Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(M4) The Sexual Self
(M4) The Sexual Self
Uploaded by
MA. LUISA ANNE SORIANO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pagesThis document discusses various topics related to sexuality, gender, and sexual orientation. It defines key terms, outlines stages of adolescent development, and summarizes research by psychologist Margie Holmes distinguishing sex, gender, and sexual orientation. The document provides definitions for lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, intersex, and queer individuals. It also examines aspects of sexual self-concept, gender identity, roles and expectations.
Original Description:
The Sexual Self
Original Title
[M4] The Sexual Self
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various topics related to sexuality, gender, and sexual orientation. It defines key terms, outlines stages of adolescent development, and summarizes research by psychologist Margie Holmes distinguishing sex, gender, and sexual orientation. The document provides definitions for lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, intersex, and queer individuals. It also examines aspects of sexual self-concept, gender identity, roles and expectations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pages(M4) The Sexual Self
(M4) The Sexual Self
Uploaded by
MA. LUISA ANNE SORIANOThis document discusses various topics related to sexuality, gender, and sexual orientation. It defines key terms, outlines stages of adolescent development, and summarizes research by psychologist Margie Holmes distinguishing sex, gender, and sexual orientation. The document provides definitions for lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, intersex, and queer individuals. It also examines aspects of sexual self-concept, gender identity, roles and expectations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
[UTS] THE SEXUAL SELF
OUTLINE Growth and Development are the continues process
I SEXUAL SELF CONCEPT
II SEX AND SEXUALITY IN ADOLESCENT
which acquire a change on individual every moment.
A Development of Sexuality
III SEX, GENDER, AND SEXUAL ORIENTATION DEVELOPMENT OF SEXUALITY
A Margarita Go-Singco Holmes Development of Sexuality begins as early as in
B Gender Expectation intrauterine life following conception and continues
C Gender Identity through Infancy, Childhood, Adolescence, Adulthood
i Common Gender Definitions
and till death.
D Gender Roles
E Gender Expressions o Infancy is defined as the first year of life after
IV ASPECTS OF SEXUALITY birth.
V SEXUAL SELF CONCEPT o Childhood it generally refers to children
A Aspects of Sexual Concept between the ages of 1 to 3 years of age.
i Sexual Self Esteem o Adolescence is the period of life between the
· Sub Factors of Sexual Self Esteem
beginning of puberty and adulthood.
ii Sexual Anxiety
iii Sexual Exploration o Adulthood proposes as a new life stage
iv Erotic Self Exploration between adolescence and young adulthood
v Sexual Self Efficacy lasting roughly from ages 18 to 25.
VI SEX AND RELATIONSHIPS According to US National Library of Medicine (2015),
A Emerging Sex Trend Adolescence can be broadly divided into three
i Partner Swapping stages:
ii Orgies
B The Online Space
o Early Stage
i Pornography o Middle Stage
ii Cyber Sex o Last Stage
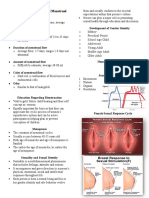
C Education, Guidance and Support
VII SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES SEX, GENDER, AND SEXUAL ORIENTATION
A Common Types of STD
i Chlamydia MARGARITA GO-SINGCO HOLMES
ii Gonorrhea Popularly known as Dr. Margie Holmes is a popular
iii Trichomoniasis Psychologist specializing in Sex Therapy in the
iv Genital Warts Philippines
v Genital Herpes In 2015, Dr. Margie Holmes gave primer on:
vi Pubic Lice o Lesbian is a female homosexual; a female
vii Scabies
viii Syphilis who experiences romantic love or sexual
B Signs and Symptoms attraction to other females.
VIII UNDERSTANDING AND SUPPORTING SEXUALITY o Gay of, relating to, or characterized by sexual
or romantic attraction to people of one’s same
THE SEXUAL SELF sex.
Characterized as a person’s evaluation of his or her Often used to refer to men only.
own sexual feelings and actions. o Bisexual sexually attracted not exclusively to
Refers to the totality of oneself as a sexual being, people of one particular gender, attracted to
including positive and negative concepts and feelings. both men and women.
