Professional Documents
Culture Documents
San Ildefonso College: Dynamic Learning Activity Sheet
San Ildefonso College: Dynamic Learning Activity Sheet
Uploaded by
Carlota TanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
San Ildefonso College: Dynamic Learning Activity Sheet
San Ildefonso College: Dynamic Learning Activity Sheet
Uploaded by
Carlota TanCopyright:
Available Formats
HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
San Ildefonso College
‘’The San Ildefonso College envision itself as faith community, globally competitive,
Academically excellent, certified and accredited.’’
S.Y. 2019-2020
DYNAMIC LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET
Name: Mrs. Angeli L. Peralta Date & Day July 7, 2020
Accomplished:
Grade & Section: 12 HUMSS Score:
Subject: ENGLISH for Academic and Professional Parent/ Guardian
Purposes Signature
(optional):
Activity Title: “Language in Academic Text”
Learning Targets: Differentiates language used in academic texts from various disciplines.
References: Ma. Joahna M. Estacio, PhD (2016) “English for the Globalized Classroom Series”
Phoenix Publishing House, Inc. Quezon City, pp.43, Valdez, Paolo Niňo M. (2016).
English for the Globalized Classroom Series English for Academic and Professional
Purposes. Quezon City, Philippines. Phoenix Publishing House Inc.
MAIN IDEA TO BE LEARNED
Academic writing is a challenging but satisfying activity. It needs great preparations. One of
the necessary preparations is on language use. Academic writing requires academic
language. Language use is a qualifying component of a text to be categorized as an
academic text.
Several definitions and explanations can be given to academic language which is considered
a formal way to present words on a certain field. In general, Academic language or text is
used in classroom setting – in textbooks, teacher-made tests and other forms of academic
disciplines.
Moreover, it includes variety of formal language skills such as vocabulary, grammar,
punctuation, syntax and the likes. These allow students to acquire knowledge and
academic skills needed to do the work of schools
EXAMPLES
Distinctive Attributes of Academic Language
A. Formality – Generally, academic writing is formal where the following should be
avoided:
*Colloquial words and expressions and idiomatic expressions
*Abbreviated words such as can’t, doesn’t, shouldn’t and others
*Two-word verbs such as put off, bring up
*Expanded terms over their abbreviated equivalents such as “as soon as possible”
instead of ASAP
B. Precision – In academic writing, facts, figures, graphs, illustrations are given
precisely. The exactness and accuracy of the data presented are visible. Writer is advised
not to use “several workers” when he/she can use “10 million workers”.
C. Explicitness – The writer makes sure that the various parts of the text are related to
one another, free from obscurity and easy to understand.
D. Accuracy – Academic writing uses vocabulary and statistics accurately that conform
to the correct value or standard. A writer chooses the appropriate word; let us say
“meeting, assembly, gathering, and conference”.
E. Hedging – Writer makes decisions about his/her stance on a particular subject. The strength
of the claims must be considered. He/She also uses cautious language.
*Introductory Verbs *Certain Lexical Verbs *Certain Modal Verbs
seem, be sure believe will, must
tend, indicate assume would, may
look like suggest might, could
appear to be
think
believe
doubt
*Adverbs of Frequency * *Modal Nouns * *That Clauses*
often assumption It could be the case that
sometimes possibility It might be suggested that
usually probability There is every hope that
*Modal Adverbs* *Modal Adjectives* *Phrases*
Certainly certain on the whole
Definitely definite more or less
Clearly clear
Probably probable
Possibly possible
perhaps
conceivably
F. Responsibility – Writer must be responsible for demonstrating and understanding of any
source text used. All evidences and justifications are provided to support the claims. Moreover,
the writer has to paraphrase and summarize the read academic text and acknowledge the source
of ideas and information through proper citations.
G. Organization – Academic writing is well-organized where the ideas are presented in a
logical manner.
Activity 1
Directions: Read the statements carefully. Write True if the statement is correct or False if wrong in the
blanks provided.
1. Jargons are the specific terms used in a particular course or field.____________
2. The words such as “haven’t”, “you’re” and “could’ve” are examples of acronyms.____________
3. The colloquial words are the denotative words found in the dictionary.____________
4. Hedges are used to express absolute certainty of a stance.____________
5. Grammar is one of the elements that need to be properly observed in an academic
writing.____________
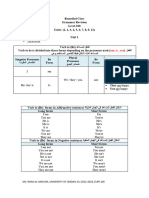
II. Directions: Analyze the sentences carefully. Replace the italicized two word verb in each sentence
with a single-word verb from the choices. Write the correct answers in the blanks.
produces conducted raised eliminate tolerate
refuses produces creates established increased
1._______________ Mothers cut down spending on grocery items.
