Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 Chemistry ChapterTests Chapter 7 Level 1 Test 1
12 Chemistry ChapterTests Chapter 7 Level 1 Test 1
Uploaded by
Maheswari RajnarayananOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 Chemistry ChapterTests Chapter 7 Level 1 Test 1
12 Chemistry ChapterTests Chapter 7 Level 1 Test 1
Uploaded by
Maheswari RajnarayananCopyright:
Available Formats
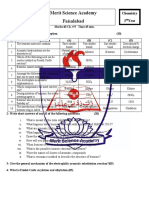
PRACTICE TEST
Level 1
CLASS: XII
Unit 7: The p-Block Elements
Full marks: 20 Time: 40 Min
Q.No Questions M
1 The oxides of the type E2O3 of nitrogen and phosphorus are acidic. 1
True/False?
2 Complete the reaction: Ca3N2 + H2O 1
3 Write the reaction for What happens when ammoniumdichromate is heated? 1
4 Write the reaction for What happens when bariumazide is heated? 1
5 Explain why dinitrogen is relatively less reactive while phosphorous is highly
reactive. 2
6 Mention the conditions required to maximise the yield of ammonia in Habers 2
process.
7 Answer the following:
i. Why does PCl3 fume in moisture?
ii. What happens when sulphur dioxide is passed through an aqueous 2
solution of Fe(III) salt?
OR
Arrange the following in the order of property indicated for each set:
(ii) HF, HCl, HBr, HI - increasing acid strength.
(iii) NH3, PH3, AsH3, SbH3, BiH3 – increasing base strength.
8 i. Elements of Group 16 generally show lower value of first ionisation
enthalpy compared to the corresponding periods of group 15. Why? 2
ii. What inspired N. Bartlett for carrying out reaction between Xe and
PtF6?
OR
i. With what neutral molecule is ClO– isoelectronic?
ii. Arrange the following in the order of increasing bond dissociation
enthalpy. F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
9 Write the conditions to maximise the yield of H2SO4 by Contact process. 2
10 1. Halogens have maximum negative electron gain enthalpy in the
respective periods of the periodic table. Why?
2. Although electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less negative as
compared to chlorine, fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than
chlorine. Why? 3
3. Fluorine exhibits only -1 oxidation state whereas other halogens
exhibit + 1, + 3, + 5 & + 7 oxidation states also. Explain.
11 Answer the following-
a. How does ammonia react with a solution of Cu2+?
b. Why does NO2 dimerise?
c. What is the covalence of nitrogen in N2O5? 3
www.tiwariacademy.com
Focus on free education
You might also like
- Principles of Life 2nd Edition Hillis Test BankDocument32 pagesPrinciples of Life 2nd Edition Hillis Test BankMelissaLeetioyq100% (17)
- Test Bank For Brown Iverson Anslyn Footes Organic Chemistry 8th Edition 8th EditionDocument29 pagesTest Bank For Brown Iverson Anslyn Footes Organic Chemistry 8th Edition 8th Editionamandawrightrwfdcombka100% (34)
- Plant Design ProjectDocument8 pagesPlant Design ProjectAbhishek SagarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry ChapterTests Chapter 7 Level 1 Test 1Document1 page12 Chemistry ChapterTests Chapter 7 Level 1 Test 1Deepan KumarNo ratings yet
- 16.p Block Element ExerciseDocument27 pages16.p Block Element ExerciseKIRAN ALLUNo ratings yet
- P Block Elements Notes For Entrance ExaminationDocument13 pagesP Block Elements Notes For Entrance ExaminationSrijan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample Paper For Class 11 ChemistryDocument11 pagesCbse Sample Paper For Class 11 ChemistryAshutosh RautNo ratings yet
- Group 15 ElementsDocument1 pageGroup 15 ElementsVaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample Paper For Class 11 ChemistryDocument11 pagesCbse Sample Paper For Class 11 ChemistrySatish Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions in P Block ElementsDocument15 pagesReasoning Questions in P Block ElementsAbhi WaliaNo ratings yet
- 12TH Chemistry Model Question Paper Term 2Document2 pages12TH Chemistry Model Question Paper Term 2someone medicoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 P-Block Elements-Ii: WWW - Nammakalvi.inDocument5 pagesUnit - 3 P-Block Elements-Ii: WWW - Nammakalvi.inAakaash C.K.100% (1)
