Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cumulative Assignment - 1: C Q B S A P D R O
Cumulative Assignment - 1: C Q B S A P D R O
Uploaded by
ASHIM GHOSHCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- (Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics) Murray H. Protter, Charles B. Jr. Morrey - Intermediate Calculus (1986, Springer)Document664 pages(Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics) Murray H. Protter, Charles B. Jr. Morrey - Intermediate Calculus (1986, Springer)Eliacim Velez67% (3)
- Answers: LESSON 1.1 - Building Blocks of GeometryDocument35 pagesAnswers: LESSON 1.1 - Building Blocks of GeometryThao Nguyen100% (4)
- Maths QuizDocument4 pagesMaths Quiznaman.bahal09No ratings yet
- Geometry 2 (Triangles) For CATDocument3 pagesGeometry 2 (Triangles) For CATSuvam BoseNo ratings yet
- QAHO1001916Document2 pagesQAHO1001916Saumya SinghNo ratings yet
- QA: BBA + IPM Specific: Geometry & Modern MathsDocument13 pagesQA: BBA + IPM Specific: Geometry & Modern MathsTitiksha JoshiNo ratings yet
- IMPORTANT QA-25 Geometry 1 With Solutions (1) QA-28 Geometry 4 With SolutionsDocument8 pagesIMPORTANT QA-25 Geometry 1 With Solutions (1) QA-28 Geometry 4 With SolutionsgauravNo ratings yet
- 2014 BcexamDocument2 pages2014 BcexamBo WangNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 4-ST&CR (16.04.2020)Document12 pagesAssignment - 4-ST&CR (16.04.2020)KaushikNo ratings yet
- 10 CongruencyDocument2 pages10 CongruencyMohanlal PereraNo ratings yet
- Tangent To A CircleDocument2 pagesTangent To A CircleYashh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Abhay Mahajan: B.Tech. IIT RoorkeeDocument41 pagesAbhay Mahajan: B.Tech. IIT RoorkeeLakshya SehgalNo ratings yet
- QA-28 Geometry-4 Questions PDFDocument4 pagesQA-28 Geometry-4 Questions PDFDhwani BarchhaNo ratings yet
- Best Approach: Iit Jee Mains + AdvancedDocument10 pagesBest Approach: Iit Jee Mains + AdvancedAtulNo ratings yet
- Geometry 2 - TrianglesDocument21 pagesGeometry 2 - TrianglesSaurav BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 06 Solution of Triangle - Sheet-ExtractedDocument7 pages06 Solution of Triangle - Sheet-Extractedudoy1974No ratings yet
- 3 Solutions: B P N QDocument19 pages3 Solutions: B P N QMinh 123No ratings yet
- Vectors - Question PaperDocument4 pagesVectors - Question PaperCelestial GhandatNo ratings yet
- MECExercise 1Document7 pagesMECExercise 1prakharNo ratings yet
- 9 - Class INTSO Work Sheet - 1 - Basic Concepts of GeometryDocument2 pages9 - Class INTSO Work Sheet - 1 - Basic Concepts of GeometrypradyumnnileshtapdiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapters 10 - 11 Circles Theorems - Point & LinesDocument11 pagesChapters 10 - 11 Circles Theorems - Point & LinesXie ChenxinNo ratings yet
- Single Answer Type Vectors & 3D: A, B, C A 3, B 4, C 5Document7 pagesSingle Answer Type Vectors & 3D: A, B, C A 3, B 4, C 5Celestial GhandatNo ratings yet
- The Distance Between The Circumcenter and Any Point in The Plane of The TriangleDocument10 pagesThe Distance Between The Circumcenter and Any Point in The Plane of The Trianglevijay9290009015No ratings yet
- Finding Tangents and Secants Measurement PDFDocument5 pagesFinding Tangents and Secants Measurement PDFJeff AragonNo ratings yet
- Geometry Properties of Triangles QDocument4 pagesGeometry Properties of Triangles Qlalit kumawatNo ratings yet
- NTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Document16 pagesNTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Apex Institute100% (1)
- Assignment Class X Similar Triangles: A D E B CDocument2 pagesAssignment Class X Similar Triangles: A D E B CCRPF School100% (1)
- Circum RevDocument46 pagesCircum RevVroojak KhoshrooNo ratings yet
- Part-A: Single Answer TypeDocument7 pagesPart-A: Single Answer TypeFaiz KhanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry RevisionDocument3 pagesTrigonometry RevisionBindiya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv2 E-1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- SSC CGL Tier - II: Pure Maths Handout: Geometry - IDocument4 pagesSSC CGL Tier - II: Pure Maths Handout: Geometry - IKenny CharlesNo ratings yet
- 2 A Sec A ) C B (2 2 A Sin A ) C B (2 2 A Cos A ) C B (2 2 A Cosec ADocument4 pages2 A Sec A ) C B (2 2 A Sin A ) C B (2 2 A Cos A ) C B (2 2 A Cosec AJonathan ParkerNo ratings yet
- Attempt This Question.: Geometrical Reasoning ADocument5 pagesAttempt This Question.: Geometrical Reasoning AFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- H Shape Space and Measure Revision MatDocument1 pageH Shape Space and Measure Revision MatehmaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Circle (Part-1 To 08) 20230922061125Document16 pagesGeometry Circle (Part-1 To 08) 20230922061125Rishabh KumarNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument2 pagesGeometrySandeep MuniNo ratings yet
