Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Keys Lab Experiment
Answer Keys Lab Experiment
Uploaded by
Markrisha OLAIVARCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Introduction To Immunology 1: Chapter 16 & 17 of Tortora PG 465 - 517Document42 pagesIntroduction To Immunology 1: Chapter 16 & 17 of Tortora PG 465 - 517ATIRAH100% (1)
- Biochem Finals Module 1 FinalsDocument10 pagesBiochem Finals Module 1 FinalsJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Phi Lo 3Document66 pagesPhi Lo 3Johnrico Carl A. FolloscoNo ratings yet
- Formal Biochem Lab Report - Isolation and Hydrolysis of GlutenDocument1 pageFormal Biochem Lab Report - Isolation and Hydrolysis of GlutenIke BravoNo ratings yet
- Margaret NewmanDocument2 pagesMargaret Newmancandy perezNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal Systemstar fireNo ratings yet
- (Ha Lab) Sas#9Document9 pages(Ha Lab) Sas#9Erwin RomeroNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry-No1-Canlas, Louie Andrei G.Document2 pagesBiochemistry-No1-Canlas, Louie Andrei G.Eloisa Canlas - QuizonNo ratings yet
- Dietary ModificationDocument38 pagesDietary ModificationPauline AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument1 pageEthicsNadineNo ratings yet
- Bio 024 - Quiz Cfu Sas 3 (Answer Key)Document4 pagesBio 024 - Quiz Cfu Sas 3 (Answer Key)ELLE WOODSNo ratings yet
- Tabalba 1-Y1-2 Lab Exercise 3Document4 pagesTabalba 1-Y1-2 Lab Exercise 3Shane V. TabalbaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Normative EthicsDocument9 pagesPhilosophy Normative EthicsAngeline LimNo ratings yet
- Turpentine OilDocument1 pageTurpentine OilDDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- Week 9: Course Task-Case Analysis Renal DisordersDocument4 pagesWeek 9: Course Task-Case Analysis Renal DisordersBELTRAN, JEANNE MAURICENo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 8 Isolation of PolysaccharidesDocument3 pagesEXPERIMENT 8 Isolation of PolysaccharidesDarlene Mae GerosagaNo ratings yet
- Funda Finals NotesDocument16 pagesFunda Finals NotesRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Parenterals Guide Question AnswersDocument5 pagesParenterals Guide Question AnswersPatricia Camryne AmbidaNo ratings yet
- Essay - Lesson 2Document1 pageEssay - Lesson 2Nica Rose GrozenNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnit Iii Guide QuestionsIvan Matthew SuperioNo ratings yet
- Essay Mental HealthDocument2 pagesEssay Mental HealthFada Azkadina ZNo ratings yet
- Protein ChemistryDocument11 pagesProtein ChemistryCarmina DinerosNo ratings yet
- Studi Kasus Bioetika Semester Gasal 2015-2016 PDFDocument8 pagesStudi Kasus Bioetika Semester Gasal 2015-2016 PDFShokhikhun NatiqNo ratings yet
- FNCP New EditedDocument13 pagesFNCP New EditedMelissa Joy DollagaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document5 pagesExperiment 8Jancee Harri Leynes MelendresNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Population and Sample?: 1. Principles of SamplingDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Population and Sample?: 1. Principles of SamplingStefanie LucresiaNo ratings yet
- The Six Principles of Movement: BreathDocument8 pagesThe Six Principles of Movement: BreathRey Camillo RamasNo ratings yet
- John Q Movie QuestionsDocument2 pagesJohn Q Movie QuestionsS MannNo ratings yet
- Week 1: 1/1 ComplianceDocument12 pagesWeek 1: 1/1 ComplianceJerald Ginn OrtizNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document7 pagesExperiment 7kimber_gado100% (2)
- Maravilla, Dessa Fe N. BSN 3Y1-2S: Health Problem Health-RelatedDocument4 pagesMaravilla, Dessa Fe N. BSN 3Y1-2S: Health Problem Health-RelatedALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: A Perspective On EntrepreneurshipDocument21 pagesChapter 1: A Perspective On EntrepreneurshipMar MasupilNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Cardiorespiratory Endurance ExercisesDocument8 pagesBenefits of Cardiorespiratory Endurance ExercisesFarhah RahimanNo ratings yet
