Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science7 - q1 - Mod3 - Two Worlds Apart Pure Substances vs. Mixtures
Science7 - q1 - Mod3 - Two Worlds Apart Pure Substances vs. Mixtures
Uploaded by
anna teresa calayagOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science7 - q1 - Mod3 - Two Worlds Apart Pure Substances vs. Mixtures
Science7 - q1 - Mod3 - Two Worlds Apart Pure Substances vs. Mixtures
Uploaded by
anna teresa calayagCopyright:
Available Formats
Science 7 Week 3
Two Worlds Apart:Pure Substances vs Mixtures
What is It
Pure Substances are one of the classes of matter. Substances are
homogeneous or with uniform composition and appearance are the same all
throughout. The temperature of a substance is fixed and sharp. During melting, a
substance melts completely/smoothly within a short time.
Activity No. 1.1
The figure below shows separating technique for the components of pure
substances. Another set of properties that distinguishes substances from mixtures.
Electrolysis of Water
Guide Questions:
A. What is the name of the pure substance H2O?
B. What are the components of water?
C. In the picture, can we separate Hydrogen (H) from Oxygen (O)?
D. What is the process that separates components H and O of water?
In pure substances, the components are chemically combined. The
component parts are difficult to separate except for water. During the process
called electrolysis or by-passing electric current the components Hydrogen (H) and
Oxygen (O) of water are separated.
Activity No. 1.2
Consider activity guides no. 1 and 2. Study first the given table and scenario.
Table 1: Boiling point of two liquid samples
Temperature in ˚C
SAMPLES Before After 5 After 8 After 10 After 12 After 14 After 16
heating minutes minutes minutes minutes minutes minutes
Liquid A 28 40 65 90 100 100 100
Liquid B 30 45 65 97 105 108 113
Scenario 1: Melting point of two solid samples
Chef Matt and his assistant observed two solid samples: Solid A and Solid B.
Both substances are white crystalline powder. They cannot determine which is a
substance and mixture just by looking at it. So, to distinguish which is which, they
heated the two samples using an improvised melting dish. Both the two samples
were heated at the same time and received an equal amount of heat. After a few
minutes, they had observed that Solid A melts completely within a short period of
time; while Solid B has portions that seem to be not melting.
To find out if you have understood the important concepts of the lesson,
answer the following questions below.
1. Which liquid sample is a pure substance?
Table 1: Boiling point of two liquid samples
Samples Temperature Observation while heating
Liquid A
Liquid B
2. Which solid sample is a pure substance?
Scenario 1: Melting point of two solid samples
Samples Appearance Observation while melting
Solid A
Solid B
During boiling, the temperature of a substance changes at the start then it
becomes the same and constant. During melting, a substance melts completely/
smoothly within a short time.
What’s More
Decide how to separate these pure substances? If it is not possible, please
write “cannot be separated” on the space provided.
Substance 1 Oxygen
Substance 2 Water
Substance 3 Gold
Substance 4 Carbon Dioxide
Substance 5 Carbon
Here is another Enrichment Activity for you. Read the paragraph below and
answer the questions that follow.
A
Joseph wants to compare the chemical properties of two substances. In
doing it, he prepared two flasks containing the substances and labeled them Liquid
A and Liquid B. He monitored the boiling points of the liquids and found that the
boiling points were 100˚C for substance A and 110˚C - 112˚C for liquid B. How
would you classify the two liquids?
Answer: Which liquid sample is a pure substance?
B
A student tests the melting point of a certain sample of potassium
alum/tawas. It starts melting at 91˚C and melts completely until the temperature is
92.5˚C. According to a data book, the melting point of potassium alum is 92.5˚C.
What can you say about the sample?
Answer: The sample is a .
Activity 1.1
Find out if the poem really helped you to discover and understand some of
the important concepts of the lesson. Answer the following questions below.
