Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Roll Pressure and It's Distribution: Slab Method of Analysis Under Plane Strain Assumption
Roll Pressure and It's Distribution: Slab Method of Analysis Under Plane Strain Assumption
Uploaded by
Sahil SundaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Roll Pressure and It's Distribution: Slab Method of Analysis Under Plane Strain Assumption
Roll Pressure and It's Distribution: Slab Method of Analysis Under Plane Strain Assumption
Uploaded by
Sahil SundaCopyright:
Available Formats
18
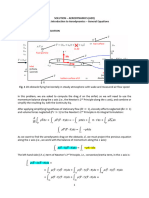
Roll pressure and it’s distribution
Slab method of analysis under plane strain assumption 𝜃
𝑂
𝑝
𝑑𝜃
𝑅 𝜇𝑝
ℎ
ℎ
𝜎 𝜃 𝜎 𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑦
𝑉 𝑉
𝜎 𝑑𝜎 𝜎
𝑑𝑥
𝑂 𝜇𝑝
𝑝
Considering horizontal equilibrium of forces on strip of length 𝑑𝑥
2 𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝜎 𝑑𝜎 2𝑦𝜎 2𝜇𝑝𝑅 cos 𝜃𝑑𝜃 2𝑅𝑝 sin 𝜃𝑑𝜃 0 (Before NP)
S. Mukhopadhyay Bulk Deformation Processes
19
Roll pressure and it’s distribution
Neglecting higher order terms and rearranging:
𝜃
𝑑 𝜎 𝑦 𝑝
𝜇 𝜃 𝑅𝑝 0
𝑑𝜃 𝜇𝑝
𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑦
Friction is low (see assumptions) so plane on 𝜎 𝑑𝜎 𝜎
which 𝑝 acts can be assumed to be a principal
plane. Applying von‐Mises criterion: 𝜇𝑝
𝜎 𝜎 𝜎 𝜎 𝜎 𝜎 2 𝜎 6𝐾 𝑝
1 1
𝜎 𝜎 𝑝 𝜎 𝑝 𝑝 𝑝 𝜎 6𝐾
2 2
𝑝 𝜎 2𝐾
S. Mukhopadhyay Bulk Deformation Processes
20
Roll pressure and it’s distribution
𝑑 𝜎 𝑦 𝑑 2𝐾 𝑝 𝑦
𝜇 𝜃 𝑅𝑝 0 𝜇 𝜃 𝑅𝑝 0
𝑑𝜃 𝑑𝜃
After NP (neutral point), the direction of friction is reversed. We indicate this
by changing sign of 𝜇 and generalizing the above equation to:
𝑑 2𝐾 𝑝 𝑦
𝜇 𝜃 𝑅𝑝 0 Applicable to the entire working region
𝑑𝜃
Shear yield strength 𝐾 increases while y decreases due to rolling. The product 𝐾𝑦
remains approximately constant.
𝑝
𝑑 1
2𝐾y 2𝐾 ∓𝜇 𝜃 𝑅𝑝 0
𝑑𝜃
S. Mukhopadhyay Bulk Deformation Processes
21
Roll pressure and it’s distribution
Any thickness can be expressed in terms of final thickness and angle subtended at
the roll centre:
2𝑦 ℎ 2𝑅 1 cos 𝜃
ℎ 𝑅𝜃
𝑦 For small 𝜃
2 2
Substituting 𝑦 in previous equation and rearranging:
𝑝
𝑑 2𝑅 𝜃 ∓ 𝜇 𝑑𝜃
2𝐾
𝑝 ℎ 𝑅𝜃
2𝐾
Integrating:
𝑝 𝑦 𝑅 𝑅
𝐶 𝑒∓ Where: 𝜆 2 tan 𝜃
2𝐾 𝑅 ℎ ℎ
S. Mukhopadhyay Bulk Deformation Processes
22
Roll pressure and it’s distribution
Before Neutral Point After Neutral Point
𝑝 𝑦 𝑝 𝑦
𝐶 𝑒 𝐶 𝑒
2𝐾 𝑅 2𝐾 𝑅
At beginning of rolling After neutral point
𝑝 𝜎 ℎ 𝑝 𝜎 ℎ
1 𝐶 𝑒 1 𝐶
2𝐾 2𝐾 2𝑅 2𝐾 2𝐾 2𝑅
2𝑅 𝜎 2𝑅 𝜎
𝐶 1 𝑒 with, 𝐶 1
ℎ 2𝐾 ℎ 2𝐾
𝑅 𝑅
𝜆 2 tan 𝜃
ℎ ℎ
Finally, Finally,
𝑝 2𝑦 𝜎 𝑝 2𝑦 𝜎
1 𝑒 1 𝑒
2𝐾 ℎ 2𝐾 2𝐾 ℎ 2𝐾
S. Mukhopadhyay Bulk Deformation Processes
23
Roll pressure and it’s distribution
𝑝
2𝐾
Effect of 𝜇 on rolling Pressure distribution as function of front and
pressure distribution. With back tension. As the front tension increases,
𝜇=0, there would be neutral point shifts and area of curve
slippage and neutral point decreases reduction of roll‐force.
