacteria; and coagulase- preclinical studies), Hypersensitivity
the bacterial enzyme reactions – pain, dose with 8 oz (240 ml) of
le negative megaloblastic Hematologic:
involved in this local irritation, water on an empty
Staphylococcus anemia due to
Thrombocytopenia, stomach.
reaction is more species, including S. folate deficiency. inflammation, and
readily inhibited than leukopenia,
saprophyticus rarely
the mammalian thrombophlebitis neutropenia, Contraindicated in patients with
Brand Name: enzyme. megaloblastic anemia, known hypersensitivity to
Treatment of acute
methemoglobinemia, trimethoprim or sulfonamides,
otitis media due to
susceptible strains of Use cautiously with elevated serum or with documented
Streptococcus hepatic or renal transaminase and megaloblastic anemia
Actrim Septra, pneumonia and impairment, bilirubin, increased secondary to folate deficiency.
Bactrim, Haemophilus lactation. BUN and serum Dilute each 5 mL ampoule with
influenzae in children creatinine levels, 125 mL of D5W or NS, the
hyperkalemia, prepared solution must be kept
Sulfatrim at room temperature (solution
Unlabeled uses: With hyponatremia
stable for 24 hours) in fluid
dapsone for restriction: each 5 mL ampule
treatment of initial
Other: Fever
episodes of may be diluted with 75 mL D5W
Pneumocystis jiroveci or NS (solution stable for a total
(carinii) pneumonia in of 3 hours, including infusion
patients who cannot period) –each 5 mL ampule
tolerate co- may be diluted with 50 mL D5W
Classification: trimoxazole; or NS (Solution stable for a
treatment and total of 1.5 hours, including
prevention of infusion period)- discard if there
traveler’s diarrhea is cloudiness or precipitation.
Antibacterial
Dose, Route & Timing:
100 mg PO every 12
hr or 200 mg every
24 hr fo 10 days for
acute
uncomplicated
UTIs.
Reference/s: Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide
Drug Study: RIMANTIDINE
Complete the drug study of the ordered drug below. You may use a drug handbook such as Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide as your reference.
Dr. Postrano ordered the drug: Rimantidine 100mg PO BID x 5 days
Patient HRN: 1234567 Age/Gender: 30/F Rm: 102
Admitting Diagnosis: Influenza A Birthday: 10/24/1990
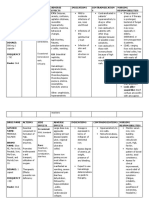
Drug Mechanism of Action Indications or Purpose Contraindications Side Effects Adverse Reactions Nursing Responsibilities
Advise patient to take medication
Generic Name: Trouble sleeping as directed at evenly spaced
Prophylaxis and times for full course of therapy,
treatment of illness Contraindicated
nausea even if feeling well. Take missed
caused by influenza with allergy to
Rimantidine A virus in adults amantadine, CNS: Light- doses as soon as possible unless
Synthetic antiviral rimantadine; headedness, almost time for next dose; do not
agent that inhibits viral Prophylaxis against lactation. vomiting dizziness, insomnia,
double up on missed doses.
replication, possibly by influenza A virus in confusion, irritability,
Brand Name: preventing the ataxia, psychosis, May cause dizziness. Advice
children
uncoating of the virus. depression, patient to avoid driving or other
loss of appetite
Use cautiously with hallucinations,
Unlabeled uses: seizures, liver or seizures
activities that require alertness until
Treatment and renal disease, response to the drug is known.
Flumadine prophylaxis of H1N1 pregnancy. dry mouth Inform patient that frequent mouth
(swine flu) infection, CV: HF, orthostatic
rinses, good oral hygiene, and
treatment of influenza hypotension, dyspnea
A in children weakness sugarless gum or candy may
Classification: decrease dry mouth.
GI: Nausea,
Instruct patient and family to notify
dizziness
health care professional if influenza
Antiviral symptoms occur.
Drowsiness or
nervousness may
Dose, Route & Timing: occur.
Prophylaxis: 100
mg/day PO bid. for
7 days from initial
onset of symptoms.
Reference/s: Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide
Drug Study: DOXORUBICIN
Complete the drug study of the ordered drug below. You may use a drug handbook such as Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide as your reference.
