Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 - Changing States: SCIENCE 5 - Note #1
Chapter 1 - Changing States: SCIENCE 5 - Note #1
Uploaded by
Eko Sulistiyaning Warni0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesThis document provides an overview of different states of matter and phase changes. It discusses boiling, melting, evaporation, condensation, and the water cycle. Boiling occurs at the boiling point and turns a liquid into a gas, while melting is the change from solid to liquid state at the melting point. Evaporation changes a liquid to a gas at any temperature, while boiling only occurs at the specific boiling point temperature. Condensation is the reverse process of evaporation, where a gas turns back into a liquid. The water cycle involves the continuous process of evaporation of water from oceans and lakes into vapor, condensation of vapor into clouds, and precipitation of water back to the Earth's surface as rain or snow.
Original Description:
summary science Primary 5 Chapter 1
Original Title
Science 5 IM 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of different states of matter and phase changes. It discusses boiling, melting, evaporation, condensation, and the water cycle. Boiling occurs at the boiling point and turns a liquid into a gas, while melting is the change from solid to liquid state at the melting point. Evaporation changes a liquid to a gas at any temperature, while boiling only occurs at the specific boiling point temperature. Condensation is the reverse process of evaporation, where a gas turns back into a liquid. The water cycle involves the continuous process of evaporation of water from oceans and lakes into vapor, condensation of vapor into clouds, and precipitation of water back to the Earth's surface as rain or snow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesChapter 1 - Changing States: SCIENCE 5 - Note #1
Chapter 1 - Changing States: SCIENCE 5 - Note #1
Uploaded by
Eko Sulistiyaning WarniThis document provides an overview of different states of matter and phase changes. It discusses boiling, melting, evaporation, condensation, and the water cycle. Boiling occurs at the boiling point and turns a liquid into a gas, while melting is the change from solid to liquid state at the melting point. Evaporation changes a liquid to a gas at any temperature, while boiling only occurs at the specific boiling point temperature. Condensation is the reverse process of evaporation, where a gas turns back into a liquid. The water cycle involves the continuous process of evaporation of water from oceans and lakes into vapor, condensation of vapor into clouds, and precipitation of water back to the Earth's surface as rain or snow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
SCIENCE 5 – Note #1 Semester I/ 2021 – 2022
Chapter 1 – Changing States
1. a. Boiling is the changes of a liquid into a gas at its boiling point. The boiling
point of water is 100 ○C
b. Melting is the changes of a solid into a liquid. The melting point of ice is 0 ○C.
2. Evaporation is the change of a liquid into a gas.
Examples: Drying the clothes, perspiration and evaporation of perfume
3. Differences between evaporation and boiling
Evaporation Boiling
at any temperature at the boiling point
at the surface of liquid throughout the liquid
no bubbles are formed bubbles are formed
4. Factors that affects the rate of evaporation are
a. The temperature of the surrounding
b. The presence of wind
c. Surface area
5. Condensation is the change of a gas into a liquid. It is reverse of evaporation.
Examples: Mist on bathroom mirror, spectacles misting up, dewdrops on the
leaves in the morning and white mist forming above boiling water.
6. The differences between condensation and evaporation
Condensation Evaporation
change from a gas to a liquid change from a liquid to a gas
matter loses heat matter gains heat
SCIENCE 5 – Note #1 Semester I/ 2021 – 2022
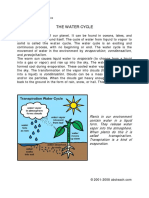
7. Water cycle is the continuous movement of water from the Earth’s surface to
the air and back to the Earth’s surface. Water cycle is important to provide
living things with a constant supply of fresh water.
Processes of water cycle are the following:
a. Evaporation: water from the ocean, lakes and stream evaporates
transpiration (evaporation) from plant because of the heat energy
from the Sun.
b. Condensation: Water vapour rises up and cools down. It condenses
to form tiny water droplets and make clouds.
c. Precipitation: Tiny water droplets form bigger droplets, then it falls as
rain. It also falls as snow if the temperature is lower.
d. Collection: water lands on Earth and moves across the land, soak into
the Earth or moves underground.