- Alteration in OxygenationDocument8 pagesAlteration in Oxygenationraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- AllergiesDocument9 pagesAllergiesClark Angelo JuanNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial HistoryDocument3 pagesPsychosocial HistoryMaxinne Allyssa Cancino RoseñoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Laboratory Activity Chemical Tests For The Components of Nucleic AcidDocument4 pagesExperiment 3 - Laboratory Activity Chemical Tests For The Components of Nucleic AcidDelosreyes ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Journal - Bacteria Virtual LabDocument1 pageJournal - Bacteria Virtual Labapi-348935712No ratings yet
- Proteins Experiment 2 Guide QuestionsDocument3 pagesProteins Experiment 2 Guide QuestionsRuchie Ann Pono BaraquilNo ratings yet
- Family Care PlanDocument3 pagesFamily Care PlanAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Session 14: Common Humanity: Our Lady of Fatima University Veritas Et MisericordiaDocument6 pagesSession 14: Common Humanity: Our Lady of Fatima University Veritas Et MisericordiaDarling Rose De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - MergedDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan - MergedJuls Flares SycaycoNo ratings yet
- Ritgen ManueverDocument2 pagesRitgen ManueverGustavo Gonzalez CabreraNo ratings yet
- Datasheet On Factors Affecting BuffersDocument14 pagesDatasheet On Factors Affecting BuffersNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- HTN Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesHTN Lesson Planapi-383984403No ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For Registered NursesDocument7 pagesCode of Ethics For Registered NursespampamaosNo ratings yet
- Disease N Immunity NotesDocument4 pagesDisease N Immunity NotesFrozenYtNo ratings yet
- Ecologic ModelDocument3 pagesEcologic ModelHazel Regencia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Concepts: Overview of The LessonDocument24 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Concepts: Overview of The LessonKASSANDRA THERESE G. DAITOLNo ratings yet
- Biography of NightingaleDocument5 pagesBiography of Nightingalejulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Assessing General Health Status and Vital SignsDocument1 pageAssessing General Health Status and Vital SignsCyril Joy N. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Medically Significant AlgaeDocument4 pagesMedically Significant AlgaeKaren SanrilleNo ratings yet
- Blood and UrineDocument11 pagesBlood and UrineNaraNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis & Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesPathogenesis & Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDini Fajriah OmariNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument10 pagesLipidsladyNo ratings yet
- Moral TheoriesDocument31 pagesMoral TheoriesIon CerneiNo ratings yet
- Askep Thermoregulasi Nanda Nic Noc PDFDocument12 pagesAskep Thermoregulasi Nanda Nic Noc PDFCamelia NuraNo ratings yet
- Pharma OutlineDocument2 pagesPharma OutlineHassen ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 POST LABDocument13 pagesExperiment 2 POST LABJuliano, Jhanielle Faye B.No ratings yet
- Formal Report Expt 5 ColloidsDocument6 pagesFormal Report Expt 5 ColloidsJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Pita Calvo2017Document58 pagesPita Calvo2017Xanh XanhNo ratings yet
- SOLAF 2014 Biologi SPM Modul 3: JPN Perak 1Document7 pagesSOLAF 2014 Biologi SPM Modul 3: JPN Perak 1AZIANA YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Definitions Inorganic Chemistry I AQA Chemistry A LevelDocument3 pagesDefinitions Inorganic Chemistry I AQA Chemistry A LevelZainab JassimNo ratings yet
- Design Note of Lvup CH-115+837Document61 pagesDesign Note of Lvup CH-115+837vishal bhardwaj100% (1)
- Wall Wash Test Procedures On Chemical TankersDocument3 pagesWall Wash Test Procedures On Chemical TankersPavel Viktor100% (1)
- 10194-Article Text-58671-2-10-20220312Document9 pages10194-Article Text-58671-2-10-20220312NoviNo ratings yet
- Characterization and Evaluation of Human Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Tin Mine Tailings in Selected Area of Plateau State, NigeriaDocument8 pagesCharacterization and Evaluation of Human Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Tin Mine Tailings in Selected Area of Plateau State, NigeriaEgah GodwinNo ratings yet
- Dyeing of Nylon With Reactive Dyes. Part 1. The Effect of Changes in Dye Structure On The Dyeing of Nylon With Reactive DyesDocument9 pagesDyeing of Nylon With Reactive Dyes. Part 1. The Effect of Changes in Dye Structure On The Dyeing of Nylon With Reactive DyesArif HidayatNo ratings yet