Sexual self-concept defined as an individual's o Transgender people whose gender identity is
evaluation of his or her own sexual feelings and different from the gender they were thought to
actions be at birth.
o Proposed as an important predictor of o Intersex a person born with reproductive or
contraceptive behavior among teenagers. sexual anatomy that doesn’t fit the boxes of
o Associated with frequency of contraceptive use “female” or “male”
and use at most recent intercourse. o Queer attraction to people of many genders
and don’t conform to cultural norms around
SEX AND SEXUALITY IN ADOLESCENT gender and/or sexuality.
Sex is a primary category of Human Social In 2015, Margie Holmes, a psychologist gave
Perception. informative writing on LQBTQ issues and definition.
o At birth, each individual is classified by She differentiated Sex and Gender
biological sex. o Sex: all about biological chromosomes, gonads
Biological Sex is an identification of the individual if it and hormones (pure science).
is a girl or a boy. o Gender is psychological and cultural. (How a
Judging a person as a male or female has been person views himself/ herself outside her
described as an automatic social cognitive process science anatomy) studies include; gender
that is effortless, unintended, and involuntary. identity, gender roles, gender stereotypes.
Sex can be also defined using:
o Chromosomes GENDER EXPECTATION
o Gonads Gender Expectation: Male falls to Female vice versa
but here there are a lot of lot of Sexual Orientation
o Gonadal Hormones
Forms these area follows:
o Internal Accessory Organs
o Heterosexual is an attraction and behavior
o External Genitalia
towards opposite sex.
Individuals with mixed sexual configurations using o Homosexual is attraction to the same sex
these different biological criteria are known as
intersexed or intersexual.
o Bisexual is an attraction to both male and Masculine present as a man
female. Feminine present in feminine way
o Asexual is a person who do not have Androgynous mixed of both masculine
attraction towards any sex or gender. and feminine
o Pansexual have the ability to attract to anyone [DR. MARGIE HOLMES STUDY] Showed that
regardless of sex Transphobia-Antagonism (dislike of or prejudice
o Intersexed are those who falls outside the against trans) towards transsexual and transgender is
male and female dichotomy. worse than homophobia (dislike or prejudice against
gay people).
GENDER IDENTITY
Gender Identity refers to intimate knowledge and ASPECTS OF SEXUALITY
experience of the individual’s own gender. Sexual Pleasure: emotional satisfaction that arises
o It is perceived as subjective and based on self- from the movement of those organs.
identification. Sexual Satisfaction: feeling fulfilled and satisfied
o It is a personal conception of oneself as with one’s sexual life.
male or female a blend both, or neither how Sexual Desire: motivational state that generates
individuals perceive themselves and what they increased attention to sexual stimuli.
call themselves. Sexual Agency: the ability to act in a way that
o Can be different from sex assigned birth, which accomplishes your goals.
is often confuse it was often assumed that it is o In sexuality, when we say “sexual agency”, it
match on one’s biological sex. is composed of complex group of skills, rights
o But it proved that one’s biological sex may and abilities:
not always match on one’s gender (Golden o According to Madsen (2014), sexual agency
2009) includes the following:
In gender-binary / heteronormative paradigm (only The ability to define yourself sexually
male and female are the only acceptable genders). The ability to choose whether or not you
Transgender and Transsexual are excluded to this. want to experience sexual activity
Human experience shows proof that one’s biological The ability to choose how you want to
sex may not always mate one’s psychological gender engage in sexual activity.
o Kevin Balot
o BB Gandang Hari SEXUAL SELF CONCEPT
o Jake Zyrus It is also known as sexual self-view
o Aiza Seguerra Sexual self-concept is a multidimensional construct
o Geraldine Roman that refers to an individual’s positive and negative
perceptions and feelings about him or herself as a
COMMON GENDER DEFINITIONS sexual being.
Trans-people are persons identifies with the opposite A good indicator of what kind of relationship with tend
gender – those who identify themselves opposite to to get into, and how we tend to behave within
their sexual assigned birth and eventually to their relationships, with an emphasis on sexual
gender. satisfaction.
o BB Gandang Hari / Rustom Padilla legal
identity has changed his gender from male to ASPECTS OF SEXUAL CONCEPT
female. (Under the rule of court of Los SEXUAL SELF ESTEEM
Angeles) A feeling of self-worth and sexual situation.
