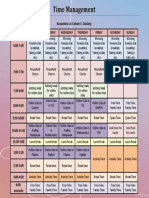
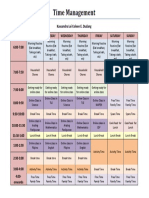
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 1
Lab 1
Uploaded by
Mark MarkCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- EXPERIMENT NO 5 (Hounsfield Tensometer)Document13 pagesEXPERIMENT NO 5 (Hounsfield Tensometer)Hanzlah Naseer50% (2)
- Lesson 3: Velocities in MachinesDocument13 pagesLesson 3: Velocities in MachinesMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Validation AutoclaveDocument638 pagesValidation AutoclaveWormInch100% (5)
- Universal Testing MachineDocument14 pagesUniversal Testing MachineMoreno, Leanne B.No ratings yet
- Familiarization With Parts and Function of Universal and Testing MachineDocument4 pagesFamiliarization With Parts and Function of Universal and Testing MachineNevin SongduanNo ratings yet
- CMT Chapter7 UTMDocument9 pagesCMT Chapter7 UTMAidan Paul Arlanza EscotoNo ratings yet
- Universal Testing MachineDocument28 pagesUniversal Testing MachineMarc Anthony de VillaNo ratings yet
- Study of Universal Testing MachineDocument12 pagesStudy of Universal Testing MachineAfia S HameedNo ratings yet
- Universal Testing MachineDocument17 pagesUniversal Testing MachineCharleston S. OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Components of Universal Testing Machine (UTM)Document4 pagesComponents of Universal Testing Machine (UTM)michael john aquinoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document5 pagesLab Report 221pwind0685No ratings yet
- Engr Jennifer A. Buenconsejo-ValdezDocument10 pagesEngr Jennifer A. Buenconsejo-ValdezMitchell MarvilNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument24 pagesStrength of Materialsmech bhabhaNo ratings yet
- OBJECT: - To Study The Various Component Parts of The Universal TestingDocument8 pagesOBJECT: - To Study The Various Component Parts of The Universal TestingDream CafeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Familiarization of With The Parts and Functions of Universal Testing MachineDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Familiarization of With The Parts and Functions of Universal Testing MachineNoel Bonn FacuribNo ratings yet
- UTMDocument1 pageUTMKARTHIKEYAN K.DNo ratings yet
- What Is Compressive StressDocument7 pagesWhat Is Compressive StressTalal Ahmad khalilNo ratings yet
- Diploma 3 Strength - of - MaterialsDocument26 pagesDiploma 3 Strength - of - MaterialsKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Parts of Universal Testing MachineDocument5 pagesParts of Universal Testing MachineFaisal NaeemNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material LabDocument44 pagesStrength of Material LabDeepak SahNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: THIRD SEMESTER B.Tech MechanicalDocument45 pagesLaboratory Manual: THIRD SEMESTER B.Tech MechanicalhanNo ratings yet
- Sir J C Bose School of Engineering (Diploma: Adv Strength of Materials Lab ManualDocument47 pagesSir J C Bose School of Engineering (Diploma: Adv Strength of Materials Lab ManualdibyenindusNo ratings yet
- Universaltestingmachines PDFDocument27 pagesUniversaltestingmachines PDFarulmuruguNo ratings yet
- Utm ProjectDocument17 pagesUtm ProjectRABINDRA NATH NAYAKNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Universal Testing MachineDocument14 pagesPresentation On: Universal Testing MachineJoseNo ratings yet
- Theory 1Document2 pagesTheory 1Jerome AmbaganNo ratings yet
- Mos Lab ManualDocument71 pagesMos Lab ManualAtul GaurNo ratings yet
- 1.Strength-of-Materials V+Document36 pages1.Strength-of-Materials V+sriramNo ratings yet
- AMT 2 Dipak PhokeDocument20 pagesAMT 2 Dipak PhokeAVINASH BHUSARENo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Layout of LabDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 1: Layout of LabAthar RafiqNo ratings yet
- Tension Test On Steel Rod - Procedure and ResultsDocument6 pagesTension Test On Steel Rod - Procedure and ResultsTapabrata RoyNo ratings yet
- SME1912 Week 3 Linear N ForceDocument56 pagesSME1912 Week 3 Linear N ForceLanceal TanNo ratings yet
