Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basics of Mathematics
Basics of Mathematics
Uploaded by
Abhishek JainCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Iquanta Quant Formulae EbookDocument59 pagesIquanta Quant Formulae Ebookonha100% (1)
- Maths D FormulaDocument21 pagesMaths D FormulaMdMizanurRahman100% (1)
- A When A Best Selling Book Was First Released in PaperbackDocument1 pageA When A Best Selling Book Was First Released in Paperbacktrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Brand RevivalDocument32 pagesBrand Revivalbuffon100% (20)
- FIN 542 - Answer Scheme APR2010Document8 pagesFIN 542 - Answer Scheme APR2010Rafiedah Omar100% (2)
- Quant Kit TcyDocument14 pagesQuant Kit Tcysukritisingh900No ratings yet
- College AlgebraDocument113 pagesCollege Algebraraveenadevi100% (1)
- The Real Number System: 1. Natural Numbers Are The Set of Counting NumbersDocument13 pagesThe Real Number System: 1. Natural Numbers Are The Set of Counting NumbersRheyniel FloresNo ratings yet
- Formulas & Fundas: For CAT, XAT & Other MBA Entrance ExaminationsDocument63 pagesFormulas & Fundas: For CAT, XAT & Other MBA Entrance ExaminationsNithyanandha SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Handa Ka Funda - Math Formulas 5.0 PDFDocument64 pagesHanda Ka Funda - Math Formulas 5.0 PDFAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- PPT1-Basic AlgebraDocument25 pagesPPT1-Basic AlgebraAde Irma RuswandiNo ratings yet
- FTC MATH 1010 Week 1 OverviewDocument93 pagesFTC MATH 1010 Week 1 OverviewLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Review of Mathematical RulesDocument4 pagesReview of Mathematical RulesCindy ArizoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - ComputationDocument34 pagesWeek 1 - ComputationRicardo Sage2 HarrisNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class - X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Document24 pagesICSE Class - X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Apex Institute100% (3)
- IECS273 03 Encapsulation1 PracticeDocument8 pagesIECS273 03 Encapsulation1 Practicetanjuner01No ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 1A PreCalc ConceptsDocument9 pagesModule 1 Unit 1A PreCalc Conceptskorleon gNo ratings yet
- Oundation Mathematics Group TEN Summarize OF Overall SyllabusDocument114 pagesOundation Mathematics Group TEN Summarize OF Overall SyllabusMohamad Arif Nasaruddin100% (1)
- Gened Math Part 1Document77 pagesGened Math Part 1Iancrist IcNo ratings yet
- Complex NumbersDocument30 pagesComplex NumbersOrpheo NgadimanNo ratings yet
- Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational NumbersDocument32 pagesRational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational NumbersAjiteshPadda100% (1)
- Statistics For Managers - Unit1Document51 pagesStatistics For Managers - Unit1kunalbaldwa7No ratings yet
- Accounting For Managers: Module 2: Calculations and Solving EquationsDocument19 pagesAccounting For Managers: Module 2: Calculations and Solving EquationsTrixine BrozasNo ratings yet
- Mathcounts Toolbox: Facts, Formulas and TricksDocument9 pagesMathcounts Toolbox: Facts, Formulas and TricksSridhar NamaNo ratings yet
- Concept-Techniques (2022)Document84 pagesConcept-Techniques (2022)Jay Ann RosaceñaNo ratings yet
- Ebook - IQuanta IPMAT Quant FormulaeDocument51 pagesEbook - IQuanta IPMAT Quant FormulaehyfeheuNo ratings yet
- 1 Real NumbersDocument61 pages1 Real NumbersMonic RomeroNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer MathDocument10 pagesLET Reviewer MathJohn Carlo Telan Panganiban80% (5)
- 4 Let Arithmetic - pdf9Document9 pages4 Let Arithmetic - pdf9novey_casio50% (2)
- Chapter - 1 Rational - NumbersDocument21 pagesChapter - 1 Rational - NumbersAditya GawandeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Apex Formula SheetDocument26 pagesClass 10 Apex Formula Sheetchaitanyaproinstydies123No ratings yet
- MATH - QW3 Algebraic Equations TransformableDocument51 pagesMATH - QW3 Algebraic Equations TransformablePal, Julia HanneNo ratings yet
- Formulas Topic Wise NewDocument29 pagesFormulas Topic Wise Newridwanmd100% (1)