- Quadriletral and Area of Parallelogram PDFDocument4 pagesQuadriletral and Area of Parallelogram PDFQSQFNo ratings yet
- Lines Angles and TrianglesDocument7 pagesLines Angles and Trianglesprinkit patelNo ratings yet
- Ace of Pace ADV Question PaperDocument6 pagesAce of Pace ADV Question PaperAyush ShindeNo ratings yet
- Yr10 Yearly 2009Document9 pagesYr10 Yearly 2009Ye ZhangNo ratings yet
- 1819 Mat S3 Ut2 Q&aDocument24 pages1819 Mat S3 Ut2 Q&a陳梓傑CHAN TSZ KITNo ratings yet
- ODocument2 pagesOElaiza Araquel100% (1)
- Algebra 2 PracticeDocument3 pagesAlgebra 2 Practiceaksharap.gudipatiNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument12 pagesGeometryP K SinghNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarterly ExamDocument3 pages2nd Quarterly ExamOdinah Mariano Bantolo100% (1)
- 5 - Radii of CircleDocument4 pages5 - Radii of CircleIndian gardeningNo ratings yet
- Casey's Theorem - Shailesh Shirali - X PDFDocument5 pagesCasey's Theorem - Shailesh Shirali - X PDFAakash GurungNo ratings yet
- Properties of Solution & Triangle-04 - ExerciseDocument23 pagesProperties of Solution & Triangle-04 - ExerciseRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- M11 - Quant Home Work AssignmentDocument12 pagesM11 - Quant Home Work Assignmentparshvaj0312No ratings yet
- Geometry - 3: Number of Questions: 30 CirclesDocument12 pagesGeometry - 3: Number of Questions: 30 CirclespratikNo ratings yet
- TriangleDocument2 pagesTrianglehardikvimal52No ratings yet
- Class-9 - DIGITAL - CLASSROOM - November - KB PDFDocument39 pagesClass-9 - DIGITAL - CLASSROOM - November - KB PDFSubhdra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Geometry 03Document4 pagesGeometry 03AbhishekNo ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv1 E-1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv1 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- Class - 9 - Nstse - PQP - 10 Papers - 2019-20 - 2 in A4 PDFDocument106 pagesClass - 9 - Nstse - PQP - 10 Papers - 2019-20 - 2 in A4 PDFriddhi100% (4)
- Recurring Crux Configurations 5 Cyclic Orthodiagonal 38.2Document3 pagesRecurring Crux Configurations 5 Cyclic Orthodiagonal 38.2ŁØNɆ ⱲØŁꞘNo ratings yet
- Dao's Theorem On Six Circumcenters AssociatedDocument4 pagesDao's Theorem On Six Circumcenters AssociatedNam Vu PhươngNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry and Quadratic Kvpy PYQDocument6 pagesTrigonometry and Quadratic Kvpy PYQTanay AgrawalNo ratings yet
- MBA-IBA Math 10Document8 pagesMBA-IBA Math 10muftibinhabibNo ratings yet
- QA - 50 (Line Triangle) OMETsDocument6 pagesQA - 50 (Line Triangle) OMETsRuchaNo ratings yet
- Coordinates (Answer Sheet)Document7 pagesCoordinates (Answer Sheet)LaureeyNo ratings yet
- 2016-03-31 The Incenter-Excenter Lemma, by Evan Chen PDFDocument4 pages2016-03-31 The Incenter-Excenter Lemma, by Evan Chen PDFAngela Angie BuseskaNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Soal Olimpiade Matematika Dari Seluruh DuniaDocument11 pagesKumpulan Soal Olimpiade Matematika Dari Seluruh DuniaAkalNo ratings yet
- Coordinates: Distance Between Two PointsDocument7 pagesCoordinates: Distance Between Two PointsMuralee VeeramalaiNo ratings yet
- INMOTC 2020 Problem SetDocument7 pagesINMOTC 2020 Problem SetShamim AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Isogonal Conjugates 1Document12 pagesIsogonal Conjugates 1Zadaci AopsNo ratings yet
- 中三 三角形的特殊線和中心 (Special Lines and Centres in a Triangle) - V3 - Final - GDocument61 pages中三 三角形的特殊線和中心 (Special Lines and Centres in a Triangle) - V3 - Final - G丛头越No ratings yet
- Mathematics (71) Geometry - Prelim Ii - Paper - 3 (E) Seat No. 2014 - 1100Document14 pagesMathematics (71) Geometry - Prelim Ii - Paper - 3 (E) Seat No. 2014 - 1100KhushilNo ratings yet
- Advanced GeometryDocument7 pagesAdvanced GeometryGenelle Mae MadrigalNo ratings yet
- CGT 5 G 1aDocument19 pagesCGT 5 G 1aJames BorNo ratings yet
- Geometry-Solutions 3 PDFDocument5 pagesGeometry-Solutions 3 PDFสฮาบูดีน สาและNo ratings yet
- Quadriletral and Area of Parallelogram PDFDocument4 pagesQuadriletral and Area of Parallelogram PDFQSQFNo ratings yet
- Lemmas in Olympiad GeometryDocument9 pagesLemmas in Olympiad GeometryAbdelmalek Boudouh67% (3)
- Coordinategeometry 1Document13 pagesCoordinategeometry 1shahulNo ratings yet
- BASIC DRAWING AIDS FOR CAD Lesson For TodayDocument7 pagesBASIC DRAWING AIDS FOR CAD Lesson For TodayJoel ManioNo ratings yet