2._______________ Scientists come up with a good solution to the problem.
3._______________ Teachers brought up some issues on cheating during examinations.
4._______________ Private schools nowadays get rid of tuition fee hike.
5._______________ The team leader turns down the first project proposal because of its
inconvenience for the members.
You might also like
- ITEP Prep GuideDocument139 pagesITEP Prep GuideCarlos Argel Gallardo Valerio100% (2)
- Learning Activity Sheet English For Academic and Professional Purposes 11Document27 pagesLearning Activity Sheet English For Academic and Professional Purposes 11Dave Billona100% (1)
- English Grammar Quiz Bee Grade 2Document2 pagesEnglish Grammar Quiz Bee Grade 2Jhomar Lat100% (4)
- TEST 4 - ToEFL PBT PracticeDocument9 pagesTEST 4 - ToEFL PBT PracticeVanHa DangHoang100% (4)
- Skin Like Milk Hair of Silk What Are Similes and MDocument36 pagesSkin Like Milk Hair of Silk What Are Similes and MOlivia brianneNo ratings yet
- Development Assessment MRCPCH WebsiteDocument1 pageDevelopment Assessment MRCPCH WebsiteRajiv Kabad100% (3)
- Week1 EappDocument10 pagesWeek1 EappRonalis PowellNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes Lesson 1: Language in Academic TextsDocument5 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes Lesson 1: Language in Academic TextsJhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesNo ratings yet
- EAPP - Q1 - W1 - Mod1 - Divisions of City School Manila 11 PagesDocument11 pagesEAPP - Q1 - W1 - Mod1 - Divisions of City School Manila 11 Pageswriter100% (7)
- Lesson 1 Languange Used in Academic TextDocument50 pagesLesson 1 Languange Used in Academic TextAndrea M. IbañezNo ratings yet
- EAPPG11 q1 - Mod1 Reading-For-Acadtext v2-2Document9 pagesEAPPG11 q1 - Mod1 Reading-For-Acadtext v2-2Nicole BernardoNo ratings yet
- Eapp Q1 W1Document10 pagesEapp Q1 W1Keith Andrea De LeonNo ratings yet
- Quarter 12 EAPP MODULE With WHLPDocument23 pagesQuarter 12 EAPP MODULE With WHLPZavel ZinNo ratings yet
- Academic Language Used From Various Disciplines.Document18 pagesAcademic Language Used From Various Disciplines.JoelynBitosNo ratings yet
- Eap 2 Q3Document69 pagesEap 2 Q3Mis SyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Academic Language Used From Various DisciplinesDocument27 pagesLesson 1 Academic Language Used From Various Disciplineschen11ogalescoNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 4 - Module 1Document26 pagesEnglish: Quarter 4 - Module 1gerlie maeNo ratings yet
- Language Used in Academic Text PDFDocument16 pagesLanguage Used in Academic Text PDFJeanica Delacosta Cespon100% (1)
- Eapp Week 4Document10 pagesEapp Week 4Roi Vincent Cuaresma BlasNo ratings yet
- MELC No. 1 - MELC No. 2Document8 pagesMELC No. 1 - MELC No. 2Niña Camille Arrozal David100% (3)
- ENG7 L1 4thQDocument28 pagesENG7 L1 4thQLovie DumpNo ratings yet
- Adapting For The: OccasionDocument41 pagesAdapting For The: OccasionLinkwid GreganaNo ratings yet
- Mod.2 - Language Used in Academic Texts From Various DisciplinesDocument3 pagesMod.2 - Language Used in Academic Texts From Various DisciplinesHonelyn FernandezNo ratings yet
- Eapp FirstlessonDocument26 pagesEapp FirstlessonRosales Keian G.No ratings yet
- Logical Organization, Precise Word Choice, Formal Tone and Evidence-Based Arguments Are Important Characteristics of Academic WritingDocument13 pagesLogical Organization, Precise Word Choice, Formal Tone and Evidence-Based Arguments Are Important Characteristics of Academic WritingMardia GadjaliNo ratings yet
- Academic Language Functions ToolkitDocument16 pagesAcademic Language Functions Toolkitwraysp100% (2)
- Bbi2002 Lecture Notes 1Document19 pagesBbi2002 Lecture Notes 1Iain Choong WKNo ratings yet
- Easp Q1 W1Document42 pagesEasp Q1 W1quandtshoNo ratings yet
- EAPP Week 1-5Document10 pagesEAPP Week 1-5Mon Rey B. DuranNo ratings yet
- English12 English For Academic and Professional Purposes Q1 Week1 Tiu Juliza S. Dacanay Lorlaine RDocument13 pagesEnglish12 English For Academic and Professional Purposes Q1 Week1 Tiu Juliza S. Dacanay Lorlaine RELSA CALUNODNo ratings yet
