Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alzheimer'S Disease Definition: Signs and Symptoms
Alzheimer'S Disease Definition: Signs and Symptoms
Uploaded by
Mauren DazaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alzheimer'S Disease Definition: Signs and Symptoms
Alzheimer'S Disease Definition: Signs and Symptoms
Uploaded by
Mauren DazaCopyright:
Available Formats
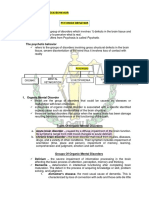
ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE Signs and Symptoms:
Memory Impairment
Definition: Agnosia
Is a neurodegenerative disorder marked by cognitive and Difficulty Concentrating
behavior impairment that significantly interferes with social Problem finishing daily tasks
and occupational. Common cause of dementia. Dementia
Amnesia
Anatomy and Physiology:
Complications:
Depression
Wandering
Malnutrition and Dehydration
Falls
Restlessness
Brain
In Alzheimer’s Disease, plaques develop in the
hippocampus, a structure deep in the brain that helps
encode memories, and in other areas of the cerebral cortex
that are involved in thinking and making decisions.
Formation of neurofibrillary tangles may result in
communication between neurons and later in the death of
the cells.
Predisposing Factors:
Modifiable Factors: Non-Modifiable Factors
1. Plaques in the Hippocampus 1. Age: 60-65 years old
2. Diabetes Mellitus 2. Gender: More common in
3. High Blood pressure male
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
Brain Mental Status Examination
Is the psychological equivalent of a physical exam that
describes the mental state and behaviors of the person
Neurofibrilliary tangels and filaments wrapped in the neurons of being seen. It includes both objective observations of the
cerebral cortex clinician and subjective descriptions given by the patient.
Normal Findings:
Decreased acetylcholinesterase and choline acethyltransferase Mental status reveal that the patient is able to respond
properly on the test and has a good grade in the examination
such speech, affect, cognitive, behavior, appearance and
Hippocampus atrophy and cerebral atrophy mood.
Significance:
The MSE provides information for diagnosis and assessment
Memory impairment and decreased intellectual functioning of disorder and response to treatment.
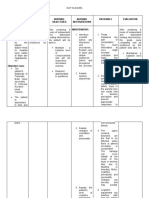
NURSING DIAGNOSIS:
Cognitive impairment and impaired motor function
1. Disturbed sensory perception related to changes in
perception
Dementia 2. Self-care deficit related to neuromuscular impairment
3. Disturbed personal identity related to organic brain
disease
Alzheimer’s Disease
#1. Disturbed sensory perception related to changes in
perception
Desired outcome:
Regain or maintain usual level of cognition.
Recognize and correct or compensate for sensory
impairments.
Nursing Interventions Rationale
1. Identify client with condition Specific clinical concerns of the
that can affect sensing, present condition.
interpreting and communicating
stimuli.
2. Review results of sensory and To note presence or possible
motor neurological testing and cause of changes in response to
laboratory studies. sensory stimuli #3. Disturbed personal identity related to organic brain disease
3. Interpret stimuli and offer To assist client to separate from
feedback fantasy or altered perception Desired Outcomes
4. Monitor drug regimen To identify prescription with side Verbalize acceptance of changes that have occurred
effects that may cause Integrate threat in a healthy, positive manner
perceptual problems
5. Collaborate with other health To achieve maximal gains in Nursing Interventions Rationale
team members in providing function and psychosocial well- 1. Provide calm environment Help client remain calm and
rehabilitative therapies. being. able to discuss important issues
2. Allow client to deal with May be unable to cope with
#2. Self-care deficit related to neuromuscular impairment situation in small steps larger picture when stress is
overload
Desired Outcome: 3. Maintain reality orientation with Client may become defensive,
Demonstrate techniques and lifestyle changes to meet self- confronting client’s irrational blocking opportunity to look at
care needs beliefs other possibilities
Perform self-care activities within level of own ability. 4. Provide accurate information Helps client make positive
about threat. decisions for future.