- Philippine Mathematical OlympiadDocument11 pagesPhilippine Mathematical OlympiadRosen Dominic Escoto100% (1)
- Mathematics Grade 10 Test I.: Fourth Periodical ExaminationDocument2 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Test I.: Fourth Periodical ExaminationBhela NumbNo ratings yet
- AnswerKeyGrade10mathematics2 46872Document18 pagesAnswerKeyGrade10mathematics2 46872Lahari.u Lahari.uNo ratings yet
- Midline TheoremDocument19 pagesMidline TheoremArlene Polis Delos Reyes100% (4)
- Quantitative Ability 1Document23 pagesQuantitative Ability 1Akhil SinglaNo ratings yet
- TLE-TD-MDL-for-students-WEEK 3Document8 pagesTLE-TD-MDL-for-students-WEEK 3Arjay SerranoNo ratings yet
- IMO Shortlist 2009 OriginalDocument90 pagesIMO Shortlist 2009 OriginalMark Jason CelizNo ratings yet
- MathDocument5 pagesMathLastTheaterNo ratings yet
- Geometry Handout #5 Answers and SolutionsDocument9 pagesGeometry Handout #5 Answers and SolutionsWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Midterms To Finals MATH 6100Document44 pagesMidterms To Finals MATH 6100Sean Chua83% (6)
- Coordinate Geometry (MJ 18 To 2005)Document5 pagesCoordinate Geometry (MJ 18 To 2005)Burhan AzharNo ratings yet
- Basic Proportionality Theorem & Similar TrianglesDocument1 pageBasic Proportionality Theorem & Similar TrianglesdwdadNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Document1 pageFormula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Roberto DiscutidoNo ratings yet
Cumulative Assignment - 1: C Q B S A P D R O
Cumulative Assignment - 1: C Q B S A P D R O
Uploaded by
ASHIM GHOSHOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cumulative Assignment - 1: C Q B S A P D R O
Cumulative Assignment - 1: C Q B S A P D R O
Uploaded by
ASHIM GHOSHCopyright:
Available Formats
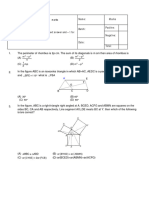
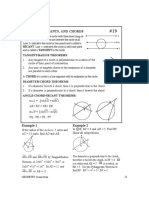
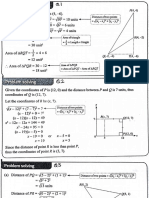
C l a s s -I X M a t he m a t i c s W o r k s h e e t B o o k l et
Q
Cumulative assignment - 1 D C
P
1. In a trapezium ABCD, AB is parallel
to CD. BD is perpendicular to AD. AC A B
is perpendicular to BC. If AD = BC = O
15 cm and AB = 25 cm, then the area
of the trapezium is
A) 192 cm2 B) 232 cm2
C)172 cm 2
D) none of these 22 7
A) B)
2. In the adjoining figure AT and BT are 7 22
the to two tangents at A and B
respectively CD is also a trangent at 7
C) D) can't be determined
P. Ther e are some m ore circles 12
touching each other and the tangents 5. ABCD is a rectangle of dimensions
AT and BT also. Which one of the 6cm × 8cm. DE and BF are t he
following is true? perpendiculars drawn on the diagonal
A of the rectangle. Then the ratio of the
C shaded to that of unshaded region is
E
G D C
I
P
Q R S
T
F H J
B D
E
A) PC + CT = PD + DT
B) RG + GT = RH + HT
A B
C) PC + QE = CE
D) all of these A) 7 : 3 B) 16 : 9
3. In the adjoining figure 'O' is the centre
C) 4 : 3 2 D) data insufficient
of the circle AOD = 120o . If the radius
of the circle is 'r', then the sum of the 6. ABC is an isosceles triangle in
areas of quadrilateral AODP and OBQC which AB = AC and A = 2 B , AB
is = 4 cm. Then the ratio of inradius to
the circumradius is
A C
o
A
90o 90
P Q
R O S
D B
3 2 C
A) r B) 3 3r2 B
2
C) 3r 2 D) none of these A) 1 : 2 B) 2 1 :1
4. In the adjoining figure 'O' is the centre
of the circle and AB is the diameter.
C) 1: 2 2 1 D) none of these
Tangent PQ touches the circle at D. 7. The semiperimeter of a right angled
BDQ = 48 . Then 0
the ratio of triangle is 126 cm and the shortest median
is 53 cm. Then the area of a triangle which
DBA : DCB is has the largest median as its longest side is
A) 1560 cm2 B) 1260 cm2
44 ShomeSir Maths Foundation Program
Mathematics Worksheet Booklet Class -IX
C) 1060 cm 2
D) none of these
A
8. In a right angled triangle ABC, B is
right angle, side AB is half of the O
hypotenuse. AE is parallel to median B D
BD and CE is parallell to BA. Then the
ratio of length of BC to that of EC is T
C
A) 2 :1 B) 3 :2 A) 27 cm B) 30 cm
C) 25 cm D) 31 cm
C) 5: 3 D) none of these
9. In the adjoining figure 'O' is the
12. In the following figure there is a
centre of the circle and PQ, PR and
semicircle with centre 'O' and diameter
ST are t he t hr ee
AB (= 2r). PQRS is a square of maximum
tangents. QPR = 50o , then the value possible area. P and Q lie on the diameter
of SOT is AB and R, S lie on the arc of the
semicircle, there are two more squares
Q of maximum possible area EFGP and
S CDQH. Then the sum of lengths of RC
and FS is
O M
50 o P S R
R T D C
F E
A) 30 o
B) 75o
C) 65 o
D)can't be determined
10. In the adjoining figure O is the
AG P O Q HB
centre of the circle with radius'r'.