Transexual are people who has opposite gender to Tends to positively evaluates one’s own capacity
their biological sex. SUB FACTORS OF SEXUAL SELF ESTEEM
o Gender Reassignment o Sexual Behavior
Transgender covers a range of identities or Express their sexual self through their
behaviors. Often used to describe non-traditional intimate relationships.
gender behaviors or identities. How people from romantic relationships
o Kevin Balot, first transgender who won and meet their needs of attachment.
crowned as the Miss International Queen 2012 o Sexual Conduct
held in Pattaya Thailand.
Is a feeling of adequacy of behavior in
o Jake Zyrus, (born Charmaine Clarice Relucio
sexual situations and with partners
Pempengco; May 10, 1992), who performed
It is a set of characteristics that are
under the mononym Charice until his gender
ascribed to how normal and how real
transition to male as Filipino singer who rose to
men and women should act.
popularity through Youtube.
o Sexual Attractiveness
Intersex refers to a range of conditions where a
Feelings of sexual appearance and
person’s sex is not strictly male or female
desirability.
(biologically).
o This may due to underdeveloped primary sex SEXUAL ANXIETY
characteristics. The feelings of tension discomfort and anxiety
about the sexual aspects of one’s life.
GENDER ROLES Sexuality is seen as shameful for women who are
Gender Roles refers to societal roles relating to not married and or not committed.
perceived sex. Married and committed are expected to yell their
Gender Expressions is how gender is expressed; partner sexual desire.
Outward presentation.
o How she or he dress, wears make up etch.
o It may not match to someone’s gender identity SEXUAL EXPLORATION
Includes initiation of adolescence and increases as It can be presented in a variety of media which
part of the normative development of adolescence includes books, magazines, photographs, sculpture,
and sexual identity. drawing, painting, animation, sound recording, writing,
o Knowing your sexual self is knowing your own film, video, and video games.
pleasure and satisfaction. Primary Subjects of Present-Day Pornographic
According to study, the best way to know your own Depictions
pleasure when exploring it alone is by means of o People who pose for still photographs.
erotic thoughts. o Pornographic Actors, or Porn Stars.
o Fantasizing and thinking of something that may CYBER SEX
help you feel arouse the feeling of sexual Also called Computer Sex, Internet Sex, Net Sex,
pleasure and or desire. and in colloquial terms: Cyber, or Cybering.
EROTIC SELF EXPLORATION An encounter in which two or more people connect
First step to realize a healthy sex life by means of remotely via either sent messages describing
erotic self-exploration. sexual experiences, videos involving nudity and such
o In order for you to give sexual pleasure that whose goal is to provide sexual pleasure through
together with your partner, you must know your the internet.
own sexual pleasure. Can occur within the context of existing or
Erotic self-exploration is believed to be part of intimate relationships: among lovers who are
sexual self-exploration in which you are fantasizing or geographically separated, or in a long-distance
thinking something that may help you obtain your relationship, or; among complete strangers.
sexual desire.
Exploring your body and or partner's body to gain and EDUCATION, GUIDANCE AND SUPPORT
give pleasure. Developing a sexual self-concept is an important
o Example of erotic self-exploration is the so- developmental task of adolescence.
called touching exercise, it persists o However, little empirical evidence describes
throughout the sex life, with each successive this development, nor how these changes are
exercise reveals more of the priceless self- related in development in sexual behavior.
knowledge that is critical for building healthy, Over a four-year time, frame, with the use of
lasting, inter and intra-personal sexual relation. longitudinal group data from adolescent women,
Erotic self-exploration helps to learn to integrate the researchers examined a reciprocal development in
mental and physical components of sex. sexual self-concept, among which include the
SEXUAL SELF EFFICACY following: sexual openness, sexual esteem, and
One of the most important issue in terms of sexual sexual anxiety.
health. o It has been found that there are notable
It refers to your ability to effectively perform the transactional effects between these
task. dimensions, and behavior: sexual self-concept
The belief in one’s capabilities in the aptitude to involved during adolescence in a manner
overcome challenges, adversities, and obstacles consistent with a less reserve, less anxiety,
in one’s life. develops a greater personal comfort with
o It is a predictor of health behavior and as the sexuality and sexual behavior.
most important part of individual behavioral Furthermore, it has been concluded that sexual self-
change: concept results from sexual behavior, and at the
same time, it regulates the future behavior.