Nursing Interventions Rationale 5. Refer to appropriate support Enhances facilitation of care for
1. Perform or assist client with To provide proper care to the groups the patient
meeting client’s needs patient
2. Develop plan of care Enhances commitment to plan, NURSING INTERVENTIONS:
appropriate to individual situation optimizing outcomes and 1. Assist patient’s ability for thought processing every shift
and desired goals and decision supporting recovery 2. Assess the level of cognitive disorders such as change to
making. orientation to people, places and time, range, attention.
3. Active client’s concerns Exhibits regard for clients values 3. Assess level of confusion and disorientation
and beliefs 4. Assess patient’s ability to cope with events
4. Assist with medication To provide treatment regimen 5. Orients patient to environment as needed.
regimen
5. Collaborate with rehabilitation To assess environmental and
professionals discharge care needs.
baseline behavior is observed.
DRUG STUDY
Caution patient and caregiver that
Generic Name CHLORPROMAZINE donepezil/memantine may cause
Trade Name THORAZINE drowsiness and dizziness.
Drug Classification ANTIPSYCHOTIC
Side Effects -Blurred Vision Caution patient to avoid activities
-Neuroceptic Malignant requiring alertness.
-Hypotension
-Constipation
Nursing Responsibility -Assess mental status
-Monitor BP and Pulse
rate
-The drug may be taken
with or without food
-Monitor for
development of
neuroleptic malignant
Generic Name DONEPEZIL HYDROCHLORIDE
Trade Name ARICEPT
Drug CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITOR
Classification
Side Effects nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
loss of appetite;
muscle pain;
sleep problems (insomnia); or.
feeling tired;.
Nursing Do not take more than prescribed
Responsibility Missed doses should be skipped
and regular schedule returned to
the following day; higher doses do
not increase effects but may
increase side effects.
Inform patient/family that it may
take wk before improvement in
You might also like
- AlzheimerDocument11 pagesAlzheimerSoniya G08No ratings yet
- Alzheimers Disease Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesAlzheimers Disease Nursing Care PlanMary Josette NavarraNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation of EclampsiaDocument72 pagesCase Presentation of EclampsiaMauren Daza100% (4)
- NCM 117 - Psychiatric Nursing (MODULE 4)Document7 pagesNCM 117 - Psychiatric Nursing (MODULE 4)Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- ALZHEIMERDocument2 pagesALZHEIMERLorelyn Santos CorpuzNo ratings yet
- DialoguesClinNeurosci 10 153Document11 pagesDialoguesClinNeurosci 10 153Llrss AdnNo ratings yet
- Millan2012 PDFDocument28 pagesMillan2012 PDFYami StrikeNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial Assessment Components: Catergory Observation Clinical ImplicationDocument4 pagesPsychosocial Assessment Components: Catergory Observation Clinical ImplicationbudzcazNo ratings yet
- Mental StatusDocument6 pagesMental StatusIgor Oliveira100% (1)
- Scenario: Hallucinations and Delusions Are Often Taken As Signs of A Failure of RealityDocument5 pagesScenario: Hallucinations and Delusions Are Often Taken As Signs of A Failure of RealityJoshua TercenoNo ratings yet
- Care of The Older AdultsDocument17 pagesCare of The Older AdultsL Rean Carmelle MAGALLONESNo ratings yet
- Catatonic Schizophrenia NCP (Revised)Document13 pagesCatatonic Schizophrenia NCP (Revised)Wen Silver100% (1)
- Anaphy BDDocument19 pagesAnaphy BDJamaica TuellaNo ratings yet
- Delirium and DementiaDocument12 pagesDelirium and DementiaSNo ratings yet
- Final Module in Human BehaviorDocument60 pagesFinal Module in Human BehaviorNarag Krizza50% (2)
- Psychopathology - 8Document5 pagesPsychopathology - 8NEELAMNo ratings yet
