Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer To Problem Exercise No 3
Answer To Problem Exercise No 3
Uploaded by
still jungkookOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer To Problem Exercise No 3
Answer To Problem Exercise No 3
Uploaded by
still jungkookCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer to Problem Exercise no.
3
Direction: The following problems are applications of First Law of Thermodynamics. Each problem has final
answer already. Try your best to compute and come up with correct and complete solutions.
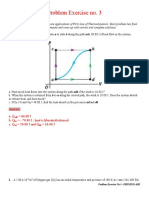
1. When a system is taken from state a to state b along the path acb, 80.00 J of heat flow in the system,
and 30.00 J of work is done.
a. How much heat flows into the system along the path adb if the work is 10.00 J?
Qacb = 80 J and Wacb = 30 J
Qadb = ? if Wadb = 10 J
Qadb = ΔUadb + Wadb, since ΔU is path independent, ΔUadb = ΔUacb
ΔUacb = Qacb – Wacb = 80 J – 30 J = 50 J = ΔUadb
Qadb = 50 J + 10 J = 60 J
b. When the system is returned from b to a along the curved path, the work is 20.00 J. Does the system absorb
or release heat, and how much?
Wba = - 20 J (compression, - since V decreses from path b to a)
Qba = ΔUba + Wba, since ΔU is path independent, ΔUab = ΔUacb = ΔUabd = 50 J
ΔUba = Ua – Ub = - (Ub – Ua)
ΔUba = - ΔUab = - 50 J
Qba = - 50 J + (- 20 J) = - 70 J (liberated/released)
Problem Exercise No.3 –PHYSENG-AHI
c. If Ua = 0 and Ud = 40.00 J, find the heat absorb in the processes ad and db.
ΔUad = Ud – Ua = 40 J
Wadb = Wad + Wdb = 10 J (isochoric)
Qad = ΔUad + Wad = 40 J + 10 J = 50 J
ΔUdb = Qdb – Wdb (isochoric)
ΔUdb =Ub – Ud, since ΔUab = Ub – Ua = 50 J
ΔUdb = 50 J – 40 J = 10 J
ΔUdb = Qdb = 10 J
Answers:
a. Qadb = 60.00 J
b. Qba = - 70.00 J ; heat is liberated/released
c. Qad = 50.00 J and Qdb = 10.00 J
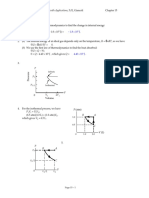
2. A 2.00 x 10-3 m3 of Oxygen gas (O2) has an initial temperature and pressure of 200 K at 1 atm (101,300 Pa).
The gas undergoes four processes:
AB: Heated at constant V to 400 K.
BC: Heated at constant P to 800 K.
CD: Cooled at constant V back to 1 atm (101,300 Pa)
DA: Cooled at constant P back to 200 K
Problem Exercise No.3 –PHYSENG-AHI
a. How many moles of O2 are present?
Consider point A: PV = nRT
3
PV ( 101,300 Pa ) ( 0.002 m )
n= = =0.1219mol
RT ( 8.31 J /mol K ) ( 200 K )
b. What is the pressure (in Pascals) at point B?
P A PB (101,300 Pa ) ( 400 K )
= PB = =202 ,600 Pa
TA TB 200 K
c. Find Q, U and W for process AB.
WAB = 0 J (isochoric)
Q AB=∆ U AB=n C v ∆ T =( 0.1219 mol ) ( 20.85 J /mol K ) ( 400 K−200 K )=508.323 J =Q AB=∆ U AB
d. What is the volume at point C (&D)?
VB VC ( 0.002 m3 ) ( 800 K )
= V C= =0.004 m3
TB TC 400 K
e. Find Q, ∆U and W for process BC.
W BC =P ∆ V =( 202 , 600 Pa ) ( 0.004 m3 −0.002m 3 ) =405.2 J
QBC =n C p ∆ T =( 0.1219 mol )( 29.16 J / mol K ) ( 800 K−400 K )=1,421.8416 J
∆ U =Q BC −W BC =1,421.8416 J −405.2 J =1016.6416 J
f. What is the temperature at point D?
PC PD (101,300 Pa ) ( 800 K )
= T D= =400 K
TC T D 202 ,600 Pa
g. Find Q, ∆U and W for process CD.
W CD =0 J (Isochoric)
QCD =n C V ∆ T =( 0.1219 mol ) ( 20.85 J / mol K ) ( 400 K−800 K ) =−1,016.646 J =QCD =∆U CD
h. Find Q, ∆U and W for process DA.