- M1 Measurement WorksheetDocument8 pagesM1 Measurement WorksheetAira SantosNo ratings yet
- Análisis de Benzoato de Denatonio en Soluciones Alcoholicas Por HPLCDocument6 pagesAnálisis de Benzoato de Denatonio en Soluciones Alcoholicas Por HPLCAugusto PuppoNo ratings yet
- Forces Stabilizing ProteinsDocument8 pagesForces Stabilizing ProteinsRizki fitriaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of CR VI Biosorption by Neem SawdustDocument7 pagesMechanism of CR VI Biosorption by Neem SawdustGiovana GhasaryNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8.2 (Application of Standard Reduction Potential)Document3 pagesExercise 8.2 (Application of Standard Reduction Potential)Luk HKNo ratings yet
- Preboard Examination Gen - Ed. Set C 1Document12 pagesPreboard Examination Gen - Ed. Set C 1Mary Ann PeregrinoNo ratings yet
- 109 (Bul)Document23 pages109 (Bul)khaled redaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: SciencedirectDocument8 pagesJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: Sciencedirectcuc12cptNo ratings yet
- Zinc Poly Carboxylate CementDocument41 pagesZinc Poly Carboxylate CementASHWINI ATHULNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Excel Periodic Table1Document1 pageUltimate Excel Periodic Table1Mark BallardNo ratings yet
- Dehydrogenation CatalystDocument4 pagesDehydrogenation CatalystWoon Xuet WeiNo ratings yet
- Nota Kuliah 3: Kolej Vokasional Batu LanchangDocument9 pagesNota Kuliah 3: Kolej Vokasional Batu LanchangMuhamad Ismail Mohd JamilNo ratings yet
- SKF Cage MaterialsDocument2 pagesSKF Cage MaterialsKamolwan WeerachatsakulNo ratings yet
- Science6 - q1 - Mod1les2 - Differentiating Solute From Solvent - FINAL08032020Document19 pagesScience6 - q1 - Mod1les2 - Differentiating Solute From Solvent - FINAL08032020Michelle IrisNo ratings yet
- AMU B.tech-2023 Paper & SolutionDocument78 pagesAMU B.tech-2023 Paper & Solutiongadsmain2100% (1)
- Released Procedures ReleasedProcedures 2904Document3 pagesReleased Procedures ReleasedProcedures 2904Vũ ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Is 11656 1986 PDFDocument22 pagesIs 11656 1986 PDFSiddharth GuptaNo ratings yet
- LavoisierDocument2 pagesLavoisierBecheikh BadraNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris X SMA IDocument3 pagesBahasa Inggris X SMA IMuhammad HusenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/34Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/34LongNo ratings yet
- Computational Modelling For Lithium Extraction From Sea WaterDocument24 pagesComputational Modelling For Lithium Extraction From Sea WaterShivansh MishraNo ratings yet
- Polymers Polymer (Or Macromolecule)Document10 pagesPolymers Polymer (Or Macromolecule)John Nelson LorenzoNo ratings yet
Answer Keys Lab Experiment
Answer Keys Lab Experiment
Uploaded by
Markrisha OLAIVAROriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer Keys Lab Experiment
Answer Keys Lab Experiment
Uploaded by
Markrisha OLAIVARCopyright:
Available Formats
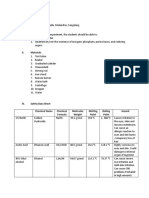
ANSWER KEY EXPT # 2: THE COLLOIDAL STATE
1. Which substance is a Colloid based on the results of the activity? Two dialysis tubes were
submerged in water. A: Ferric Hydroxide B: Potassium Chromate
Explain your answer. Ferric Hydroxide is the one that is colloid. The color of the water where the
substance was submerged remained colorless, it’s just indicates that the particles of Fe(OH) 3 did
not pass through the cellophane .
2. Can the components of a colloid be separated by dialysis process? Yes, the solute of a colloid
remains at the dialyzing membrane, selectively allowing the passage of small –sized particles
only.
3. Can a colloid be separated by the use of a filter paper? No, Fe (OH)3 passed thru the filter paper.
The colloidal particles are smaller than the openings of the filter paper. Colloids can’t be
separated by the use of filter paper.
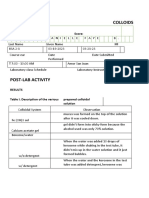
4. What did you observe when water was added with oil then shaken vigorously? The two liquid
substances did not mix together, they are immiscible; oil formed tiny droplets and suspended in
water. It formed a temporary emulsion – it separates.