- Afrin Sadia Rumana Lecturer Bangladesh University of ProfessionalsDocument37 pagesAfrin Sadia Rumana Lecturer Bangladesh University of ProfessionalsJHNo ratings yet
- Algebra Lesson 1Document11 pagesAlgebra Lesson 1Angelica CabalseNo ratings yet
- Math 7 LessonsDocument58 pagesMath 7 LessonsTrisha FerrerNo ratings yet
- Slides VB Inz MM 02 Kompl BR - PsDocument142 pagesSlides VB Inz MM 02 Kompl BR - PsVladimir BalticNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers: Lesson P.1 Algebra 5Document35 pagesReal Numbers: Lesson P.1 Algebra 5John MorrisNo ratings yet
- Bairstow Method1Document8 pagesBairstow Method1M.Y M.ANo ratings yet
- M9 Nombor NisbahDocument39 pagesM9 Nombor NisbahAlvinHamNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument14 pagesNumber Systemsapi-185034533No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 26 - 06Document11 pagesLecture 1 26 - 06namrah.khan02No ratings yet
- FOM BasicsDocument40 pagesFOM Basicslol.mishra.121No ratings yet
- Learning Unit 1a:: Numbers & OperationsDocument46 pagesLearning Unit 1a:: Numbers & OperationsCharles BongNo ratings yet
- Module1 AlgebraDocument31 pagesModule1 AlgebraBrent Reyes Palayon0% (1)
- #Pepe Ngesa BMSDocument8 pages#Pepe Ngesa BMSPhelixNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties of NumbersDocument5 pagesBasic Properties of NumberspreetiNo ratings yet
- Number Theory Module 1Document7 pagesNumber Theory Module 1Maria Teresa Ondoy100% (1)
- Sum-Product NumberDocument5 pagesSum-Product NumberBeBoNo ratings yet
- Let A, A, A ,......, A Be A Set of Numbers, Average (A + A + A ,+...... + A) /NDocument8 pagesLet A, A, A ,......, A Be A Set of Numbers, Average (A + A + A ,+...... + A) /NShaira DelmonteNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Complex Numbers PDFDocument17 pagesAn Introduction To Complex Numbers PDFGus EdiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris MatematikaDocument7 pagesTugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris MatematikaMila HarahapNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Business Math and Statistics Sneak PreviewDocument42 pagesStep by Step Business Math and Statistics Sneak PreviewMega RantyNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Document24 pagesICSE Class X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Adiba FatmaNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Real Number PropertiesDocument39 pagesDay 2 Real Number PropertiesGhenadieNo ratings yet
- SSC116: Introduction To Research Methods in Social Sciences: Math PartDocument25 pagesSSC116: Introduction To Research Methods in Social Sciences: Math PartSong XilunNo ratings yet
- Class Notes Solutions-MergedaDocument135 pagesClass Notes Solutions-MergedaSukant PabrejaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative AptituteDocument56 pagesQuantitative AptituteHemang KhatriNo ratings yet
- Master Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1From EverandMaster Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1No ratings yet
- Marketing MIX: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, Physical EvidenceDocument22 pagesMarketing MIX: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, Physical EvidenceDr. CR GopeshNo ratings yet
- Distribution and Channel Management: Berger Paints India Ltd. (BPIL)Document19 pagesDistribution and Channel Management: Berger Paints India Ltd. (BPIL)ANKIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- 1112 Fees and Charges PackageDocument77 pages1112 Fees and Charges PackageErica BarlowNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapters 10 & 11 Transactions and Economic ExposureDocument46 pagesSolutions Chapters 10 & 11 Transactions and Economic Exposurerakhiitsme83% (6)
- Business Analysis Paper Group 3Document19 pagesBusiness Analysis Paper Group 3Raljon YutucNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Enquiry Letter Samples + Final ExerciseDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Enquiry Letter Samples + Final ExerciseTang TeacherNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Microeconomics Australian Edition by Jeffrey Et Al PDFDocument42 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Microeconomics Australian Edition by Jeffrey Et Al PDFbenjamin.myers627100% (43)