W DA =P ∆V =( 101,600 Pa ) ( 0.002 m 3−0.004 m 3 ) =−203.2 J
Q DA=n C p ∆ T =( 0.1219 mol ) ( 29.16 J /mol K ) ( 200 K −400 K ) =−710.9208 J
∆ U DA =Q DA −W DA =−710.9208 J −(−203.2 ) J =−507.7208 J
i. Summarize the four processes by completing the table
Process Q W ΔU
AB 508.323 J 0J 508.323 J
Problem Exercise No.3 –PHYSENG-AHI
BC 1,421.8416 J 405.2 J 1,016.6416 J
CD −1,016.646 J 0J −1,016.646 J
DA −710.9208 J −203.2 J −507.7208 J
Total 202.5978 J 202 J 0.5978 J ~ 0 J
Answers:
a. n = 0.1219 mol
b. PB = 202, 600 Pa
c. W = 0 J; Q = ∆U = 508.323 J
d. VC = 4.00 x 10-3 m3
e. ∆U =1,016.646 J ; W = 405.2 J ; Q = 1,421.846 J
f. TD = 400 K
g. W = 0 J ; Q = ∆U = - 1,016.646 J
h. ∆U = - 508.323 J ; W = - 202.6 J ; Q = - 710.923 J
Problem Exercise No.3 –PHYSENG-AHI
You might also like
- Activity 4Document4 pagesActivity 4Mark Galerio100% (1)
- Heat & Thermodynamics (Practice Questions PDFDocument41 pagesHeat & Thermodynamics (Practice Questions PDFSaksham100% (2)
- Theory of Elasticity by Sadhu SinghDocument7 pagesTheory of Elasticity by Sadhu Singhotonbara14% (7)
- Epson 3800 3880 SMDocument306 pagesEpson 3800 3880 SMIon IonutNo ratings yet
- Problem Exercise No. 3: Answer Already. Try Your Best To Compute and Come Up With Correct and Complete SolutionsDocument3 pagesProblem Exercise No. 3: Answer Already. Try Your Best To Compute and Come Up With Correct and Complete Solutionsstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- Soal 2Document10 pagesSoal 2Norma Fitra Pusta RahmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Solutions: e W Q Q W Q WDocument32 pagesChapter 22 Solutions: e W Q Q W Q Wysrra94No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - ThermodynamicsDocument69 pagesChapter 12 - Thermodynamicszahid_polyNo ratings yet
- HC Verma Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument22 pagesHC Verma Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Laws of ThermodynamicsHorus GamingNo ratings yet
- Phys 181 CH 2122 Sample ProblemsDocument4 pagesPhys 181 CH 2122 Sample Problemsluis atenciaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsNguyễn Việt PhươngNo ratings yet
- Thermal MCQDocument42 pagesThermal MCQRanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- CLT4 Recitation Worksheet Fall 2022 Solutions PDFDocument3 pagesCLT4 Recitation Worksheet Fall 2022 Solutions PDFotlacasNo ratings yet
- Solution To Exam No. 2Document5 pagesSolution To Exam No. 2mozam haqNo ratings yet
- Me6301 QBDocument46 pagesMe6301 QBNaveen Dhanuraj100% (1)
- Physics Exercise 2Document4 pagesPhysics Exercise 2Law Jing SeeNo ratings yet
- AE 231 Thermodynamics Recitation 8 Recitation 8: Instructor: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Sinan EyiDocument13 pagesAE 231 Thermodynamics Recitation 8 Recitation 8: Instructor: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Sinan EyiOnur ÖZÇELİKNo ratings yet
- Amplifier Transistors: NPN SiliconDocument6 pagesAmplifier Transistors: NPN SiliconLagos D. RangelNo ratings yet
- Additional Tutorial 5 ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesAdditional Tutorial 5 ThermodynamicsTeeWenSengNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFDocument8 pagesThermodynamics JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFdpcdglNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Thermodynamics (NOC21-ME73) Assignment-4Document8 pagesConcepts of Thermodynamics (NOC21-ME73) Assignment-4Saurabh ManralNo ratings yet
- Solution Part 1 (2023)Document6 pagesSolution Part 1 (2023)01khanh26No ratings yet
- Equations of Use in The Closed-Book Exam (Use This Page For Your Work)Document5 pagesEquations of Use in The Closed-Book Exam (Use This Page For Your Work)mozam haqNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Kuis Hukum II TermodinamikaDocument10 pagesPembahasan Kuis Hukum II Termodinamikaastri nurmalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document73 pagesChapter 20maryamhomayoonfalNo ratings yet
- Kel 3Document13 pagesKel 3satrio wekaNo ratings yet
- Past Exam Problems of ThermodynamicsDocument44 pagesPast Exam Problems of Thermodynamicsromaehab201912No ratings yet
- Alcorcon Engineering Review Center: Power & Industrial Plant EngineeringDocument13 pagesAlcorcon Engineering Review Center: Power & Industrial Plant EngineeringNeil SequioNo ratings yet