You might also like
- Water Cycles eDocument3 pagesWater Cycles eMark Cruz72% (18)
- Level Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-9 Latent Heat PAPER-1 Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesLevel Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-9 Latent Heat PAPER-1 Multiple Choiceelty TanNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument10 pagesWater CycleJohn ChristianNo ratings yet
- Sci 8 Q3 WK 3&4Document2 pagesSci 8 Q3 WK 3&4ELVIS DOMINGONo ratings yet
- Evap CrisDocument5 pagesEvap CrisCristy Mie PagliawanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 Q3 - WEEK 3 - LAS 3 CondensationDocument2 pagesSCIENCE 8 Q3 - WEEK 3 - LAS 3 CondensationGlin BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Test II. Essay: Page 1 of 1Document1 pageTest II. Essay: Page 1 of 1precious2lojaNo ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument7 pagesThe Water Cyclekonkurs.wiedzy.o.irlandii.zschNo ratings yet
- WS Persiapan SumatifDocument3 pagesWS Persiapan SumatifChaerul LatifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Water and SolutionDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Water and Solutionarief akashahNo ratings yet
- Warm-Up: Wet Floor Is Left To Dry Up. Are These Examples of Evaporation?Document33 pagesWarm-Up: Wet Floor Is Left To Dry Up. Are These Examples of Evaporation?Fauzan AkbarNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Assignment Class 9 CBSEDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRY Assignment Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738100% (1)
- F2 Chapter 5 Water and SolutionDocument15 pagesF2 Chapter 5 Water and SolutionRohani YusofNo ratings yet
- Effect of Heat On MatterDocument9 pagesEffect of Heat On MatterIzly Izlya100% (1)
- UNIT 5 Changes of StateDocument6 pagesUNIT 5 Changes of StatePham Van Tin B1909842No ratings yet
- Sci Quiz 2Document2 pagesSci Quiz 2Nicole AlvarezNo ratings yet
- LeaP-Science-G8-Week 4-Q3Document4 pagesLeaP-Science-G8-Week 4-Q3Richard ViseyNo ratings yet
- SCI8-COT-1-FINAL - JoshuaDocument4 pagesSCI8-COT-1-FINAL - JoshuaJoshua TamonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Rain, Thunder and LightningDocument3 pagesChapter 13 Rain, Thunder and Lightningbittuchintu100% (1)
- ES Quiz 002Document2 pagesES Quiz 002Dandelion UwUNo ratings yet
- RC WatercycleDocument4 pagesRC Watercyclejimmy_kennedy_15No ratings yet
- RC Watercycle1425682040 PDFDocument4 pagesRC Watercycle1425682040 PDFsilvia2350No ratings yet
- (SciGr4) Study Guide 1 (2p)Document10 pages(SciGr4) Study Guide 1 (2p)An Na ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Website: WWW - Excellentguides.inDocument7 pagesChemistry: Website: WWW - Excellentguides.inJoyabrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Part 2Document10 pagesChemistry - Part 2BALA GANESHNo ratings yet
- Primary 5 Science Unit 4 Changing States of WaterDocument3 pagesPrimary 5 Science Unit 4 Changing States of WaterMonika DamanikNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingDocument26 pagesMatter in Our Surroundingojaswi bhatiNo ratings yet
- SLHT Sci 8 Q3 WK3 4 1Document13 pagesSLHT Sci 8 Q3 WK3 4 1irishangela789No ratings yet
- G8Document3 pagesG8Shaina Jandoc TalanginNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Moisture AND PrecipitationsDocument40 pagesAtmospheric Moisture AND PrecipitationsUsama UsamaArqemNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Quarter 1 Module 4 Week 4Document6 pagesScience 5 Quarter 1 Module 4 Week 4Vhacie TorresNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Mcknights Physical Geography A Landscape Appreciation 11 e Darrel Hess Dennis G TasaDocument35 pagesSolution Manual For Mcknights Physical Geography A Landscape Appreciation 11 e Darrel Hess Dennis G TasaHarryFreemanyszf100% (34)
- Class 9-Chemistry CW-1Document7 pagesClass 9-Chemistry CW-1aadithya.v.5502.sssmscNo ratings yet
- Foundation Chemistry 1Document60 pagesFoundation Chemistry 1Ivan OgwangNo ratings yet
- Gix - Question BankDocument8 pagesGix - Question BankDeva GuruNo ratings yet
- 6) Air Contains Smoke Dust Germs and Water VaporDocument4 pages6) Air Contains Smoke Dust Germs and Water Vaporkabirdubal232No ratings yet
- Assessment: Directions: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answers On A Separate Sheet of PaperDocument5 pagesAssessment: Directions: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answers On A Separate Sheet of Paperkim aaron marcelinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Changes in States of MatterDocument6 pagesLecture 4 Changes in States of MatterkedeshiaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Chemistry NotesDocument20 pagesClass 9 Chemistry Notesap4618720No ratings yet