will completely shift to
exit.
S. Mukhopadhyay Bulk Deformation Processes
24
Determination of neutral point
At neutral point (NP), velocity of the work is same as velocity of the roll.
Pressure profiles from before and after the neutral point also meet at this point.
Hence we equate the two pressure profiles pertaining to before and after NP:
2𝑦 𝜎 2𝑦 𝜎
1 𝑒 1 𝑒
ℎ 2𝐾 ℎ 2𝐾
𝜎
1 1 ℎ 1
𝜆 𝑙𝑛 2𝐾 𝜆
2 𝜇 ℎ 𝜎
1
2𝐾
Finally,
ℎ ℎ 𝜆
𝜃 tan
𝑅 𝑅 2
S. Mukhopadhyay Bulk Deformation Processes
You might also like
- Data Preparation For Gephi From CSV FileDocument9 pagesData Preparation For Gephi From CSV FileSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Hematra Reviewer FinalsDocument13 pagesHematra Reviewer FinalsOri SeinNo ratings yet
- Fluids Dynamics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFluids Dynamics Formula SheetMark Riley88% (8)
- Ficha Tecnica Um180821 Tds Tough Pla RB v11Document3 pagesFicha Tecnica Um180821 Tds Tough Pla RB v11Servirol CiaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 11 - Slenderness EffectDocument39 pagesPresentation 11 - Slenderness EffectseaklengNo ratings yet
- Concrete 1 November 2022Document4 pagesConcrete 1 November 2022Meverlyn Roquero100% (1)
- Exercise AER - 1.3 - SolutionDocument5 pagesExercise AER - 1.3 - SolutionJuanCB 006No ratings yet
- KSMTE 3pointcontact FinalkDocument15 pagesKSMTE 3pointcontact FinalkGibs RiveraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics LectureDocument10 pagesFluid Mechanics LectureJames Ivan AnoreNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Sturm-Liouville Boundary Value ProblemsDocument3 pages11.2 Sturm-Liouville Boundary Value ProblemsSamara ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- PHYS220 - Lecture 3.1Document5 pagesPHYS220 - Lecture 3.1Savio KhouryNo ratings yet
- CIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFDocument15 pagesCIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFCedricChanNo ratings yet
- CIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFDocument15 pagesCIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFCedricChanNo ratings yet
- Rigid Body Position and Orientation PDFDocument17 pagesRigid Body Position and Orientation PDFjoseeliasNo ratings yet
- Sentential Deduction RulesDocument2 pagesSentential Deduction RulesMatthew RumleyNo ratings yet
- Introductoin - Part 2 StuDocument33 pagesIntroductoin - Part 2 Stushivam ojhaNo ratings yet
- 2023 - Formula Sheet ExamDocument5 pages2023 - Formula Sheet ExamMohammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- 2-CE 305 MOD 2 Singly RCFDocument10 pages2-CE 305 MOD 2 Singly RCFLester Khiets RoaNo ratings yet
- Stagnation PropertiesDocument18 pagesStagnation PropertiesNadeem TanwariNo ratings yet
- VII. Time-Independent Perturbation Theory Elearn 20240312Document5 pagesVII. Time-Independent Perturbation Theory Elearn 20240312a0909665916No ratings yet
- Chapter 30-1 WireDocument1 pageChapter 30-1 WireShinta AyuningtiasNo ratings yet
- Retake Transduction and Mechanical Devices April16 2019 With AnswersDocument5 pagesRetake Transduction and Mechanical Devices April16 2019 With Answerskoen.bakker1234No ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - Angular DeformationDocument9 pagesLecture 13 - Angular DeformationjaggumeenaiitdNo ratings yet
- 2021 Formulasheet TaD-AEDocument1 page2021 Formulasheet TaD-AEhfdiosdhfio saoijdoiasjNo ratings yet
- L22 - PN Homojunction - 5 PDFDocument16 pagesL22 - PN Homojunction - 5 PDFPoddutoori Sankeerth ReddyNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 2 FormulaDocument46 pagesCFA Level 2 FormulaNguyễn Quốc ThắngNo ratings yet
- Rotor System - Section 2Document13 pagesRotor System - Section 2Mojtaba HasanluNo ratings yet
- SI TensorDocument31 pagesSI Tensoraskuma179No ratings yet
- Lecture-Slope Deflection and Moment DistributionDocument10 pagesLecture-Slope Deflection and Moment DistributionFanisNo ratings yet
- 4.1 TransmissionDocument41 pages4.1 TransmissionLIM SHANYOUNo ratings yet
