Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 3
Module 3
Uploaded by
Christian James DomingoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Polar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilDocument6 pagesPolar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilLily Stanton67% (3)
- Mckinsey - Style Practice Case #8: Ronald ChocolatesDocument12 pagesMckinsey - Style Practice Case #8: Ronald ChocolatesHiếu LươngNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Essay FinalDocument15 pagesCriminal Law Essay FinalAlexander PletschNo ratings yet
- The Polarity of A Molecule Based On Its StructureDocument35 pagesThe Polarity of A Molecule Based On Its StructureCherry-Ann BernardezNo ratings yet
- Polarity & Electronegativity Worksheet SOLVEDDocument1 pagePolarity & Electronegativity Worksheet SOLVEDLili0% (1)
- Worksheet: Polar Bears & Penguins - Electronegativity: NAMEDocument3 pagesWorksheet: Polar Bears & Penguins - Electronegativity: NAMERaymond LiuNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Polar NonpolarDocument37 pagesWeek 3 Polar NonpolarLlora JaneNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Genchem PolarityDocument29 pagesGrade 12 Genchem PolarityJohn Milen Garvida FabiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersDocument6 pagesChemistry Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersH.sNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument29 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar Moleculesshin100% (1)
- CH - 6 Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument10 pagesCH - 6 Basic Concepts of ChemistryNeel PandyaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesWeek 3 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceEunice AcunaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Modules Week 2Document6 pagesPhysical Science Modules Week 2RODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- L1 Atoms & ElementsDocument23 pagesL1 Atoms & ElementsJulioRiveraCavanillesNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument5 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- XII - The P-Block ElementsDocument6 pagesXII - The P-Block ElementsRanjan BhatNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument21 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesShhhhhhhhyeahNo ratings yet
- Ionic CovalentDocument23 pagesIonic CovalentAkniet RysbekovaNo ratings yet
- Bonding Student Study GuideDocument15 pagesBonding Student Study GuideJohn Philip NapalNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document75 pagesWeek 1Tengmantz TVNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument218 pagesChemical BondingveronicamniemNo ratings yet
- 11.chemical Bonding in A NutshellDocument24 pages11.chemical Bonding in A Nutshellmary ann leddaNo ratings yet
- CHE101 ChemicalBondingII FZDDocument203 pagesCHE101 ChemicalBondingII FZDsouadalkabirNo ratings yet
- Polar and Non PolarDocument22 pagesPolar and Non PolarRowena FloresNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity: Classifying Bond Type: Return To Bonding MenuDocument2 pagesElectronegativity: Classifying Bond Type: Return To Bonding MenuSomshuvra BasuNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 1 Review and AssessmentDocument3 pagesScience Chapter 1 Review and AssessmentanaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and SolidsDocument17 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solidselaine trazonaNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument18 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesChe PeñalesNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument10 pagesChemical BondsGAMING WITH SPELLNo ratings yet
- 5.types of Covalent CompoundsDocument17 pages5.types of Covalent CompoundsEian InganNo ratings yet