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 3 Study Material em 215020Document5 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 3 Study Material em 215020Aakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - The P Block Elements AssignmentDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - The P Block Elements AssignmentManickam Gnanashekaran0% (1)
- P Block Elements II WorkbookDocument53 pagesP Block Elements II WorkbookStudy BuddyNo ratings yet
- RE Oard XAM: Class: XII Time: 3:00 Hrs. Full Marks: 75 Subject: ChemistryDocument2 pagesRE Oard XAM: Class: XII Time: 3:00 Hrs. Full Marks: 75 Subject: ChemistryAmitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Ncert Board Full Syllabus Practice Test - SubjectiveDocument4 pagesChemistry - Ncert Board Full Syllabus Practice Test - SubjectiveRijul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Complete PaperDocument5 pagesChemistry Complete PaperNitin HansNo ratings yet
- Xi RT 3 QPDocument4 pagesXi RT 3 QPKavyasri RajaduraiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry-Alcohol, Phenol & Ether PDFDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry-Alcohol, Phenol & Ether PDFVaishnavi DurbadeNo ratings yet
- 11 ChemistryDocument3 pages11 ChemistryDushyant Singh JadonNo ratings yet
- Merit Science Academy Faisalabad: Chemistry 2 YearDocument1 pageMerit Science Academy Faisalabad: Chemistry 2 YearShakaibNo ratings yet
- Merit Science Academy Faisalabad: Chemistry 2 YearDocument1 pageMerit Science Academy Faisalabad: Chemistry 2 YearShakaibNo ratings yet
- Time - 1.5 Hrs. M.M.: 50Document3 pagesTime - 1.5 Hrs. M.M.: 50satpal chahalNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Board Exam QuestionsDocument19 pagesPrevious Year Board Exam QuestionsRishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Subjective Type Questions Also Useful For XII Board Exam.: The P - Block ElementsDocument13 pagesSubjective Type Questions Also Useful For XII Board Exam.: The P - Block ElementsAbhiNo ratings yet
- Evoke Ch-1 SubjectiveDocument2 pagesEvoke Ch-1 SubjectiveHimanshu SattiNo ratings yet
- 4 Group 17 Elements UpdatedDocument8 pages4 Group 17 Elements Updatedangie0812No ratings yet
- The P-Block Elements: White P: White Waxy/poisonous/ Soluble in CSDocument2 pagesThe P-Block Elements: White P: White Waxy/poisonous/ Soluble in CSSsNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Fluorine Chlorine Bromine and IodineDocument6 pagesGroup 7 Fluorine Chlorine Bromine and IodinePAUL KOLERENo ratings yet
- P-Block Elements (N - O Family) APSPDocument14 pagesP-Block Elements (N - O Family) APSPshreshthagupta2111No ratings yet
- 7 The P-Block Elements: Level - IDocument22 pages7 The P-Block Elements: Level - IFasahatNo ratings yet
- 1st Half BookDocument2 pages1st Half BookShakaibNo ratings yet
- ISB Chemistry GR12 PT1 QPFinal 06 05 24Document4 pagesISB Chemistry GR12 PT1 QPFinal 06 05 24definitlyfakeaccNo ratings yet
- P-Block - 10Document18 pagesP-Block - 10veenaNo ratings yet
- Answers To The Practical Problems: Problem 29. Titrimetric Determination of Fe in Different Oxidation StatesDocument5 pagesAnswers To The Practical Problems: Problem 29. Titrimetric Determination of Fe in Different Oxidation StatesLê Hoàng MinhNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistryrocky25s15aNo ratings yet
- PblockDocument10 pagesPblockSarthak VatsNo ratings yet
- How Is Reaction of ZN With Dilute HNO Different From Its Reaction With Concentrated HNO ?Document2 pagesHow Is Reaction of ZN With Dilute HNO Different From Its Reaction With Concentrated HNO ?Kamal AnandNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test - 12th Science-ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistry Test - 12th Science-ChemistryAishley ChalametNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution PDF 2012 Set 1Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution PDF 2012 Set 1shrishtisoni168No ratings yet