She is able to see herself as a person
who can make decisions about what
happens to her sexually. SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
He knows how to say yes and no to COMMON TYPES OF STD
sexual behavior and relationships. CHLAMYDIA
He knows how to ask for consent from a The Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), the
partner before engaging in sexual virus that causes Acquired Immune Deficiency
behavior and how to demand that others Syndrome (AIDS), is transmitted by blood and body
ask for consent. fluids.
SEX AND RELATIONSHIPS GONORRHOEA
EMERGING SEX TREND Gonorrhea is one of the most common STDs in the
PARTNER SWAPPING United States and can lead to infertility in men and
Sometimes called wife-swapping or partner, is a women.
non-monogamous behavior, in which both singles It is both treatable and preventable, though
and partners in a committed relationship engage in scientists have discovered a new strain of gonorrhea
sexual activities with others, may it be for recreational, that is resistant to all currently utilized antibiotics.
or social purposes. TRICHOMONIASIS
ORGIES Trichomoniasis is the most common curable STI.
Type of parties where people engage in Millions of people are infected each year in the United
unrestrained intimacies with each other. States
Can happen between strangers, or together with GENITAL WARTS
known people. HPV is the most common STD and at least 50% of
sexually active people will get it at some time in their
THE ONLINE SPACE lives.
PORNOGRAPHY The body usually clears HPV on its own without
Otherwise known as porn, it is the portrayal of causing any problems, but HPV can lead to certain
sexual object matter for the purpose of sexual kinds of cancer.
arousal. GENITAL HERPES
Herpes is a common STD and a lot of people who o It may be helpful to reiterate young people that
have it don’t even know. no one else can dictate their gender and
There is no cure for herpes, but there is treatment sexuality, and that they have the right to make
that can lessen symptoms and decrease the their own choices regarding their gender and
likelihood of passing it on to someone else. sexuality
PUBIC LICE
Pubic or “crab” lice are parasitic insects that survive
by feeding on human blood.
Pubic lice are different parasites than head or body
lice and are usually found in the pubic hair, but can
also be found in other course body hair like eyebrows,
beard, chest or armpit hair.
SCABIES
Scabies are parasites that infect the skin and cause
really intense itching.
Scabies is transferred by skin-to-skin contact and can
occur anywhere on the body.
o This means that while scabies can be passed
through sexual contact, it is usually passed
through non-sexual skin-to-skin contact.
SYPHILIS
Syphilis is spread by contact with open sores
(usually during sex).
o If left untreated, it can cause serious health
problems, including brain and nervous system
damage, blood infection and even death.
o If early action is taken, syphilis can be cured
with antibiotics.
Syphilis prevalence is growing in the United States,
particularly among men who have sex with men.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
o Painful urination
o Lower abdominal pain
o Vaginal discharge in women
o Discharge from the penis in men
o Pain during sexual intercourse in women
o Bleeding between periods in women
o Testicular pain in men
Many STDs are said to be socially stigmatized.
o In other words, people are judged or
condemned for being infected with STDs.
o Other types of disease may also carry some
level of social stigma.
In my opinion, the only real cure for STD stigma is
better sex education.
o People need to learn how common these
diseases are.
o They need to learn how easily they're treated.
Then, maybe, we can start working on making
screening more common.
o After all, one of the worst parts of STD stigma
is that doctors can suffer from it too.
Sometimes that makes it hard to get tested, even if
you don't suffer from STD stigma yourself.
UNDERSTANDING AND SUPPORTING SEXUALITY
Remember you can still contribute to an equal,
supportive and non-discriminatory society. Here are
some tips to accepting any identity.
o Try to educate people about the issues
surrounding sexual identity
o Make sure your workplace is friendly and
visibly supportive towards sexuality and gender
diverse young people.
o It is important to affirm to young people that
gender and sexuality are always diverse and
that gender and sexuality differences are
normal and healthy.