- Alcorcon PIPE Merged SolvedDocument80 pagesAlcorcon PIPE Merged SolvedBernalynMalinaoNo ratings yet
- Bab 2Document13 pagesBab 2Teguh Novri YansyahNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Capitulo 20 Paul E TippensDocument21 pagesSolucionario Capitulo 20 Paul E TippensDaniel Cruz100% (1)
- Chapter 19 The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument62 pagesChapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamicsamna insyirahNo ratings yet
- ME101 Tutorial 03 Solution PDFDocument13 pagesME101 Tutorial 03 Solution PDFalex albNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - ThermodynamicsDocument73 pagesChapter 20 - Thermodynamicswiggly18No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document81 pagesChapter 3Jasmine Jones92% (37)
- Problem 2.128Document5 pagesProblem 2.128Eric Castillo MartínezNo ratings yet
- Thermo DPT-5Document3 pagesThermo DPT-5akshatdaga1526No ratings yet
- Phy2 Q3Document2 pagesPhy2 Q3Lien My HongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20. Thermodynamics: The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument18 pagesChapter 20. Thermodynamics: The First Law of ThermodynamicsBryan CauichNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Section A - Mathcad Solutions: 5.2 Let The Symbols Q and Work Represent Rates in Kj/s. Then by Eq. (5.8)Document21 pagesChapter 5 - Section A - Mathcad Solutions: 5.2 Let The Symbols Q and Work Represent Rates in Kj/s. Then by Eq. (5.8)light2618No ratings yet
- ch2 116 118Document10 pagesch2 116 118Gonçalo CruzeiroNo ratings yet
- M Yusuf Rizaldi-206060300111011Document3 pagesM Yusuf Rizaldi-206060300111011M YUSUF RIZALDYNo ratings yet
- Dentify: C Carnot H C HDocument5 pagesDentify: C Carnot H C HCoco LinNo ratings yet
- Capítulo 20 (5th Edition)Document28 pagesCapítulo 20 (5th Edition)blinblinwebboyNo ratings yet
- NRT, So We Have NR ®T 0.: IsobaricDocument15 pagesNRT, So We Have NR ®T 0.: IsobaricJuju SaputriNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 ADocument21 pagesChapter5 ANic BlandoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1Document40 pagesThermodynamics 1Krishna Kumar G100% (1)
- CH 07Document25 pagesCH 07hirenpatel_universal100% (1)
- Environmental Engineering NumericalDocument23 pagesEnvironmental Engineering NumericalArham SheikhNo ratings yet
- Engineering Questions and AnswersDocument35 pagesEngineering Questions and Answersnoodlehead675No ratings yet
- Section e To Be Solved Set 1Document14 pagesSection e To Be Solved Set 1Neil SequioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20. Thermodynamics: The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument19 pagesChapter 20. Thermodynamics: The First Law of ThermodynamicsChristian Joseph TumbagaNo ratings yet
- 67655-NilssonSM Ch10Document57 pages67655-NilssonSM Ch10Ly RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20. Thermodynamics: The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument18 pagesChapter 20. Thermodynamics: The First Law of ThermodynamicsJhon FernandezNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem ThermoDocument25 pagesSample Problem ThermoJonnah Faye Mojares0% (1)
- Hibbeler Dynamics Ism Ch22Document35 pagesHibbeler Dynamics Ism Ch22Cherry Ann CondinoNo ratings yet
- A1Document27 pagesA1Caramel jNo ratings yet
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Air Transport and The Open Skies OptionDocument19 pagesAir Transport and The Open Skies Optionstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- Contemporary AbstractionDocument12 pagesContemporary Abstractionstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Entrepreneurship-MergedDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Entrepreneurship-Mergedstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- Earthworks - ModuleDocument77 pagesEarthworks - Modulestill jungkookNo ratings yet