- Ub JESf S8 BNP 0 Tci 32 T 3 PDocument6 pagesUb JESf S8 BNP 0 Tci 32 T 3 PDebu ka mobileNo ratings yet
- Msbshse Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 Elements of Groups 16 17 and 18Document31 pagesMsbshse Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 Elements of Groups 16 17 and 18samajadhav095No ratings yet
- Question Paper Central Outside Delhi 2016 Set 1 CBSE Class 12 ChemistryDocument6 pagesQuestion Paper Central Outside Delhi 2016 Set 1 CBSE Class 12 Chemistryanush JainNo ratings yet
- Sample PaperDocument3 pagesSample Paperaparna patwalNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XII Che Target-4 Level-2 Chapter-11Document22 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XII Che Target-4 Level-2 Chapter-11Pranav TiwariNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document2 pagesTest 1bcggNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Important Questions em 218063Document9 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Important Questions em 218063kadachitti2626No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 The P Block ElementsDocument25 pagesChapter 7 The P Block Elementspriyanka kNo ratings yet
- XI ChemiCALDocument8 pagesXI ChemiCALSakshi KantNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry The P-Block ElementsDocument41 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry The P-Block ElementsyndtfndtgndNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenols and Ethers PDFDocument13 pagesAlcohol, Phenols and Ethers PDFRahul JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Chemistry PT1 2020-21Document5 pagesGrade 12 Chemistry PT1 2020-21Sudha BhatNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) Chemistry Sample Paper 1Document1 page(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) Chemistry Sample Paper 1Neil RoyNo ratings yet
- 13 HydrocarbonsDocument2 pages13 HydrocarbonsPadhai tak : by Dr.Aditya guptaNo ratings yet
- CH 4,5 EveningDocument2 pagesCH 4,5 EveningAdeel RazaNo ratings yet
- Prefinal - 2: Part A I. Answer The FollowingDocument3 pagesPrefinal - 2: Part A I. Answer The FollowingMadhu MadhuNo ratings yet
- Question List For In-Class PresentationsDocument5 pagesQuestion List For In-Class Presentationsraygius77No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesNo ratings yet
- Palladium Reagents and Catalysts: New Perspectives for the 21st CenturyFrom EverandPalladium Reagents and Catalysts: New Perspectives for the 21st CenturyNo ratings yet
- 8086 Code CommandDocument40 pages8086 Code CommandMaheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- Biology Xii Chapterwise Diagram Based QN 2015 16Document42 pagesBiology Xii Chapterwise Diagram Based QN 2015 16Maheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I-T. Veerarajan Laplace TransformsDocument118 pagesUNIT-I-T. Veerarajan Laplace TransformsMaheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationDocument13 pagesBiotechnology and Its ApplicationMaheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- 12 Bio ch12 Full 1597571895Document49 pages12 Bio ch12 Full 1597571895Maheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- 12 Chap11 Biotech 1597571962Document67 pages12 Chap11 Biotech 1597571962Maheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- D.A.V School: Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai 600 088 Class 12 BIOLOGY Chapter 11 BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument7 pagesD.A.V School: Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai 600 088 Class 12 BIOLOGY Chapter 11 BIOTECHNOLOGYMaheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- D.A.V School: Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai 88 Class 12 BIOLOGY Chapter 11 BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument9 pagesD.A.V