You might also like
- Frequencies New CompositeDocument4 pagesFrequencies New CompositeRicardo GomesNo ratings yet
- Reference: Harmening, D. M. (2012) - Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices (6th Ed.) - Pp. 434Document5 pagesReference: Harmening, D. M. (2012) - Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices (6th Ed.) - Pp. 434Kolin N Jandoc100% (1)
- Dr. Berg Amazing TechniquesDocument17 pagesDr. Berg Amazing Techniqueslucaemigrante100% (6)
- Autism and Asperger Syndrome by Simon Baron-CohenDocument170 pagesAutism and Asperger Syndrome by Simon Baron-CohenCristina100% (3)
- Understanding The SelfDocument10 pagesUnderstanding The SelfRenz GoleNo ratings yet
- (BSN2-2) CMCA Lec - Lesson No.4Document5 pages(BSN2-2) CMCA Lec - Lesson No.4Abish Julienne PecundoNo ratings yet
- 4 6Document180 pages4 6Julianne BasilioNo ratings yet
- UTS - Module 4 Sexualself StudentDocument6 pagesUTS - Module 4 Sexualself StudentkimberlyfritzzunigaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 The Sexual SelfDocument21 pagesModule 4 The Sexual SelfRosalea Mariz Apaya100% (2)
- Humansexuality and Sexua L Dysfu N Cti Ons: 1 7 .1 Normal SexualityDocument18 pagesHumansexuality and Sexua L Dysfu N Cti Ons: 1 7 .1 Normal Sexualitymiss betawiNo ratings yet
- PD 100 - Second LectureDocument4 pagesPD 100 - Second LectureSVPSNo ratings yet
- Love, Gender, and Sexuality NotesDocument4 pagesLove, Gender, and Sexuality NotesLyra Kassandra M. BorjaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Self - Reading MaterialDocument6 pagesSexual Self - Reading MaterialGenre Monique YngayoNo ratings yet
- LGBTQDocument17 pagesLGBTQANAMIKA YADAV100% (1)
- 1.18 Psychia - Human Sexuality (Dr. Obra, 2021)Document3 pages1.18 Psychia - Human Sexuality (Dr. Obra, 2021)Danila BagrovNo ratings yet
- B. The Sexual SelfDocument37 pagesB. The Sexual SelfPaul Winston RegaladoNo ratings yet
- PDEVDocument7 pagesPDEVSteph CaronanNo ratings yet
- F2. The Sexual Self Part 1Document25 pagesF2. The Sexual Self Part 1JANINE ANN MAGQUILAT100% (1)
- Mother and Child ReviewerDocument2 pagesMother and Child ReviewerMarie anneNo ratings yet
- Lesson The Sexual SelfDocument18 pagesLesson The Sexual SelfEdison Lati Jr.No ratings yet
- GenderDocument1 pageGenderraquel dizonNo ratings yet
- Understanding Self Sex SelfDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Self Sex SelfRenan AlburoNo ratings yet
- LGBTQ YouthDocument98 pagesLGBTQ YouthApril Rose Airoso - AramburoNo ratings yet
- Gender SexualityDocument83 pagesGender SexualityBalen FarhadNo ratings yet
- GNED10A - 01 - Sex, Gender, and SexualityDocument12 pagesGNED10A - 01 - Sex, Gender, and SexualityGlenn Mark HernandezNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Reviewer GensocDocument8 pagesFinal Exam Reviewer GensocSean Oliver BiguerasNo ratings yet
- Human Sexuality Midterm FA 2017Document3 pagesHuman Sexuality Midterm FA 2017elle enjayNo ratings yet
- Gender DysphoriaDocument47 pagesGender DysphoriaAce VendNo ratings yet
- Human - Sexulaity 16 12 14 1Document85 pagesHuman - Sexulaity 16 12 14 1PAJA MARY ROSE N.No ratings yet
- Module 5Document4 pagesModule 5Arnel F. PradiaNo ratings yet
- 1ceb Mod2 Lesson2 The-Sexual-SelfDocument2 pages1ceb Mod2 Lesson2 The-Sexual-SelfJefferson SalopanNo ratings yet
- Gender Identity and Sexual Orientation Development Among TeenagersDocument9 pagesGender Identity and Sexual Orientation Development Among TeenagersCarmella PlangNo ratings yet
- Human Sexuality in A Changing World 10th Edition Rathus Solutions Manual 1Document17 pagesHuman Sexuality in A Changing World 10th Edition Rathus Solutions Manual 1michael100% (39)
- Sex and GenderDocument28 pagesSex and GenderMark Porcadilla100% (1)
- Gender .Emma and SharedelDocument15 pagesGender .Emma and SharedelAnya EleginoNo ratings yet