AB, CD and EF are the diameters of 2 2 2r
the circle. OAF = OCB = 60 o . Then
A) 2r B)
5 5
the area of the shaded region is
2
D E C) r D) none of these
5
A B
60o
O 60o
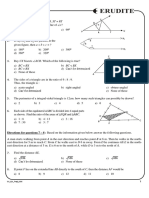
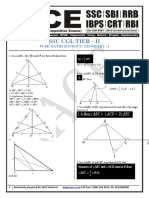
Cumulative assignment - 2
F C
1. A circle is circumscribed by the
r2 3 3 r2 3 3 Rhombus which is in turn is made up
A) B)
2 2 2 4 by joining the midpoints of a rectangle
whose sides, 12 cm and 16cm
r2 2 3 respectively. Then the area of the circle
C) 3 3 D) data is
insufficient
625 676
11. In the given diagram CT is tangent at C, A) B)
26 25
making an angle of with CD. O is the 576
4 C) D)can't be ditermined
centre of the circle. CD = 10 cm. Then 25
the perimeter of the shaded
2. In the given figure ADEC is a cyclic
region Δ AOC approximately is quadrilateral, CE and AD are extended to
meet at B. CAD = 60o and CBA = 30o .
BD = 6 cm and CE = 5 3 cm, then the
ratio of AC : AD is
ShomeSir Maths FoundationP r o g r a m 4455
C l a s s -I X M a t he m a t i c s W o r k s h e e t B o o k l et
C
C) 2 1 3 : 2 3 : 2
E D) 2 1 3 : 2 3: 3
5. In the given figure, P and Q are the
60o 30o mid-points of AC and AB. Also, PG =
A B GR and HQ = HR. Then the ratio of
D
3 4 area of PQR : area of ABC is
A) B) C
4 5 R
2 3 G
C) D) can't be determined
5 P H
3. ABCD is a square, in which a circle is
inscribed touching all the sides of
A B
square. In the four corners of square 4 Q
smaller circles of equal radii are drawn, 1 2
containing maximum possible area. A) B)
Then the ratio of the area of larger 2 3
circle to that of sum of the areas of 3
four smaller circles is C) D) none of the above
5
D C 6. In a triangle ABC, AD is the angle
bisector of BAC and BAD = 60 o .
Then the length of AD is
A
A B
A) 1:(68 – 48 2 ) B) 1 : 17 2 c
b
C) 3 : (34 – 12 2 ) D) none of these
4. In the adjoining figure three congruent D
circles are touching each other. B a C
Triangle ABC circumscribes all the bc bc
three circles. Triangle PQR is formed A) B)
by joinign the centres of the circles. bc bc
b c
2
There is a third triangle DEF. Points A,
D, P and B, E, Q and C, F, R lie in the C) b2 c 2 D)
bc
same straight lines respectively. Then
the ratio of perimeters of 7. In a triangle ABC, A ,
ΔABC : ΔDEF : ΔPQR is BA = a, AC = b on the side AC and AB,
C
points M and N are taken, M being the
midpoint of AC. Then the length of the
F
line segment MN. If the area of the
R
1
triangle AMN is of the area of the
3
P
triangle ABC is
Q
D E
A B
4a 2 b2 2ab
A) cos
A) 3 2 : 2 2 :1 9 4 3
B) 3 4 3 : 2 3 : 3 B)
4a 2 b2 2ab
cos
9 4 3
46 ShomeSir Maths Foundation Program
Mathematics Worksheet Booklet Class -IX
A
4a 2 b2 2ab
C) cos
9 4 3 D
D) none of these
8. The diagram shows if equal circles O
inscribed in equilateral triangle ABC. The
circles touch externally among them E
selves and also touch the sides of the B C
triangle. If the radius of each circle is R,
area of the triangle is A) 4 untis B) 2 units
C) 2 3 units D) none of these
A
12. In a triangle ABC, let C1 be any point on
the side AB other than A and B. Join
CC1. The line passing through A and
parallel to CC1 intersects, the line BC
extended at A1. The line passing through
B and parallel to CC1 intersects, the in
line AC extended at B1. The lengths AA1,
B C BB1, CC1 are given to be p, q, r units
respectively. Then which of the following
is true
A) 6 3 R B) 9R2
pq pq
A) r B) r
C) R 12 7 3
2
D) R 2
96 3 pq 4
9. AB is the hypotenuse in the right angled pq
C) r D) none of these
triangle ABC. N is the point inside the 2
triangle which divides the triangle in three
equal parts ABN, CAN, BCN .Then
the distance between the circumcentre Cumulative assignment - 3
of this triangle from this point N is
AB AB 1. In the figure (not drawn to scale)given
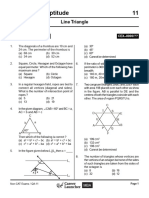
A) B) below, P is a point on AB such that
4 6 AP : PB = 4 : 3, PQ is parallel to AC and
AB AB QD is parallel to CP. In
C) D)
3 8 ARC, ARC = 90 o
and in
10. ABCD is a parallelogram in which PQS, PSQ = 90o . The length of QS is
D = 120o. The bisector of D bisects the 6 cm, then the ratio of AP : PD is
side AB. If the length of the bisector is A) 10 : 3 B) 2 : 1
5cm, then the perimeter of the C) 7 : 3 D) 8 : 3
parallegram is
2. Given two concentric circles of radii
A) 36 cm B) 30 cm R and r. From a point P on the
C) 24 cm D) none of these smaller circle, a straight line is
11. For the equilateral triangle ABC, D drawn to intersect the larger circle
and E are midpoints of AO and OB, at B and C. The perpendicular to BC
and DE = 3 units. The circumference at P intersects the smaller circle at
of the circle is equal to A. Then PA 2 + PB2 + PC2 = 2(R2 + r2)
A) R2 + r2 B)2(r2 + R2)
C)R2 – r2 D) none of these
ShomeSir Maths FoundationP r o g r a m 4477
C l a s s -I X M a t he m a t i c s W o r k s h e e t B o o k l et
3. ABC is a triangle. AD, BE and CF are C) 16 cm D) none of these
the altitudes from the vertices A, B 7. In the given figure, PQR is a triangle and
and C respectively. Show that the S is a point on QR such that the line PS
Δ'ls DEC, DBF and AEF are similar. divides QR in the ratio 2 : 1. The bisectors
of angles PSQ and PSR meet PQ and PR at
4. A ladder 130 feet long is leaning on a
T and U respectively. If PU = 128 cm, UR =
wall. The distance of the foot of the
16 cm, and PQ = 100 cm, then PT is
ladder from the foot of the wall is
120 feet. If the ladder is lifted up P
wards such the height of the point
where the ladder touches the wall 128
100
above the ground increases by 70 T U
feet, then the decrease in horizontal
distance of the foot of the ladder from 16
the foot of the the wall is
Q 2 S 1 R
A) 70 B) 60
C) 50 D) 90 A) 80 cm B) 90 cm
5. In the figure ABCD is a square of side C) 100 cm D) 112 cm
2 cm and four semicircles are drawn 8. In the given figure, AD is the angular
taking each of the sides of the square bisector of BAC. BC is a tangent to
as diameters. Then area of the shaded
the circle at D. E and F are the points on
region is (in sq. cm).