- Intro To Chemistry - Enhancement NotesDocument7 pagesIntro To Chemistry - Enhancement Notesesivaks2000No ratings yet
- chemistry-ELEMENTS AND CHEMICAL BONDINGDocument20 pageschemistry-ELEMENTS AND CHEMICAL BONDINGfelixmatchumbuza041No ratings yet
- Physical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesDocument15 pagesPhysical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesJodi RempilloNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument20 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesLYNFORD LAGONDINo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IDocument57 pagesOrganic Chemistry IMss FaixaNo ratings yet
- Polar BondsDocument8 pagesPolar BondsAnthony JohanNo ratings yet
- Eoy Review Student Questions KeyDocument4 pagesEoy Review Student Questions Keyapi-234918521No ratings yet
- Module 3 Quarter 3Document3 pagesModule 3 Quarter 3Jenevie Tagalicud100% (2)
- Chapter 8Document32 pagesChapter 8Danilo Fronda Jr.No ratings yet
- Molecular Polarity: SymmetryDocument4 pagesMolecular Polarity: SymmetryMims ChiiiNo ratings yet
- AP Chem Summer AssignmentDocument13 pagesAP Chem Summer AssignmentSophie LiNo ratings yet
- Bond PolarityDocument9 pagesBond PolarityIvy LunaNo ratings yet
- Chem RevDocument2 pagesChem RevArundhathiNo ratings yet
- MH1 Che101 CB10 S2019Document262 pagesMH1 Che101 CB10 S2019Hazrat AliNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 3Document7 pagesPhysical Science Week 3ruel rinconadaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Quarter 2-Week 1 (Module 2) Types of Intermolecular Forces Pre-TestDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Quarter 2-Week 1 (Module 2) Types of Intermolecular Forces Pre-TestDexter John Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Submitted By: Criestefiel Ann S. Lolo Grade 12 - GatesDocument13 pagesPhysical Science: Submitted By: Criestefiel Ann S. Lolo Grade 12 - GatesCriestefiel LoloNo ratings yet
- CHEM1102 Lecture Notes 2Document30 pagesCHEM1102 Lecture Notes 2Callum BiggsNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer by Aneezah PascualDocument5 pagesScience Reviewer by Aneezah Pascualdalialia136iNo ratings yet
- Ions and Electrolytes Worksheet Part 1: Ions Short Answer QuestionsDocument4 pagesIons and Electrolytes Worksheet Part 1: Ions Short Answer Questionsapi-423980580No ratings yet
- Chemistry Target Paper by Engr - Madiha Ahmed - 064534Document4 pagesChemistry Target Paper by Engr - Madiha Ahmed - 064534zoodiaamoNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument45 pagesPolarity of MoleculesAliza Liban100% (1)
- M1a1 EstradaDocument1 pageM1a1 EstradaAsia EstradaNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument3 pagesPeriodic TrendsJessica ShinNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding NotesDocument39 pagesCovalent Bonding NotesAmaris HopkinsNo ratings yet
- Special Reviewe Rnotes For Second Quarter General Chemistry 1Document25 pagesSpecial Reviewe Rnotes For Second Quarter General Chemistry 1GLUSITANIO, DIANA YSABELA JOHANA T.No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Chemistry Week 7 Lesson 1 Worksheet 1 and SolutionsDocument5 pagesGrade 10 Chemistry Week 7 Lesson 1 Worksheet 1 and SolutionsNikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- CHEM 3 Quiz 1 - Short Term: Class Discussion: SolutionsDocument7 pagesCHEM 3 Quiz 1 - Short Term: Class Discussion: SolutionsARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chemistry Grade 10Document54 pagesChemical Bonding: Chemistry Grade 10jahiem wilsonNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRDocument25 pagesQ3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRGumban Aaron Frances M.No ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4Coursehero Premium0% (1)
- Fulltext ID 110506772&PLACEBO IEDocument17 pagesFulltext ID 110506772&PLACEBO IEpkj009No ratings yet