- Riskversusresiliency: Addressing Depression in Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender YouthDocument13 pagesRiskversusresiliency: Addressing Depression in Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender YouthkvcprNo ratings yet
- The Sexual SelfDocument29 pagesThe Sexual SelfYumi GushikenNo ratings yet
- Be A Beacon 101 1 1 1 1Document37 pagesBe A Beacon 101 1 1 1 1Alicia PoweNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3.3 SOGIEDocument25 pagesChapter-3.3 SOGIEs.prosia.maviemhoniqueNo ratings yet
- Sexual SelfDocument31 pagesSexual SelfPicasales, Frenzy M.No ratings yet
- Performance Task (RWS)Document2 pagesPerformance Task (RWS)dino's bffNo ratings yet
- LESSON5 TASK5 GEELEC4 SantosAllyanaMarie - ABPOLSCI2ADocument6 pagesLESSON5 TASK5 GEELEC4 SantosAllyanaMarie - ABPOLSCI2AAllyanaMarieSantosNo ratings yet
- Gendso FinalsDocument5 pagesGendso FinalsJustin AprueboNo ratings yet
- The Sexual Self ZamoraDocument25 pagesThe Sexual Self ZamoraSENPAI HAROLDNo ratings yet
- eGEC-ELEC3 Week2 BelizonRAGDocument4 pageseGEC-ELEC3 Week2 BelizonRAGBelizon, Robie Allen G.No ratings yet
- SogieDocument8 pagesSogieDeo Nuevo CollaoNo ratings yet
- Gender, Sex & SexualityDocument20 pagesGender, Sex & SexualityIza SillerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document7 pagesChapter 6Renata FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Gender and Sexuality As A Social RealityDocument45 pagesLesson 1 Gender and Sexuality As A Social RealityJean Grace GumasingNo ratings yet
- ContractDocument2 pagesContractibanadavNo ratings yet
- Group-4-Gender and SocietyDocument4 pagesGroup-4-Gender and SocietyMarivic MiradorNo ratings yet
- Child Abuse Rape: Gender Identity and Sexual Orientation Are NotDocument82 pagesChild Abuse Rape: Gender Identity and Sexual Orientation Are NotRihanna HartNo ratings yet
- Digital Self: Who Am I in The CyberworldDocument43 pagesDigital Self: Who Am I in The Cyberworldkaren marie dela pasionNo ratings yet
- The Sexual Self-JoaquinDocument9 pagesThe Sexual Self-JoaquinJustine Guillermo JoaquinNo ratings yet
- A. Sex vs. Gender B. Sexual OrientationDocument22 pagesA. Sex vs. Gender B. Sexual Orientationkate buyuccanNo ratings yet
- Sexual SelfDocument25 pagesSexual SelfMJ OcañaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 GENSOC Lessons 1 3 1Document59 pagesWeek 2 GENSOC Lessons 1 3 1Shereen Grace GaniboNo ratings yet
- Gender and Human SexualityDocument25 pagesGender and Human SexualityAshlene CruzNo ratings yet
- MAPEHDocument11 pagesMAPEHsyvansantiago05No ratings yet
- HomosexualityDocument8 pagesHomosexualityqacsemsNo ratings yet
- BisexualityDocument3 pagesBisexualityMark PodzimekNo ratings yet
- Maging Sino Ka Man': The Lived Experiences of Men With Same Sex RelationshipDocument50 pagesMaging Sino Ka Man': The Lived Experiences of Men With Same Sex Relationshipdioneses bantaNo ratings yet
- El 2 Gender and Society Full ModulesDocument26 pagesEl 2 Gender and Society Full ModulesLindzy Lagundino LegardeNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Intersection of Gender, Identity, and SexualityFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Intersection of Gender, Identity, and SexualityNo ratings yet
- Buddhist Philosophy of Self (5Th Century B.C.E To The Present)Document3 pagesBuddhist Philosophy of Self (5Th Century B.C.E To The Present)MA. LUISA ANNE SORIANONo ratings yet
- Korean Wave: (Korean Music, Fashion, Food, Drama) : OutlineDocument3 pagesKorean Wave: (Korean Music, Fashion, Food, Drama) : OutlineMA. LUISA ANNE SORIANONo ratings yet
- (M3) The Physical SelfDocument3 pages(M3) The Physical SelfMA. LUISA ANNE SORIANONo ratings yet
- (M1) The Philosophical SelfDocument3 pages(M1) The Philosophical SelfMA. LUISA ANNE SORIANONo ratings yet