- Design of Mechanical Systems Quiz and Exam Resource: GeometryDocument27 pagesDesign of Mechanical Systems Quiz and Exam Resource: GeometryGonzalez MigueNo ratings yet
- 2-Fluid Statics-Lecture Note 2Document7 pages2-Fluid Statics-Lecture Note 2Ashan ShamikaNo ratings yet
- Cato Sem5 SepDocument24 pagesCato Sem5 SepRuthNo ratings yet
- EE 202. 03. Force in SpaceDocument27 pagesEE 202. 03. Force in SpaceJerime JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document46 pagesLec 2ahmed EmadNo ratings yet
- Class34.04.08.2024 WNDocument18 pagesClass34.04.08.2024 WNEslam UsamaNo ratings yet
- Robotics Course: LR02.3:: 3 Dimensional Homogenous TransformationDocument17 pagesRobotics Course: LR02.3:: 3 Dimensional Homogenous TransformationThiha Ye ThwayNo ratings yet
- Least Square Method: Regression Analysis Over Determined SystemsDocument5 pagesLeast Square Method: Regression Analysis Over Determined Systemsياسين رياض بندرNo ratings yet
- Template Apps of DifferentiationDocument3 pagesTemplate Apps of DifferentiationIr_tuxedoNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From ASME-B30.30-2019-Wire-RopesDocument1 pageExtracted Pages From ASME-B30.30-2019-Wire-RopesShinta AyuningtiasNo ratings yet
- Laminar Flow ppt3Document16 pagesLaminar Flow ppt3Renuja LakviduNo ratings yet
- Lec 02-8 - Longitudinal DampingDocument12 pagesLec 02-8 - Longitudinal DampingArslan MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Summer 2020 Dr. Hidir Maral Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument36 pagesSummer 2020 Dr. Hidir Maral Department of Mechanical EngineeringRıza ÜnalNo ratings yet
- A Review Study On Gas-Solid Cyclone Separator Using Lapple Model - J4rv4i1001Document5 pagesA Review Study On Gas-Solid Cyclone Separator Using Lapple Model - J4rv4i1001Journal 4 ResearchNo ratings yet
- Rolling Force, Torque and Power: Bulk Deformation Processes S. MukhopadhyayDocument8 pagesRolling Force, Torque and Power: Bulk Deformation Processes S. MukhopadhyaySahil SundaNo ratings yet
- MECN 3350 - Aircraft Design and Performance - Module 5 - Unit 5.1 - Lesson 5.1.2Document64 pagesMECN 3350 - Aircraft Design and Performance - Module 5 - Unit 5.1 - Lesson 5.1.2Jose A Rosado LopezNo ratings yet
- Inverters: Eng. Ibrahim Mahmoud IbrahimDocument9 pagesInverters: Eng. Ibrahim Mahmoud IbrahimMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- 23 - Fourier Series & Analysis-01-08-2022Document54 pages23 - Fourier Series & Analysis-01-08-2022romanNo ratings yet
- Rules For Approximating Definite Integrals: Sin, Sin, 1Document5 pagesRules For Approximating Definite Integrals: Sin, Sin, 1トシToshiNo ratings yet
- Lec#6, Torsion-2 StudentDocument21 pagesLec#6, Torsion-2 Studentchristianborlaza23No ratings yet
- Forces ProblemsDocument11 pagesForces ProblemsTaleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- Soil Exploration (Geophysical Exploration)Document15 pagesSoil Exploration (Geophysical Exploration)ZakNo ratings yet
- SB320 Thru SB3200: Schottky Barrier RectifiersDocument2 pagesSB320 Thru SB3200: Schottky Barrier RectifiersVatasaNo ratings yet
- Solution For HOMEWORK 4Document5 pagesSolution For HOMEWORK 4Rau Lance CunananNo ratings yet
- Report 1206-2Document14 pagesReport 1206-2柯以祥No ratings yet
- EE 202. 02. Force As A Vector QuantityDocument36 pagesEE 202. 02. Force As A Vector QuantityJerime JimenezNo ratings yet
- Free Earth Support Method - FinalDocument3 pagesFree Earth Support Method - Finallau lauNo ratings yet
- MathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14From EverandMathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14No ratings yet