- Test of Packaging MaterialDocument16 pagesTest of Packaging MaterialPrashanta Pokhrel100% (1)
- Exp 1 Introduction UTMDocument6 pagesExp 1 Introduction UTMSusmit AloneNo ratings yet
- Micro-Project Report To Study of Compression Testing MachineDocument15 pagesMicro-Project Report To Study of Compression Testing MachineAkash BhorNo ratings yet
- Force Measurement Using PressureDocument4 pagesForce Measurement Using PressurevigneshwarimahamuniNo ratings yet
- LAB LESSON 1 Procedure For Concrete Compression TestDocument23 pagesLAB LESSON 1 Procedure For Concrete Compression TestEarl John LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Material Testing Laboratory EquipmentsDocument23 pagesMaterial Testing Laboratory EquipmentsKiata WayuyabNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Concrete Compression Test PDFDocument23 pagesProcedure For Concrete Compression Test PDFEarl AradoNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 G5Document24 pagesExp 1 G5Abdullah Helmi100% (1)
- Universal Testing MachineDocument5 pagesUniversal Testing MachineLal KrishnaNo ratings yet
- ME136P Lab Report 1Document11 pagesME136P Lab Report 1Jason Dignos0% (1)
- Barkatullah University Institute of Technology: Presentation OnDocument20 pagesBarkatullah University Institute of Technology: Presentation OnSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Tensile Strength TestDocument2 pagesTensile Strength TestJanice VaflorNo ratings yet
- SOM Write Up1Document34 pagesSOM Write Up1KUNKRINo ratings yet
- Utm PDFDocument5 pagesUtm PDFaybi pearlNo ratings yet
- Castro - Universal Testing MachineDocument7 pagesCastro - Universal Testing MachineJulius James DelaCruz LaurestaNo ratings yet
- Mos Lab Manul by Abhidhesh YadavDocument45 pagesMos Lab Manul by Abhidhesh YadavabhiNo ratings yet
- Utm PDFDocument5 pagesUtm PDFFaisal NaeemNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Force Torque and PressureDocument38 pagesMeasurement of Force Torque and PressurePalak NaikNo ratings yet
- Uni-Axial Compression Experiment: PreparationDocument2 pagesUni-Axial Compression Experiment: PreparationYunus100% (1)
- Fatigue TestDocument9 pagesFatigue TestKaneki SSSNo ratings yet
- Measuring InstrumentsDocument40 pagesMeasuring InstrumentsDndjsjwjsjNo ratings yet
- Test MachinesDocument9 pagesTest MachineshanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 CMTDocument4 pagesChapter 6 CMTRizette PaloganNo ratings yet
- MM 1Document6 pagesMM 1Rana Naveed0% (1)
- Asl AZ - Moghavemat 18Document44 pagesAsl AZ - Moghavemat 18eqranavidNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations Lab ManualDocument22 pagesMechanical Vibrations Lab ManualTahir Hasan100% (1)
- Measurement of Force Torque and PressureDocument22 pagesMeasurement of Force Torque and Pressuregenius_1980No ratings yet
- Material Testing Lab EquipmentsDocument61 pagesMaterial Testing Lab EquipmentsEdison BoteNo ratings yet
- Model: UTN: GroupDocument4 pagesModel: UTN: GrouppoongodiskNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Time ManagementDocument1 pageTime ManagementMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Time Management: Kassandra Lei Coleen E. DudangDocument1 pageTime Management: Kassandra Lei Coleen E. DudangMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Kassandra Lei Coleen E. Dudang 7-Zircon EnglishDocument3 pagesKassandra Lei Coleen E. Dudang 7-Zircon EnglishMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Light Emitting DiodeDocument4 pagesLight Emitting DiodeMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 and 4Document10 pagesLesson 3 and 4Mark MarkNo ratings yet
- Philippine Folk DancesDocument24 pagesPhilippine Folk DancesMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2Document22 pagesLesson 1 and 2Mark MarkNo ratings yet
- ManageDocument6 pagesManageMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: (MEES 103)Document4 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies: (MEES 103)Mark MarkNo ratings yet