- Distal Radius Fractures (Broken Wrist) - OrthoInfo - AAOSDocument4 pagesDistal Radius Fractures (Broken Wrist) - OrthoInfo - AAOSmuhammad iqbal mahfuzhNo ratings yet
- OT Relevance RMTDocument12 pagesOT Relevance RMTFredy RamoneNo ratings yet
- Diseases and Pests Associated To Tomato CultivatioDocument12 pagesDiseases and Pests Associated To Tomato CultivatioKarl DiomoNo ratings yet
- Times of India Chennai 04.04.2020 PDFDocument18 pagesTimes of India Chennai 04.04.2020 PDFnts1020No ratings yet
- Module 1 QuizDocument15 pagesModule 1 QuizCarmela Therese SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Rekap Jaga 14 Januari 2021 2Document2 pagesRekap Jaga 14 Januari 2021 2yafidyNo ratings yet
- Food Safety W07Document7 pagesFood Safety W07MelanieNo ratings yet
- 4 Metabolic Disorders Related To Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument18 pages4 Metabolic Disorders Related To Carbohydrate Metabolismsaxawan100% (3)
- Formulation and Evaluation of Nail Lacquer Containing Anti Fungal Griseofulvin For The Treatment of OnychomycosisDocument13 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Nail Lacquer Containing Anti Fungal Griseofulvin For The Treatment of OnychomycosisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Monster Girl Doctor - Volume 3Document318 pagesMonster Girl Doctor - Volume 3Will TedjoNo ratings yet
- PG Ujian Masuk PPDS Periode JuliDocument5 pagesPG Ujian Masuk PPDS Periode JuliGuntur Sulistyo100% (1)
- Rheumatology: - Syrian - Notes - CK - 2 - Step - Usmle - Pieces/8806 - Bits - CK - 2 - Step - Student - HTMLDocument5 pagesRheumatology: - Syrian - Notes - CK - 2 - Step - Usmle - Pieces/8806 - Bits - CK - 2 - Step - Student - HTMLLoyla RoseNo ratings yet
- Anti Carcinogenesis KomalDocument22 pagesAnti Carcinogenesis KomalrohitalurkarNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Allocation LetterDocument2 pagesVaccine Allocation LetterNEWS CENTER MaineNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid DrugsDocument46 pagesAntithyroid Drugsalhsnym820No ratings yet
- Four Phases of Intravenous Fluid Therapy - A Conceptual Model PDFDocument8 pagesFour Phases of Intravenous Fluid Therapy - A Conceptual Model PDFboby abdul rahmanNo ratings yet
- Health 7: 3 Quarter Week 7Document11 pagesHealth 7: 3 Quarter Week 7gio rizaladoNo ratings yet
- History Psychiatry 1Document28 pagesHistory Psychiatry 1medicine lifeNo ratings yet
- 10 Surprising Uses of Insects in MedicineDocument8 pages10 Surprising Uses of Insects in Medicinebashirlone786No ratings yet
- SV300 Service Training-Basic V1.0Document82 pagesSV300 Service Training-Basic V1.0WALTER HUGO GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Biology Project: Lung CancerDocument12 pagesBiology Project: Lung CancerKarm ParmarNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGY (Quizlet)Document9 pagesPARASITOLOGY (Quizlet)Allyssa AniNo ratings yet
- 8 Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin D DeficiencyDocument14 pages8 Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin D DeficiencyM. K. HossainNo ratings yet
- National Parivar Mediclaim Policy PDFDocument30 pagesNational Parivar Mediclaim Policy PDFSathya S ChammathilNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine Surgery: Arthroplasty Versus Fusion Versus Posterior ForaminotomyDocument10 pagesCervical Spine Surgery: Arthroplasty Versus Fusion Versus Posterior ForaminotomyKyle RobinNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Stress and Inflammation As Targets For Novel Preventive and Therapeutic Approches in Non Communicable DiseasesDocument272 pagesOxidative Stress and Inflammation As Targets For Novel Preventive and Therapeutic Approches in Non Communicable DiseasesRoberta MorganaNo ratings yet