Professional Documents
Culture Documents
13 Data Independence
13 Data Independence
Uploaded by
sethuraman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesLogical data independence allows changes to the conceptual schema without affecting external schemas or application programs. Physical data independence separates the conceptual schema from the internal schema and allows changes to the physical storage structures without impacting the conceptual schema. While physical data independence can be achieved, logical data independence is more difficult because it must accommodate changes to the database structure without affecting applications.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLogical data independence allows changes to the conceptual schema without affecting external schemas or application programs. Physical data independence separates the conceptual schema from the internal schema and allows changes to the physical storage structures without impacting the conceptual schema. While physical data independence can be achieved, logical data independence is more difficult because it must accommodate changes to the database structure without affecting applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pages13 Data Independence
13 Data Independence
Uploaded by
sethuramanLogical data independence allows changes to the conceptual schema without affecting external schemas or application programs. Physical data independence separates the conceptual schema from the internal schema and allows changes to the physical storage structures without impacting the conceptual schema. While physical data independence can be achieved, logical data independence is more difficult because it must accommodate changes to the database structure without affecting applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
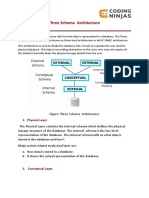
Data Independence
In this lesson, we will look at one of the results of the three-schema architecture.
WE'LL COVER THE FOLLOWING
• 1. Logical data independence
• 2. Physical data independence
• Does data independence work in reality?
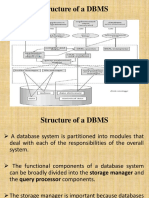
Data independence is defined as a property of the database management
system that helps to change the database schema at one level of a database
system without changing the schema at the next highest level. The three-
schema architecture can be used to further explain the concept of data
independence. We outline the two types of data independence:
1. Logical data independence #
The ability to change the conceptual schema without changing the external
schema or user view is called logical data independence. For example, the
addition or removal of new entities, attributes or relationships to this
conceptual schema should be possible without having to change existing
external schemas or rewriting existing application programs.
In other words, changes to the conceptual schema (e.g., alterations to the
structure of the database, like adding a column or other tables) should not
affect the function of the application (external views).
2. Physical data independence #
Physical data independence helps you to separate the conceptual schema from
the internal schema. It allows you to provide a logical description of the
database without the need to specify physical structures.
So for example, there is a change to the internal schema because some
physical files were reorganized, for example, by creating additional access
structures to improve the performance of retrieval or updates. Physical data
independence makes sure that these changes to the internal schema do not
affect the conceptual schema. In turn, the external schemas need not be
changed as well.
Does data independence work in reality? #
Generally, physical data independence exists in most databases and file
environments where physical details, such as the exact location of data on
disk or the type of storage device, are hidden from the user. On the other
hand, logical data independence is harder to achieve because it must
accommodate changes in the structure of the database without affecting
application programs; which is a much stricter requirement.
In the next lesson, we will outline the different classifications of database
management systems.
You might also like
- 307pro Technical ManualDocument98 pages307pro Technical ManualFaysbuk Koto100% (1)
- First Level of Data IndependenceDocument2 pagesFirst Level of Data IndependencePragya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Brief Answer QuestionDocument3 pagesBrief Answer QuestionSandeepNo ratings yet
- Types of Data IndependenceDocument9 pagesTypes of Data IndependenceAshish TyagiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Part 1Document66 pagesUnit 1 - Part 1Pawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Why would-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesWhy would-WPS OfficeLouie VillamorNo ratings yet