- Springfield Building Department Inspectional Services Notice of ViolationsDocument6 pagesSpringfield Building Department Inspectional Services Notice of ViolationsThe Republican/MassLive.comNo ratings yet
- AFP Brochure08Document4 pagesAFP Brochure08YongoloooNo ratings yet
- Macro Curriculum Changes 2023 Part 2Document6 pagesMacro Curriculum Changes 2023 Part 2Al VelNo ratings yet
- May 2014Document48 pagesMay 2014debtwiggNo ratings yet
- CIED Surgical Guidance Dec21Document16 pagesCIED Surgical Guidance Dec21SamNo ratings yet
- Beef Short Ribs Asian Style Recipe - Chef Jean PierreDocument2 pagesBeef Short Ribs Asian Style Recipe - Chef Jean Pierrevasilescu2No ratings yet
- Interfacial PhenomenaDocument75 pagesInterfacial Phenomenanejaabera12No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Structure of The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - Structure of The Nervous Systemmanilyn dacoNo ratings yet
- 2.transmission Line Theory PDFDocument89 pages2.transmission Line Theory PDFSara AhmedNo ratings yet
- 9137-AN/898: Airport Services ManualDocument170 pages9137-AN/898: Airport Services ManualAndry NapitupuluNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 77Document2 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 77Kimberly MaeNo ratings yet
- Becoming Acquainted With Statistical ConceptsDocument3 pagesBecoming Acquainted With Statistical ConceptsCorteza, Ricardo Danilo E. UnknownNo ratings yet
- 3 - Trainees Record BookDocument6 pages3 - Trainees Record BookNelgen PiolaNo ratings yet
- TPMC Updated Offer On 2nd List 20200110Document2 pagesTPMC Updated Offer On 2nd List 20200110gabriel240371No ratings yet
- Vitodens 100w wb1b SeriesDocument100 pagesVitodens 100w wb1b Seriesclaudyu_fNo ratings yet
- Delhi Gang Rape CaseDocument3 pagesDelhi Gang Rape CasePriyesha MaliNo ratings yet
- Tipe A - Test Admin Shopee ExpressDocument6 pagesTipe A - Test Admin Shopee ExpressHapsyah MarniNo ratings yet
- Explore Learning MeiosisDocument7 pagesExplore Learning MeiosisAmarna BarnesNo ratings yet
- d000523 Doseuse RemplisseuseDocument2 pagesd000523 Doseuse RemplisseuseEnzo QuatremareNo ratings yet
- Escritura AutoguardadoDocument7 pagesEscritura AutoguardadoEren JaegerNo ratings yet
- JL Components Blower LubricationDocument4 pagesJL Components Blower LubricationMAZENNo ratings yet
- Structural Chemistry Organic Chemistry Summary: Alkynes: Structure, Conformations, PropertiesDocument20 pagesStructural Chemistry Organic Chemistry Summary: Alkynes: Structure, Conformations, PropertiesMohanraj ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Boundary Line: Plan of Gpuff Temporary JettyDocument1 pageBoundary Line: Plan of Gpuff Temporary Jettyshafiq_05No ratings yet
- Why Integration Is The Key To Asia's Economic Progress? Explain Your AnswerDocument2 pagesWhy Integration Is The Key To Asia's Economic Progress? Explain Your AnswerQueeny JavierNo ratings yet
- Morphology McqsDocument8 pagesMorphology McqsHiba Shah100% (2)
- Exercise LMTDocument4 pagesExercise LMTapi-276845347No ratings yet
Module 3
Module 3
Uploaded by
Christian James DomingoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 3
Module 3
Uploaded by
Christian James DomingoCopyright:
Available Formats
CHRISTIAN JAMES J.
DOMINGO
12-Chaucer
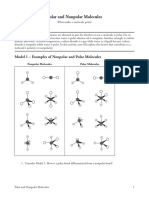
Activity 1: Polar and Non-polar Bond
1. NF = Polar
2. HCl = Polar
3. N2= Non polar
4. CS2= Non polar
5. N2O = Polar
6. O3= Polar
7. NI3= Polar
8. Br2= Non polar
9. CH2O = Polar
10. BCl3= Non polar
Q1. How are polar molecules different from nonpolar? = Polar molecules occur when there is an
electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms. Nonpolar molecules occur when electrons are
shared equal between atoms of a diatomic molecule or when polar bonds in a larger molecule cancel
each other out.
