Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 1
Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
NazrinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 1
Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
NazrinCopyright:
Available Formats
KNS 2113 Fluid Mechanics Sesi 1 2008/2009
Tutorial 1: Basic Properties of Fluids
1) If 6m3 of oil has a mass of 4900 kg, calculate its weight, density, specific weight,
specific gravity and specific volume.
2) Determine the dimensions, in both the FLT system and MLT system, for (a) the
product of force times volume, (b) the product of pressure times mass divided by
area, and (c) moment of a force divided by velocity.
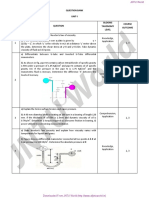
3) Two layers of fluid be dragged along by the motion of an upper plate as shown in Figure
1 below. The bottom plate is stationary. The top fluid puts a shear stress on the upper
plate, and the lower fluid puts a shear stress on the bottom plate. Determine the ratio of
these two shear stresses.
Figure 1.
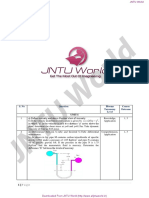
4) A Newtonian fluid having a specific gravity of 0.92 and kinematic viscocity of 4 x 10 -4
m2/s flows past a fixed surface (See Figure 2). Due to non-slip condition, the velocity at
the fixed surface is zero and the velocity profile near the surface is as shown in the Figure
3 below. Determine the magnitude and direction of the shearing stress developed on the
plate. Express your answer in terms of U and δ, with U and δ expressed in units of meters
per second and meters, respectively.
Prepared By: Dr Charles Bong
KNS 2113 Fluid Mechanics Sesi 1 2008/2009
Figure 2.
5) Calculate the density, specific weight and specific volume of air when its absolute
pressure and temperature are respectively 140 kPa and 50 oC (assume R = 287
J/kgK).
6) An open, clean glass tube (θ = 0°) is inserted vertically into a pan of water. What tube
diameter is needed if the water level in the tube is to rise one tube diameter (due to
surface tension)?
Prepared By: Dr Charles Bong
You might also like
- Review Problems PDFDocument22 pagesReview Problems PDFArman Malekloo0% (1)
- Assignment II FM2019Document19 pagesAssignment II FM2019Drkumar SwamyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1bDocument2 pagesTutorial 1bNazrinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: Basic Properties of Fluids: KNS 2113 Fluid Mechanics Sesi 1 2016/2017Document2 pagesTutorial 1: Basic Properties of Fluids: KNS 2113 Fluid Mechanics Sesi 1 2016/2017Darren Ðavenç0% (1)
- Assignment #1Document1 pageAssignment #1Shane Danikka LlorinNo ratings yet
- ME20022 Jan2021Document9 pagesME20022 Jan2021signupNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Essam Radwan BerikaaNo ratings yet
- FMDocument2 pagesFMepnaseefNo ratings yet
- Solution Major#1Document8 pagesSolution Major#1uunsyNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 Tutorial 2Document2 pagesCIVL2611 Tutorial 2MohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- Appendix L Odd-Numbered Problems PDFDocument50 pagesAppendix L Odd-Numbered Problems PDFlonerstarNo ratings yet
- ENGR207 - Assignment#1Document4 pagesENGR207 - Assignment#1Mohamed KhairyNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFMechanics EngineerNo ratings yet
- Sheet 01 20-21 Properties of Fluid RevDocument2 pagesSheet 01 20-21 Properties of Fluid RevBibaswan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 Introduction and Fluid PropertiesDocument5 pagesSheet 1 Introduction and Fluid PropertiesMohamed EzzNo ratings yet
- Cve 240-Assignment 1 - Chapter 2Document2 pagesCve 240-Assignment 1 - Chapter 2Ehab WilsonNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1이동근No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Rce 303Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics Rce 303Raju RøyNo ratings yet
- Terms 1. Is The Instrument Used To Measure The Absolute Pressure of The Atmosphere? (Barometer)Document2 pagesTerms 1. Is The Instrument Used To Measure The Absolute Pressure of The Atmosphere? (Barometer)JoryNo ratings yet
- R ProblemsDocument22 pagesR ProblemsTrolldaddyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank PDFDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank PDFMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Plate Exercises 1 BES108 ME2ADocument4 pagesPlate Exercises 1 BES108 ME2AMike Raphy T. VerdonNo ratings yet
- ENGR207 - Assignment#1Document5 pagesENGR207 - Assignment#1GendyNo ratings yet
- UEME2123 Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 1Document3 pagesUEME2123 Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 1Ah WenNo ratings yet