Guide Questions:
1. What is a mixture?
2. What are the sets of properties of mixtures?
3. Tabulate your answer about the properties of matter.
Set of Properties Mixtures
Appearance
Melting point
Boiling point
Substances and mixtures are classes of matter. Mixtures are heterogeneous
or without uniform composition and appearance are not the same all throughout.
The temperature of a mixture is different at different times. During melting, a
mixture has portions that seem to be not melting.
Activity No. 1.2
Figures below show separating techniques for the components of mixtures.
Another set of properties that distinguishes substances from mixtures.
Figure A Figure B Figure C
Figure D Figure E Figure F
What is It
Find out if you have discovered and understood the important concepts of
the lesson, you will be asked to answer the following questions below.
A. Which pictures show filtration or straining?
B. Which picture shows filter paper being used?
C. Which picture shows pieces of iron being separated?
D. Which picture shows decantation?
E. Which picture shows dissolving?
F. Which picture shows evaporation?
There are a lot of ways to separate mixtures. Physical manipulation
separates using a spoon or any scooping material or by picking. The use of magnet
can be done to separate the metallic materials from nonmetallic materials.
Filtration is the separation of an insoluble solid from a liquid mixture using filter
paper. In decantation, the large particles of insoluble solid are separated from the
liquid mixture. Evaporation separates the soluble solid from the liquid
component of the solution by evaporating the liquid substance.
Consider activity guides no. 1 and 2. If you are ready, start! Study fist table
1 and scenario 1.
Table 1: Boiling point of two liquid samples
Temperature in ˚C
Before After 5 After 8 After 10 After 12 After 14 After 16
SAMPLES heating minutes minutes minutes minutes minutes minutes
Liquid A 28 40 65 90 100 100 100
Liquid B 30 45 65 97 105 108 113
Scenario 1: Melting point of two solid samples
Chef Matt and his assistant observed two solid samples: Solid A and Solid
B. Both substances are white crystalline powder. They cannot determine which
is a substance and mixture just by looking at it. So, to distinguish which is
which, they heated the two samples using an improvised melting dish. Both the
two samples were heated at the same time and received an equal amount of
heat. After a few minutes, they had observed that Solid A melts completely
within a short period of time; while Solid B has portions that seem to be not
Guide Questions:
1. Which liquid sample is a substance?
Table 1: Boiling point of two liquid samples
Samples Temperature Observation while heating
Liquid A
Liquid B
2. Which solid sample is a substance?
Scenario 1: Melting point of two solid samples
Samples Appearance Observation while melting
Solid A
Solid B
During boiling, the temperature of a mixture is different at different times.
During melting, a mixture has portions that seem to be not melting.
What’s More
Decide how to separate these mixture? If it is not possible, please write
“cannot be separated” on the space provided.
Mixture 1 salt and iron filings
Mixture 2 water and pebbles
Mixture 3 salty water
Mixture 4 salt, iron filings and water
Mixture 5 gravel, sand and sugar
Mixture 6 gravel, sand, sugar and iron filings
Figure A A magnet is used to separate iron Figure B Water is used to dissolve a solid
Figure C A strainer is used to separate large Figure D Decanting water with insoluble
solids materials into the other container
Figure E Evaporation is used to separate Figure F Filtration is used to separate very
already dissolve solids. small solids.
Read the paragraph below and answer the questions that follow.
A
Joseph wants to compare the chemical properties of two substances. In
doing it, he prepared two flasks containing the substances and labeled them
Liquid A and Liquid B. He monitored the boiling points of the liquids and found
that the boiling points were 100˚C for substance A and 110˚C - 112˚C for liquid
B. How would you classify the two liquids?
Answer: Liquid A is .
Liquid B is .
B
A student tests the melting point of a certain sample of potassium
alum/tawas. It starts melting at 87-89˚C but does not melt completely until the
temperature is 91˚C. According to a data book, the melting point of potassium
alum is 92.5˚C. What can you say about the sample?
Answer: The sample is a .