- Far660 - July 2020 Set 1 SolutionDocument8 pagesFar660 - July 2020 Set 1 SolutionHanis ZahiraNo ratings yet
- Marketing MixDocument46 pagesMarketing MixJames PootatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 General Equilibrium Theory: A. Interdependence in The EconomyDocument3 pagesChapter 22 General Equilibrium Theory: A. Interdependence in The EconomyishtiaqlodhranNo ratings yet
- Financing For Farmer Producer Organisations PDFDocument18 pagesFinancing For Farmer Producer Organisations PDFRaghuram BhallamudiNo ratings yet
- IIMIndore GeekMythologyDocument7 pagesIIMIndore GeekMythologyArti ModakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document20 pagesChapter 10RosyLeeNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics 2nd Periodic ExamDocument4 pagesApplied Economics 2nd Periodic ExamKrisha FernandezNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal Memorial State University: The Premier University in Zamboanga Del NorteDocument55 pagesJose Rizal Memorial State University: The Premier University in Zamboanga Del NorteCesar Ian AbilaNo ratings yet
- Business Plan of Lesstr3ss CoffeeDocument9 pagesBusiness Plan of Lesstr3ss CoffeeFRANKLYN TRONCONo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Money-9dbc86Document25 pagesThe Psychology of Money-9dbc86Shakti Tandon100% (5)
- Spare Parts Pricing OptimizationDocument11 pagesSpare Parts Pricing OptimizationCognizant100% (2)
- Module 2 - 3rd Edition - 2016-08Document29 pagesModule 2 - 3rd Edition - 2016-08Warsono HadisubrotoNo ratings yet
- Asia's Trade Performance After The Currency Crisis - COREDocument13 pagesAsia's Trade Performance After The Currency Crisis - COREHanrian AnggaNo ratings yet
- PmanagementDocument17 pagesPmanagementAcua RioNo ratings yet
- Zero Cost CollarsDocument3 pagesZero Cost CollarsRishabh ValechaNo ratings yet
- Management Tools FrameworksDocument89 pagesManagement Tools FrameworksSyam Cheruvu50% (2)
- Monitoring Inventory RotablesDocument6 pagesMonitoring Inventory RotablesVebeNo ratings yet
- EpW Contract FarmingDocument8 pagesEpW Contract FarmingtayaltaniNo ratings yet
- Liberty Global NewDocument9 pagesLiberty Global NewNamith SreekumarNo ratings yet
- List of Attempted Questions and AnswersDocument28 pagesList of Attempted Questions and Answersnk20No ratings yet
Basics of Mathematics
Basics of Mathematics
Uploaded by
Abhishek JainOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics of Mathematics
Basics of Mathematics
Uploaded by
Abhishek JainCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics of
Business Mathematics
Introduction:
Mathematics is the soul of any business. Because a business primarily revolves around the
transaction of money or products that have some monetary value. Involvement of money makes
it extremely important to have sufficient knowledge about the basics of calculations. This is where
business mathematics comes into play.
It deals with the fundamental topics that one needs to carry out business related calculations. So,
here we are going to learn about the mathematical tools needed for business calculations
along with their applications.
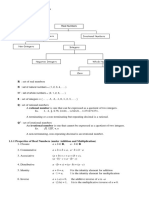
Types of Numbers:
Natural Numbers - Common counting numbers.
Prime Number - A natural number greater than 1 which has only 1 and itself as factors.
Composite Number - A natural number greater than 1 which has more factors than 1 and itself.
Whole Numbers - The set of Natural Numbers with the number 0 adjoined.
Integers - Whole Numbers with their opposites (negative numbers) adjoined.
Rational Numbers - All numbers which can be written as fractions.
Irrational Numbers - All numbers which cannot be written as fractions.
Real Numbers - The set of Rational Numbers with the set of Irrational Numbers adjoined.
Complex Number - A number which can be written in the form a + bi where a and b are real
numbers and i is the square root of -1.
A general example to help you recognize patterns and spot the information you're looking for
A list of types of numbers and examples.