- Eapp - Q1 - Week1 2021-2022Document6 pagesEapp - Q1 - Week1 2021-2022KZ DeMac OngNo ratings yet
- Language Features of Academic Texts: English For Academic and Professional Purposes Activity No. 1Document6 pagesLanguage Features of Academic Texts: English For Academic and Professional Purposes Activity No. 1Evanessa VillacrusisNo ratings yet
- EappDocument9 pagesEappgaeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Language Used in Academic Text From Various DisciplinesDocument33 pagesLesson 1 Language Used in Academic Text From Various Disciplinesstephbanico1197No ratings yet
- Eng Teaching Eng in Elem Grades Chapter 7Document7 pagesEng Teaching Eng in Elem Grades Chapter 7GeminiNo ratings yet
- Eapp Module 1Document5 pagesEapp Module 1MC Do100% (4)
- Ok English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument23 pagesOk English For Academic and Professional PurposesGlen Welle SuarezNo ratings yet
- English For Academic Professional Purposes12 q3 w1 v4Document10 pagesEnglish For Academic Professional Purposes12 q3 w1 v4Jehl T DuranNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes (EAPP)Document10 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes (EAPP)Jodemarie Rivera RullanNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes (EAPP) Q1/Q3-Module 1 Language Used in Academic TextDocument11 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes (EAPP) Q1/Q3-Module 1 Language Used in Academic Textjared alonzoNo ratings yet
- English 7 Q4 Week 1 8Document34 pagesEnglish 7 Q4 Week 1 8Chubs Gerard BeliranNo ratings yet
- Academic Language Includes Language Used in Textbooks, in Classrooms, On TestsDocument10 pagesAcademic Language Includes Language Used in Textbooks, in Classrooms, On TestsAster JadeNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Module 3 Reading and WritingDocument10 pagesQuarter 3 Module 3 Reading and WritingNicka MaganteNo ratings yet
- Reflecting On Teaching Productive Skills To Second Language LearnersDocument6 pagesReflecting On Teaching Productive Skills To Second Language LearnersjemNo ratings yet
- EAPP LessonsDocument7 pagesEAPP LessonsKelly Misha NoolNo ratings yet
- Say If Is Postivie or NegativeDocument19 pagesSay If Is Postivie or NegativeTani LereleNo ratings yet
- Prototype Lesson Plan ENGLISH10 Q3 WK3Document9 pagesPrototype Lesson Plan ENGLISH10 Q3 WK3Lyke Therese Sungahid - BagsacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 OutlineDocument2 pagesLesson 1.2 OutlineJing-Jing KimayongNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument13 pagesQuarter 1 English For Academic and Professional PurposesSelloria DansellNo ratings yet
- Engl7 - Q4 - M2 - W1-FeaturesOfAcademicWriting - JeneferAbul - V1-ReviewedDocument14 pagesEngl7 - Q4 - M2 - W1-FeaturesOfAcademicWriting - JeneferAbul - V1-ReviewedjohbaguilatNo ratings yet
- EAPP Module 1Document11 pagesEAPP Module 1JessaMae Albaracin100% (2)
- EAPPQ1 - Module1 Week1-2Document36 pagesEAPPQ1 - Module1 Week1-2Sheena Mae SimborioNo ratings yet
- Eapp Q1 W1Document10 pagesEapp Q1 W1C YamixtheGamerNo ratings yet
- EAPP LAS W Gen. DirectionsDocument26 pagesEAPP LAS W Gen. DirectionsNhicole MianoNo ratings yet
- Composition WritingDocument4 pagesComposition WritingCRYSTAL ANNE PEREZNo ratings yet
- Language in Academic Text StudentsDocument23 pagesLanguage in Academic Text StudentsbobonlikeNo ratings yet
- EAPP 12 Q1 - w1Document6 pagesEAPP 12 Q1 - w1Rey Butaslac RolunaNo ratings yet
- Семінар риторика 1Document23 pagesСемінар риторика 1Юлия НиколаевнаNo ratings yet
- Differentiating Language Used in Academic Texts From Various DisciplinesDocument38 pagesDifferentiating Language Used in Academic Texts From Various DisciplinesDiane SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture Eaap Week 1Document4 pagesLecture Eaap Week 1beeyahNo ratings yet
- CVBGDocument5 pagesCVBGdaphne marisNo ratings yet