- The Death of Inflation Roger BootleDocument5 pagesThe Death of Inflation Roger BootleFrederico SoteroNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Considerations Property v. Things: Real or ImmovableDocument8 pagesPreliminary Considerations Property v. Things: Real or ImmovableSZNo ratings yet
- V PCDocument14 pagesV PCGiga Networkers100% (1)
- Paperwise Exemption Syllabus17-1Document2 pagesPaperwise Exemption Syllabus17-1ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Immuno and InfectiousDocument17 pagesImmuno and Infectiousgreen_archerNo ratings yet
- Polaris Outlaw 90 - Sportsman 90 Owners ManualDocument200 pagesPolaris Outlaw 90 - Sportsman 90 Owners Manualrafa_r0No ratings yet
- Marine Corps Museum Store Catalog 2011Document25 pagesMarine Corps Museum Store Catalog 2011Chuck Achberger100% (1)
- FH6000 Alarm ListDocument90 pagesFH6000 Alarm ListAbdul Leon100% (1)
- Project Report On Mergers and AcquisitionsDocument48 pagesProject Report On Mergers and AcquisitionsAvtaar SinghNo ratings yet
- Classification of FolkdanceDocument2 pagesClassification of FolkdanceMica CasimeroNo ratings yet
- Educational Implications of Classical ConditioningDocument2 pagesEducational Implications of Classical Conditioningmekit bekeleNo ratings yet
- r16 Syllabus Cse JntuhDocument58 pagesr16 Syllabus Cse Jntuhramakanth83No ratings yet
- Comparative-Superlative R. Murphy 4th Edt ExercisesDocument6 pagesComparative-Superlative R. Murphy 4th Edt ExercisesSoledad CampañaNo ratings yet
- Activitiesclasswork Unit 2 Lesson 3 Great Civilizations Emerge Maya Religion Ans Social HierarchyDocument25 pagesActivitiesclasswork Unit 2 Lesson 3 Great Civilizations Emerge Maya Religion Ans Social Hierarchyapi-240724606No ratings yet
- A Film Review General Luna and Macario SDocument5 pagesA Film Review General Luna and Macario SjasminjajarefeNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Fundamentals of PartnershipDocument8 pagesAssignment On Fundamentals of Partnershipsainimanish170gmailc100% (1)
- Arts Ccmas Final December 26, 2022Document600 pagesArts Ccmas Final December 26, 2022nimcwatNo ratings yet
- Let Go, Let Go (D) Embracing The New Normal Among The Youth: ProgramDocument2 pagesLet Go, Let Go (D) Embracing The New Normal Among The Youth: Programmary graceNo ratings yet
- Passion in EntrepreneurshipDocument12 pagesPassion in EntrepreneurshipCharisse WooNo ratings yet
- Skills Framework For Design Technical Skills and Competencies (TSC) Reference DocumentDocument2 pagesSkills Framework For Design Technical Skills and Competencies (TSC) Reference DocumentdianNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction-BIO282 LMSDocument19 pagesL1 Introduction-BIO282 LMSGaayithri RNo ratings yet
- Falin-Math of Finance and Investment 3 PDFDocument97 pagesFalin-Math of Finance and Investment 3 PDFAlfred alegadoNo ratings yet
- 「山場」與「岩韻」:武夷茶的風土條件與市場價値結構Document38 pages「山場」與「岩韻」:武夷茶的風土條件與市場價値結構szeon100% (1)
- Mohamed Atef Mohamed Abdelrhman Arab (Report - 2) PDFDocument8 pagesMohamed Atef Mohamed Abdelrhman Arab (Report - 2) PDFdragon for pc gamesNo ratings yet
- Johnrey For Demo DLPDocument8 pagesJohnrey For Demo DLPmelany r. malvarosaNo ratings yet
- HR Recruiter ResumeDocument5 pagesHR Recruiter Resumexjfahwegf100% (1)
- Get Set Go! 5. Workbook (PDFDrive)Document113 pagesGet Set Go! 5. Workbook (PDFDrive)Maureen BravoNo ratings yet
- Matrix PBX Product CatalogueDocument12 pagesMatrix PBX Product CatalogueharshruthiaNo ratings yet
- Action Report - TamilNadu - Shallots, PerambalurDocument6 pagesAction Report - TamilNadu - Shallots, PerambalurKajal YadavNo ratings yet
Lab 1
Lab 1
Uploaded by
Mark MarkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 1
Lab 1
Uploaded by
Mark MarkCopyright:
Available Formats
Universal Testing Machine or UTM also known as Universal Tester, Tensile Tester, Bend tester and
Compression Tester is generally defined as a machine used to test the tensile stress and compressive
strength of materials, the function of this machine is not limited for tensile test and compression test it
is a great multi-purpose instrument; it is also used for bend test, peel test and puncture test.