Type of Number Example
Natural Numbers N=1,2,3,4,...N=1,2,3,4,...
Prime Number P=2,3,5,7,11,13,17,…P=2,3,5,7,11,13,17,…
Composite Number 4,6,8,9,10,12,...4,6,8,9,10,12,...
Whole Numbers W=0,1,2,3,4,…W=0,1,2,3,4,…
Integers Z=…,−3,−2,−1,0,1,2,3,…Z=…,−3,−2,−1,0,1,2,3,…
Rational Numbers Q=−12,0.33333…,52,1110,…Q=−12,0.33333…,52,1110,…
Irrational Numbers F=...,π,2–√,0.121221222...F=...,π,2,0.121221222...
Real Numbers R=...,−3,−1,0,15,1.1,2–√,2,3,π,…R=...,−3,−1,0,15,1.1,2,2,3,π,…
Complex Number C=...,−3+2i,0,1+3i,…
Important Algebraic formulas:
• a2 – b2 = (a – b) (a + b)
• (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
• a2 + b2 = (a + b)2 – 2ab
• (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2
• (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
• (a – b – c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 – 2ab + 2bc – 2ca
• (a + b)3 = a3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + b3 ; (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab(a + b)
• (a – b)3 = a3 – 3a2b + 3ab2 – b3 = a3 – b3 – 3ab (a – b)
• a3 – b3 = (a – b) (a2 + ab + b2)
• a3 + b3 = (a + b) (a2 – ab + b2)
• (a + b)4 = a4 + 4a3b + 6a2b2 + 4ab3 + b4
• (a – b)4 = a4 – 4a3b + 6a2b2 – 4ab3 + b4
• a4 – b4 = (a – b) (a + b)(a2 + b2)
• a5 – b5 = (a – b) (a4 + a3b + a2b2 + ab3 + b4)
• If n is a natural number an – bn = (a – b) (an-1 + an-2b+…+ bn-2a + bn-1)
• If n is even (n = 2k), an + bn = (a + b) (an-1 – an-2b +…+ bn-2a – bn-1)
• If n is odd (n = 2k + 1), an + bn = (a + b) (an-1 – an-2b +an-3b2…- bn-2a + bn-1)
• (a + b + c + …)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + … + 2(ab + ac + bc + ….)
• Laws of Exponents (am)(an) = am+n ; (ab)m = ambm ; (am)n = amn
Roots of Quadratic Equation:
o For a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 where a ≠ 0, the roots will be given
by the equation as
o Δ = b2 − 4ac is called the discriminant
o For real and distinct roots, Δ > 0
o For real and coincident roots, Δ = 0
o For non-real roots, Δ < 0
o If α and β are the two roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 then, α + β = (-b /
a) and α × β = (c / a).
o If the roots of a quadratic equation are α and β, the equation will be (x − α)(x −
β) = 0
Baisc Properties of Logarithm:
Time Value of Money Related Concepts:
Basics of Set Theory:
Discounts:
Discounts are reductions in the selling price of an article or the amount of a bill. Discounts
are expressed as rates or percent.
The list price of an article is the original price. The net price is the list price minus the
discount.
To find the amount of a discount, multiply the list price, or base, by the rate of discount.
Formula: P = B x R
Example: A used car listed at $925.00 was sold at a discount of 10%. Find the discount.
B = INR 925, R = 10% P=?
P = B x R; P = INR 925 x .10 = INR 92.50
Commission:
Commission is the amount of money paid to an agent for buying or selling goods. When the
commission is some percent of the value of the services performed, that rate percent is called
the rate of commission.
Gross proceeds or selling price is the money received by the agent for his employer. In
commission calculations this is called the base. Net proceeds is the gross proceeds minus the
commission.
To find the commission, multiply the principle amount, or base, by the rate of commission.
Formula: Commission (P) = Base (B) x R (R),
or... P = B x R
Example: A real estate agent sold a piece of property
for INR 50,000. His commission is 7.5%.
How much does he receive?
P = INR 50,000, B = 7.5% P =?
INR 50,000 x .075 = INR 3,750.00 commission
Profit and Loss Basic Concepts:
Let us learn profit and loss concepts in maths. It is well explained in terms of cost price and
selling price.