- ME-361 Manufacturing Science and Technology Bulk Deformation ProcessDocument16 pagesME-361 Manufacturing Science and Technology Bulk Deformation ProcessSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology (ME 361) - Lecture 20: Engineering MetrologyDocument35 pagesManufacturing Technology (ME 361) - Lecture 20: Engineering MetrologySahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Rolling Force, Torque and Power: Bulk Deformation Processes S. MukhopadhyayDocument8 pagesRolling Force, Torque and Power: Bulk Deformation Processes S. MukhopadhyaySahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Drawing: Dr. Supratik MukhopadhyayDocument12 pagesDrawing: Dr. Supratik MukhopadhyaySahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (ME 361) Lecture 14: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument27 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME 361) Lecture 14: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (ME 361) Lecture-17: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument21 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME 361) Lecture-17: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology-: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument34 pagesManufacturing Technology-: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil Sunda100% (1)
- Manufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 15: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument54 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 15: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (ME 361) - Lecture 16: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument33 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME 361) - Lecture 16: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 11: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument30 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 11: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 13: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument28 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 13: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (ME 361) Lecture-6: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument15 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME 361) Lecture-6: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (ME 361) - Lecture 7: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument14 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME 361) - Lecture 7: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology (ME361) Lecture 12: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument33 pagesManufacturing Technology (ME361) Lecture 12: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (ME 361) - Lecture 8: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument13 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME 361) - Lecture 8: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Science (ME361) : Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument18 pagesManufacturing Science (ME361) : Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Manufacturing TechnologyDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Manufacturing TechnologySahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology (ME361) - Lecture 5: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument22 pagesManufacturing Technology (ME361) - Lecture 5: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology (ME361) - Lecture 3: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument20 pagesManufacturing Technology (ME361) - Lecture 3: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology (ME361) Lecture 2: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument21 pagesManufacturing Technology (ME361) Lecture 2: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology (ME 361) - Lecture 4: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument21 pagesManufacturing Technology (ME 361) - Lecture 4: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Ocial Edia Ining: Network MeasuresDocument28 pagesOcial Edia Ining: Network MeasuresSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Properties of MaterialsDocument7 pagesNature and Properties of MaterialsSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- L1 ME222m CourseHandout MergedDocument927 pagesL1 ME222m CourseHandout MergedSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Properties of Materials: Credits: 2-0-0-0Document6 pagesNature and Properties of Materials: Credits: 2-0-0-0Sahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Graph Basics: Social Media Mining Social Media MiningDocument33 pagesGraph Basics: Social Media Mining Social Media MiningSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Covalent Bonding Web QuestDocument5 pagesIonic Covalent Bonding Web QuestFiona IsbellNo ratings yet