C
Teacher Joy placed two white solid substances in two different beakers.
She labeled the beakers as Solid A and Solid B. She said that Solid A is a
substance and Solid B is a mixture. If you are going to test the melting point of
the two samples what would you expect to the melting point of Solid A and Solid
B?
Answer: .
What I Have Learned
Read the paragraph carefully and fill in the correct words that fit in the given
sentences found in the box below.
magnet mixtures filtration different
manipulation evaporation liquid
(1) are separated without any chemical reactions. There are many
different kinds of mixtures. Different mixtures are separated in (2)
ways.
Physical (3) separates the components of varying sizes using a
spoon or any scooping material or by picking. The use of (4) can be
done to separate the metallic materials from nonmetallic materials. (5)
is the separation of an insoluble solid from a liquid mixture using a
semipermeable membrane like filter paper.
In decantation, the large particles of insoluble solid are separated from the
(6) mixture. (7) separates the soluble solid from the liquid
You might also like
- Unit 3 - Worksheet 2: Name Date PDDocument2 pagesUnit 3 - Worksheet 2: Name Date PDRobert B.75% (4)
- Open Channel Flow Measurement Handbook PDFDocument23 pagesOpen Channel Flow Measurement Handbook PDFÁrpád Vass100% (1)
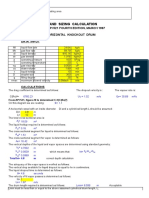
- Design and Sizing Calculation: Based On Api 521 Fourth Edition, March 1997 Horizontal Knockout Drum Data InputDocument2 pagesDesign and Sizing Calculation: Based On Api 521 Fourth Edition, March 1997 Horizontal Knockout Drum Data InputChitu Ionut Laurentiu100% (2)
- Problems Involving SetsDocument9 pagesProblems Involving SetsJedylon AgumNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs2Document2 pagesModal Verbs2mohd ridhwan100% (1)
- Summative Math-7Document3 pagesSummative Math-7Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- ADM Science7 Q2 M4of9.ppsxDocument33 pagesADM Science7 Q2 M4of9.ppsxEssaNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document23 pagesModule 6Gabrielle Kacy Gacela100% (1)
- Science 7 First Periodic Examination 2022 2023Document3 pagesScience 7 First Periodic Examination 2022 2023Sheena AcayanNo ratings yet
- Las Science 9 Melc 2 q2 Week2Document6 pagesLas Science 9 Melc 2 q2 Week2Geralyn Zuniega100% (1)
- Fist Periodical Exam Science 7 Name: - Grade & Section: - ScoreDocument4 pagesFist Periodical Exam Science 7 Name: - Grade & Section: - ScoreJuliet Saburnido AntiquinaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 5 6 Earths Resources Human Activities That Affect Natural Resources and Ways To Prevent The Effects of Human Activities On Natural Resources 1Document7 pagesModule 4 5 6 Earths Resources Human Activities That Affect Natural Resources and Ways To Prevent The Effects of Human Activities On Natural Resources 1kali dizonNo ratings yet
- The Microscope - Summative TestDocument11 pagesThe Microscope - Summative TestJulie Maezar Aparre100% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesMae CudalNo ratings yet