AC such that DE and BF are parallel. G,
which lies on BF, is the midpoint of AD.
A B
If AH and AI are the tangents to the
circle and AC = 6 cm, then the length of
EC is
A
O
F
D C G E
1
A) 4 B) 16 – 2 B C
2 2 D
C) 8 – 2 D) none of these H I
6. In the below figure, BAC = ADC . If
AB= 15 cm, AD = 20 cm, then CD is
(Similar triangles)
A) 3 cm B) 2 cm
A
C) 2.5 cm D) 2.33 cm
9. ABC is a triangle. O is a point inside
the triangle. The bisectors of
AOB, BOC and AOC intersect the
sides AB, BC and AC at D,E and F
B C D respectively. If the points D and F
divides the sides AB and AC of the
A) 12 cm B) 14 cm
48 ShomeSir Maths Foundation Program
Mathematics Worksheet Booklet Class -IX
triangle in the ratio 2 : 3.
If EC = 10 cm. Then the length of BC is additional reading material
A) 25 cm B) 16.66 cm
C) 20 cm D) 21.33 cm 1. The vertices of a right angled triangle
are on a circle of radius R and the sides
10. In the given figue, PQRS is a of the triangle are tangent to another
parallelogram. If T is the midpoint of
circle of radius r. If the lengths of the
RQ and the line ST when extended
sides about the right angle are 16 and
meets PQ at U. Then the ratio of
30. Then the value of R + r is
lengths of PQ and QU is
A) 33 B) 23
P Q C) 43 D) 13
U
2. Pentagon ABCDE has side CD AB and has
side BC parallel to side EA. Also the
T lengths of sides AB, BC, CD, DE and EA
are 26, 45, 13, 15 and 41 units
respectively. Then the area of pentagon
S R ABCDE is
A) 1 : 1 B) 1 : 2 A) 996 Sq. units B) 1556 Sq. units
C) 1 : 3 D) 1 : 4 C) 1896 Sq. units D) 1056 Sq. units
11. If BC passes through the centre of
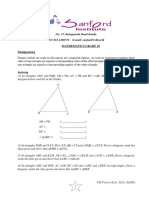
3. Let ABC be equilateral and let D, E,
the circle, t hen the area of the
shaded region in the given figure is F be points on sides BC, CA, AB
respectively with FA = 9, AE = EC =
6, CD = 4. Then DEF is
B
A) 45o B) 60o
a
O C) 90 o
D) 15o
a
4. An equilateral triangle is circumscribed,
A C
and a square is inscribed in a circle of
radius ‘r’. The area of the triangle is T and
the area of the square is S. Then T/S
a2 2
A) 3 B) a 1
2 2 3 3 2
A) B)
a2 2 3 3
C) 2a 2 1 D) 1
2 2 3 3 1
C) D)
5 3 3
12. A circle is inscribed in a triangle whose 5. ABCD is a trapezium with AB and CD
sides are 40, 40 and 48 cm respectively. as par allel si des. The diagonals
A smaller circle is touching two equal intersect at O . The area of t he
sides of the triangle and to the first triangle ABO is p and that of the
circle. Then the radius of smaller circle triangle CDO is q. Then the area of
is the trapezium is
A) 1 B) 2 A) p q B) p q
C) 3 D) 4
2 2
C) p q D) p q
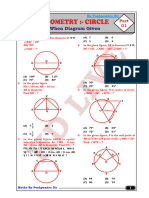
6. In every cyclic quadrilateral ABCD
with AB CD . Then which of the
following is true
ShomeSir Maths FoundationP r o g r a m 4499
C l a s s -I X M a t he m a t i c s W o r k s h e e t B o o k l et
A) AD = BC, AC BD 10. AB is a line 48 cm in length and C is
B) AD BC, AC BD its middle point. On AB, AC, CB
semicircles are described. Then the
C) AD BC, AC = BD
radius of the circle inscribed in the
D) AD = BC, AC = BD
space enclosed by three semicircles.