5. What kind of mixture when the combination of water and oil was added with soap solution? 10
ml H2O + coco oil + soap solution = it formed a permanent emulsion 🡪 homogenous in
appearance ; not clear.
6. What is the role of soap solution in the oil-water mixture? Soap acts as an emulsifying agent.
7. Which electrolyte did not produce precipitates when it was added with As 2S3?
2 ml of As2S3 + .1 N NaCl = no coagulation
8. Which electrolyte produced most precipitates when added with AS 2S3? ml of As2S3 + 0.1 CrCl3 =
1 drop to coagulate – green ppt
9. Explain the difference in the effect of the various electrolytes. One property of Colloids is that
they carry electrical charge. They adsorb ions present in the dispersing medium. Depending on
the colloid, particles attract either (+) or (–) ions, not both.
1. (+) (-) 🡪 precipitation occurs
2. NaCl – is a strong electrolyte – they repel
10. What did you observe when Fe(OH )3 was added with AS2S3? 2 ml As2S3 + Fe (OH)3 =
precipitates formed
11. What happened when the mixture of Fe(OH )3 and AS2S3 was added with the gel? 2 ml As2S3 +
gel + Fe (OH)3 = no precipitates
Explain the function of the gel in the above procedure? Gel coats the other colloid, preventing the
attraction of each. Function of gel is a Protective colloid.
You might also like
- Introduction To Immunology 1: Chapter 16 & 17 of Tortora PG 465 - 517Document42 pagesIntroduction To Immunology 1: Chapter 16 & 17 of Tortora PG 465 - 517ATIRAH100% (1)
- Biochem Finals Module 1 FinalsDocument10 pagesBiochem Finals Module 1 FinalsJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Phi Lo 3Document66 pagesPhi Lo 3Johnrico Carl A. FolloscoNo ratings yet
- Formal Biochem Lab Report - Isolation and Hydrolysis of GlutenDocument1 pageFormal Biochem Lab Report - Isolation and Hydrolysis of GlutenIke BravoNo ratings yet
- Margaret NewmanDocument2 pagesMargaret Newmancandy perezNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal Systemstar fireNo ratings yet
- (Ha Lab) Sas#9Document9 pages(Ha Lab) Sas#9Erwin RomeroNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry-No1-Canlas, Louie Andrei G.Document2 pagesBiochemistry-No1-Canlas, Louie Andrei G.Eloisa Canlas - QuizonNo ratings yet
- Dietary ModificationDocument38 pagesDietary ModificationPauline AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument1 pageEthicsNadineNo ratings yet
- Bio 024 - Quiz Cfu Sas 3 (Answer Key)Document4 pagesBio 024 - Quiz Cfu Sas 3 (Answer Key)ELLE WOODSNo ratings yet
- Tabalba 1-Y1-2 Lab Exercise 3Document4 pagesTabalba 1-Y1-2 Lab Exercise 3Shane V. TabalbaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Normative EthicsDocument9 pagesPhilosophy Normative EthicsAngeline LimNo ratings yet
- Turpentine OilDocument1 pageTurpentine OilDDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- Week 9: Course Task-Case Analysis Renal DisordersDocument4 pagesWeek 9: Course Task-Case Analysis Renal DisordersBELTRAN, JEANNE MAURICENo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 8 Isolation of PolysaccharidesDocument3 pagesEXPERIMENT 8 Isolation of PolysaccharidesDarlene Mae GerosagaNo ratings yet
- Funda Finals NotesDocument16 pagesFunda Finals NotesRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Parenterals Guide Question AnswersDocument5 pagesParenterals Guide Question AnswersPatricia Camryne AmbidaNo ratings yet
- Essay - Lesson 2Document1 pageEssay - Lesson 2Nica Rose GrozenNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnit Iii Guide QuestionsIvan Matthew SuperioNo ratings yet
- Essay Mental HealthDocument2 pagesEssay Mental HealthFada Azkadina ZNo ratings yet
- Protein ChemistryDocument11 pagesProtein ChemistryCarmina DinerosNo ratings yet
- Studi Kasus Bioetika Semester Gasal 2015-2016 PDFDocument8 pagesStudi Kasus Bioetika Semester Gasal 2015-2016 PDFShokhikhun NatiqNo ratings yet
- FNCP New EditedDocument13 pagesFNCP New EditedMelissa Joy DollagaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document5 pagesExperiment 8Jancee Harri Leynes MelendresNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Population and Sample?: 1. Principles of SamplingDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Population and Sample?: 1. Principles of SamplingStefanie LucresiaNo ratings yet