What is the working Principle of UTMs?
Today's Universal Testing Machines use a rotating ball screw in order to drive a load-bearing crosshead
up and down. An electrical motor powers a series of pulleys and gears which turn the screw, creating
the crosshead motion. The motion of the electrical motor is controlled using pulse width modulation
(PWM) by an astable oscillator circuit. Tensile testers are relatively robust in design and therefore have
a small amount of failure modes. Therefore universal testing machines need relatively little maintenance
and are easy to fix in the event of a break down.
Aside from the machine, a few other components are required to make up the complete system. A load
cell is used to measure the force during the test. A position sensor, most commonly an encoder, is used
to measure the location of the crosshead. Most machines are controlled using the position data channel,
and will move at a software controlled rate of speed according to the desired ASTM test or similar
procedure.
How does a test in a UTC done and work
Tensile Test
Clamp a single piece of anything on each of its ends and pull it apart until it breaks. This measures how
strong it is (tensile strength) how stretchy it is (elongation), and how stiff it is (tensile modulus).
Compression Test
The exact opposite of a tensile test. This is where you compress an object between two level plates until
a certain load or distance has been reached or the product breaks. The typical measurements are the
maximum force sustained before breakage (compressive force), or load at displacement (i.e. 55 pounds
at 1” compression), or displacement at load (i.e. 0.28” of compression at 20 pounds of force).
Bend Test: This is a compression test where you support a length of material by spanning it across two
supports on each end. There is nothing supporting the middle portion underneath of it. Then you press
down from above directly in the middle of the span of material until the supported material breaks or
reaches a specific distance. This test measures how strong the material in flexure (flexural strength) and
how stiff it is (flexural modulus).
Peel Test or Adhesion Test
Similar to a tensile test. However, instead of pulling apart a single piece, you pull apart two materials
that have been bonded together. In this test, you one clamp holds one material and the other clamp
holds the other materials. Then you pull them apart for a few inches. The force is measured up to 1000
times per second during the test and the average of all of the force readings are reported as the
“average peel force”.
Puncture Test
In this test you secure a circular section of material around its perimeter. Then you come down from
above and press the material with a “puncture probe” until the material punctures. The force when the
product breaks is called the “puncture resistance”.
Now that we have a general idea on what does a Universal Testing Machine do, let’s discuss its
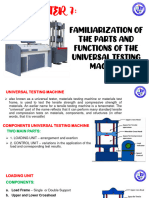
components. Universal Testing Machine consists of two main units, Loading Unit and Control Unit.
Loading Unit consists of:
Load Frame
The load frame of a universal testing machine can be made either by single support or by double
support. The load Frame consists of a table (where the specimen is placed for the compression test),
upper crosshead, and lower crosshead.
Upper Crosshead and Lower Crosshead
The upper crosshead is used to clamp one end of the test specimen. The lower crosshead in the load
frame is the movable crosshead whose screws can be loosened for height adjustment and tightened.
Both the crossheads have a tapered slot at the center. This slot has a pair of racked jaws that is intended
to grip and hold the tensile test specimen.
Elongation Scale
The relative movement of the lower and upper table is measured by an elongation scale which is
provided along with the loading unit.
Control Unit Consist of:
Hydraulic Power Unit
This unit consists of an oil pump that provides non-pulsating oil flow into the main cylinder of the load
unit. This flow helps in the smooth application of load on the specimen. The oil pump in a hydraulic
power unit is run by an electric motor and sump.
Load Measuring Unit
This unit has a pendulum dynamometer unit that has a small cylinder with a piston which moves with
the non-pulsating oil flow. The pendulum is connected to the piston by pivot lever. The pivot lever
deflects based on the load applied to the specimen. This deflection is converted to the load pointer and
displays as the load on the dial.
The range of load application can be adjusted by means of a knob in the load measuring unit (0-100 kN;
0-250 kN; 0-500 kN and 0-1000 kN). The accuracy of measuring unit controls the overall accuracy of the
machine.