7. In the triangle ABC, the altitude, angle
A) 7cm B) 8cm
bisector and median from C divide the
angle C into four equal angles. Then C) 9cm D) 6cm
the angles of the triangle are 11. The radius of the incircle of a triangle
A) 67.5o, 22.5o,90o B) 62.5o, 27.5o,90o is 24cm, and the segments into which
C) 60.5 , 29.5 90
o o, o
D)none of these one side is divided by the point of contact
8. If the radius of each circle is 1cm, are 36cm and 48cm. Then the lengths
then the area of the shaded region is of the other two sides of the triangle
are
A) 90cm, 78cm B) 84cm, 64cm
C) 80cm, 20cm D) 24cm, 80cm
12. In a right triangle ABC right-angled at
A B
A, the radius of the inscribed circle is
2cm. Further, the radius of the ex-
circle touching the side BC and also
the sides AB and AC produced is 15cm.
C Then the sides a, b, c of the triangle
are
A) 5, 12, 13 B) 13, 14, 15
C) 3, 4, 5 D) None of these
A) 2 B) 3
3 13. Two circles S1 and S2 with centres O
and O ' lie in the plane such that S2 is
C) 3 D) None of these entirely contained in S1. Let AB be a
2
diameter of S 1 passing through O '
9. ABCD is a circle and circles are drawn meeting S2 in C and D. Further EF is
with AO, CO, DO and OB as diameters. a chord of the circle S1 parallel to AB
E and intersecting the circle S2 in G and
Areas E and F are shaded, then is H. Prove that AB2 + GH2 = EF2 + CD2.
F
equal to 14. In a ABC , the incircle touches the sides
BC, CA and AB respectively at D, E, F
1 respectively. If the radius of the incircle is
A) 1 B)
2 4 units. Also BD, CE and AF are
consecutive integers. Then the sides of
the ABC are
C) D)
2 4
A) 13, 14, 15 B) 16, 15, 14
C) 12, 13, 14 D) None of these
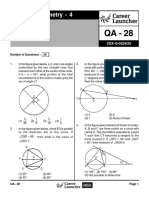
C 15. OPQ is a quadrant of a circle and
semicircles are drawn on OP and OQ.
E F F E
Shaded areas are a and b in the given
G F F G figure. Then the relation between a
A D and b is
G F F G
E F F E
50 ShomeSir Maths Foundation Program
Mathematics Worksheet Booklet Class -IX
Q 47
A) 23 B)
2
b
49
C) 24 D)
2
a
22. Circles with centres A, B and C are
O P exteriorly tangent to one another. The
radius of the circle centred at A is 3
A) a = 2b B) a = b and that of the circle centred at B is
C) a = 3b D) a b 23. If the triangle ABC, cos A = 11/16,
16. ABC is an isosceles triangle. XY is then cos B is
drawn to the base cutting the sides in 16 8
X and Y, show that B, C, X, Y lies on a A) B)
11 7
circle.
17. The chord of the larger of two 7 11
C) D)
concentric circles is tangent to the 8 16
smaller circle and has length a. Then 24. A circle with centre ‘O’ is tangent to
the area of the annulus is the coordinate axes. AB = 1. Then the
radius of circle from the given
a 2
A) a 2 B) diagram.
2
Y
a 2 a 2
C) D)
4 3
18. A point A is taken out side a circle M O
of radius R. Two secants are drawn
C
from this point. One passes through P
the centre, the other at a distance
of R/2 from the centre. Find the
A X
area of the circular region enclosed B L
between the two secants.
19. A and B are two points on a circle A) 3 3 B) 3 2 C )
with centre O and C lies outside the
circle on ray AB. Given that AB = 3 3 32
D)
24cm, BC = 28cm, OA = 15cm. Find 2 2
OC. 25. Given the sides of a triangle (a, b and
20. If AB, AC, PQ are tangents in the figure c). Prove that the median ma drawn
and AB = 5cm, then the perimeter of to the side a can be computed by the
APQ is 1
formula ma = 2b2 + 2c2 - a2 .