- The Six Principles of Movement: BreathDocument8 pagesThe Six Principles of Movement: BreathRey Camillo RamasNo ratings yet
- John Q Movie QuestionsDocument2 pagesJohn Q Movie QuestionsS MannNo ratings yet
- Week 1: 1/1 ComplianceDocument12 pagesWeek 1: 1/1 ComplianceJerald Ginn OrtizNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document7 pagesExperiment 7kimber_gado100% (2)
- Maravilla, Dessa Fe N. BSN 3Y1-2S: Health Problem Health-RelatedDocument4 pagesMaravilla, Dessa Fe N. BSN 3Y1-2S: Health Problem Health-RelatedALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: A Perspective On EntrepreneurshipDocument21 pagesChapter 1: A Perspective On EntrepreneurshipMar MasupilNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Cardiorespiratory Endurance ExercisesDocument8 pagesBenefits of Cardiorespiratory Endurance ExercisesFarhah RahimanNo ratings yet
- Alteration in OxygenationDocument8 pagesAlteration in Oxygenationraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- AllergiesDocument9 pagesAllergiesClark Angelo JuanNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial HistoryDocument3 pagesPsychosocial HistoryMaxinne Allyssa Cancino RoseñoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Laboratory Activity Chemical Tests For The Components of Nucleic AcidDocument4 pagesExperiment 3 - Laboratory Activity Chemical Tests For The Components of Nucleic AcidDelosreyes ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Journal - Bacteria Virtual LabDocument1 pageJournal - Bacteria Virtual Labapi-348935712No ratings yet
- Proteins Experiment 2 Guide QuestionsDocument3 pagesProteins Experiment 2 Guide QuestionsRuchie Ann Pono BaraquilNo ratings yet
- Family Care PlanDocument3 pagesFamily Care PlanAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Session 14: Common Humanity: Our Lady of Fatima University Veritas Et MisericordiaDocument6 pagesSession 14: Common Humanity: Our Lady of Fatima University Veritas Et MisericordiaDarling Rose De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - MergedDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan - MergedJuls Flares SycaycoNo ratings yet
- Ritgen ManueverDocument2 pagesRitgen ManueverGustavo Gonzalez CabreraNo ratings yet
- Datasheet On Factors Affecting BuffersDocument14 pagesDatasheet On Factors Affecting BuffersNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- HTN Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesHTN Lesson Planapi-383984403No ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For Registered NursesDocument7 pagesCode of Ethics For Registered NursespampamaosNo ratings yet
- Disease N Immunity NotesDocument4 pagesDisease N Immunity NotesFrozenYtNo ratings yet
- Ecologic ModelDocument3 pagesEcologic ModelHazel Regencia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Concepts: Overview of The LessonDocument24 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Concepts: Overview of The LessonKASSANDRA THERESE G. DAITOLNo ratings yet
- Biography of NightingaleDocument5 pagesBiography of Nightingalejulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Assessing General Health Status and Vital SignsDocument1 pageAssessing General Health Status and Vital SignsCyril Joy N. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Medically Significant AlgaeDocument4 pagesMedically Significant AlgaeKaren SanrilleNo ratings yet
- Blood and UrineDocument11 pagesBlood and UrineNaraNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis & Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesPathogenesis & Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDini Fajriah OmariNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument10 pagesLipidsladyNo ratings yet
- Moral TheoriesDocument31 pagesMoral TheoriesIon CerneiNo ratings yet
- Askep Thermoregulasi Nanda Nic Noc PDFDocument12 pagesAskep Thermoregulasi Nanda Nic Noc PDFCamelia NuraNo ratings yet
- Pharma OutlineDocument2 pagesPharma OutlineHassen ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 POST LABDocument13 pagesExperiment 2 POST LABJuliano, Jhanielle Faye B.No ratings yet