School: Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai 88 Class 12 BIOLOGY Chapter 11 BIOTECHNOLOGYMaheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- Dav School, Adambakkam Class-Xii Chemistry 7. The P-Block Elements (Class Notes)Document18 pagesDav School, Adambakkam Class-Xii Chemistry 7. The P-Block Elements (Class Notes)Maheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- CH ActivationDocument22 pagesCH ActivationIsabella ThomasNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument69 pagesChemical EquilibriumShashank JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument26 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesKartik ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Reversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 1 MSDocument10 pagesReversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 1 MSJunYuuuNo ratings yet
- Es8b01195 Si 001 PDFDocument24 pagesEs8b01195 Si 001 PDFAHMEDNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Polynuclear CompoundsDocument45 pagesPresentation of Polynuclear Compoundsjasmeet ghumanNo ratings yet
- Vivek Rathore, Sudha Tyagi, Bharat Newalkar, R.P. Badoni: HighlightsDocument12 pagesVivek Rathore, Sudha Tyagi, Bharat Newalkar, R.P. Badoni: HighlightsFarah TalibNo ratings yet
- Week 1 N 2Document2 pagesWeek 1 N 2Neng Mariana MahmudNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Science (Double Award) TSM Issue 2Document52 pagesIGCSE Science (Double Award) TSM Issue 2frogfloydNo ratings yet
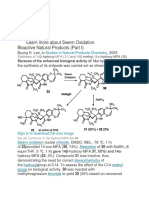
- Learn More About Swern OxidationDocument18 pagesLearn More About Swern OxidationAndra Ch123No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Redox ReactionsDocument9 pagesChapter 8 Redox ReactionsNitish MehraNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Chemical Reactions and EquationsMalancha high school HS50% (2)
- Ammonium Nickel Sulphate Mediated Nitration of Aromatic Compounds With Nitric Acid PDFDocument8 pagesAmmonium Nickel Sulphate Mediated Nitration of Aromatic Compounds With Nitric Acid PDFrabiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Planner - Physical Chemistry - Lakshya JEE 2025Document3 pagesLecture Planner - Physical Chemistry - Lakshya JEE 2025dudhkumarghosh425No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Cbse Sample Paper For Class-12Document7 pagesChemistry: Cbse Sample Paper For Class-12Chunky ChipmunkNo ratings yet
- MiniProject Stage 1 - Process Dynamic & ControlDocument4 pagesMiniProject Stage 1 - Process Dynamic & ControlFarihah EyfaNo ratings yet
- Eftekhari Sis2013Document86 pagesEftekhari Sis2013Luis MartinezNo ratings yet
- 4.3 How Fast - RatesDocument26 pages4.3 How Fast - Ratescrazieeiraqi100% (1)
- Experiment 8 Sem2Document12 pagesExperiment 8 Sem2Fatin NurhudaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis, Characterization and Modification of Silicone Resins - An "Augmented Review"Document29 pagesSynthesis, Characterization and Modification of Silicone Resins - An "Augmented Review"ana.luiza.nanyNo ratings yet
- THE SALT Water Fuel Cell Car 1Document5 pagesTHE SALT Water Fuel Cell Car 1Madhan Ganesan0% (1)
- Mechanical Alloying of Mosi With Ternary Alloying Elements. Part 2 Computer SimulationDocument7 pagesMechanical Alloying of Mosi With Ternary Alloying Elements. Part 2 Computer SimulationJasbir S RyaitNo ratings yet
- How Chemical Changes Take PlaceDocument39 pagesHow Chemical Changes Take Placesheyn same100% (1)
- Modeling The Kinetics of Bimolecular ReactionsDocument67 pagesModeling The Kinetics of Bimolecular ReactionsFredrick MutungaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank For 10th STDDocument4 pagesChemistry Question Bank For 10th STDsameeraNo ratings yet
- 0620 w10 QP 31Document16 pages0620 w10 QP 31Mennatallah Mohamed HamedNo ratings yet
- C7-1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument24 pagesC7-1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsUYÊN NGUYỄN NGỌC QUỲNHNo ratings yet