A) 10cm B) 15cm 2
C) 20cm D) None of these
21. In the figure AB & CD are diameters
of the circle with centre O, AB CD
and chord DF intersect AB at E. If DE
= 6 & EF = 2, then the area of the circle
is
ShomeSir Maths FoundationP r o g r a m 5511
You might also like
- (Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics) Murray H. Protter, Charles B. Jr. Morrey - Intermediate Calculus (1986, Springer)Document664 pages(Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics) Murray H. Protter, Charles B. Jr. Morrey - Intermediate Calculus (1986, Springer)Eliacim Velez67% (3)
- Answers: LESSON 1.1 - Building Blocks of GeometryDocument35 pagesAnswers: LESSON 1.1 - Building Blocks of GeometryThao Nguyen100% (4)
- Maths QuizDocument4 pagesMaths Quiznaman.bahal09No ratings yet
- Geometry 2 (Triangles) For CATDocument3 pagesGeometry 2 (Triangles) For CATSuvam BoseNo ratings yet
- QAHO1001916Document2 pagesQAHO1001916Saumya SinghNo ratings yet
- QA: BBA + IPM Specific: Geometry & Modern MathsDocument13 pagesQA: BBA + IPM Specific: Geometry & Modern MathsTitiksha JoshiNo ratings yet
- IMPORTANT QA-25 Geometry 1 With Solutions (1) QA-28 Geometry 4 With SolutionsDocument8 pagesIMPORTANT QA-25 Geometry 1 With Solutions (1) QA-28 Geometry 4 With SolutionsgauravNo ratings yet
- 2014 BcexamDocument2 pages2014 BcexamBo WangNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 4-ST&CR (16.04.2020)Document12 pagesAssignment - 4-ST&CR (16.04.2020)KaushikNo ratings yet
- 10 CongruencyDocument2 pages10 CongruencyMohanlal PereraNo ratings yet
- Tangent To A CircleDocument2 pagesTangent To A CircleYashh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Abhay Mahajan: B.Tech. IIT RoorkeeDocument41 pagesAbhay Mahajan: B.Tech. IIT RoorkeeLakshya SehgalNo ratings yet
- QA-28 Geometry-4 Questions PDFDocument4 pagesQA-28 Geometry-4 Questions PDFDhwani BarchhaNo ratings yet
- Best Approach: Iit Jee Mains + AdvancedDocument10 pagesBest Approach: Iit Jee Mains + AdvancedAtulNo ratings yet
- Geometry 2 - TrianglesDocument21 pagesGeometry 2 - TrianglesSaurav BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 06 Solution of Triangle - Sheet-ExtractedDocument7 pages06 Solution of Triangle - Sheet-Extractedudoy1974No ratings yet
- 3 Solutions: B P N QDocument19 pages3 Solutions: B P N QMinh 123No ratings yet
- Vectors - Question PaperDocument4 pagesVectors - Question PaperCelestial GhandatNo ratings yet
- MECExercise 1Document7 pagesMECExercise 1prakharNo ratings yet
- 9 - Class INTSO Work Sheet - 1 - Basic Concepts of GeometryDocument2 pages9 - Class INTSO Work Sheet - 1 - Basic Concepts of GeometrypradyumnnileshtapdiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapters 10 - 11 Circles Theorems - Point & LinesDocument11 pagesChapters 10 - 11 Circles Theorems - Point & LinesXie ChenxinNo ratings yet
- Single Answer Type Vectors & 3D: A, B, C A 3, B 4, C 5Document7 pagesSingle Answer Type Vectors & 3D: A, B, C A 3, B 4, C 5Celestial GhandatNo ratings yet
- The Distance Between The Circumcenter and Any Point in The Plane of The TriangleDocument10 pagesThe Distance Between The Circumcenter and Any Point in The Plane of The Trianglevijay9290009015No ratings yet
- Finding Tangents and Secants Measurement PDFDocument5 pagesFinding Tangents and Secants Measurement PDFJeff AragonNo ratings yet
- Geometry Properties of Triangles QDocument4 pagesGeometry Properties of Triangles Qlalit kumawatNo ratings yet
- NTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Document16 pagesNTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Apex Institute100% (1)
- Assignment Class X Similar Triangles: A D E B CDocument2 pagesAssignment Class X Similar Triangles: A D E B CCRPF School100% (1)
- Circum RevDocument46 pagesCircum RevVroojak KhoshrooNo ratings yet
- Part-A: Single Answer TypeDocument7 pagesPart-A: Single Answer TypeFaiz KhanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry RevisionDocument3 pagesTrigonometry RevisionBindiya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv2 E-1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- SSC CGL Tier - II: Pure Maths Handout: Geometry - IDocument4 pagesSSC CGL Tier - II: Pure Maths Handout: Geometry - IKenny CharlesNo ratings yet
- 2 A Sec A ) C B (2 2 A Sin A ) C B (2 2 A Cos A ) C B (2 2 A Cosec ADocument4 pages2 A Sec A ) C B (2 2 A Sin A ) C B (2 2 A Cos A ) C B (2 2 A Cosec AJonathan ParkerNo ratings yet
- Attempt This Question.: Geometrical Reasoning ADocument5 pagesAttempt This Question.: Geometrical Reasoning AFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- H Shape Space and Measure Revision MatDocument1 pageH Shape Space and Measure Revision MatehmaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Circle (Part-1 To 08) 20230922061125Document16 pagesGeometry Circle (Part-1 To 08) 20230922061125Rishabh KumarNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument2 pagesGeometrySandeep MuniNo ratings yet
- Quadriletral and Area of Parallelogram PDFDocument4 pagesQuadriletral and Area of Parallelogram PDFQSQFNo ratings yet
- Lines Angles and TrianglesDocument7 pagesLines Angles and Trianglesprinkit patelNo ratings yet
- Ace of Pace ADV Question PaperDocument6 pagesAce of Pace ADV Question PaperAyush ShindeNo ratings yet
- Yr10 Yearly 2009Document9 pagesYr10 Yearly 2009Ye ZhangNo ratings yet
- 1819 Mat S3 Ut2 Q&aDocument24 pages1819 Mat S3 Ut2 Q&a陳梓傑CHAN TSZ KITNo ratings yet