- Formal Report Expt 5 ColloidsDocument6 pagesFormal Report Expt 5 ColloidsJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Pita Calvo2017Document58 pagesPita Calvo2017Xanh XanhNo ratings yet
- SOLAF 2014 Biologi SPM Modul 3: JPN Perak 1Document7 pagesSOLAF 2014 Biologi SPM Modul 3: JPN Perak 1AZIANA YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Definitions Inorganic Chemistry I AQA Chemistry A LevelDocument3 pagesDefinitions Inorganic Chemistry I AQA Chemistry A LevelZainab JassimNo ratings yet
- Design Note of Lvup CH-115+837Document61 pagesDesign Note of Lvup CH-115+837vishal bhardwaj100% (1)
- Wall Wash Test Procedures On Chemical TankersDocument3 pagesWall Wash Test Procedures On Chemical TankersPavel Viktor100% (1)
- 10194-Article Text-58671-2-10-20220312Document9 pages10194-Article Text-58671-2-10-20220312NoviNo ratings yet
- Characterization and Evaluation of Human Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Tin Mine Tailings in Selected Area of Plateau State, NigeriaDocument8 pagesCharacterization and Evaluation of Human Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Tin Mine Tailings in Selected Area of Plateau State, NigeriaEgah GodwinNo ratings yet
- Dyeing of Nylon With Reactive Dyes. Part 1. The Effect of Changes in Dye Structure On The Dyeing of Nylon With Reactive DyesDocument9 pagesDyeing of Nylon With Reactive Dyes. Part 1. The Effect of Changes in Dye Structure On The Dyeing of Nylon With Reactive DyesArif HidayatNo ratings yet
- M1 Measurement WorksheetDocument8 pagesM1 Measurement WorksheetAira SantosNo ratings yet
- Análisis de Benzoato de Denatonio en Soluciones Alcoholicas Por HPLCDocument6 pagesAnálisis de Benzoato de Denatonio en Soluciones Alcoholicas Por HPLCAugusto PuppoNo ratings yet
- Forces Stabilizing ProteinsDocument8 pagesForces Stabilizing ProteinsRizki fitriaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of CR VI Biosorption by Neem SawdustDocument7 pagesMechanism of CR VI Biosorption by Neem SawdustGiovana GhasaryNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8.2 (Application of Standard Reduction Potential)Document3 pagesExercise 8.2 (Application of Standard Reduction Potential)Luk HKNo ratings yet
- Preboard Examination Gen - Ed. Set C 1Document12 pagesPreboard Examination Gen - Ed. Set C 1Mary Ann PeregrinoNo ratings yet
- 109 (Bul)Document23 pages109 (Bul)khaled redaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: SciencedirectDocument8 pagesJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: Sciencedirectcuc12cptNo ratings yet
- Zinc Poly Carboxylate CementDocument41 pagesZinc Poly Carboxylate CementASHWINI ATHULNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Excel Periodic Table1Document1 pageUltimate Excel Periodic Table1Mark BallardNo ratings yet
- Dehydrogenation CatalystDocument4 pagesDehydrogenation CatalystWoon Xuet WeiNo ratings yet
- Nota Kuliah 3: Kolej Vokasional Batu LanchangDocument9 pagesNota Kuliah 3: Kolej Vokasional Batu LanchangMuhamad Ismail Mohd JamilNo ratings yet
- SKF Cage MaterialsDocument2 pagesSKF Cage MaterialsKamolwan WeerachatsakulNo ratings yet
- Science6 - q1 - Mod1les2 - Differentiating Solute From Solvent - FINAL08032020Document19 pagesScience6 - q1 - Mod1les2 - Differentiating Solute From Solvent - FINAL08032020Michelle IrisNo ratings yet
- AMU B.tech-2023 Paper & SolutionDocument78 pagesAMU B.tech-2023 Paper & Solutiongadsmain2100% (1)
- Released Procedures ReleasedProcedures 2904Document3 pagesReleased Procedures ReleasedProcedures 2904Vũ ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Is 11656 1986 PDFDocument22 pagesIs 11656 1986 PDFSiddharth GuptaNo ratings yet
- LavoisierDocument2 pagesLavoisierBecheikh BadraNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris X SMA IDocument3 pagesBahasa Inggris X SMA IMuhammad HusenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/34Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/34LongNo ratings yet
- Computational Modelling For Lithium Extraction From Sea WaterDocument24 pagesComputational Modelling For Lithium Extraction From Sea WaterShivansh MishraNo ratings yet
- Polymers Polymer (Or Macromolecule)Document10 pagesPolymers Polymer (Or Macromolecule)John Nelson LorenzoNo ratings yet