- Science - Grade 7 Learner Activity Sheets Quarter 1, Week No. 1 Title: Components of Scientific Investigation First Edition, 2021Document11 pagesScience - Grade 7 Learner Activity Sheets Quarter 1, Week No. 1 Title: Components of Scientific Investigation First Edition, 2021MA EDYLYN NOGUERRANo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Examination Science 7Document3 pagesFirst Quarterly Examination Science 7Jorgen De Guzman-SalonNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 Mod2 LifethroughtheLens v4Document35 pagesScience7 Q2 Mod2 LifethroughtheLens v4SPEILBERG LUMBAY100% (1)
- First Periodical Test G7 ScienceDocument4 pagesFirst Periodical Test G7 ScienceArvin Angelo MatiasNo ratings yet
- (Week 3 Module 7..) Science8-Q3-Slm3Document16 pages(Week 3 Module 7..) Science8-Q3-Slm3Ron FamilaranNo ratings yet
- Modules in Home Economics CookeryDocument16 pagesModules in Home Economics CookeryWilliam Laguisma BonaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Summative TestDocument8 pages2nd Quarter Summative TestJoelmarMondonedo100% (1)
- Science Quarter 4 Module 2Document3 pagesScience Quarter 4 Module 2Christian AlbosNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Sci.7. 4th QuarterDocument3 pagesAssessment in Sci.7. 4th QuarterBillones Rebalde MarnelleNo ratings yet
- 4A and 4B Science7Document29 pages4A and 4B Science7Jonnah Faye MojaresNo ratings yet
- LONG TEST IN TLE 7 (Fourth Quarter)Document1 pageLONG TEST IN TLE 7 (Fourth Quarter)Jeo MillanoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2-Module 2 - Nutrients Needed in Our BodyDocument15 pagesQuarter 2-Module 2 - Nutrients Needed in Our BodyCes Michaela Cadivida100% (1)
- S7Q2 ExamDocument2 pagesS7Q2 ExamCatleah ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ModuleDocument1 pageUnit 3 ModuleKristine Ibarreta-Jazul100% (1)
- Consumer Chemistry 9 - First Quarter ExaminationDocument5 pagesConsumer Chemistry 9 - First Quarter ExaminationGabriela FernandezNo ratings yet
- Tle 8 ReviewDocument33 pagesTle 8 ReviewLlemor Soled SeyerNo ratings yet
- NLC Lesson 2Document14 pagesNLC Lesson 2Sol AclonNo ratings yet
- Science6 - q1 - Mod1les4 - Solutions and Their Characteristics - EDITEDDocument10 pagesScience6 - q1 - Mod1les4 - Solutions and Their Characteristics - EDITEDGene-Beth Cacho GarceNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Earth's Atmosphere: Grade 7 ScienceDocument43 pagesExploring The Earth's Atmosphere: Grade 7 ScienceRiza Bustamante AcedoNo ratings yet
- S7 - Q2 - Answer KeyDocument11 pagesS7 - Q2 - Answer KeyRaniel LacuarinNo ratings yet
- Science7 q1 Mod3 Two Worlds Apart Pure Substances vs. Mixtures FINAL08122020Document32 pagesScience7 q1 Mod3 Two Worlds Apart Pure Substances vs. Mixtures FINAL08122020Hector PantiNo ratings yet
- Math 8 QTR 2 Week 5Document8 pagesMath 8 QTR 2 Week 5dahNo ratings yet
- Answer Key To Summative Test No. 1 English 7: Guro Ko ChannelDocument8 pagesAnswer Key To Summative Test No. 1 English 7: Guro Ko ChannelMa Ria LizaNo ratings yet
- Science-9-Q4-Week5-MELC05-Module5-Batangan-Archiemedez ReadytoprintDocument25 pagesScience-9-Q4-Week5-MELC05-Module5-Batangan-Archiemedez ReadytoprintAngelica Marie JacintoNo ratings yet
- ADM Science7 Q2 M6of9Document32 pagesADM Science7 Q2 M6of9EssaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Q1 - Mod5 - Quantity Really MattersDocument22 pagesScience 7 - Q1 - Mod5 - Quantity Really MattersMomshie Ella0% (1)
- Science 7 - Summative Test 1st QuarterDocument4 pagesScience 7 - Summative Test 1st QuarterEsther Mae Ann Trugillo0% (1)