Control Devices
The control devices can be electric or hydraulic. Electric control devices make use of switches to move
the crossheads and switch on/off the unit. A hydraulic control device consists of two valves, Right
Control Valve and Left Control Valve or Release Valve. A right control valve is used to apply load on the
specimen. The left control valve is used to release the load application.
You might also like
- EXPERIMENT NO 5 (Hounsfield Tensometer)Document13 pagesEXPERIMENT NO 5 (Hounsfield Tensometer)Hanzlah Naseer50% (2)
- Lesson 3: Velocities in MachinesDocument13 pagesLesson 3: Velocities in MachinesMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Validation AutoclaveDocument638 pagesValidation AutoclaveWormInch100% (5)
- Universal Testing MachineDocument14 pagesUniversal Testing MachineMoreno, Leanne B.No ratings yet
- Familiarization With Parts and Function of Universal and Testing MachineDocument4 pagesFamiliarization With Parts and Function of Universal and Testing MachineNevin SongduanNo ratings yet
- CMT Chapter7 UTMDocument9 pagesCMT Chapter7 UTMAidan Paul Arlanza EscotoNo ratings yet
- Universal Testing MachineDocument28 pagesUniversal Testing MachineMarc Anthony de VillaNo ratings yet
- Study of Universal Testing MachineDocument12 pagesStudy of Universal Testing MachineAfia S HameedNo ratings yet
- Universal Testing MachineDocument17 pagesUniversal Testing MachineCharleston S. OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Components of Universal Testing Machine (UTM)Document4 pagesComponents of Universal Testing Machine (UTM)michael john aquinoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document5 pagesLab Report 221pwind0685No ratings yet
- Engr Jennifer A. Buenconsejo-ValdezDocument10 pagesEngr Jennifer A. Buenconsejo-ValdezMitchell MarvilNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument24 pagesStrength of Materialsmech bhabhaNo ratings yet
- OBJECT: - To Study The Various Component Parts of The Universal TestingDocument8 pagesOBJECT: - To Study The Various Component Parts of The Universal TestingDream CafeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Familiarization of With The Parts and Functions of Universal Testing MachineDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Familiarization of With The Parts and Functions of Universal Testing MachineNoel Bonn FacuribNo ratings yet
- UTMDocument1 pageUTMKARTHIKEYAN K.DNo ratings yet
- What Is Compressive StressDocument7 pagesWhat Is Compressive StressTalal Ahmad khalilNo ratings yet
- Diploma 3 Strength - of - MaterialsDocument26 pagesDiploma 3 Strength - of - MaterialsKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Parts of Universal Testing MachineDocument5 pagesParts of Universal Testing MachineFaisal NaeemNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material LabDocument44 pagesStrength of Material LabDeepak SahNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: THIRD SEMESTER B.Tech MechanicalDocument45 pagesLaboratory Manual: THIRD SEMESTER B.Tech MechanicalhanNo ratings yet
- Sir J C Bose School of Engineering (Diploma: Adv Strength of Materials Lab ManualDocument47 pagesSir J C Bose School of Engineering (Diploma: Adv Strength of Materials Lab ManualdibyenindusNo ratings yet
- Universaltestingmachines PDFDocument27 pagesUniversaltestingmachines PDFarulmuruguNo ratings yet
- Utm ProjectDocument17 pagesUtm ProjectRABINDRA NATH NAYAKNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Universal Testing MachineDocument14 pagesPresentation On: Universal Testing MachineJoseNo ratings yet
- Theory 1Document2 pagesTheory 1Jerome AmbaganNo ratings yet
- Mos Lab ManualDocument71 pagesMos Lab ManualAtul GaurNo ratings yet
- 1.Strength-of-Materials V+Document36 pages1.Strength-of-Materials V+sriramNo ratings yet
- AMT 2 Dipak PhokeDocument20 pagesAMT 2 Dipak PhokeAVINASH BHUSARENo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Layout of LabDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 1: Layout of LabAthar RafiqNo ratings yet