Q2. What types of elements combine to form a polar molecule and a non-polar
molecule? = • Polar covalent bonds form between two nonmetal atoms that have sufficiently different
electronegativities from each other. Because the electronegativity values are slightly different, the
bonding electron pair isn't equally shared between the atoms. While, nonpolar molecule has no
separation of charge, so no positive or negative poles are formed. In other words, the electrical charges
of nonpolar molecules are evenly distributed across the molecule. Polar molecules tend to dissolve well
in water and other polar solvents
ACTIVITY 2 Electronegativity Difference Polar or Nonpolar Molecules
1. H - O (in H2O) 1.4 POLAR
2. Cl - Cl (in Cl2) 0 NON POLAR
3. N - H (in NH3) 0.9 POLAR
4. C - H (in CH4) 0.4 NON POLAR
5. H H (in H2) 0 NON POLAR
6. C - P 0.4 NON POLAR
7. F - Cl 0.8 POLAR
8. Fe - O 1.6 POLAR
9. P - Cl 1.0 POLAR
10. I – I 0 NON POLAR
Q1. What is the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules in terms of their
electronegativity difference? = For a bond to be polar, the electronegativity difference between the two
elements needs to be between 0.5 to 1.6. If the electronegativity difference is less than 0.5, the bond is
nonpolar. Any more than 1.6 and the molecules become charged ions and form ionic bonds instead\
Q2. What is electronegativity?= is a measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons to itself. On
the periodic table, electronegativity generally increases as you move from left to right across a period
and decreases as you move down a group.
You might also like
- Polar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilDocument6 pagesPolar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilLily Stanton67% (3)
- Mckinsey - Style Practice Case #8: Ronald ChocolatesDocument12 pagesMckinsey - Style Practice Case #8: Ronald ChocolatesHiếu LươngNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Essay FinalDocument15 pagesCriminal Law Essay FinalAlexander PletschNo ratings yet
- The Polarity of A Molecule Based On Its StructureDocument35 pagesThe Polarity of A Molecule Based On Its StructureCherry-Ann BernardezNo ratings yet
- Polarity & Electronegativity Worksheet SOLVEDDocument1 pagePolarity & Electronegativity Worksheet SOLVEDLili0% (1)
- Worksheet: Polar Bears & Penguins - Electronegativity: NAMEDocument3 pagesWorksheet: Polar Bears & Penguins - Electronegativity: NAMERaymond LiuNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Polar NonpolarDocument37 pagesWeek 3 Polar NonpolarLlora JaneNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Genchem PolarityDocument29 pagesGrade 12 Genchem PolarityJohn Milen Garvida FabiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersDocument6 pagesChemistry Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersH.sNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument29 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar Moleculesshin100% (1)
- CH - 6 Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument10 pagesCH - 6 Basic Concepts of ChemistryNeel PandyaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesWeek 3 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceEunice AcunaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Modules Week 2Document6 pagesPhysical Science Modules Week 2RODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- L1 Atoms & ElementsDocument23 pagesL1 Atoms & ElementsJulioRiveraCavanillesNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument5 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- XII - The P-Block ElementsDocument6 pagesXII - The P-Block ElementsRanjan BhatNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument21 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesShhhhhhhhyeahNo ratings yet
- Ionic CovalentDocument23 pagesIonic CovalentAkniet RysbekovaNo ratings yet
- Bonding Student Study GuideDocument15 pagesBonding Student Study GuideJohn Philip NapalNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document75 pagesWeek 1Tengmantz TVNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument218 pagesChemical BondingveronicamniemNo ratings yet