- Two Storey Residential BuildingDocument52 pagesTwo Storey Residential BuildingMaiko Laine CarbonelNo ratings yet
- Lorenz Number of Pure MetalDocument4 pagesLorenz Number of Pure MetalAvishekDeyProtikNo ratings yet
- Part 2Document12 pagesPart 2علي مؤيد مطشر صدامNo ratings yet
- Thin Solid FilmsDocument6 pagesThin Solid FilmsIjaz TalibNo ratings yet
- HA3 - Diego Larra EspinoDocument4 pagesHA3 - Diego Larra EspinoDiegoNo ratings yet
- Stress PDFDocument13 pagesStress PDF9966197483No ratings yet
- E 8018 B2Document1 pageE 8018 B2ElMacheteDelHuesoNo ratings yet
- 04 CreepDocument58 pages04 CreepYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Pushing The Boundaries of Steel Machining.: ISO Insert Series For Steel TurningDocument24 pagesPushing The Boundaries of Steel Machining.: ISO Insert Series For Steel TurningAlexandre SouzaNo ratings yet
- Cai Present OFW10 18Document31 pagesCai Present OFW10 18CehanNo ratings yet
- Test For Electrochemical Reactivation (EPR) To Detect Sensitization of AISI Type 304 and 304L Stainless SteelsDocument3 pagesTest For Electrochemical Reactivation (EPR) To Detect Sensitization of AISI Type 304 and 304L Stainless SteelsJaveed A. KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.7264 (Germany / WN) : Group Subgroup Structural and Constructional Steels Heat Treatable Alloyed Crmnmo Steel MaterialDocument2 pages1.7264 (Germany / WN) : Group Subgroup Structural and Constructional Steels Heat Treatable Alloyed Crmnmo Steel MaterialfarhadNo ratings yet
- Good Thesis PDFDocument444 pagesGood Thesis PDFZarr AkshNo ratings yet
- Tadmor 2017 Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 25 071001Document4 pagesTadmor 2017 Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 25 071001Sandya KaranamNo ratings yet
- TSADocument44 pagesTSAdraj1875977No ratings yet
- Finite Element Simulation of Low Concrete Strength Beam Beam-Column Joint Strengthened With CFRPDocument10 pagesFinite Element Simulation of Low Concrete Strength Beam Beam-Column Joint Strengthened With CFRPlalitha kandikaNo ratings yet
- Low-Temperature Sintering of Barium Hexaferrites With Bi O /cuo AdditivesDocument4 pagesLow-Temperature Sintering of Barium Hexaferrites With Bi O /cuo AdditivesMohammedNo ratings yet
- 3 Flexure.6278.1598780738.8088 PDFDocument79 pages3 Flexure.6278.1598780738.8088 PDFpattrapong pongpattraNo ratings yet
- SIMSOLID Validation Manual Release 1 1 PDFDocument66 pagesSIMSOLID Validation Manual Release 1 1 PDFadigraduNo ratings yet
- Fretting Corrosion or False BrinellingDocument4 pagesFretting Corrosion or False Brinellingfalconesas100% (1)
- Lug 0-5 Ton DesignDocument6 pagesLug 0-5 Ton DesignkalpanaadhiNo ratings yet
- Rhe OlogyDocument48 pagesRhe OlogyAhmed ImranNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: International Journal of PlasticityDocument78 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: International Journal of PlasticityzhuhaitingtaoNo ratings yet
- Tensile TestingDocument2 pagesTensile TestingFsNo ratings yet
- Influence of Confinement On High Strength Concrete BehaviorDocument9 pagesInfluence of Confinement On High Strength Concrete BehaviorMarimuthu KaliyamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Module 43 Solution Randomly Varying Stresses and Miner S RuleDocument3 pagesModule 43 Solution Randomly Varying Stresses and Miner S RuleWolf Lord100% (1)
- Small-Amplitude Oscillatory ShearDocument9 pagesSmall-Amplitude Oscillatory ShearNeemias Almeida DiasNo ratings yet
- Astm B850Document3 pagesAstm B850Somesh Ravichandran100% (1)