- English 3 - LP - Week 1 3Document5 pagesEnglish 3 - LP - Week 1 3Aizel Nova AranezNo ratings yet
- Discovering Voice: Lessons to Teach Reading and Writing of Complex TextFrom EverandDiscovering Voice: Lessons to Teach Reading and Writing of Complex TextNo ratings yet
- Orthography: As Outlined in the State Course of Study for IllinoisFrom EverandOrthography: As Outlined in the State Course of Study for IllinoisNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English For Academic and Professional Purposes Grade & Section: 12-Time Frame: 40 Minutes Content StandardDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in English For Academic and Professional Purposes Grade & Section: 12-Time Frame: 40 Minutes Content StandardCarlota TanNo ratings yet
- Adjectives: ArticlesDocument3 pagesAdjectives: ArticlesCarlota TanNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Q1 M2Document13 pagesOral Communication Q1 M2Carlota TanNo ratings yet
- San Ildefonso College: Dynamic Learning Activity SheetDocument4 pagesSan Ildefonso College: Dynamic Learning Activity SheetCarlota TanNo ratings yet
- ChristologyDocument4 pagesChristologyCarlota TanNo ratings yet
- Debate Grading RubricDocument5 pagesDebate Grading RubricCarlota TanNo ratings yet
- Arnis: (Combative Sports)Document40 pagesArnis: (Combative Sports)Carlota TanNo ratings yet
- Evolve Digital Level 1B Grammar SummariesDocument13 pagesEvolve Digital Level 1B Grammar SummariesSantos Erico Ávila ParedesNo ratings yet
- Temas Prueba Pensar 2 InglesDocument12 pagesTemas Prueba Pensar 2 Inglesheberth bermudezNo ratings yet
- Comparison Short AdjectivesDocument2 pagesComparison Short Adjectivesinfinityline11102No ratings yet
- The-Problematics-Of-Grammatical-Homonymy-The-Subject-And-Object-Complements - Content File PDFDocument6 pagesThe-Problematics-Of-Grammatical-Homonymy-The-Subject-And-Object-Complements - Content File PDFAlina CosticaNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Good Word ChoiceDocument9 pagesFactors That Influence Good Word ChoiceFauzia Siddiqui50% (2)
- Ensino Médio Módulo 4-1Document10 pagesEnsino Médio Módulo 4-1Rogério MaruyamaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Chinese Beginner 2Document6 pagesLesson 1 - Chinese Beginner 2lymacsauokNo ratings yet
- Ficha 15 de OctubreDocument3 pagesFicha 15 de OctubreyolandaanteiesNo ratings yet
- Starting Out Episode 3Document3 pagesStarting Out Episode 3kenken2No ratings yet
- Comparative DegreeDocument25 pagesComparative DegreeAgung PriyanaNo ratings yet
- Experiential Metafunction PracticalDocument67 pagesExperiential Metafunction PracticalMuhammad Usman MelayuNo ratings yet
- ELPR 100 Grammar Revision PDFDocument21 pagesELPR 100 Grammar Revision PDFopportunityroseNo ratings yet
- Do As Directed-Exercise 3Document2 pagesDo As Directed-Exercise 3Babita Bst50% (2)
- Booklet A1.1Document100 pagesBooklet A1.1Banfiel TroyaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences & Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesConditional Sentences & Passive Voicesfhrdia19No ratings yet
- Evaluación Octavo InglesDocument3 pagesEvaluación Octavo InglesJacky MalacatusNo ratings yet
- You Had Better StudyDocument7 pagesYou Had Better StudyAbel QuispeNo ratings yet
- Beyond A2 Workbook Pg8Document1 pageBeyond A2 Workbook Pg8Rafael WilhelmsNo ratings yet
- The Penguin Dictionary of English GrammarDocument164 pagesThe Penguin Dictionary of English GrammarKaren Leiva100% (1)
- Actividad Semana 4 Grado DecimoDocument4 pagesActividad Semana 4 Grado DecimoJuan David Casanova50% (2)
- Verbs Types Tenses TimeDocument14 pagesVerbs Types Tenses Timeashwin0% (1)
- The Twits S2Document19 pagesThe Twits S2S TANCREDNo ratings yet
- English q1 Wk1Document9 pagesEnglish q1 Wk1Edelyn Unay0% (1)
- L3 Unit 10 Grammar Basic AmEDocument1 pageL3 Unit 10 Grammar Basic AmEGENESIS NICOLE PALLO AUSAYNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect and Simple PastDocument16 pagesPresent Perfect and Simple PastDepartemen KaderisasiNo ratings yet