- Use The Mole Concept To Express Mass of Substances (S9Mt-Iii-19)Document4 pagesUse The Mole Concept To Express Mass of Substances (S9Mt-Iii-19)ChelleyOllitroNo ratings yet
- Grade 7-MODULE 1 ASSESSMENTDocument3 pagesGrade 7-MODULE 1 ASSESSMENTCristinë SËij ÄlatanNo ratings yet
- CLMD4A ScieG7Document40 pagesCLMD4A ScieG7Ronan Thaddeus Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- LAS-SCI5 - 4 - Plants PartsDocument4 pagesLAS-SCI5 - 4 - Plants Partscristina quiambaoNo ratings yet
- Science: Third Quarter - Module 6 Heat TransferDocument42 pagesScience: Third Quarter - Module 6 Heat TransferJonnah Faye Mojares100% (1)
- 1 Bmy Ds OO0 OKd 4 LSZD K9 M7 U 0 VG 6 ZUZ7 GvaDocument35 pages1 Bmy Ds OO0 OKd 4 LSZD K9 M7 U 0 VG 6 ZUZ7 GvaRica Mae EsmenosNo ratings yet
- Q1 Math7 Module2 Problems Involving SetsDocument21 pagesQ1 Math7 Module2 Problems Involving SetsZarahbeth Claire G. ArcederaNo ratings yet
- Isotope and Ions Practice Worksheet Part I: IsotopesDocument3 pagesIsotope and Ions Practice Worksheet Part I: IsotopesZarifah AdrianaNo ratings yet
- For Grade 9 Regular: Science Instructional PacketsDocument107 pagesFor Grade 9 Regular: Science Instructional PacketsFhranscea KimNo ratings yet
- Health: Gender and Human SexualityDocument34 pagesHealth: Gender and Human SexualityCHERIE NEDRUDA0% (1)
- BPP 7&8 Module 4Document31 pagesBPP 7&8 Module 4LEVI RUTH ADUNANo ratings yet
- Science 7: First Quarter ExaminationDocument2 pagesScience 7: First Quarter Examinationmacren septemberNo ratings yet
- Adverb5 Eating With Adverbs PDFDocument2 pagesAdverb5 Eating With Adverbs PDFMuhammadAsifNo ratings yet
- Music - Arts - Physical Education - HealthDocument12 pagesMusic - Arts - Physical Education - Healthnujnuj nitagac100% (1)
- Arts8 - q1 - Mod3 - Appreciating Southeast Asian Artworks and Artifacts - FINAL08032020Document20 pagesArts8 - q1 - Mod3 - Appreciating Southeast Asian Artworks and Artifacts - FINAL08032020HERNAN JAY BUYOKNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document1 pageScience 9Rafael John Rubio100% (1)
- 3rd Grading Exam - Science 7Document6 pages3rd Grading Exam - Science 7Diane Marr Nicolas DencioNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Test in ScienceDocument6 pagesFirst Periodical Test in ScienceGrace GaraldeNo ratings yet
- M2 Unit 3 G8Document8 pagesM2 Unit 3 G8Julia Geonzon LabajoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Module 3Document32 pagesScience 7 Module 3Lilah Blair100% (4)
- G7 To PrintDocument2 pagesG7 To Printkathleen de jesusNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 3Document2 pagesSummative Test 3lermaNo ratings yet
- Science8 - q1 - Mod4 - Effect of Temperature To The Speed of Sound - FINAL07282020Document4 pagesScience8 - q1 - Mod4 - Effect of Temperature To The Speed of Sound - FINAL07282020anna teresa calayagNo ratings yet
- Science8 - q1 - Mod3 - Potential and Kinetic Energy - FINAL07282020Document5 pagesScience8 - q1 - Mod3 - Potential and Kinetic Energy - FINAL07282020anna teresa calayagNo ratings yet
- What I Have Learned: Science 7 Week 5 Quantities Really MattersDocument1 pageWhat I Have Learned: Science 7 Week 5 Quantities Really Mattersanna teresa calayagNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippinesanna teresa calayagNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Week 5Document2 pagesScience 8 Week 5anna teresa calayagNo ratings yet