- ODocument2 pagesOElaiza Araquel100% (1)
- Algebra 2 PracticeDocument3 pagesAlgebra 2 Practiceaksharap.gudipatiNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument12 pagesGeometryP K SinghNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarterly ExamDocument3 pages2nd Quarterly ExamOdinah Mariano Bantolo100% (1)
- 5 - Radii of CircleDocument4 pages5 - Radii of CircleIndian gardeningNo ratings yet
- Casey's Theorem - Shailesh Shirali - X PDFDocument5 pagesCasey's Theorem - Shailesh Shirali - X PDFAakash GurungNo ratings yet
- Properties of Solution & Triangle-04 - ExerciseDocument23 pagesProperties of Solution & Triangle-04 - ExerciseRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- M11 - Quant Home Work AssignmentDocument12 pagesM11 - Quant Home Work Assignmentparshvaj0312No ratings yet
- Geometry - 3: Number of Questions: 30 CirclesDocument12 pagesGeometry - 3: Number of Questions: 30 CirclespratikNo ratings yet
- TriangleDocument2 pagesTrianglehardikvimal52No ratings yet
- Class-9 - DIGITAL - CLASSROOM - November - KB PDFDocument39 pagesClass-9 - DIGITAL - CLASSROOM - November - KB PDFSubhdra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Geometry 03Document4 pagesGeometry 03AbhishekNo ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv1 E-1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv1 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- Class - 9 - Nstse - PQP - 10 Papers - 2019-20 - 2 in A4 PDFDocument106 pagesClass - 9 - Nstse - PQP - 10 Papers - 2019-20 - 2 in A4 PDFriddhi100% (4)
- Recurring Crux Configurations 5 Cyclic Orthodiagonal 38.2Document3 pagesRecurring Crux Configurations 5 Cyclic Orthodiagonal 38.2ŁØNɆ ⱲØŁꞘNo ratings yet
- Dao's Theorem On Six Circumcenters AssociatedDocument4 pagesDao's Theorem On Six Circumcenters AssociatedNam Vu PhươngNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry and Quadratic Kvpy PYQDocument6 pagesTrigonometry and Quadratic Kvpy PYQTanay AgrawalNo ratings yet
- MBA-IBA Math 10Document8 pagesMBA-IBA Math 10muftibinhabibNo ratings yet
- QA - 50 (Line Triangle) OMETsDocument6 pagesQA - 50 (Line Triangle) OMETsRuchaNo ratings yet
- Coordinates (Answer Sheet)Document7 pagesCoordinates (Answer Sheet)LaureeyNo ratings yet
- 2016-03-31 The Incenter-Excenter Lemma, by Evan Chen PDFDocument4 pages2016-03-31 The Incenter-Excenter Lemma, by Evan Chen PDFAngela Angie BuseskaNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Soal Olimpiade Matematika Dari Seluruh DuniaDocument11 pagesKumpulan Soal Olimpiade Matematika Dari Seluruh DuniaAkalNo ratings yet
- Coordinates: Distance Between Two PointsDocument7 pagesCoordinates: Distance Between Two PointsMuralee VeeramalaiNo ratings yet
- INMOTC 2020 Problem SetDocument7 pagesINMOTC 2020 Problem SetShamim AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Isogonal Conjugates 1Document12 pagesIsogonal Conjugates 1Zadaci AopsNo ratings yet
- 中三 三角形的特殊線和中心 (Special Lines and Centres in a Triangle) - V3 - Final - GDocument61 pages中三 三角形的特殊線和中心 (Special Lines and Centres in a Triangle) - V3 - Final - G丛头越No ratings yet
- Mathematics (71) Geometry - Prelim Ii - Paper - 3 (E) Seat No. 2014 - 1100Document14 pagesMathematics (71) Geometry - Prelim Ii - Paper - 3 (E) Seat No. 2014 - 1100KhushilNo ratings yet
- Advanced GeometryDocument7 pagesAdvanced GeometryGenelle Mae MadrigalNo ratings yet
- CGT 5 G 1aDocument19 pagesCGT 5 G 1aJames BorNo ratings yet
- Geometry-Solutions 3 PDFDocument5 pagesGeometry-Solutions 3 PDFสฮาบูดีน สาและNo ratings yet
- Quadriletral and Area of Parallelogram PDFDocument4 pagesQuadriletral and Area of Parallelogram PDFQSQFNo ratings yet
- Lemmas in Olympiad GeometryDocument9 pagesLemmas in Olympiad GeometryAbdelmalek Boudouh67% (3)
- Coordinategeometry 1Document13 pagesCoordinategeometry 1shahulNo ratings yet
- BASIC DRAWING AIDS FOR CAD Lesson For TodayDocument7 pagesBASIC DRAWING AIDS FOR CAD Lesson For TodayJoel ManioNo ratings yet
- Philippine Mathematical OlympiadDocument11 pagesPhilippine Mathematical OlympiadRosen Dominic Escoto100% (1)
- Mathematics Grade 10 Test I.: Fourth Periodical ExaminationDocument2 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Test I.: Fourth Periodical ExaminationBhela NumbNo ratings yet
- AnswerKeyGrade10mathematics2 46872Document18 pagesAnswerKeyGrade10mathematics2 46872Lahari.u Lahari.uNo ratings yet
- Midline TheoremDocument19 pagesMidline TheoremArlene Polis Delos Reyes100% (4)
- Quantitative Ability 1Document23 pagesQuantitative Ability 1Akhil SinglaNo ratings yet
- TLE-TD-MDL-for-students-WEEK 3Document8 pagesTLE-TD-MDL-for-students-WEEK 3Arjay SerranoNo ratings yet
- IMO Shortlist 2009 OriginalDocument90 pagesIMO Shortlist 2009 OriginalMark Jason CelizNo ratings yet
- MathDocument5 pagesMathLastTheaterNo ratings yet
- Geometry Handout #5 Answers and SolutionsDocument9 pagesGeometry Handout #5 Answers and SolutionsWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Midterms To Finals MATH 6100Document44 pagesMidterms To Finals MATH 6100Sean Chua83% (6)
- Coordinate Geometry (MJ 18 To 2005)Document5 pagesCoordinate Geometry (MJ 18 To 2005)Burhan AzharNo ratings yet
- Basic Proportionality Theorem & Similar TrianglesDocument1 pageBasic Proportionality Theorem & Similar TrianglesdwdadNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Document1 pageFormula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Roberto DiscutidoNo ratings yet