- DadaismDocument42 pagesDadaismstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- SasagutanDocument2 pagesSasagutanstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- Resumes & Cover Letters: Undergraduate Resource SeriesDocument12 pagesResumes & Cover Letters: Undergraduate Resource Seriesstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- Addition of Vectors - Practice ProblemDocument2 pagesAddition of Vectors - Practice Problemstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- Problem Exercise No. 3: Answer Already. Try Your Best To Compute and Come Up With Correct and Complete SolutionsDocument3 pagesProblem Exercise No. 3: Answer Already. Try Your Best To Compute and Come Up With Correct and Complete Solutionsstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- Answer For Problem Exercise: 1. Conceptual QuestionDocument2 pagesAnswer For Problem Exercise: 1. Conceptual Questionstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- Answer For Problem Exercise: 1. Conceptual QuestionDocument2 pagesAnswer For Problem Exercise: 1. Conceptual Questionstill jungkookNo ratings yet
- Pay Per Month Position Title Pay Per Month 13 Month PayDocument1 pagePay Per Month Position Title Pay Per Month 13 Month Paystill jungkookNo ratings yet
- DC Jow Ga Beginner CurriculumDocument2 pagesDC Jow Ga Beginner CurriculumKevinNo ratings yet
- CR Unit 1 &11 (Part A &B)Document12 pagesCR Unit 1 &11 (Part A &B)durai muruganNo ratings yet
- James Coleman (October Files) by George BakerDocument226 pagesJames Coleman (October Files) by George Bakersaknjdasdjlk100% (1)
- (HMI-LP-RT30 + R131-A - User Manual) A06 - ENDocument110 pages(HMI-LP-RT30 + R131-A - User Manual) A06 - ENrehanNo ratings yet
- Yuxi CatalogueDocument16 pagesYuxi CatalogueSoltani AliNo ratings yet
- Jewellery Shop Design 3dDocument5 pagesJewellery Shop Design 3dTrường Thọ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Normal DistributionDocument30 pagesThe Normal DistributionJohn Rich CaidicNo ratings yet
- Da0bl7mb6d0 Rev DDocument44 pagesDa0bl7mb6d0 Rev DFerreira da CunhaNo ratings yet
- Visual Storytelling The Digital Video Documentary - Original PDFDocument44 pagesVisual Storytelling The Digital Video Documentary - Original PDFjparanoti100% (1)
- Sri Lank An Airline IndustryDocument29 pagesSri Lank An Airline IndustryTuan RifkhanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Cooling: Mechanical Power Engineering DeptDocument22 pagesElectronics Cooling: Mechanical Power Engineering DeptneilNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Fundamentals of Semiconductor Fabrication Gary S May Simon M Sze Isbn 0471232793 Isbn 978-0-471 23279 7 Isbn 9780471232797Document16 pagesSolution Manual For Fundamentals of Semiconductor Fabrication Gary S May Simon M Sze Isbn 0471232793 Isbn 978-0-471 23279 7 Isbn 9780471232797warepneumomxkhf100% (17)
- Toro Homelite 3354-726Document8 pagesToro Homelite 3354-726Cameron ScottNo ratings yet
- Nepra ManualDocument60 pagesNepra Manualabdulwasay_bzuNo ratings yet
- Speech Patterns: Christine Martin - Steph Estavillo - Melanie PadillaDocument24 pagesSpeech Patterns: Christine Martin - Steph Estavillo - Melanie PadillaChristineMartinNo ratings yet
- Neisseria Gonorrhoeae and Neisseria MeningitidesDocument3 pagesNeisseria Gonorrhoeae and Neisseria MeningitidesAmador Gielas0% (1)
- WATERGUARD 45 (Acrylic Waterproofing Coating)Document3 pagesWATERGUARD 45 (Acrylic Waterproofing Coating)Santosh Kumar PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Sample Ale ExamDocument37 pagesSample Ale ExamMarian Lim100% (1)
- ISA - Study Guide Table of ContentsDocument3 pagesISA - Study Guide Table of Contentsasdf123asdfasdfNo ratings yet
- ProductSheet Iq200 Rackmount SatelliteModemDocument2 pagesProductSheet Iq200 Rackmount SatelliteModemAsim Penkar PenkarNo ratings yet
- MGje 6 Fix GX PK Yp RBJ LBRDocument9 pagesMGje 6 Fix GX PK Yp RBJ LBRBANOTH KUMARNo ratings yet
- The Harrod-Domar Growth ModelDocument6 pagesThe Harrod-Domar Growth ModelSimeonNo ratings yet
- 5 - Introduction Q-Series Vs2 Customer Version2Document49 pages5 - Introduction Q-Series Vs2 Customer Version2mahreza189100% (1)
- Psychoanalythic TheoryDocument1 pagePsychoanalythic TheorySilver BroochNo ratings yet
- MEP MyanmarDocument27 pagesMEP Myanmarempty87No ratings yet
- Material Balance PDFDocument31 pagesMaterial Balance PDFApril Joy HaroNo ratings yet
- Contoh Form Rko Obat PRB Per ApotekDocument19 pagesContoh Form Rko Obat PRB Per ApoteksaddamNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture Corrosion Current Practice 2023Document12 pagesCarbon Capture Corrosion Current Practice 2023Wayne MonneryNo ratings yet
- EQUILIBRIUMDocument1 pageEQUILIBRIUMMohammed IliasNo ratings yet