- Delirium The Role of PsychiatryDocument10 pagesDelirium The Role of PsychiatrymunsifzmiNo ratings yet
- PSYCHIATRIC NURSING AnjaliDocument47 pagesPSYCHIATRIC NURSING AnjaliAnjali GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Brain Disease Model of Addiction: Butler Center For Research May 2021Document2 pagesThe Brain Disease Model of Addiction: Butler Center For Research May 2021cultura84No ratings yet
- (PSYCH) Neurocognitive DisordersDocument14 pages(PSYCH) Neurocognitive DisordersThesa TagalogNo ratings yet
- Cap. Delirium - Bradley's Neurology in Clinical PracticDocument11 pagesCap. Delirium - Bradley's Neurology in Clinical PracticArthur André RegovichiNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Midterms Topic 6 Cognitive Disorders NotesDocument4 pagesNCM 116 Midterms Topic 6 Cognitive Disorders NotesMyat LluvidoNo ratings yet
- Depressive DisorderDocument59 pagesDepressive DisorderJoshua RingorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Cognitive DisordersDocument5 pagesChapter 9 Cognitive DisordersDessirie EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Organic Mental Disorders Due To Brain DiseasesDocument45 pagesOrganic Mental Disorders Due To Brain DiseasesMEDS easyNo ratings yet
- NCP ALZHEIMERS DISEASE DX IMDocument3 pagesNCP ALZHEIMERS DISEASE DX IMPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- NeuropsychologyDocument13 pagesNeuropsychologyReyalyn AntonioNo ratings yet
- 1st LessonDocument1 page1st LessonNonie CastroNo ratings yet
- Personalit Y Disorder: Group 6Document30 pagesPersonalit Y Disorder: Group 6Kyra RMNo ratings yet
- Personality DisorderDocument1 pagePersonality DisorderAirelle NolynnNo ratings yet
- Biofeedback Neurofeedback and Cognitive RehabDocument29 pagesBiofeedback Neurofeedback and Cognitive RehabDr Nader KorhaniNo ratings yet
- Obsessive - Compulsive DisorderDocument3 pagesObsessive - Compulsive DisorderCatherine FaithNo ratings yet
- Topic-5 Psychosis BehaviorDocument6 pagesTopic-5 Psychosis BehaviorKYLA STEFANIE MATULACNo ratings yet
- SP20 PSY381 Examples and DefinitionsDocument75 pagesSP20 PSY381 Examples and Definitionsvasudha_kurugantiNo ratings yet
- DLP HEALTH - April 18 2023Document3 pagesDLP HEALTH - April 18 2023Wein OrtizNo ratings yet
- Depression: Dammam University. College of Nursing. Psychiatric & Mental Health Nursing (1610 - 331)Document6 pagesDepression: Dammam University. College of Nursing. Psychiatric & Mental Health Nursing (1610 - 331)Hebah AlzahraniNo ratings yet
- Obsessive Compulsive DisorderDocument26 pagesObsessive Compulsive DisorderIshmarika 54No ratings yet
- Care of Older Adults (Finals)Document14 pagesCare of Older Adults (Finals)Ax’l SisterNo ratings yet
- Pre-Finals Mental Disorders and Criminality: Rossel B. Sanchez, RGCDocument14 pagesPre-Finals Mental Disorders and Criminality: Rossel B. Sanchez, RGCAruba De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Sas 22-23Document15 pagesSas 22-23Jilkiah Mae Alfoja CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Bio Assignment Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesBio Assignment Nervous SystemLyra IsraelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document8 pagesChapter 7Ellyza EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Neurocognitive DisordersDocument13 pagesNeurocognitive Disorders18105101No ratings yet
- Decreased Level of Consciousness and Coma OLADocument17 pagesDecreased Level of Consciousness and Coma OLAMuath ASNo ratings yet
- Fdar - Schizophrenia Jan 11-13Document2 pagesFdar - Schizophrenia Jan 11-13Grape Juice100% (1)