- 11.chemical Bonding in A NutshellDocument24 pages11.chemical Bonding in A Nutshellmary ann leddaNo ratings yet
- CHE101 ChemicalBondingII FZDDocument203 pagesCHE101 ChemicalBondingII FZDsouadalkabirNo ratings yet
- Polar and Non PolarDocument22 pagesPolar and Non PolarRowena FloresNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity: Classifying Bond Type: Return To Bonding MenuDocument2 pagesElectronegativity: Classifying Bond Type: Return To Bonding MenuSomshuvra BasuNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 1 Review and AssessmentDocument3 pagesScience Chapter 1 Review and AssessmentanaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and SolidsDocument17 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solidselaine trazonaNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument18 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesChe PeñalesNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument10 pagesChemical BondsGAMING WITH SPELLNo ratings yet
- 5.types of Covalent CompoundsDocument17 pages5.types of Covalent CompoundsEian InganNo ratings yet
- Intro To Chemistry - Enhancement NotesDocument7 pagesIntro To Chemistry - Enhancement Notesesivaks2000No ratings yet
- chemistry-ELEMENTS AND CHEMICAL BONDINGDocument20 pageschemistry-ELEMENTS AND CHEMICAL BONDINGfelixmatchumbuza041No ratings yet
- Physical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesDocument15 pagesPhysical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesJodi RempilloNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument20 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesLYNFORD LAGONDINo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IDocument57 pagesOrganic Chemistry IMss FaixaNo ratings yet
- Polar BondsDocument8 pagesPolar BondsAnthony JohanNo ratings yet
- Eoy Review Student Questions KeyDocument4 pagesEoy Review Student Questions Keyapi-234918521No ratings yet
- Module 3 Quarter 3Document3 pagesModule 3 Quarter 3Jenevie Tagalicud100% (2)
- Chapter 8Document32 pagesChapter 8Danilo Fronda Jr.No ratings yet
- Molecular Polarity: SymmetryDocument4 pagesMolecular Polarity: SymmetryMims ChiiiNo ratings yet
- AP Chem Summer AssignmentDocument13 pagesAP Chem Summer AssignmentSophie LiNo ratings yet
- Bond PolarityDocument9 pagesBond PolarityIvy LunaNo ratings yet
- Chem RevDocument2 pagesChem RevArundhathiNo ratings yet
- MH1 Che101 CB10 S2019Document262 pagesMH1 Che101 CB10 S2019Hazrat AliNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 3Document7 pagesPhysical Science Week 3ruel rinconadaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Quarter 2-Week 1 (Module 2) Types of Intermolecular Forces Pre-TestDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Quarter 2-Week 1 (Module 2) Types of Intermolecular Forces Pre-TestDexter John Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Submitted By: Criestefiel Ann S. Lolo Grade 12 - GatesDocument13 pagesPhysical Science: Submitted By: Criestefiel Ann S. Lolo Grade 12 - GatesCriestefiel LoloNo ratings yet
- CHEM1102 Lecture Notes 2Document30 pagesCHEM1102 Lecture Notes 2Callum BiggsNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer by Aneezah PascualDocument5 pagesScience Reviewer by Aneezah Pascualdalialia136iNo ratings yet
- Ions and Electrolytes Worksheet Part 1: Ions Short Answer QuestionsDocument4 pagesIons and Electrolytes Worksheet Part 1: Ions Short Answer Questionsapi-423980580No ratings yet
- Chemistry Target Paper by Engr - Madiha Ahmed - 064534Document4 pagesChemistry Target Paper by Engr - Madiha Ahmed - 064534zoodiaamoNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument45 pagesPolarity of MoleculesAliza Liban100% (1)
- M1a1 EstradaDocument1 pageM1a1 EstradaAsia EstradaNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument3 pagesPeriodic TrendsJessica ShinNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding NotesDocument39 pagesCovalent Bonding NotesAmaris HopkinsNo ratings yet