- Tension Test On Steel Rod - Procedure and ResultsDocument6 pagesTension Test On Steel Rod - Procedure and ResultsTapabrata RoyNo ratings yet
- SME1912 Week 3 Linear N ForceDocument56 pagesSME1912 Week 3 Linear N ForceLanceal TanNo ratings yet
- Test of Packaging MaterialDocument16 pagesTest of Packaging MaterialPrashanta Pokhrel100% (1)
- Exp 1 Introduction UTMDocument6 pagesExp 1 Introduction UTMSusmit AloneNo ratings yet
- Micro-Project Report To Study of Compression Testing MachineDocument15 pagesMicro-Project Report To Study of Compression Testing MachineAkash BhorNo ratings yet
- Force Measurement Using PressureDocument4 pagesForce Measurement Using PressurevigneshwarimahamuniNo ratings yet
- LAB LESSON 1 Procedure For Concrete Compression TestDocument23 pagesLAB LESSON 1 Procedure For Concrete Compression TestEarl John LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Material Testing Laboratory EquipmentsDocument23 pagesMaterial Testing Laboratory EquipmentsKiata WayuyabNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Concrete Compression Test PDFDocument23 pagesProcedure For Concrete Compression Test PDFEarl AradoNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 G5Document24 pagesExp 1 G5Abdullah Helmi100% (1)
- Universal Testing MachineDocument5 pagesUniversal Testing MachineLal KrishnaNo ratings yet
- ME136P Lab Report 1Document11 pagesME136P Lab Report 1Jason Dignos0% (1)
- Barkatullah University Institute of Technology: Presentation OnDocument20 pagesBarkatullah University Institute of Technology: Presentation OnSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Tensile Strength TestDocument2 pagesTensile Strength TestJanice VaflorNo ratings yet
- SOM Write Up1Document34 pagesSOM Write Up1KUNKRINo ratings yet
- Utm PDFDocument5 pagesUtm PDFaybi pearlNo ratings yet
- Castro - Universal Testing MachineDocument7 pagesCastro - Universal Testing MachineJulius James DelaCruz LaurestaNo ratings yet
- Mos Lab Manul by Abhidhesh YadavDocument45 pagesMos Lab Manul by Abhidhesh YadavabhiNo ratings yet
- Utm PDFDocument5 pagesUtm PDFFaisal NaeemNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Force Torque and PressureDocument38 pagesMeasurement of Force Torque and PressurePalak NaikNo ratings yet
- Uni-Axial Compression Experiment: PreparationDocument2 pagesUni-Axial Compression Experiment: PreparationYunus100% (1)
- Fatigue TestDocument9 pagesFatigue TestKaneki SSSNo ratings yet
- Measuring InstrumentsDocument40 pagesMeasuring InstrumentsDndjsjwjsjNo ratings yet
- Test MachinesDocument9 pagesTest MachineshanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 CMTDocument4 pagesChapter 6 CMTRizette PaloganNo ratings yet
- MM 1Document6 pagesMM 1Rana Naveed0% (1)
- Asl AZ - Moghavemat 18Document44 pagesAsl AZ - Moghavemat 18eqranavidNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations Lab ManualDocument22 pagesMechanical Vibrations Lab ManualTahir Hasan100% (1)
- Measurement of Force Torque and PressureDocument22 pagesMeasurement of Force Torque and Pressuregenius_1980No ratings yet
- Material Testing Lab EquipmentsDocument61 pagesMaterial Testing Lab EquipmentsEdison BoteNo ratings yet
- Model: UTN: GroupDocument4 pagesModel: UTN: GrouppoongodiskNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Time ManagementDocument1 pageTime ManagementMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Time Management: Kassandra Lei Coleen E. DudangDocument1 pageTime Management: Kassandra Lei Coleen E. DudangMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Kassandra Lei Coleen E. Dudang 7-Zircon EnglishDocument3 pagesKassandra Lei Coleen E. Dudang 7-Zircon EnglishMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Light Emitting DiodeDocument4 pagesLight Emitting DiodeMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 and 4Document10 pagesLesson 3 and 4Mark MarkNo ratings yet