- AbPsy ReviewerDocument70 pagesAbPsy ReviewerAdam VidaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Psych Summary QsDocument6 pagesClinical Psych Summary Qssathmijayasinghe2007No ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science in Psychology: Program Curriculum Ay 2020 - 2021Document6 pagesBachelor of Science in Psychology: Program Curriculum Ay 2020 - 2021Rosemarie AngelesNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders: Michael D. Jibson, M.D., Ph.D. Ira D. Glick, M.D. Rajiv Tandon, M.DDocument14 pagesSchizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders: Michael D. Jibson, M.D., Ph.D. Ira D. Glick, M.D. Rajiv Tandon, M.Dserene_tha067746No ratings yet
- Neuropsychology of Agnosia and Perceptual DisturbancesDocument7 pagesNeuropsychology of Agnosia and Perceptual DisturbancessabaasifadvNo ratings yet
- Dissociative 20240607 155031 0000Document10 pagesDissociative 20240607 155031 0000sania saxenaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Nervous System 1Document4 pagesDiseases of The Nervous System 1emaceeNo ratings yet
- Piprams Lesson Plan On Topic: Subject:: Mental Status Examination Mental Health NursingDocument20 pagesPiprams Lesson Plan On Topic: Subject:: Mental Status Examination Mental Health NursingVaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- Journey Into The BrainDocument8 pagesJourney Into The BrainihaveagtaforyouNo ratings yet
- Maldonado2017 PDFDocument30 pagesMaldonado2017 PDFLuis Miguel HernándezNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Mood Disorders Grief Loss MENTAL HEALTH NURSING PDFDocument19 pagesSchizophrenia Mood Disorders Grief Loss MENTAL HEALTH NURSING PDFnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Lezak5 CH2 - FullDocument11 pagesLezak5 CH2 - Fullypatel11No ratings yet
- NCP AshraDocument4 pagesNCP AshraSherry RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CBD Team e PsychiatryDocument44 pagesCBD Team e PsychiatrydindanovitamNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DisordersDocument3 pagesCognitive DisordersCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- Dissociative DisordersDocument13 pagesDissociative DisordersManasik AltahirNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Brain Re-Thinking Epilepsy Diagnosis And Treatment Through The Mind-Body ConnectionFrom EverandBeyond The Brain Re-Thinking Epilepsy Diagnosis And Treatment Through The Mind-Body ConnectionNo ratings yet
- Seizure: Focal/partial SeizuresDocument7 pagesSeizure: Focal/partial SeizuresMauren DazaNo ratings yet
- AbuseandviolenceDocument8 pagesAbuseandviolenceMauren DazaNo ratings yet
- Common Psychotherapeutic InterventionsDocument4 pagesCommon Psychotherapeutic InterventionsMauren DazaNo ratings yet
- Family History of Diabetes and Hypertension Family History of CKD Old Age: 45 and AboveDocument1 pageFamily History of Diabetes and Hypertension Family History of CKD Old Age: 45 and AboveMauren DazaNo ratings yet
- AQALDocument2 pagesAQALMauren Daza0% (1)
- Adulthood: By: BeverlycovitaDocument20 pagesAdulthood: By: BeverlycovitaMauren DazaNo ratings yet
- Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) - Photobiomodulation (PBM) - Red - NIR Phototherapy Studies - A Comprehensive Database by Vladimir Heiskanen - Taulukko1Document76 pagesLow Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) - Photobiomodulation (PBM) - Red - NIR Phototherapy Studies - A Comprehensive Database by Vladimir Heiskanen - Taulukko1nepretipNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease ResearchDocument61 pagesAlzheimer's Disease ResearchshayneNo ratings yet
- 2357 - KERUSAKAN OTAK DAN NEUROPLASTISITAS Biopsikologi 2018Document67 pages2357 - KERUSAKAN OTAK DAN NEUROPLASTISITAS Biopsikologi 2018Nurul HikmahNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's - Alzheimer's Disease - Kaj Blennow, Mony J de Leon, Henrik ZeterbergDocument17 pagesAlzheimer's - Alzheimer's Disease - Kaj Blennow, Mony J de Leon, Henrik ZeterbergCatinean DanielaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Alzheimers Disease Facts and Figures 2021Document80 pages2021 Alzheimers Disease Facts and Figures 2021adinta saniyyahNo ratings yet