Dr. Postrano ordered the drug: Doxorubicin 60–75 mg/m2 as a single IV dose; repeat every 21 d
Patient HRN: 1234567 Age/Gender: 30/F Rm: 102
Admitting Diagnosis: Leukemia Birthday: 10/24/1990
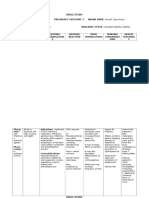
Drug Mechanism of Action Indications or Purpose Contraindications Side Effects Adverse Reactions Nursing Responsibilities
Contraindicated CV: Cardiac toxicity,
Generic Name: with allergy to heart failure,
doxorubicin phlebosclerosis
hydrochloride, Dermatologic:
To produce malignant Complete but
regression in the melanoma, kidney reversible alopecia,
DOXOrubicin following neoplasms: carcinoma, large Nausea hyperpigmentation of
ALL, AML, Wilms bowel carcinoma, nailbeds and dermal
hydrochloride tumor, brain tumors, CNS creases, facial flushing
neuroblastoma, soft metastases, GI: Nausea, vomiting,
tissue and bone myelosuppression, Vomiting mucositis, anorexia,
sarcoma, breast cardiac disease diarrhea
carcinoma, ovarian (may predispose to
Brand Name: GU: Red urine
carcinoma, cardiac toxicity),
transitional cell Hematologic:
pregnancy, Myelosuppression,
bladder carcinoma, lactation. Diarrhea
thyroid carcinoma, hyperuricemia due to
Use cautiously with cell lysis
Adriamycin Hodgkin and non- impaired hepatic
Hodgkin lymphomas, Hypersensitivity:
function, previous Fever, chills, urticaria,
Cytotoxic: Binds to bronchogenic courses of
carcinoma Stomatitis anaphylaxis
DNA and inhibits DNA doxorubicin or Local: Severe local Stop infusion, remove IV
synthesis in daunorubicin needle, and notify physician
Classification: Liposomal form: cellulitis, vesication
susceptible cells, therapy (may promptly if patient complains of
Treatment of AIDS- and tissue necrosis if
causing cell death. predispose to stinging or burning sensation at
related Kaposi extravasation occurs
cardiac toxicity), Esophagitis the injection site. Monitor any
sarcoma, ovarian Other: Carcinogenesis
prior mediastinal (documented in area of extravasation closely for
Antibiotic cancer that has irradiation,
progressed or experimental models) 3–4 wk. If ulceration begins
concurrent (usually 1–4 weeks after
recurred after cyclophosphamide
Antineoplastic extravasation), a plastic
platinum-based therapy (predispose
chemotherapy surgeon should be consulted.
to cardiac toxicity).
Dose, Route & Timing:
60–75 mg/m2 as a
single IV injection
administered at 21-
day intervals.
Alternate schedule:
30 mg/m2 IV on
each of 3
successive days,
repeated every 4
wk.
Reference/s: Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide
You might also like
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Gentamycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesGentamycin Drug StudyShin Guevara100% (3)
- Doxove Liposome Doxorubicin Compared To DoxilDocument3 pagesDoxove Liposome Doxorubicin Compared To DoxilPeter ZhangNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Tañeza BSN2CDocument9 pagesDrug Study Tañeza BSN2CGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Drug Study Tañeza BSN2CDocument9 pagesDrug Study Tañeza BSN2CGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Tablets - 100, 200 MG Side Effects: Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTablets - 100, 200 MG Side Effects: Drug StudyMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- CU5Document13 pagesCU5kuu faal100% (3)
- ClindamycinDocument2 pagesClindamycinassilamorNo ratings yet
- Sulfamethaxazole, Salbu + IpraDocument5 pagesSulfamethaxazole, Salbu + IpraGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Cu9 CaralosDocument13 pagesCu9 CaralosCarla Mae CaralosNo ratings yet
- Cefixime: Suprax Class and CategoryDocument3 pagesCefixime: Suprax Class and CategoryArianne Joy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology of The Antihelminthic DrugsDocument20 pagesClinical Pharmacology of The Antihelminthic DrugsGemson RosalesNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCefuroxime Drug StudyJC LumayaNo ratings yet
- JM Drug Study CaseDocument4 pagesJM Drug Study CaseMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument9 pagesDrug Study CefuroximeRio Ramon HilarioNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin, Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesAmoxicillin, Ferrous SulfateAngelyn BucasoNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin Drug-Study GaloloDocument3 pagesAmoxicillin Drug-Study Galolo40-GALOLO ANDREA PAULINENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument79 pagesDrug StudyShea Janson MercurioNo ratings yet