- Water Cycle Atomospheric ConditionsDocument26 pagesWater Cycle Atomospheric ConditionsEUNICE CORREANo ratings yet
- Name: Air, Water and Weather Subject:Science Grade & Section: Practice Work DateDocument2 pagesName: Air, Water and Weather Subject:Science Grade & Section: Practice Work DateSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument27 pagesChapter - 1: Matter in Our SurroundingsJai SheokandNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument7 pagesWater CycleRenz DaguploNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6: Changes Around Us: Basic Concepts - A Flow ChartDocument26 pagesChapter - 6: Changes Around Us: Basic Concepts - A Flow ChartSupriya CNo ratings yet
- Demo WCDocument16 pagesDemo WCnorma majid abbangNo ratings yet
- Sci 8 Week 4 AssessmentDocument2 pagesSci 8 Week 4 AssessmentHen RyNo ratings yet
- Chapter at A Glance: Matter in Our SurroundingDocument8 pagesChapter at A Glance: Matter in Our Surroundingdl9s6547No ratings yet
- Free Must Know Water Cycles and Exam QuestionsDocument17 pagesFree Must Know Water Cycles and Exam QuestionsaaravNo ratings yet
- G7 - Change of StateDocument15 pagesG7 - Change of StateListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Matter Unit Test Answer SheetDocument3 pagesMatter Unit Test Answer Sheetapi-264643152No ratings yet
- Evaporation: Group 5Document58 pagesEvaporation: Group 5RAZEL ROSE ESTRADANo ratings yet
- Water Cycle Weather Matter Assessment Studentand Teacher VersionsDocument34 pagesWater Cycle Weather Matter Assessment Studentand Teacher VersionsJulia Meirelles100% (2)
- Melting Boiling and EvaporationDocument19 pagesMelting Boiling and EvaporationAnmol MalgotraNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Cycle - 3rd GroupDocument10 pagesHydrological Cycle - 3rd GroupChika SheilaNo ratings yet
- Changes Around UsDocument2 pagesChanges Around UsPranav ShindeNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument2 pagesWater Cycleanu3vsNo ratings yet
- WaterCycle - Lesson 2 InquiryDocument21 pagesWaterCycle - Lesson 2 InquiryshaniceNo ratings yet
- PracticeWithPhaseChangesWorksheet StudentDocument2 pagesPracticeWithPhaseChangesWorksheet Studentcaleb zimmermanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For The 2 Monthly Test For The 1 Quarter: Science 4Document3 pagesReviewer For The 2 Monthly Test For The 1 Quarter: Science 4ajirah kharell navaNo ratings yet
- Science #6Document17 pagesScience #6Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- Science #7Document2 pagesScience #7Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G3C2Document17 pagesTR G3C2Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- Degree #2Document5 pagesDegree #2Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- Science #8 (Force)Document9 pagesScience #8 (Force)Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G2C6Document9 pagesTR G2C6Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- Science #10Document7 pagesScience #10Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G3C3Document10 pagesTR G3C3Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- Fizzy EyeDocument10 pagesFizzy EyeEko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G3C4Document9 pagesTR G3C4Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G2C2Document9 pagesTR G2C2Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G1C7Document9 pagesTR G1C7Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- Geography: Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesGeography: Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationEko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G1C1Document6 pagesTR G1C1Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G2C3Document6 pagesTR G2C3Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- Science 5 IM 3Document2 pagesScience 5 IM 3Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G1C5Document9 pagesTR G1C5Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G1C6Document10 pagesTR G1C6Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- TR G1C4Document9 pagesTR G1C4Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- Geography: University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesGeography: University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationEko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet
- Science 5 IM 2Document1 pageScience 5 IM 2Eko Sulistiyaning WarniNo ratings yet