- Data IndependenceDocument3 pagesData IndependenceNipun ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- Pgdca DBMS MaterialsDocument3 pagesPgdca DBMS MaterialsAbassNo ratings yet
- 3 Schema ArchitectureDocument11 pages3 Schema Architectureminu pouloseNo ratings yet
- Database Management NotesDocument20 pagesDatabase Management NotesPrachiti ChavanNo ratings yet
- DATA INDEPENDECE - PPTX MIS PRESENTATIONDocument7 pagesDATA INDEPENDECE - PPTX MIS PRESENTATIONDivyaNo ratings yet
- Data AbstractionDocument9 pagesData AbstractionShruti ShindeNo ratings yet
- Physical Vs Logical Data IndependenceDocument2 pagesPhysical Vs Logical Data Independence11tiger92100% (5)
- Three Schema Architecture: 1. Physical LayerDocument3 pagesThree Schema Architecture: 1. Physical Layerpartha sarathi guggiriNo ratings yet
- 3 Schema ArchitectureDocument11 pages3 Schema Architectureminu pouloseNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Introduction To DBMSDocument19 pages1.1. Introduction To DBMSVarshini SenthilNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument5 pagesDBMSOperation ResearchNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Part 1Document44 pagesUnit 1 - Part 1Harsh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Dbms Assignment 1Document17 pagesDbms Assignment 1SaladAss GamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument9 pagesChapter Two Database System Concepts and ArchitecturertyiookNo ratings yet
- Introduction of DBMSDocument89 pagesIntroduction of DBMSStory TellingNo ratings yet
- Data Abstraction and Data IndependenceDocument1 pageData Abstraction and Data IndependencepthepronabNo ratings yet
- Structure of A DBMSDocument26 pagesStructure of A DBMSmaneesh sNo ratings yet
- DBMS QueDocument16 pagesDBMS QueVishalNo ratings yet
- Team:B.TECH (CSE 2018-2022) Channel:DBMS: Data IndependenceDocument14 pagesTeam:B.TECH (CSE 2018-2022) Channel:DBMS: Data IndependenceVijay PalNo ratings yet
- Database Components and Database Concepts, Data Independence, Structural IndependenceDocument3 pagesDatabase Components and Database Concepts, Data Independence, Structural IndependenceYelena BytenskayaNo ratings yet
- What Does The Term Data Independence Mean, and Why Is It An Important Goal? AnswerDocument3 pagesWhat Does The Term Data Independence Mean, and Why Is It An Important Goal? AnswerArif AbdullahNo ratings yet
- SWE DataBaseDocument56 pagesSWE DataBasenkoloamandineNo ratings yet
- Dbms QB Solution Tt-1Document15 pagesDbms QB Solution Tt-1Ojas PatilNo ratings yet
- Dbms Mid NotesDocument18 pagesDbms Mid Notesmishaverma433No ratings yet
- Cse CSPC403 DBMSDocument98 pagesCse CSPC403 DBMSArvind MehraNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 EntityRelationshipModelDocument25 pagesChapter2 EntityRelationshipModelduonglluyen240824No ratings yet
- DBMSDocument20 pagesDBMSRpp YmtNo ratings yet
- DBMS Full 1st SemDocument147 pagesDBMS Full 1st SemAnziya AbdulkhaderNo ratings yet
- DBMS QB SolutionDocument9 pagesDBMS QB Solutionadishree jalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- GFG - DBMSDocument393 pagesGFG - DBMSKaran100% (1)
- DBMS Notes: Database: Database Is A Collection of Inter-Related Data Which Helps in EfficientDocument22 pagesDBMS Notes: Database: Database Is A Collection of Inter-Related Data Which Helps in EfficientMypersonal ForrandomshitNo ratings yet
- Technical Questions Based On Database Management SystemDocument26 pagesTechnical Questions Based On Database Management SystemShail SinghNo ratings yet
- DBMS Module-1Document36 pagesDBMS Module-1Krittika HegdeNo ratings yet
- DBMS Chap 01Document46 pagesDBMS Chap 01radwanNo ratings yet
- Architecture of DbmsDocument20 pagesArchitecture of Dbmsrr3870044No ratings yet
- DBMS Concepts and ArchitectureDocument6 pagesDBMS Concepts and ArchitectureRajNo ratings yet
- Database - E R ModelDocument4 pagesDatabase - E R ModelhuyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document46 pagesUnit 1Raj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- DB Assgmt 1Document6 pagesDB Assgmt 1Taonga NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- DBMS AssignmentDocument4 pagesDBMS AssignmentPiyush SakhujaNo ratings yet
- Physical Data IndependenceDocument5 pagesPhysical Data Independencelycosexcellence22No ratings yet
- DBMS Chap 01Document46 pagesDBMS Chap 01Kamada Akshay VarmaNo ratings yet
- MergedDocument393 pagesMergedRAVINo ratings yet
- Database Management System: (BCAC-401)Document16 pagesDatabase Management System: (BCAC-401)Akash HalsanaNo ratings yet
- Abstraction Data IndependenceDocument7 pagesAbstraction Data IndependencePRADNYA KASHIKARNo ratings yet