Profit(P)
The amount gained by selling a product with more than its cost price.
Loss(L)
The amount the seller incurs after selling the product less than its cost price, is mentioned as a
loss.
Cost Price (CP)
The amount paid for a product or commodity to purchase it is called a cost price. Also,
denoted as CP. This cost price is further classified into two different categories:
Fixed Cost: The fixed cost is constant, it doesn’t vary under any circumstances
Variable Cost: It could vary depending as per the number of units
Selling Price (SP)
The amount for which the product is sold is called Selling Price. It is usually denoted as SP.
Also, sometimes called a sale price.
Marked Price Formula (MP)
This is basically labelled by shopkeepers to offer a discount to the customers in such a way
that,
Discount = Marked Price – Selling Price
And Discount Percentage = (Discount/Marked price) x 100
Profit and Loss Formulas
The profit or gain is equal to the selling price minus cost price.
Loss is equal to cost price minus selling price.
Profit or Gain = Selling price – Cost Price
Loss = Cost Price – Selling Price
The formula for the profit and loss percentage is:
Profit percentage = (Profit /Cost Price) x 100
Loss percentage = (Loss / Cost price) x 100
Videos on some important topics:
S. No. Topic Video Link
1 Logarithms - Basics https://youtu.be/4UNkQcBrLaQ
2 Rules of Logarithms https://youtu.be/bPLyCH1WaEY
3 Matrices https://youtu.be/JMjbPh1Mjn8
4 Linear Equations in Two Variables https://youtu.be/ycLK0nAqGVI
THE END
You might also like
- Iquanta Quant Formulae EbookDocument59 pagesIquanta Quant Formulae Ebookonha100% (1)
- Maths D FormulaDocument21 pagesMaths D FormulaMdMizanurRahman100% (1)
- A When A Best Selling Book Was First Released in PaperbackDocument1 pageA When A Best Selling Book Was First Released in Paperbacktrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Brand RevivalDocument32 pagesBrand Revivalbuffon100% (20)
- FIN 542 - Answer Scheme APR2010Document8 pagesFIN 542 - Answer Scheme APR2010Rafiedah Omar100% (2)
- Quant Kit TcyDocument14 pagesQuant Kit Tcysukritisingh900No ratings yet
- College AlgebraDocument113 pagesCollege Algebraraveenadevi100% (1)
- The Real Number System: 1. Natural Numbers Are The Set of Counting NumbersDocument13 pagesThe Real Number System: 1. Natural Numbers Are The Set of Counting NumbersRheyniel FloresNo ratings yet
- Formulas & Fundas: For CAT, XAT & Other MBA Entrance ExaminationsDocument63 pagesFormulas & Fundas: For CAT, XAT & Other MBA Entrance ExaminationsNithyanandha SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Handa Ka Funda - Math Formulas 5.0 PDFDocument64 pagesHanda Ka Funda - Math Formulas 5.0 PDFAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- PPT1-Basic AlgebraDocument25 pagesPPT1-Basic AlgebraAde Irma RuswandiNo ratings yet
- FTC MATH 1010 Week 1 OverviewDocument93 pagesFTC MATH 1010 Week 1 OverviewLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Review of Mathematical RulesDocument4 pagesReview of Mathematical RulesCindy ArizoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - ComputationDocument34 pagesWeek 1 - ComputationRicardo Sage2 HarrisNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class - X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Document24 pagesICSE Class - X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Apex Institute100% (3)
- IECS273 03 Encapsulation1 PracticeDocument8 pagesIECS273 03 Encapsulation1 Practicetanjuner01No ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 1A PreCalc ConceptsDocument9 pagesModule 1 Unit 1A PreCalc Conceptskorleon gNo ratings yet
- Oundation Mathematics Group TEN Summarize OF Overall SyllabusDocument114 pagesOundation Mathematics Group TEN Summarize OF Overall SyllabusMohamad Arif Nasaruddin100% (1)
- Gened Math Part 1Document77 pagesGened Math Part 1Iancrist IcNo ratings yet
- Complex NumbersDocument30 pagesComplex NumbersOrpheo NgadimanNo ratings yet
- Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational NumbersDocument32 pagesRational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational Numbers Rational NumbersAjiteshPadda100% (1)
- Statistics For Managers - Unit1Document51 pagesStatistics For Managers - Unit1kunalbaldwa7No ratings yet
- Accounting For Managers: Module 2: Calculations and Solving EquationsDocument19 pagesAccounting For Managers: Module 2: Calculations and Solving EquationsTrixine BrozasNo ratings yet
- Mathcounts Toolbox: Facts, Formulas and TricksDocument9 pagesMathcounts Toolbox: Facts, Formulas and TricksSridhar NamaNo ratings yet
- Concept-Techniques (2022)Document84 pagesConcept-Techniques (2022)Jay Ann RosaceñaNo ratings yet
- Ebook - IQuanta IPMAT Quant FormulaeDocument51 pagesEbook - IQuanta IPMAT Quant FormulaehyfeheuNo ratings yet
- 1 Real NumbersDocument61 pages1 Real NumbersMonic RomeroNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer MathDocument10 pagesLET Reviewer MathJohn Carlo Telan Panganiban80% (5)
- 4 Let Arithmetic - pdf9Document9 pages4 Let Arithmetic - pdf9novey_casio50% (2)
- Chapter - 1 Rational - NumbersDocument21 pagesChapter - 1 Rational - NumbersAditya GawandeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Apex Formula SheetDocument26 pagesClass 10 Apex Formula Sheetchaitanyaproinstydies123No ratings yet
- MATH - QW3 Algebraic Equations TransformableDocument51 pagesMATH - QW3 Algebraic Equations TransformablePal, Julia HanneNo ratings yet
- Formulas Topic Wise NewDocument29 pagesFormulas Topic Wise Newridwanmd100% (1)
- Afrin Sadia Rumana Lecturer Bangladesh University of ProfessionalsDocument37 pagesAfrin Sadia Rumana Lecturer Bangladesh University of ProfessionalsJHNo ratings yet
- Algebra Lesson 1Document11 pagesAlgebra Lesson 1Angelica CabalseNo ratings yet
- Math 7 LessonsDocument58 pagesMath 7 LessonsTrisha FerrerNo ratings yet
- Slides VB Inz MM 02 Kompl BR - PsDocument142 pagesSlides VB Inz MM 02 Kompl BR - PsVladimir BalticNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers: Lesson P.1 Algebra 5Document35 pagesReal Numbers: Lesson P.1 Algebra 5John MorrisNo ratings yet
- Bairstow Method1Document8 pagesBairstow Method1M.Y M.ANo ratings yet
- M9 Nombor NisbahDocument39 pagesM9 Nombor NisbahAlvinHamNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument14 pagesNumber Systemsapi-185034533No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 26 - 06Document11 pagesLecture 1 26 - 06namrah.khan02No ratings yet
- FOM BasicsDocument40 pagesFOM Basicslol.mishra.121No ratings yet
- Learning Unit 1a:: Numbers & OperationsDocument46 pagesLearning Unit 1a:: Numbers & OperationsCharles BongNo ratings yet
- Module1 AlgebraDocument31 pagesModule1 AlgebraBrent Reyes Palayon0% (1)
- #Pepe Ngesa BMSDocument8 pages#Pepe Ngesa BMSPhelixNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties of NumbersDocument5 pagesBasic Properties of NumberspreetiNo ratings yet
- Number Theory Module 1Document7 pagesNumber Theory Module 1Maria Teresa Ondoy100% (1)
- Sum-Product NumberDocument5 pagesSum-Product NumberBeBoNo ratings yet
- Let A, A, A ,......, A Be A Set of Numbers, Average (A + A + A ,+...... + A) /NDocument8 pagesLet A, A, A ,......, A Be A Set of Numbers, Average (A + A + A ,+...... + A) /NShaira DelmonteNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Complex Numbers PDFDocument17 pagesAn Introduction To Complex Numbers PDFGus EdiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris MatematikaDocument7 pagesTugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris MatematikaMila HarahapNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Business Math and Statistics Sneak PreviewDocument42 pagesStep by Step Business Math and Statistics Sneak PreviewMega RantyNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Document24 pagesICSE Class X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Adiba FatmaNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Real Number PropertiesDocument39 pagesDay 2 Real Number PropertiesGhenadieNo ratings yet