- (Readings From The Encyclopedia of Neuroscience) ADELMAN, HOBSON - Abnormal States of Brain and Mind-Birkhäuser Boston (1989) PDFDocument132 pages(Readings From The Encyclopedia of Neuroscience) ADELMAN, HOBSON - Abnormal States of Brain and Mind-Birkhäuser Boston (1989) PDFMauro CracchioloNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease Case StudyDocument5 pagesAlzheimer's Disease Case Studyjisoo100% (1)
- AlzheimerDocument9 pagesAlzheimerbruno lopez lucasNo ratings yet
- And Current Use: Drosophila Melanogaster: A Fly Through Its HistoryDocument6 pagesAnd Current Use: Drosophila Melanogaster: A Fly Through Its Historyjonatas Cassiano da silvaNo ratings yet
- Visual Summary Issue PDFDocument132 pagesVisual Summary Issue PDFMauro RojasNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument82 pagesThesisJ.S. GharatNo ratings yet
- Mrcpsych Paper 2 Revision Neurosciences Answers & Lecture Notes May 2010Document74 pagesMrcpsych Paper 2 Revision Neurosciences Answers & Lecture Notes May 2010Naeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 11-2Document60 pagesWeek 11-2Wong ChocolateNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Biomarkers in Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument150 pagesBiochemical Biomarkers in Alzheimer's DiseaseInternational Medical PublisherNo ratings yet
- Dementia of Early OnsetDocument11 pagesDementia of Early OnsetIzzyinOzzieNo ratings yet
- Etiology of PsychopathologyDocument61 pagesEtiology of PsychopathologyAdrishya100% (4)
- Alzheimer S Disease PDFDocument469 pagesAlzheimer S Disease PDFWatermelon MUANo ratings yet
- Football Point CounterpointDocument6 pagesFootball Point CounterpointJenna IntersimoneNo ratings yet
- (1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) Testosterone and Cognitive Function - Current Clinical Evidence of A RelationshipDocument9 pages(1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) Testosterone and Cognitive Function - Current Clinical Evidence of A RelationshipAlan LuiNo ratings yet
- How Does Alzheimer's Disease Affect The Brain?Document2 pagesHow Does Alzheimer's Disease Affect The Brain?TUTORMAENo ratings yet
- Paper 39 Is The Incidence of Dementia DecliningDocument20 pagesPaper 39 Is The Incidence of Dementia DecliningEhsan MohammadiNo ratings yet
- EGCG AlCl3 in ADDocument13 pagesEGCG AlCl3 in ADFarhan Royan PermanahadiNo ratings yet
- Kefir AlzheimersDocument14 pagesKefir AlzheimersAnanyaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Alzheimer DiseaseDocument8 pagesLiterature Review Alzheimer Diseaseea7e9pm9100% (1)
- Photobiomodulation With Near Infrared Light Helmet in A Pilot Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial in Dementia Patients Testing MemorDocument8 pagesPhotobiomodulation With Near Infrared Light Helmet in A Pilot Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial in Dementia Patients Testing MemorarexixNo ratings yet
- Smart Nutrients A Guide To Nutrients That Can Prevent and Reverse Senility PDFDocument213 pagesSmart Nutrients A Guide To Nutrients That Can Prevent and Reverse Senility PDFjisiwa6367upcmaill.comNo ratings yet
- Compendium of Selected Recent Publications Cell and Molecular Biology ResearchDocument16 pagesCompendium of Selected Recent Publications Cell and Molecular Biology ResearchXyza Kim OlivaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4B.Alzheimer Disease - Pharmacotherapy Handbook, Tenth Edition (2017)Document9 pagesUnit 4B.Alzheimer Disease - Pharmacotherapy Handbook, Tenth Edition (2017)Josa Camille BungayNo ratings yet
- DementiaDocument38 pagesDementiarajikakurupNo ratings yet