- DBMS Architecture and Data IndependanceDocument9 pagesDBMS Architecture and Data IndependanceAshwitha NaileshNo ratings yet
- DBMS Chapter2 Concepts and ArchitectureDocument20 pagesDBMS Chapter2 Concepts and ArchitectureVcoid GrenadeNo ratings yet
- 1.architecture of DBMSDocument27 pages1.architecture of DBMSanishaNo ratings yet
- Deck 01 Database TechnologyDocument29 pagesDeck 01 Database TechnologyEida IzanamiNo ratings yet
- Database Schema: InstanceDocument9 pagesDatabase Schema: Instancekings cliffNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Logical and Physical Data Independence?Document1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between Logical and Physical Data Independence?mahilataNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 DBMS SolutionDocument13 pagesAssignment 1 DBMS SolutionAbhishek DwivediNo ratings yet
- 3-Database System CharacteristicsDocument12 pages3-Database System Characteristicsbhumika.verma00No ratings yet
- EdYoda Web Developer TA - ProjectDocument3 pagesEdYoda Web Developer TA - ProjectVenki KingNo ratings yet
- Debate Writing 11Document3 pagesDebate Writing 11arhamkapadiapargNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization & Assembly Language (COAL)Document14 pagesComputer Organization & Assembly Language (COAL)Asadullah KhanNo ratings yet
- 18CSL58-DBMS LAB Excercise-1 Library DatabaseDocument9 pages18CSL58-DBMS LAB Excercise-1 Library Database1HK18IS031 -Jeevitha.NNo ratings yet
- Number: PT0-001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 MinDocument17 pagesNumber: PT0-001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Minscastell77No ratings yet
- Iso 02909-2002Document14 pagesIso 02909-2002ГалинаNo ratings yet
- CRM ProcessDocument17 pagesCRM ProcessSaurabh Rinku86% (7)
- Digital Circuits - Shift RegistersDocument7 pagesDigital Circuits - Shift RegistersB.Prashant JhaNo ratings yet
- MC60 Series GNSS: AT Commands ManualDocument22 pagesMC60 Series GNSS: AT Commands ManualAdimaro MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Pages From MMR-SP-60-001-A4 - Rev3 - Instrument General Specification-SignedDocument6 pagesPages From MMR-SP-60-001-A4 - Rev3 - Instrument General Specification-SignedKykyRizkyNo ratings yet
- Aras Innovator 12.0 - Microsoft Reporting Services 2016 Guide PDFDocument51 pagesAras Innovator 12.0 - Microsoft Reporting Services 2016 Guide PDFLuis Gerardo Ventosa GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1MIS Interview Questions and Answers PDF DownloadDocument4 pages1MIS Interview Questions and Answers PDF DownloadVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- JimpDocument30 pagesJimpAditya PandeyNo ratings yet
- C3134 - Oops Notes - Module IiiDocument15 pagesC3134 - Oops Notes - Module IiiSoumya KSNo ratings yet
- A Journal Paper Vs Screen: An Analysis On Student's Reafing Perspectives in The Digital AgeDocument14 pagesA Journal Paper Vs Screen: An Analysis On Student's Reafing Perspectives in The Digital AgeDisty Ariyanti RukmanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Redbus Test Cases-1Document4 pagesAssignment Redbus Test Cases-1Akshay Patil100% (1)
- BlockchainDocument11 pagesBlockchainbhoomikaNo ratings yet
- Micom P44X: Numerical Distance Protection RelayDocument152 pagesMicom P44X: Numerical Distance Protection RelayKuenley TiNy OndeNo ratings yet
- Gate Successful Ques PDFDocument26 pagesGate Successful Ques PDFSureshNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Modern Introduction 4th Edition David Poole Solutions ManualDocument37 pagesLinear Algebra Modern Introduction 4th Edition David Poole Solutions Manualdrohheritagebigdr6100% (12)
- SysadminDocument300 pagesSysadminahmedkhush2006No ratings yet
- List of Basic Autocad Commands: Shortcut / Command DescriptionDocument1 pageList of Basic Autocad Commands: Shortcut / Command DescriptionJeremia MaghinangNo ratings yet
- How To Enable Wi-Fi On MacBook, Mac Mini, MacBook Air For Ubuntu:Linux:Debian:Mint:Mate OS GitHubDocument2 pagesHow To Enable Wi-Fi On MacBook, Mac Mini, MacBook Air For Ubuntu:Linux:Debian:Mint:Mate OS GitHubwariszNo ratings yet
- Thomas Calculus PaperDocument1 pageThomas Calculus PaperMobeen YaseenNo ratings yet
- Bisagras ParkerDocument10 pagesBisagras ParkerHUGO ARMANDO ROJAS GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- AS400 Glossary: A AIX - ApacheDocument6 pagesAS400 Glossary: A AIX - ApacheCharles JacobNo ratings yet
- Sap Practice Exercise Installation StepsDocument4 pagesSap Practice Exercise Installation Stepswas reuyNo ratings yet
- Vcenter Server and Host Management VMware Vsphere6.5 - ESXi6.5 - Vcenter Server6.5 PDFDocument184 pagesVcenter Server and Host Management VMware Vsphere6.5 - ESXi6.5 - Vcenter Server6.5 PDFSisayNo ratings yet
- FC12Document9 pagesFC12Shiva Prakasam PernetiNo ratings yet