- AmpicillinDocument1 pageAmpicillinIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- In (Ampinex, Clovilin, Vatacil)Document2 pagesIn (Ampinex, Clovilin, Vatacil)karenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument2 pagesCEFUROXIMEMelvz BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyapi-3717941100% (6)
- Discharge PlanDocument14 pagesDischarge PlanAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University of Northern Philippines Tamag, Vigan City 2700 Ilocos SurDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University of Northern Philippines Tamag, Vigan City 2700 Ilocos SurMariam Yiani Aspiras RacelesNo ratings yet
- FinaDocument20 pagesFinaJahn MyrilleeNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indications/Contraindicati Ons Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations BeforeDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mode of Action Indications/Contraindicati Ons Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations BeforeMikko McDonie VeloriaNo ratings yet
- Drud Study For DutyDocument9 pagesDrud Study For DutyAnonymous AlphaNo ratings yet
- Amoxicilin + Clavulanate PotassiumDocument2 pagesAmoxicilin + Clavulanate PotassiumHaidee GervacioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - AmoxicillinVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudySwag MasterNo ratings yet
- CeferoximeDocument1 pageCeferoximeGwen Stefanie Lagrimas ValloyasNo ratings yet
- RUG Tudy: College of NursingDocument3 pagesRUG Tudy: College of NursingYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyPark JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study2Document3 pagesDrug Study2Anjulie Austria SoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Tobramycin & CelebrexDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Tobramycin & CelebrexjbespirituNo ratings yet
- Tangina Mo BizarDocument1 pageTangina Mo BizarJhon eric EscultorNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesSALWANo ratings yet
- Furosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaDocument9 pagesFurosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaRanee Diane AnanayoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY AmoxicillinDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY AmoxicillinAzhly AntenorNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Sulfate Drug StudyDocument1 pageFerrous Sulfate Drug Studyjanice paralejas100% (1)
- Drug Study FinalDocument6 pagesDrug Study FinalAraw GabiNo ratings yet
- Gabato - Drug Study 1-3Document6 pagesGabato - Drug Study 1-3Denise GabatoNo ratings yet
- CotrimoxazoleDocument3 pagesCotrimoxazolecsy123No ratings yet
- Cefu, Metro, KetoDocument4 pagesCefu, Metro, KetoSethlyn_Gomez_5337No ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP For Eamc Ob-Gyne Ward Case PresDocument4 pagesDrug Study and NCP For Eamc Ob-Gyne Ward Case PresvirnzrobzNo ratings yet
- QUIMSON, JADEN Drug StudyDocument3 pagesQUIMSON, JADEN Drug StudyJaden QuimsonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyCourtney Dela FierraNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Bronchitis CorsigaDocument8 pagesDRUG STUDY Bronchitis CorsigaKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- 7 Case ScenarioDocument3 pages7 Case ScenarioLucas JelmarNo ratings yet
- Prophylaxis Action: Tetanus: Injection: 5 To 10 LF Units ofDocument10 pagesProphylaxis Action: Tetanus: Injection: 5 To 10 LF Units ofElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Cefpodoxima MergedDocument25 pagesCefpodoxima MergedKristelNo ratings yet
- DRUG SUMMARY TABLE: CHAPTER 33 Principles of Antimicrobial and Antineoplastic PharmacologyDocument3 pagesDRUG SUMMARY TABLE: CHAPTER 33 Principles of Antimicrobial and Antineoplastic PharmacologyNiki NourNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Balido, John Emmanuel A. BSN223/Grp89 Drug Study: 8 G/dayDocument1 pageBalido, John Emmanuel A. BSN223/Grp89 Drug Study: 8 G/dayEmman BalidoNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin DSDocument2 pagesAmpicillin DSEden RelacionNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDivine Grace Arreglo AbingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of Generation Antibiotics Mohamedzein, Nura Mohamedzein, SalwaDocument8 pagesDrug Study of Generation Antibiotics Mohamedzein, Nura Mohamedzein, SalwaNone BbNo ratings yet