- Philippine Folk DancesDocument24 pagesPhilippine Folk DancesMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2Document22 pagesLesson 1 and 2Mark MarkNo ratings yet
- ManageDocument6 pagesManageMark MarkNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: (MEES 103)Document4 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies: (MEES 103)Mark MarkNo ratings yet
- The Death of Inflation Roger BootleDocument5 pagesThe Death of Inflation Roger BootleFrederico SoteroNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Considerations Property v. Things: Real or ImmovableDocument8 pagesPreliminary Considerations Property v. Things: Real or ImmovableSZNo ratings yet
- V PCDocument14 pagesV PCGiga Networkers100% (1)
- Paperwise Exemption Syllabus17-1Document2 pagesPaperwise Exemption Syllabus17-1ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Immuno and InfectiousDocument17 pagesImmuno and Infectiousgreen_archerNo ratings yet
- Polaris Outlaw 90 - Sportsman 90 Owners ManualDocument200 pagesPolaris Outlaw 90 - Sportsman 90 Owners Manualrafa_r0No ratings yet
- Marine Corps Museum Store Catalog 2011Document25 pagesMarine Corps Museum Store Catalog 2011Chuck Achberger100% (1)
- FH6000 Alarm ListDocument90 pagesFH6000 Alarm ListAbdul Leon100% (1)
- Project Report On Mergers and AcquisitionsDocument48 pagesProject Report On Mergers and AcquisitionsAvtaar SinghNo ratings yet
- Classification of FolkdanceDocument2 pagesClassification of FolkdanceMica CasimeroNo ratings yet
- Educational Implications of Classical ConditioningDocument2 pagesEducational Implications of Classical Conditioningmekit bekeleNo ratings yet
- r16 Syllabus Cse JntuhDocument58 pagesr16 Syllabus Cse Jntuhramakanth83No ratings yet
- Comparative-Superlative R. Murphy 4th Edt ExercisesDocument6 pagesComparative-Superlative R. Murphy 4th Edt ExercisesSoledad CampañaNo ratings yet
- Activitiesclasswork Unit 2 Lesson 3 Great Civilizations Emerge Maya Religion Ans Social HierarchyDocument25 pagesActivitiesclasswork Unit 2 Lesson 3 Great Civilizations Emerge Maya Religion Ans Social Hierarchyapi-240724606No ratings yet
- A Film Review General Luna and Macario SDocument5 pagesA Film Review General Luna and Macario SjasminjajarefeNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Fundamentals of PartnershipDocument8 pagesAssignment On Fundamentals of Partnershipsainimanish170gmailc100% (1)
- Arts Ccmas Final December 26, 2022Document600 pagesArts Ccmas Final December 26, 2022nimcwatNo ratings yet
- Let Go, Let Go (D) Embracing The New Normal Among The Youth: ProgramDocument2 pagesLet Go, Let Go (D) Embracing The New Normal Among The Youth: Programmary graceNo ratings yet
- Passion in EntrepreneurshipDocument12 pagesPassion in EntrepreneurshipCharisse WooNo ratings yet
- Skills Framework For Design Technical Skills and Competencies (TSC) Reference DocumentDocument2 pagesSkills Framework For Design Technical Skills and Competencies (TSC) Reference DocumentdianNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction-BIO282 LMSDocument19 pagesL1 Introduction-BIO282 LMSGaayithri RNo ratings yet
- Falin-Math of Finance and Investment 3 PDFDocument97 pagesFalin-Math of Finance and Investment 3 PDFAlfred alegadoNo ratings yet
- 「山場」與「岩韻」:武夷茶的風土條件與市場價値結構Document38 pages「山場」與「岩韻」:武夷茶的風土條件與市場價値結構szeon100% (1)
- Mohamed Atef Mohamed Abdelrhman Arab (Report - 2) PDFDocument8 pagesMohamed Atef Mohamed Abdelrhman Arab (Report - 2) PDFdragon for pc gamesNo ratings yet
- Johnrey For Demo DLPDocument8 pagesJohnrey For Demo DLPmelany r. malvarosaNo ratings yet
- HR Recruiter ResumeDocument5 pagesHR Recruiter Resumexjfahwegf100% (1)
- Get Set Go! 5. Workbook (PDFDrive)Document113 pagesGet Set Go! 5. Workbook (PDFDrive)Maureen BravoNo ratings yet
- Matrix PBX Product CatalogueDocument12 pagesMatrix PBX Product CatalogueharshruthiaNo ratings yet
- Action Report - TamilNadu - Shallots, PerambalurDocument6 pagesAction Report - TamilNadu - Shallots, PerambalurKajal YadavNo ratings yet