- Che 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Document7 pagesChe 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Bao-Ngoc HoangNo ratings yet
- FM QBDocument5 pagesFM QBChinki Rockzz.. ..No ratings yet
- Tutorial Q Unit OneDocument3 pagesTutorial Q Unit OneAbenezer KassahunNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Properties of FluidsDocument1 pageAssignment 1 - Properties of Fluidsgoyema5840No ratings yet
- Homework 1 PDFDocument4 pagesHomework 1 PDFعلي علي صالح انقعNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsLokendra Singh JhalaNo ratings yet
- Che 333 Exam AnswersDocument17 pagesChe 333 Exam AnswersPraise BamwaNo ratings yet
- HW#1-Fluid Mechanics IDocument3 pagesHW#1-Fluid Mechanics IsalymoonismNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tunku Abdul RahmanDocument15 pagesUniversiti Tunku Abdul RahmanfreeloadNo ratings yet
- Ce 371 Home Exercises-1 1) The Velocity Distribution For The Flow of ADocument3 pagesCe 371 Home Exercises-1 1) The Velocity Distribution For The Flow of AEnes YavuzNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Basic Properties of Fluids Fluid Statics: KNS2113 Fluid Mechanics Sesi 1 2016/20017Document4 pagesAssignment 1 Basic Properties of Fluids Fluid Statics: KNS2113 Fluid Mechanics Sesi 1 2016/20017ismailNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tunku Abdul RahmanDocument6 pagesUniversiti Tunku Abdul RahmanfreeloadNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Chapter 1: Introduction)Document10 pagesAssignment 1 (Chapter 1: Introduction)Ragh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Wren201 Tutorial Questions-2Document12 pagesWren201 Tutorial Questions-2yemivibezNo ratings yet
- 10 FluidDynamicsDocument39 pages10 FluidDynamicsSyed Raheel AdeelNo ratings yet
- Dodl Past Exam Questions - 240417 - 095612Document22 pagesDodl Past Exam Questions - 240417 - 095612omtyson72100% (1)
- CGM - FM Assignment 1 PDFDocument4 pagesCGM - FM Assignment 1 PDFcharlesgmartinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Ch1 ProblemDocument5 pagesTutorial Ch1 ProblemKiat HauNo ratings yet
- Physics Term2 Opener QSDocument10 pagesPhysics Term2 Opener QSElijah KirigaNo ratings yet
- C1Document259 pagesC1Undinchu JaeNo ratings yet
- IMPORTANT QUESTIONS For Final (KEC) Fluid Mechanic - Line Academy Part 1Document45 pagesIMPORTANT QUESTIONS For Final (KEC) Fluid Mechanic - Line Academy Part 1आदित्य राज अधिकारीNo ratings yet
- Fluids of Mechanics QuestionsDocument6 pagesFluids of Mechanics QuestionsMohamed HanyNo ratings yet
- Problem of RehologyDocument4 pagesProblem of RehologyShagufta AfaqueNo ratings yet
- Vm235: Thermodynamics Homework 2: Assigned Tues May 24, 2016 Due Tues May 31 at The Start of ClassDocument3 pagesVm235: Thermodynamics Homework 2: Assigned Tues May 24, 2016 Due Tues May 31 at The Start of Classtony960129No ratings yet
- Assignment Fluid MechanicsDocument9 pagesAssignment Fluid MechanicsAmirul AshrafNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document3 pagesHW 1Madison CallowayNo ratings yet
- Characteristic of Fluids A Fluid Is Defined As A Substance That Deforms Continuously When Acted On by A Shearing Stress at Any MagnitudeDocument30 pagesCharacteristic of Fluids A Fluid Is Defined As A Substance That Deforms Continuously When Acted On by A Shearing Stress at Any MagnitudeBlack SkyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 FMDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 FMSanthoshMBSanthuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids and Hydraulic Machines Question BankDocument7 pagesMechanics of Fluids and Hydraulic Machines Question Bankstalinrajesh143No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document88 pagesLecture 1amitanshubehera0705No ratings yet
- CLL 231 Tutorial 1Document3 pagesCLL 231 Tutorial 1ranaaditay783No ratings yet
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryFrom EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNo ratings yet
- KNS1633 73592Document2 pagesKNS1633 73592NazrinNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 11-07-2023 23.16Document3 pagesCamScanner 11-07-2023 23.16NazrinNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 11-05-2023 03.02Document18 pagesCamScanner 11-05-2023 03.02NazrinNo ratings yet
- Review Exercises Beams 61123Document2 pagesReview Exercises Beams 61123NazrinNo ratings yet
- Tuto 8 Q2 - 73592Document1 pageTuto 8 Q2 - 73592NazrinNo ratings yet
- Name List Grouping Proj 1 KNS 1022Document1 pageName List Grouping Proj 1 KNS 1022NazrinNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument4 pagesIlovepdf MergedNazrinNo ratings yet
- Rubric - Lab ReportDocument2 pagesRubric - Lab ReportNazrinNo ratings yet