- Hommes Transport Gas Pipelines Internal Corrosion 2015Document1 pageHommes Transport Gas Pipelines Internal Corrosion 2015Pasquale CutriNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief SystemDocument33 pagesPressure Relief SystemRanchojiNo ratings yet
- Volcano ActivityDocument6 pagesVolcano ActivityRafaela Estrella ManalangNo ratings yet
- Volume 1 Spine BFSUDocument65 pagesVolume 1 Spine BFSUKelly HuttonNo ratings yet
- Output Summary: SI UnitsDocument42 pagesOutput Summary: SI UnitsAkhil JoseNo ratings yet
- Foxboro Bubbler App Note Mi020328Document28 pagesFoxboro Bubbler App Note Mi020328Anonymous zdCUbW8HfNo ratings yet
- MINIVAP VP - Service - Manual V1.04 - 1.61 - EnglishDocument22 pagesMINIVAP VP - Service - Manual V1.04 - 1.61 - EnglishKratos EspejoNo ratings yet
- Determination of Certified Relieving CapacitiesDocument6 pagesDetermination of Certified Relieving CapacitiesGustavo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Basic Hydraulics - Fluid Power PhysicsDocument14 pagesBasic Hydraulics - Fluid Power PhysicsmkNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Biochemistry - WaterDocument24 pagesAspects of Biochemistry - WaterGiovanni SlackNo ratings yet
- LaboratoryapparatussespptDocument39 pagesLaboratoryapparatussespptMapeh EditingNo ratings yet
- Our Fragile Planet - Hydrosphere - Freshwater Sytems and PollutionDocument209 pagesOur Fragile Planet - Hydrosphere - Freshwater Sytems and Pollutionlelo2k3No ratings yet
- Fractional Distillation of Crude OilDocument3 pagesFractional Distillation of Crude OilTracy Michelle Thomas100% (1)
- 11 Electric CurrentDocument52 pages11 Electric CurrentDev Raju0% (1)
- Rxyq T PDFDocument57 pagesRxyq T PDFValentin MalihinNo ratings yet
- Yang 2010Document10 pagesYang 2010Li DongyueNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning (2161908) : A Laboratory Manual ForDocument62 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning (2161908) : A Laboratory Manual ForAbhishek RaiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Fluid Power PDFDocument141 pagesIndustrial Fluid Power PDFchidambaram kasi50% (4)
- Ionic Liquids-An Overview: Stewart A. Forsyth, Jennifer M. Pringle, and Douglas R. MacfarlaneDocument7 pagesIonic Liquids-An Overview: Stewart A. Forsyth, Jennifer M. Pringle, and Douglas R. Macfarlaneshubhang2392No ratings yet
- Sci.7 - q1 - Mod3 - Two Worlds Apart Pure Substances vs. Mixtures PDFDocument35 pagesSci.7 - q1 - Mod3 - Two Worlds Apart Pure Substances vs. Mixtures PDFJohnsun Galado88% (8)
- ASTMD2440 - Standard Test Method For Oxidation Stability of Mineral Insulating Oil PDFDocument6 pagesASTMD2440 - Standard Test Method For Oxidation Stability of Mineral Insulating Oil PDFMohan RaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Intermolecular Forces Abm Gas HumssDocument3 pagesLesson 8 Intermolecular Forces Abm Gas HumssJOHN RUZZELNo ratings yet
- Chap1F Scale UpDocument19 pagesChap1F Scale Upmohan804No ratings yet
- Ankit Gola Class:-XII - E Roll NoDocument16 pagesAnkit Gola Class:-XII - E Roll NoGaurav Gola100% (1)
- Study of The Factors Affecting The Sensitivity of Liquid PenetrantDocument59 pagesStudy of The Factors Affecting The Sensitivity of Liquid PenetrantfallalovaldesNo ratings yet
- Gesamtkatalog - Dsentechnik 2012 - Englisch PDFDocument194 pagesGesamtkatalog - Dsentechnik 2012 - Englisch PDFjpsingh75No ratings yet