- SSC116: Introduction To Research Methods in Social Sciences: Math PartDocument25 pagesSSC116: Introduction To Research Methods in Social Sciences: Math PartSong XilunNo ratings yet
- Class Notes Solutions-MergedaDocument135 pagesClass Notes Solutions-MergedaSukant PabrejaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative AptituteDocument56 pagesQuantitative AptituteHemang KhatriNo ratings yet
- Master Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1From EverandMaster Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1No ratings yet
- Marketing MIX: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, Physical EvidenceDocument22 pagesMarketing MIX: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, Physical EvidenceDr. CR GopeshNo ratings yet
- Distribution and Channel Management: Berger Paints India Ltd. (BPIL)Document19 pagesDistribution and Channel Management: Berger Paints India Ltd. (BPIL)ANKIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- 1112 Fees and Charges PackageDocument77 pages1112 Fees and Charges PackageErica BarlowNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapters 10 & 11 Transactions and Economic ExposureDocument46 pagesSolutions Chapters 10 & 11 Transactions and Economic Exposurerakhiitsme83% (6)
- Business Analysis Paper Group 3Document19 pagesBusiness Analysis Paper Group 3Raljon YutucNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Enquiry Letter Samples + Final ExerciseDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Enquiry Letter Samples + Final ExerciseTang TeacherNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Microeconomics Australian Edition by Jeffrey Et Al PDFDocument42 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Microeconomics Australian Edition by Jeffrey Et Al PDFbenjamin.myers627100% (43)
- Far660 - July 2020 Set 1 SolutionDocument8 pagesFar660 - July 2020 Set 1 SolutionHanis ZahiraNo ratings yet
- Marketing MixDocument46 pagesMarketing MixJames PootatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 General Equilibrium Theory: A. Interdependence in The EconomyDocument3 pagesChapter 22 General Equilibrium Theory: A. Interdependence in The EconomyishtiaqlodhranNo ratings yet
- Financing For Farmer Producer Organisations PDFDocument18 pagesFinancing For Farmer Producer Organisations PDFRaghuram BhallamudiNo ratings yet
- IIMIndore GeekMythologyDocument7 pagesIIMIndore GeekMythologyArti ModakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document20 pagesChapter 10RosyLeeNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics 2nd Periodic ExamDocument4 pagesApplied Economics 2nd Periodic ExamKrisha FernandezNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal Memorial State University: The Premier University in Zamboanga Del NorteDocument55 pagesJose Rizal Memorial State University: The Premier University in Zamboanga Del NorteCesar Ian AbilaNo ratings yet
- Business Plan of Lesstr3ss CoffeeDocument9 pagesBusiness Plan of Lesstr3ss CoffeeFRANKLYN TRONCONo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Money-9dbc86Document25 pagesThe Psychology of Money-9dbc86Shakti Tandon100% (5)
- Spare Parts Pricing OptimizationDocument11 pagesSpare Parts Pricing OptimizationCognizant100% (2)
- Module 2 - 3rd Edition - 2016-08Document29 pagesModule 2 - 3rd Edition - 2016-08Warsono HadisubrotoNo ratings yet
- Asia's Trade Performance After The Currency Crisis - COREDocument13 pagesAsia's Trade Performance After The Currency Crisis - COREHanrian AnggaNo ratings yet
- PmanagementDocument17 pagesPmanagementAcua RioNo ratings yet
- Zero Cost CollarsDocument3 pagesZero Cost CollarsRishabh ValechaNo ratings yet
- Management Tools FrameworksDocument89 pagesManagement Tools FrameworksSyam Cheruvu50% (2)
- Monitoring Inventory RotablesDocument6 pagesMonitoring Inventory RotablesVebeNo ratings yet
- EpW Contract FarmingDocument8 pagesEpW Contract FarmingtayaltaniNo ratings yet
- Liberty Global NewDocument9 pagesLiberty Global NewNamith SreekumarNo ratings yet
- List of Attempted Questions and AnswersDocument28 pagesList of Attempted Questions and Answersnk20No ratings yet