- I. Drug Study: AllopurinolDocument1 pageI. Drug Study: Allopurinolkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- BenadrylDocument2 pagesBenadrylsamfandood10No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyIsagani Socrates Loreto100% (1)
- Sputnik VDocument4 pagesSputnik Vbobo gamingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 4Document9 pagesDrug Study 4bobo gamingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: METOPROLOL: Metoprolol 200mg Tab PO OD X 30 DaysDocument3 pagesDrug Study: METOPROLOL: Metoprolol 200mg Tab PO OD X 30 Daysbobo gamingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Acetaminophen: Generic NameDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Acetaminophen: Generic Namebobo gamingNo ratings yet
- AntimetaboliteDocument53 pagesAntimetaboliteRahul LokhandeNo ratings yet
- MOH BluebookDocument210 pagesMOH BluebookSay LeeNo ratings yet
- CONCHEM q4 m4 Anticancerdrugs-V3Document24 pagesCONCHEM q4 m4 Anticancerdrugs-V3NovaNo ratings yet
- Breast SurgeryDocument6 pagesBreast SurgeryDeedee Rocha100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakaMaulinaNo ratings yet
- Oncology Drug ListDocument11 pagesOncology Drug Listashrafh100% (1)
- Product Information: Adriamycin Solution For InjectionDocument18 pagesProduct Information: Adriamycin Solution For InjectionArya GuganNo ratings yet
- 8 - Cancer - ManagementDocument90 pages8 - Cancer - ManagementMaviel Maratas SarsabaNo ratings yet
- Reversal of Multidrug Resistance in Vitro and in Vivo by 5-N-Formylardeemin, A New Ardeemin DerivativeDocument8 pagesReversal of Multidrug Resistance in Vitro and in Vivo by 5-N-Formylardeemin, A New Ardeemin Derivativeali99No ratings yet
- DoxorubicinDocument3 pagesDoxorubicinApol Pen100% (2)
- DoxorubicinDocument12 pagesDoxorubicinWely Tiffani YpNo ratings yet
- Short Report: G. Catimel, F. Chauvin, J. P. Guastalla, P. Rebattu, P. B I R o N M. ClavelDocument3 pagesShort Report: G. Catimel, F. Chauvin, J. P. Guastalla, P. Rebattu, P. B I R o N M. ClavelApril NNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Importance of Nardostachys Jatamansi DC A Potential Therapeutic Agent in Different Pathological Ailments PDFDocument8 pagesPharmacological Importance of Nardostachys Jatamansi DC A Potential Therapeutic Agent in Different Pathological Ailments PDFadilnnjNo ratings yet
- Fasting and Fasting-Mimicking Diets For ChemotherapyDocument16 pagesFasting and Fasting-Mimicking Diets For ChemotherapyHuman ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Krishna Institute of Nursing Science, Karad: Practice Teaching-8Document19 pagesKrishna Institute of Nursing Science, Karad: Practice Teaching-8Shreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Anti Cancer DrugsDocument29 pagesAnti Cancer DrugsFrances RamosNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument21 pagesBreast CancerfrankNo ratings yet
- LYCHOP Protocol 1aug2014Document3 pagesLYCHOP Protocol 1aug2014Nararto PrijogoNo ratings yet
- Brajac - ProtocolDocument13 pagesBrajac - Protocolthanh ngôNo ratings yet
- Recent Updates On Nanomedicine Based Products: Current Sce-Nario and Future OpportunitiesDocument13 pagesRecent Updates On Nanomedicine Based Products: Current Sce-Nario and Future OpportunitiesvijuNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy ReviewDocument6 pagesChemotherapy ReviewkemisseNo ratings yet
- Nanoengineered Silica-Properties PDFDocument18 pagesNanoengineered Silica-Properties PDFkevinNo ratings yet
- Vinca Alkaloids - Anti Cancer DrugsDocument11 pagesVinca Alkaloids - Anti Cancer DrugsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapeutic Drug Induced Nail Changes A Prospective Observational StudyDocument5 pagesChemotherapeutic Drug Induced Nail Changes A Prospective Observational StudyDr SrigopalNo ratings yet
- Treating Wilms TumorDocument21 pagesTreating Wilms TumorBasile SiezaNo ratings yet
- Protokol SarcomaDocument4 pagesProtokol SarcomaHep PutNo ratings yet
- Artículo LeuconiquiaDocument17 pagesArtículo LeuconiquiaSMIBA Medicina100% (1)
- ALL - Interim Guideline v3Document59 pagesALL - Interim Guideline v3Awais Ul Hassan67% (3)
- Liposomal Doxorubicin ExtravasationDocument2 pagesLiposomal Doxorubicin ExtravasationjathieNo ratings yet