- Special Reviewe Rnotes For Second Quarter General Chemistry 1Document25 pagesSpecial Reviewe Rnotes For Second Quarter General Chemistry 1GLUSITANIO, DIANA YSABELA JOHANA T.No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Chemistry Week 7 Lesson 1 Worksheet 1 and SolutionsDocument5 pagesGrade 10 Chemistry Week 7 Lesson 1 Worksheet 1 and SolutionsNikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- CHEM 3 Quiz 1 - Short Term: Class Discussion: SolutionsDocument7 pagesCHEM 3 Quiz 1 - Short Term: Class Discussion: SolutionsARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chemistry Grade 10Document54 pagesChemical Bonding: Chemistry Grade 10jahiem wilsonNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRDocument25 pagesQ3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRGumban Aaron Frances M.No ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4Coursehero Premium0% (1)
- Fulltext ID 110506772&PLACEBO IEDocument17 pagesFulltext ID 110506772&PLACEBO IEpkj009No ratings yet
- Springfield Building Department Inspectional Services Notice of ViolationsDocument6 pagesSpringfield Building Department Inspectional Services Notice of ViolationsThe Republican/MassLive.comNo ratings yet
- AFP Brochure08Document4 pagesAFP Brochure08YongoloooNo ratings yet
- Macro Curriculum Changes 2023 Part 2Document6 pagesMacro Curriculum Changes 2023 Part 2Al VelNo ratings yet
- May 2014Document48 pagesMay 2014debtwiggNo ratings yet
- CIED Surgical Guidance Dec21Document16 pagesCIED Surgical Guidance Dec21SamNo ratings yet
- Beef Short Ribs Asian Style Recipe - Chef Jean PierreDocument2 pagesBeef Short Ribs Asian Style Recipe - Chef Jean Pierrevasilescu2No ratings yet
- Interfacial PhenomenaDocument75 pagesInterfacial Phenomenanejaabera12No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Structure of The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - Structure of The Nervous Systemmanilyn dacoNo ratings yet
- 2.transmission Line Theory PDFDocument89 pages2.transmission Line Theory PDFSara AhmedNo ratings yet
- 9137-AN/898: Airport Services ManualDocument170 pages9137-AN/898: Airport Services ManualAndry NapitupuluNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 77Document2 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 77Kimberly MaeNo ratings yet
- Becoming Acquainted With Statistical ConceptsDocument3 pagesBecoming Acquainted With Statistical ConceptsCorteza, Ricardo Danilo E. UnknownNo ratings yet
- 3 - Trainees Record BookDocument6 pages3 - Trainees Record BookNelgen PiolaNo ratings yet
- TPMC Updated Offer On 2nd List 20200110Document2 pagesTPMC Updated Offer On 2nd List 20200110gabriel240371No ratings yet
- Vitodens 100w wb1b SeriesDocument100 pagesVitodens 100w wb1b Seriesclaudyu_fNo ratings yet
- Delhi Gang Rape CaseDocument3 pagesDelhi Gang Rape CasePriyesha MaliNo ratings yet
- Tipe A - Test Admin Shopee ExpressDocument6 pagesTipe A - Test Admin Shopee ExpressHapsyah MarniNo ratings yet
- Explore Learning MeiosisDocument7 pagesExplore Learning MeiosisAmarna BarnesNo ratings yet
- d000523 Doseuse RemplisseuseDocument2 pagesd000523 Doseuse RemplisseuseEnzo QuatremareNo ratings yet
- Escritura AutoguardadoDocument7 pagesEscritura AutoguardadoEren JaegerNo ratings yet
- JL Components Blower LubricationDocument4 pagesJL Components Blower LubricationMAZENNo ratings yet
- Structural Chemistry Organic Chemistry Summary: Alkynes: Structure, Conformations, PropertiesDocument20 pagesStructural Chemistry Organic Chemistry Summary: Alkynes: Structure, Conformations, PropertiesMohanraj ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Boundary Line: Plan of Gpuff Temporary JettyDocument1 pageBoundary Line: Plan of Gpuff Temporary Jettyshafiq_05No ratings yet
- Why Integration Is The Key To Asia's Economic Progress? Explain Your AnswerDocument2 pagesWhy Integration Is The Key To Asia's Economic Progress? Explain Your AnswerQueeny JavierNo ratings yet
- Morphology McqsDocument8 pagesMorphology McqsHiba Shah100% (2)
- Exercise LMTDocument4 pagesExercise LMTapi-276845347No ratings yet